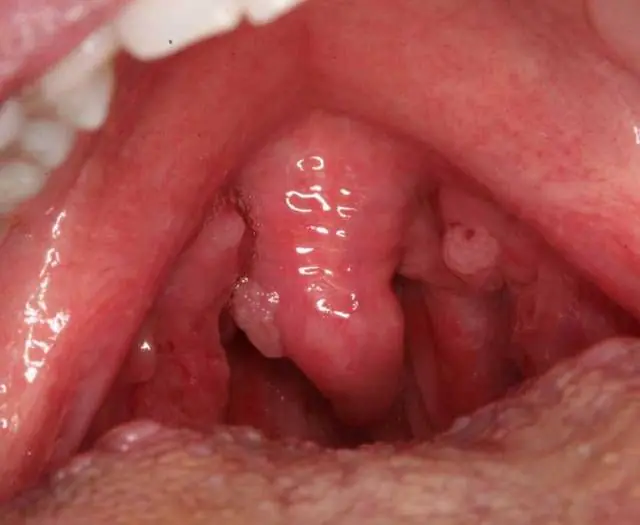
- What is a polyp
- What does papilloma look like?
- What is the difference
The difference between a polyp and a papilloma is a list of signs by which the type of neoplasm can be determined. Contrary to popular myth, polyps and papillomas are different formations. They have striking differences in both appearance and nature of origin. These growths are also treated according to different schemes.
What is a polyp?
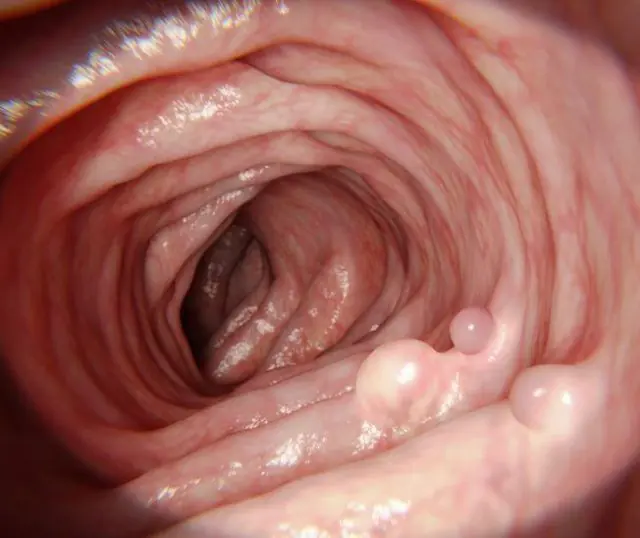
Photo of polyps in the intestines
A polyp is a single or multiple formation that affects the mucous membrane of a person’s internal organs or cavities. Such growths may have an irregular or rounded shape. Most often they are found in the uterus, intestines, urinary or gall bladder, and sinuses.
Essentially, polyps are unnatural growths of epithelial tissue. But they always affect the mucous membranes or the lining surface of certain internal organs. This is how polyps differ from papillomas.
The nature of these growths is non-viral. The cause of polyps can be various factors:
- Hormonal imbalances in patients over 35-40 years of age;
- Sluggish chronic infections - dysbacteriosis, diseased teeth, helminthiases, fungal diseases;
- Digestive disorders caused by unhealthy food, poor diet;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nasopharynx, urinary and reproductive systems;
- Lack of physical activity;
- Nervous stress, fatigue;
- Poor metabolic process.
These growths can have different appearances: on a stalk or a voluminous base, smooth or uneven. Their color ranges from whitish to pink. Depending on the reasons for their appearance, polyps can be inflammatory (localized at the site of inflammation), hyperplastic (healthy mucous membrane grows), neoplastic (considered a precancerous condition).
As a rule, polyps do not cause discomfort to the patient. They are usually discovered during a routine medical examination.
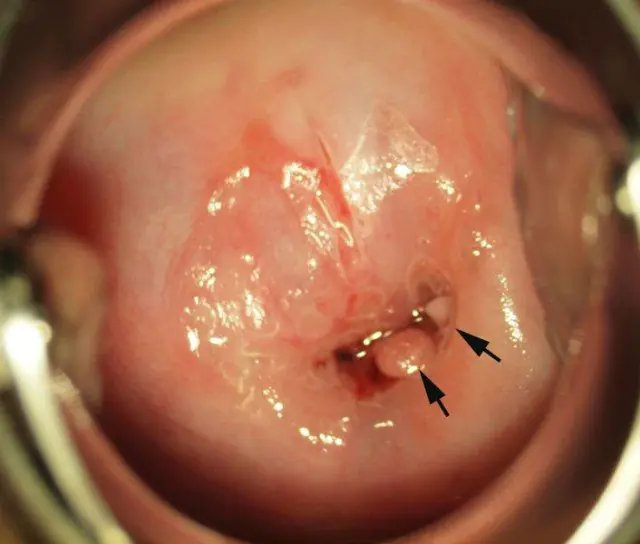
The photo shows a polyp in the uterus
If the polyp is large, certain symptoms may appear, depending on the location of the growth:
- If the polyp is located in the uterus, then heavy discharge (bloody or whitish) and pain during intercourse may occur.
- When a polyp is localized in the intestines, constipation sometimes occurs, mucus or blood appears in the feces.
- If the neoplasm affects the nasal cavity, breathing may be difficult, chronic runny nose, snoring, and headaches may appear.
- If a growth is found in the bladder, various impurities may appear in the urine and the urge to go to the toilet may become more frequent.
What does papilloma look like?
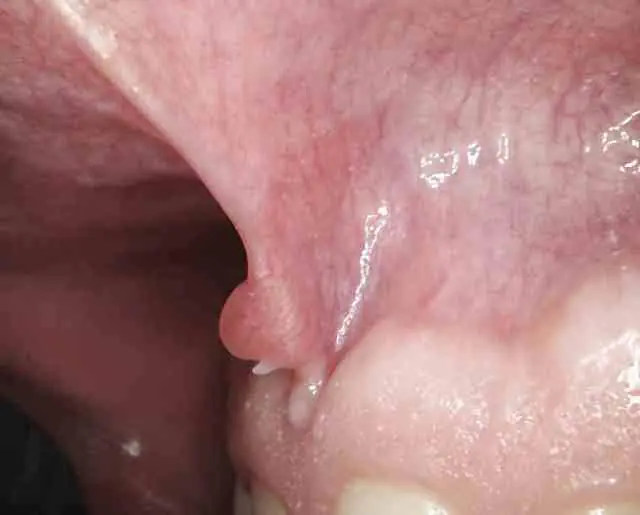
Photo of papilloma on the oral mucosa
Papilloma is a viral neoplasm on the skin or mucous membrane. Most often, such a growth is located on the neck, armpits, face, limbs, and genitals. Papillomas, unlike polyps, are very rare on the nasal mucosa or vocal cords. Sometimes the cervix can be affected.
If you are interested in the difference between a polyp and a papilloma, then the main one is the reason for the appearance of these growths. Papillomas are a waste product of HPV in the human body. An infected patient often experiences external manifestations of the disease in the form of growths on the body.
The prevalence of HPV is very high. According to various estimates, about 80-90% of people on the planet are infected with it. The virus is transmitted sexually, domestically, and sometimes from mother to baby during childbirth.
Papillomas can have different types. Filamentous are thin growths on a stalk; they can have an oblong or papillary shape. Flat papillomas protrude slightly above the surface of the skin in the form of nodules without folds with a smooth surface. Pointed papillomas are called condylomas, and they are located on the genitals of men and women.The virus can remain in the blood for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. With accompanying factors, HPV is activated and new growths appear on the skin. Most often, papillomas occur with decreased immunity, chronic illnesses, colds, hormonal imbalances, alcohol abuse, smoking, frequent stress and overwork.
As a rule, papillomas do not cause any discomfort in the patient. Normally, they are painless and have a flesh-colored or pinkish tint.
- Read also: what are the differences between papilloma and warts?
How are polyps different from papillomas?
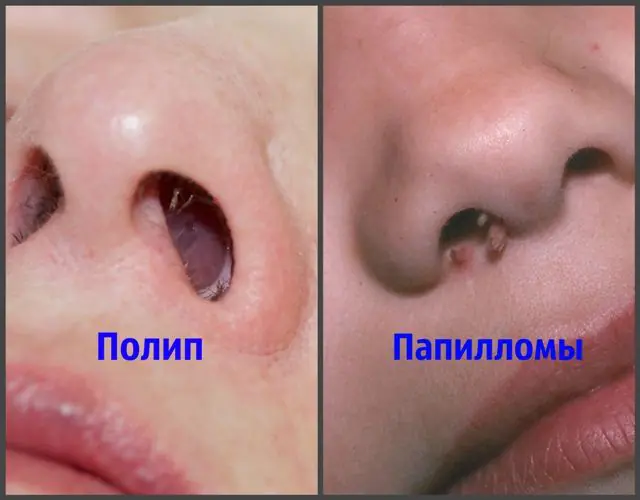
You should understand the difference between polyps and papillomas. This determines the further treatment of these tumors. Despite their external similarity, these growths have a number of significant differences that help to identify them.
Let's look at the main differences between polyps and papillomas:
- Location. Polyps are concentrated on the mucous membranes and lining surfaces of internal organs and cavities. Papillomas can affect both the mucous membrane and the skin. Most often they are found on the epidermis.
- Appearance, size. Polyps, as a rule, have a round shape and a different surface (smooth or uneven). Papillomas can resemble a broccoli inflorescence or be in the form of threads, papillae, or nodules on the skin.
- Growth pattern. Polyps are constantly growing slowly. Papillomas can maintain their size for a long time and increase sharply if there are contributing factors, for example, trauma, and they also grow during malignant degeneration.
- Reasons for appearance. Polyps, unlike papillomas, are non-viral in nature. They occur with a general decrease in immunity or hormonal disorders. Papillomas always form as a result of human infection with papillomavirus.
- Diagnostics. It is quite difficult to detect a polyp at an early stage, since in most cases it is hidden from view (located on internal organs). It is usually diagnosed during an ultrasound examination. It is quite easy to detect papilloma - as a rule, it is located on visible parts of the body.
- Patient age. Polyps most often affect people in adulthood - 35 years and older. Papillomas can occur at any age, even in infants, if the route of transmission of the virus is from mother to child.
- Features of treatment. Polyps can be removed surgically - curettage, excision and other methods. In this case, the growth disappears without a trace, what is the difference between polyps and papillomas. In the latter case, you can only get rid of the external manifestation of HPV. The virus itself will remain in the blood, and relapses are possible.
It is worth noting that both polyps and papillomas can degenerate into malignant tumors. The risk of malignancy is higher in papillomas, since there is a group of HPV strains with high oncogenicity. Especially dangerous are growths that affect the cervix in women. In most cases, this is a pathogen with a high tendency to malignancy of papillomas.
- Read also about the reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the body
How to get rid of polyps - watch the video:
Only doctors can determine the difference between a polyp and a papilloma during a special examination. It is imperative to treat these neoplasms, as they pose a threat of malignancy. In addition, the appearance of these growths indicates a malfunction of the body and a general decrease in immunity. Therefore, this condition requires not only surgical removal of formations, but also conservative therapy.
- Related article: What tests need to be taken for papillomas



