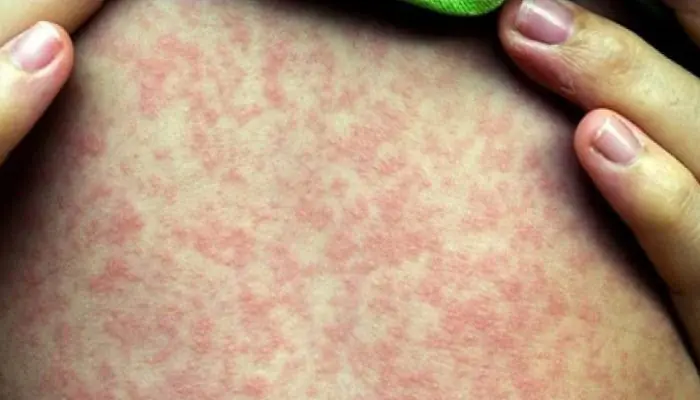
A rash similar to chickenpox also occurs when infected with other diseases. Similar symptoms appear if the patient is sick with whooping cough, smallpox, rubella, dermatitis, herpes, measles or herpes zoster. In addition, a similar rash can be found in some people due to an allergic reaction to an irritant.
Smallpox as one of the reasons
This disease is considered one of the most terrible and dangerous in the world. Nowadays, thanks to treatment and vaccinations, outbreaks of infection rarely occur in the world. Virus samples are kept only in special storage facilities in Russia and the USA. Chickenpox used to be considered a mild form of smallpox, but later scientists and doctors discovered many more differences. It has now been proven that chickenpox (chickenpox) is a completely different disease.
Smallpox raged strongly at different periods of history. The countries that suffered most from it were China, Africa, and India. This viral disease is transmitted through household items and by airborne droplets. The virus is very resistant to environmental conditions: in severe frost or heat, it lives for up to a year and can even withstand drought. After the death of an infected person, the virus remained on the dried wounds, so the bodies were burned.
The main symptoms of the disease are:
- blisters on the body and red spots;
- crusts that remained from burst blisters;
- fever and fever;
- wounds and ulcers.
Every two weeks the situation worsened, accompanied by waves of severe pain. When purulent wounds appeared on the body, it meant that the patient would soon die if treatment was not started.
All children are vaccinated to prevent smallpox. To treat this disease, drugs such as immunoglobulin and metisazone have been developed.
Rubella is a possible option
Rubella is a disease that is also similar to chickenpox.
Viral disease most often goes away in childhood, and quite easily.
However, there are rare cases when adults get sick and the disease is severe. The virus is very unstable: it dies from ultraviolet radiation in 12 minutes. Rubella can be contracted through respiratory droplets from an infected patient.
The only common symptom is a red rash on the body. The disease can progress in different ways, depending on the individual characteristics of the person. During the first 2 weeks, symptoms are not detectable. On the 12th day, you can notice a gradual spread of red spots on the body.
As soon as spots appear, body temperature immediately rises. Lymph nodes increase in size and become too sensitive. In general, the symptoms of the disease are similar to the common cold. The distinctive sign is a red rash.
To prevent infection, vaccines are given at a young age. However, the vaccine can only be valid until the age of 14, then it needs to be renewed. In addition, the vaccine causes many side effects and does not provide one hundred percent protection against the virus. Drugs such as Ervevax, Rudivax and others have been developed for the treatment of rubella.
Measles is a cause for concern
Rashes can also occur with measles, so it can easily be confused with chickenpox. You can catch the disease at any age. The virus is transmitted to a healthy person by airborne droplets.
The symptoms are similar to the flu or a cold, except for one sign - a rash. The patient develops a severe cough, weakness, and body temperature rises to 39 degrees. The conjunctiva turns red, the palate becomes covered with blisters, red spots appear on the body, which after 4 days begin to peel off.
You need to be treated at home; only patients with a severe form of the disease are allowed for inpatient treatment. During fever and fever, it is necessary to lie down constantly. There are no drugs that can cure measles. You can only alleviate the symptoms; the disease itself goes away on its own. You definitely need to eat fruits and vegetables. If you have a cough, an expectorant will do. You should not open windows as it irritates your eyes. You can drop Albucid into your eyes 3 times a day.
The main means of prevention is vaccination. It protects for up to 15 years. Complications after measles include bronchitis, bronchiolitis, keratoconjunctivitis and pneumonia. Rarely, hepatitis, myocarditis and glomerulonephritis occur.
The cause of the rash is whooping cough
Most often, children suffer from this type of infectious disease. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Whooping cough develops very quickly. Its main difference from chickenpox is the risk of recurrence.
The first sign is fatigue, weakness and malaise. But it is difficult to identify the disease at the first stage. Later, more obvious symptoms appear. A person suffers greatly from a rough cough, which can lead to suffocation. Symptoms include a runny nose and fever. The patient becomes irritable. The cough is constantly getting worse, and tremors occur. During such periods, the tongue protrudes strongly, and the veins in the neck swell.
Although a person can die from such coughing attacks, whooping cough is not considered a fatal disease. Treatment is carried out at home. If the disease has reached a severe stage or if the patient is under 1 year of age, then treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. Antibiotics are used when the acute stage begins.
The most commonly used are erythromycin and azithromycin. You can use chloramphenicol and tetracycline. But not all of them are allowed for children. It is necessary to maintain bed rest, go for short walks, and take vitamins. It is necessary to eliminate all the causes that cause the cough.
Shingles
Herpes zoster, or shingles, is a fairly common disease, since almost every person on the planet is infected with the herpes virus, which may not manifest itself throughout life. The virus that causes chickenpox is the same as the virus that causes herpes. But children can only get chickenpox, but adults can also get shingles.
Chickenpox generally has no cure. But you need to fight lichen, otherwise it won’t go away. But a drug that can completely eliminate the disease has not yet been developed, although so many decades have passed. The symptoms are almost the same as those of chickenpox, but the itching will be much stronger. In addition, in places where scratching appears, the skin hurts greatly. Painful sensations are associated with the fact that the virus attacks the nerves. The entire treatment process can take one and a half months. The doctor eliminates suppuration and treats the affected tissue so that the virus does not spread. You can take special medications that can relieve pain.
But you need to start using them no later than the fifth day from the moment the first rash appears. You should not swim during the course of the disease, as the virus can be spread throughout the body, resulting in a second wave of the disease.
The only thing that saves you from the virus is strengthening your immune system. The virus can remain in the human body all its life, but be passive due to good immune protection.
Rash is a symptom of dermatitis
A red rash occurs on the skin due to environmental irritants. There are two types of disease: dermatitis and taxidermy. The first type includes the appearance of pimples, blackheads, dandruff, as well as eczema, neurodermatitis, etc. Most often, the disease goes away quickly.
The main symptoms of the disease are blisters on the body, heat and fever, itching, burning, inflammation and swelling. If they appear, you should consult a doctor. Symptoms may disappear when the main irritant is eliminated. Similar symptoms occur due to the body’s allergic reaction to external irritants.
When the first symptoms of such diseases appear, under no circumstances should you go outside or come into contact with other people. These diseases are highly contagious. A doctor must be called to your home.
Diseases similar to chickenpox that cause a rash on a child’s skin are always a cause for concern for parents. This could be chicken pox, another infection, an allergic reaction, or just a burn. How to distinguish one rash from another, provide assistance, and in which cases you need to immediately consult a doctor, you can learn from this article.
What diseases in children are similar?
Chickenpox is one of the most common childhood infectious diseases, which most often affects children from 3 to 7 years old.
You can become infected through contact with a sick person, regardless of the season. The carrier of the virus becomes dangerous to others 2 days before the formation of the rash and continues to remain infectious for 5 days after the appearance of the last elements of the rash.
The incubation period for this childhood infection ranges from 10 to 21 days.
Classic chickenpox, as a rule, does not cause any difficulties in diagnosis:
A distinctive feature of typical chickenpox is the appearance of a rash on the scalp and mucous membranes (in the mouth, on the eyelids), as well as severe itching.
However, if chickenpox occurs in a pustular or rudimentary form, it can easily be confused with other diseases. Difficulties may arise when diagnosing the disease on the first day, when the rash that precedes chickenpox can lead to misdiagnosis.
The list of diseases similar to chickenpox includes:
- Simple herpes.
- Enteroviral fever (Coxsackie).
- Measles, rubella, scarlet fever.
- Streptoderma.
- Allergic reactions, including to insect bites.
The first signs of the disease before the appearance of a specific rash resemble the clinical picture of other viral infections. Headache, weakness, drowsiness, loss of appetite and fever occur with almost all diseases, ranging from colds to rare infections.
Until recently, thanks to mass vaccination, measles was considered a rare disease in children. In recent years, due to interruptions in the supply of vaccines and the popularity of the anti-vaccination movement, the incidence has increased again. Vaccination against measles does not guarantee lifelong immunity, so adults and older people can get this disease.
Measles is similar to the initial stage of chickenpox, as well as its rudimentary form. The pathology begins with fever, pain and sore throat, cough, conjunctivitis. Symptoms of ARVI are accompanied by the appearance of a specific rash on the buccal mucosa - Filatov-Koplik spots.
On days 3-5, a red spotty rash appears on the skin of the face and neck, the next day the rash spreads to the torso, and a day later to the limbs.
When a rash appears, the fever decreases and the patient’s well-being improves.
The main differences between chickenpox and measles:
- Measles rash does not appear simultaneously with fever, but on the 3-5th day of illness.
- The spots are large, bright red, and often merge with each other.
- Measles rash does not have blisters.
- With measles, the rash appears in stages.
In addition, the measles rash does not affect the scalp and mucous membranes, and the disappearance of the rash is accompanied by pigmentation and peeling.
Rubella
Rudimentary chickenpox and rubella are very similar to each other in the morphological elements of the rash. Both of these diseases are accompanied by the appearance of pink-red spots on the patient’s skin.
Like chickenpox, rubella is caused by a virus. The incubation period in the presence of the latter is 11-24 days.
A person is contagious from the 7th day from the onset of the disease to 4 days after the complete disappearance of the rash.
The main manifestations of rubella are fever, the appearance of a small spotted pink rash, and enlargement of the posterior cervical lymph nodes.
Unlike chickenpox, rubella:
- The rash appears on the first day of the disease. This happens simultaneously with an increase in temperature.
- Mottled pink spots appear throughout the body, concentrated on the face, buttocks, and extensor surfaces of the arms and legs.
- Rubella is not characterized by pimples, crusts, or pigmentation.
Compared to chickenpox, the rash with rubella is smaller and is not accompanied by itchy skin.
The pathology is especially dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause developmental defects in the fetus. That is why doctors recommend checking the titer of antibodies to rubella and, if necessary, re-introducing the vaccine to girls and women planning pregnancy.
Enteroviral fever
Chickenpox leaves behind lifelong immunity, so in most cases it occurs once in a lifetime. However, many people believe that they have had chickenpox twice. This may be due to the fact that several decades ago it was mistaken for enteroviral fever caused by the currently known Coxsackie virus.
The source of infection is a sick person who is dangerous to others within 7-10 days from the onset of the disease. The peak incidence is recorded in late summer – early autumn.
When infected with the Coxsackie virus, the disease begins with symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection, fever, then itchy spots and a blistering rash appear on the skin, the same as with chickenpox.
The difference between enterovirus infection and chickenpox:
- The peak incidence of Coxsackie occurs in the hot season - August, early September, while chicken pox can be recorded all year round.
- The rash with enteroviral fever is most often localized on the flexor surfaces of the feet and palms, as well as in the mouth - on the tongue, palate, and gums.
- After the rash, the skin flakes and peels off like a sunburn.
Due to the characteristic localization of the rash, the disease has a second meaning of “hand-foot-mouth”. Rashes with enteroviral fever on other surfaces of the body are rare, which is usually associated with a severe course of the disease.
Coxsackie infection, unlike chickenpox, is characterized by stomatitis - profuse blistering rashes on the oral mucosa.
Hives
An itchy blistering rash, but not chickenpox, may indicate an allergic reaction - hives. This is a condition that occurs when there is an individual intolerance to a certain food product or cosmetic product. Reddish spots first appear on the skin of the body and limbs, then irregularly shaped blisters rising above its surface.
Differences between urticaria and chickenpox:
- Urticaria is not a contagious disease and cannot be transmitted from one person to another.
- An allergic reaction can occur in response to food allergens, cosmetics, pollen, and exposure to physical factors (cold, heat, solar radiation).
- Sometimes blisters appear in response to the development of microbial infections or the medications used to treat them.
- With urticaria, there are no symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection and rarely an increase in body temperature, however, upon examination, a local increase in skin temperature over the blisters may be noted.
Acutely developed urticaria requires mandatory medical consultation, because severe allergies can lead to serious complications such as angioedema or anaphylactic shock. Chronic, indolent urticaria also requires examination by a specialist to identify the trigger of the disease and select treatment.
Roseola (sixth disease)
Currently, in addition to classic childhood infections (chickenpox, measles, rubella, scarlet fever), sudden exanthema or sixth disease is distinguished.
Just like chickenpox, it is caused by a virus from the herpes family, which is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. Most often this occurs through airborne droplets when talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Difference between chickenpox and roseola:
- The sixth disease begins with general malaise and increased body temperature. Unlike chickenpox, the rash does not occur during the fever, but after it subsides, i.e. on days 3-5 of illness.
- The rashes are small- and medium-spotted, pink in color, do not itch and do not form blisters.
- The typical localization of the rash is the torso and limbs.
The rash with sudden exanthema goes away on its own without any treatment 5 days after its appearance, leaving behind no peeling, areas of pigmentation or depigmentation. After roseola, as well as after chickenpox, stable lifelong immunity is formed.
Streptoderma
Besides childhood infections and allergies, the symptoms of chickenpox are similar to those of some bacterial infections. In this regard, if pustular chickenpox is suspected, a differential diagnosis with streptoderma should be carried out.
The main differences between streptococcal impetigo and chickenpox are:
- The vesicles with impetigo are “flaccid”, in contrast to the dense, tense vesicles with chickenpox.
- With streptoderma, pustules quickly appear on the skin.
- Bursting blisters leave behind erosions and ulcers.
- As the rash elements heal, characteristic yellowish crusts form.
Streptoderma is not characterized by increased body temperature and general malaise. The rash usually affects the trunk and limbs. Despite the fact that streptococcal impetigo is a contagious disease, it is less contagious than chickenpox.
Disseminated herpes
Diseases such as disseminated herpes and herpes zoster may resemble classic chickenpox.
Disseminated herpes is caused by a virus from the group of the same name, type 1. Typically, this microorganism provokes the local appearance of a blistering rash on the mucous membrane of the lips and around them, which is popularly called a “cold on the lips.”
However, with a significant decrease in immunity, for example, during treatment with immunosuppressants, with HIV/AIDS, or while undergoing high-dose chemotherapy, the infection can spread throughout the body and lead to the appearance of an itchy, blistering rash throughout the body.
Shingles
Shingles is caused by the same virus as chickenpox. Most often it develops:
- After suffering serious illnesses.
- In elderly and weakened people.
- Against the background of radiation and chemotherapy for oncological processes.
- While taking high doses of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs.
A characteristic feature of herpes zoster, in contrast to chickenpox, is the thickening of vesicular rashes along the nerve trunks - on the face in the projection of the facial nerve, in the intercostal spaces, along the sciatic nerve.
If blistering rashes appear on the skin of the face, body and limbs, you should consult a doctor to establish the correct diagnosis and select treatment.
How is differential diagnosis carried out?
Chickenpox in its typical course should be differentiated from a disseminated form of herpes, herpes zoster, enterovirus infection and sudden exanthema. In official guidelines you can find a clause stating that chickenpox should be distinguished from smallpox, however, at present, cases of this dangerous infection are casuistry.
Differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of:
- Epidemiological history. The doctor examines the vaccination card data, determines whether there was possible contact with infectious patients or with an allergen (food, pollen, detergents), and walks down the street without using repellents.
- Visual inspection. The localization and nature of the rash on the skin, damage to the mucous membranes, nails, and lymph nodes are studied.
The erased form of chickenpox should be distinguished from measles, rubella, bacterial impetigo, allergic reactions and even insect bites. The final diagnosis is made based on:
- Anamnesis data.
- Determining how long ago the child was ill and how the disease developed.
- On what day did the rash appear, the stages of its appearance.
It is especially important to carry out differential diagnosis of the disease in persons with immune pathologies, patients with immunosuppression, pregnant women and women planning pregnancy.
To determine an accurate diagnosis, additional research methods are used:
- Isolation of the virus from the liquid of the vesicles (by PCR or propagation in cell culture).
- Determination of antigens to the herpes zoster virus (by direct immunofluorescence in scrapings from the bottom of the vesicle).
- Serological. Determination of antibody titer by ELISA.
It is important to remember that serological diagnostic methods are not recommended by experts to determine the formed immune response after vaccination.
Where to contact?
If you feel unwell, have a fever and a rash appears, it is important to consult a specialist as soon as possible. To do this, you need to call a local pediatrician or a private doctor at home, or, if the child’s condition is serious and life-threatening conditions develop, call an ambulance.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or give your child any medications, especially antivirals and antibiotics, until examined by a doctor and determined what disease is present. The exceptions are Paracetamol and Ibuprofen at elevated body temperatures.
To simplify the diagnostic process and avoid false diagnoses, doctors do not recommend treating skin rashes with coloring antiseptics. Despite the fact that chickenpox is usually treated with Fukortsin or brilliant green, this cannot be done, since staining the skin green or red makes it difficult to study the morphological elements and difficulties in making a final diagnosis.
Repeatedly, young parents asked the pediatrician the same question - how to distinguish chickenpox from allergies, if the external signs of these diseases are similar to each other.
Skin rashes almost always appear due to allergic diseases. But an infectious disease such as chickenpox is also characterized by the appearance of a rash on the skin. To find out what kind of pathology we are talking about, you need to have a general idea of each.
What is chickenpox?
Chickenpox is an infectious disease that, as the name suggests, spreads in communities with lightning speed, almost like the wind. That is, it is very easy to get chickenpox. Children usually suffer from this disease, and they tolerate it quite easily. The same cannot be said about adults - for them, chickenpox becomes a real challenge. Fortunately, once you have had this disease, your body develops lifelong immunity to it.
The disease begins with an incubation period, the duration of which varies between 1–3 weeks. That is, a person who has had one contact with a patient with chickenpox may experience signs of this infection during this period. A person with chickenpox can infect someone two days before the rash and another five days after it.
- rash on the skin;
- severe itching;
- elevated temperature;
- general discomfort.
The main symptom of chickenpox is specific rashes.
Initially, they look like small pink spots that appear on the scalp, but very quickly begin to spread throughout the body. Soon these spots become papules - blisters with liquid contents.
After a few days, these papules should burst, after which small ulcerations - vesicles - remain on the skin, which should be treated with any antiseptic (usually brilliant green is preferred) to prevent infection. The rash process continues cyclically for at least 7 days. At the same time, new spots, papules, and vesicles can be observed on the skin at the same time.
After a few days, the ulcers become covered with crusts, which cause itching and soon disappear. If these crusts are severely scratched, characteristic scars may remain on the skin after the disease.
The disease progresses individually in each patient. If someone has a few pimples and the disease goes away easily, with a slight increase in temperature, then others may be covered with rashes from head to toe, and papules can be found even in the mouth and on the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Another noticeable symptom of chickenpox is severe itching. The rashes begin to itch after the vesicles dry out and crusts appear on them. In this case, antihistamines will come to the rescue.
What is an allergy?
An allergy is a disease whose symptoms may include itching, skin rashes, swelling, runny nose, lacrimation and much more. Rashes are frequent accompaniments of allergies, and they appear after direct contact of the body with an allergen.
Allergens, as provocateurs of the disease, can be very different. Typically, allergic diseases accompanied by skin rashes are caused by:
- drinking products;
- chemical substances;
- plant pollen;
- dust mites;
- animal fur.
Treatment of allergies is based on the exclusion of interactions with allergens that provoke the disease and the oral administration of antihistamines.
Currently, allergies are being detected more and more often. Every year more and more children with allergies are born. Therefore, knowing how to distinguish allergies from chickenpox is important for all parents.
Chickenpox or allergies?
It will be more convenient to consider the difference between chickenpox and allergies in the following table.
| Symptoms and treatment | Allergy | Chickenpox |
|---|---|---|
| Skin rashes | They are not always symptoms of allergies. The nature of the allergic rash resembles nettle burns, so this disease is usually called urticaria. | An obligatory symptom of the disease. The rashes change cyclically from pink spots to blisters with liquid contents and ulcers covered with crusts. |
| Body temperature | In most cases, there is no increase in body temperature. | Hyperthermic syndrome always accompanies chickenpox. |
| Features of the course of the disease | An allergy rash is a primary symptom that will go away on its own if contact with the allergen is avoided and the appropriate medication is taken. | Chickenpox rashes are a secondary symptom, since the disease will always be preceded by a long incubation period, during which the human immune system is suppressed, which is manifested by the development of hyperthermic syndrome and the development of general ailments. |
| Features of treatment | Clinical signs during allergies are quickly eliminated by taking an antihistamine. | Antiallergic drugs are also prescribed during chickenpox, but since the disease is not allergic in nature, they cannot cure it. These medications are prescribed as adjunctive therapy to relieve itching. |
| Additional symptoms | A rash during an allergy mainly appears only on the skin. | With chickenpox, rashes can appear not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. |
Another important point that can tell whether a patient has chickenpox or an allergy is knowledge of the fact that it preceded the onset of the development of the disease?
If there can be no question of any questionable contacts, then between the diseases - allergies and chickenpox, the assumption would be an allergic reaction. The disease can occur as a result of eating a new product (in young children a clear example is complementary foods, in older children and adults - dishes from an unfamiliar kitchen), treatment with certain medications, etc.
Once you are sure that the skin rash is actually caused by an allergy, it is necessary to take decisive measures aimed at eliminating the allergen. But, under no circumstances should you self-medicate, since both of these diseases are serious in nature and, therefore, can result in complications. Only a qualified specialist can determine how an allergy may differ from chickenpox, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.