Nevi on the body are otherwise called birthmarks, moles, and are benign formations that appear on the skin. Moles are either at the same level with the skin or rise above it; the reasons for their appearance are varied, mainly genetic predisposition and a certain skin type. The sizes of the nevi shown in the photographs below vary from very small (1-2 mm) to large (15-25 cm).
The color, depending on the cells that formed it, can be:
Benign formations can occur not only on the skin, but also on mucous membranes (for example, in the vagina), connective membranes, edges of the lips, blood vessels of the eye as a spot, a skin phenomenon consisting of nevoid cells.
Nevi can be congenital or acquired. Educational cells appear in the prenatal state of the developing human body. They originate in the neural crest, a “cellular reservoir” that serves as the basis for the formation of various anatomical structures.
According to statistics, almost 80% of white-skinned representatives of the world's population have nevi on their bodies. In adults, the number can be 30 pieces or more. In childhood, they may not exist, but during puberty, during pregnancy, under the influence of sun activity, nevi appear on the skin.
A benign formation, developing, goes through several phases:
- intraepithelial (initial);
- border;
- intradermal (at the age of 30 years);
- reverse (in old age, the cells “return” to the layers of the skin).
Nevi are accumulated nevocytes containing large amounts of melanin. Neocytes are called changed melanocytes - cells that determine the shade of human skin. When exposed to sunlight, melanin appears in them, giving the skin a tan color.
It is important to know! The shapes and sizes of birthmarks are so diverse that they are confused with some dermatological pathologies: “cutaneous horn” (fibroma), seborrheic keratosis, papillomas. Therefore, only a specialist is able to make an accurate diagnosis through differentiation. This often requires a histological analysis to study the taken tissue biomaterial.
Causes of nevi
Disturbed embryogenesis causes the development of congenital nevi. They can have hereditary traits and serve as proof of belonging to the same genus.
“Children’s” melanocytic nevi appear under the following predisposing conditions:
- the effects of toxic compounds and radiation on a woman carrying a child;
- the presence of pathologies in pregnant women that have developed in the urogenital tract;
- toxicosis, threats of abortion;
- hereditary unfavorable predisposition.
The following provoking factors contribute to the occurrence of acquired nevi:
- hormonal “explosion” during puberty;
- pregnancy period with hormonal fluctuations;
- oral contraceptives taken;
- skin pathologies of infectious and allergic nature;
- injury to the skin as a result of mechanical impact;
- insolation (exposure to direct solar radiation);
- influence of radiation and x-rays on the human body;
- diseases of viral etiology.
Types of nevi
Classification of nevi according to histological characteristics provides an assessment of the characteristic features of any type of formation, which contributes to an effective prognosis of the course of the disease. There are more than 50 types of birthmarks, of which ten nevi are common.
The conditionality of division into groups concerns tumors:
- Melanoma-hazardous (having a tendency to degenerate into malignant formations).
- Melanoma-hazardous (without a tendency to degenerate into malignant formations).
Melanoma formations include the following types of nevi:
Blue
Such a single formation, which is an accumulation of melancites, is in a precancerous state, although it is called benign. At the same time, it has no tendency to undergo oncological degeneration. The color of the nevus - bluish or blue-black - depends on the active production of melanin by the nevus cells. It has the correct shape, evenly outlined contours. Due to its elevation at the skin level, such a nevus can often be injured by items of clothing, jewelry, etc. Patients with such a birthmark should be regularly examined for preventive purposes to prevent degeneration into a malignant tumor.
| Blue nevus |
Borderline pigmented
This is a congenital formation that manifests its characteristics immediately in the first periods of a person’s life. The nevus develops along with the growing organism, even without the influence of any external factor. The brown/brown/black spot can reach a diameter of 1.5 mm to two to three or more centimeters. Such nevi “settle” on the palms and soles. Malignancy can manifest itself after injury or prolonged exposure to the sun.
| Borderline pigmented nevus |
Giant pigment
Nevus, reaching up to 50 cm in diameter, is a congenital formation. It differs from other formations in shades of gray/brown and rises above the skin level. The formation has cracks, grooves, warts, so there is a high risk of possible trauma and degeneration into a malignant tumor. In this case, the patient is recommended to solve the problem surgically.
| Giant pigmented nevus |
Nevus Ota
The manifestation of the skin phenomenon is directly dependent on the nervous factor. The spot, consisting of a large amount of melanin, is localized on the most exposed part of the body - the face. Black-blue formation of genetic orientation is found in representatives of the Asian race.
| Nevus Ota |
Dysplastic
Congenital nevus is registered in half of the registered cases. Spots of this type can be detected in members of the same family. Dark brown multiple formations are small in diameter: no more than half a centimeter. They are located throughout the body and have a smooth, flat surface. A high rate of transformation of dysplastic nevus into melanoma is recorded - 90-95% of cases.
| Dysplastic nevus |
Melanomic nevi , in turn, there are several types:
Intradermal pigment
These moles, which form in the dermal layer, under the skin, are mainly reported during adolescence. They are initially small in size, but grow and develop along with the teenager’s body. Nevi of this type are practically unable to degenerate into malignant ones. Only under the influence of certain factors there is a risk of melanoma.
Such formations can be located on the neck, in the groin area, armpits, under the mammary glands, sometimes on the upper and lower extremities, and the skin of the body.
| Intradermal pigmented nevus |
Papillomatous
This type of nevus has a repulsive appearance, being a cosmetic defect. A brown or pink mole in the form of a growth rises above the skin level, has a soft granular surface, and is painful when touched.
Such moles are found on the head under the hair, and are also found on the body. The growth of formations is slow, transformation into a malignant formation is practically not recorded.
| Papillomatous nevus |
Galonevus
This birthmark is also called Setton's nevus. It appears in people with weakened immunity due to hormonal imbalances and autoimmune pathologies.
Halonevus is characterized by an oval shape, large size, and elevation on the skin. The formation is localized on the trunk, upper and lower extremities. There are both single and multiple nevi, but they do not degenerate into malignant tumors.
| Galonevus |
Mongolian spot
A similar type of mole is observed in newborns, sometimes found in adults, appearing on the skin in the form of a fifteen-centimeter spot in diameter as a result of a hormonal pigment disorder. As the name suggests, this phenomenon is often recorded in Mongolia: in almost 92% of cases. The nevus is “located” on the child’s sacrum or buttocks. Conversion to melanoma is not observed. The stain may generally disappear over time.
| Mongolian spot |
Fibroepithelial
This type of congenital or acquired nevus is often recorded. It appears under the influence of hormonal changes in old age. Soft reddish/pinkish moles are large in size and can be localized throughout the body. They rarely transform into malignant ones and are easily removed. They cannot “fall away” on their own.
| Fibroepithelial nevus |
Symptoms
The main distinguishing features of nevi are their appearance: shape, color, size. Some have hair follicles, roughness, warts and other “accompanying” elements. Others are distinguished by their smoothness, localization, and invisibility. Only a specialist is able to distinguish formations, give their descriptions, assign them to certain groups and identify the danger using diagnostic measures.
Diagnostics
The study of moles is an important point in diagnosis, with the goal of identifying the danger of transformation of benign nevus cells into malignant ones.
Diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
- Visual, anamnesis collection. By asking questions to the patient, the doctor finds out:
- period of nevus formation, whether it is congenital or acquired;
- whether changes in the appearance of the formation are noted;
- reasons for the changes that occurred (burns, injuries, etc.);
- whether there was an attempt to remove the mole, and in what way.
Important to remember! A timely visit to a dermatologist (at the first signs of transformation of a mole) for diagnosis can save a person’s life, preventing the formation of a malignant tumor.
A biopsy is not performed for diagnostic purposes!
Treatment of nevi
The treatment of pigmented formations is carried out by a dermatologist-oncologist. The therapeutic approach is carried out in a clinical setting using surgical intervention.
| Excision and laser therapy of nevus on the face |
First of all, we take into account moles that are subject to regular injury or risk of injury and are located:
- under the hair;
- in women on the back, in the area of the bra clasp;
- in men on the neck, face, chin (dangerous when shaving);
- in the groin area, skin folds;
- “on a leg” (they can tear or come off completely).
To remove nevi, use the following methods:
- Resection. The nevus (usually large in size) is excised along with three centimeters of the surrounding skin using a scalpel under local anesthesia. The disadvantage of this type is the presence of a scar after surgery and pain. The removed lesion undergoes histological examination.
- Cryodestruction. This is a procedure for freezing a nevus using liquid nitrogen. This method can also eliminate small formations. The advantages of cryodestruction are the absence of scars and the need for additional pain relief.
- Electrocoagulation. The nevus is cauterized using an electric current. Children undergo the procedure under general anesthesia, adults - under local anesthesia. Suitable for removing small and medium-sized moles.
- Laser therapy. Used to remove moles on the face and neck. Possessing high precision, the laser does not leave scars on the skin. The main point of this procedure is the depth of penetration of the laser beam under the skin to completely destroy the nevus cells.
| Laser mole removal |
Postoperative complications
Removing birthmarks does not always go smoothly; sometimes complications arise, including:
- development of the inflammatory process in cases of improper wound care in the postoperative period;
- malignancy (the process of formation of cancer cells) in the place where the nevus was not completely removed;
- cosmetic defect - the presence of a scar.
It is important to know! The method of surgical intervention is determined by the doctor, taking as a basis the characteristics of the nevus and the functionality of the medical institution. The patient can express his wishes, but his opinion is not decisive.
Prevention of melanoma
To prevent the development of melanoma, a malignant tumor, exposure to pathological factors should be excluded. Melanoma is dangerous because it can metastasize to the brain, liver, and other organs. Death from skin cancer occurs in 50% of cases.
Of course, complete prevention of transformation into melanoma is impossible, but some recommendations, carefully followed, reduce the risk of benign cells degenerating into cancerous ones.
Tips concern:
- reducing the time spent under the sun's rays, especially during periods of sun exposure
special activity (from 12 noon to 17 pm);
- avoiding ultraviolet radiation that affects nevi;
- careful handling of moles so as not to injure them;
- timely contact a dermatologist-oncologist at the first signs of changes in moles regarding their shape, size, color.
Cosmetics designed to reduce the impact of ultraviolet radiation on the skin are not able to protect nevi from harmful effects.
Birthmarks (moles) are formations on the skin that many people do not pay attention to. And they are only interested in them if another mole is suddenly discovered on the body. What does the process of the appearance of new birthmarks indicate, and does it pose a health hazard?
What are birthmarks
Moles, or, as doctors say, nevi, are accumulations of special cells – melanocytes – in the layers of the skin. The purpose of melanocytes is to produce the pigment melanin, which protects the skin from harmful ultraviolet radiation. Normally, most melanocytes are located between the top layer of skin - the epidermis and the middle layer - the dermis. Melanocytes are usually distributed evenly over the surface of the skin. However, this does not always happen. Irregularities in the distribution of melanocytes lead to the formation of birthmarks.
Moles are usually dark or brown in color. Less commonly, almost black nevi can occur. Blue or purple moles are also observed.
Nevi are usually evenly colored, although on their surface there may be single darker and lighter areas compared to the background. A typical mole is round or oval in shape and has a diameter of no more than 5 mm. Moles larger than 10 mm are called giant. There are also birthmarks of irregular shape and uneven color - dysplastic nevi.
The most dangerous type of mole is a dysplastic nevus.
Nevi are also divided into intradermal and epidermal - depending on the depth of the accumulation of melanocytes.
Moles can be located on any part of the body. There are a lot of them on the arms, torso, and neck. However, most often (relative to the unit area) moles are found on the face. Moles can also form on mucous membranes, although this is rare.
Usually nevi do not protrude above the skin level. However, there are also protruding (convex) moles.
Lentigo and freckles
There is also a type of skin spots called lentigo. They are usually larger in size than a typical nevus, but also have a less intense, pale brown color and less clear boundaries. Their appearance is also associated with increased melanin production.
Another type of melanin-containing spots are freckles. Lentigines are most often observed in adults and the elderly, freckles - in children and adolescents. Lentigines and freckles are not usually classified as moles, although they have a similar origin.
Angiomas
Angiomas are also often classified as moles. These are red, slightly raised formations on the skin that are vascular in nature. If you press on such a formation, it will turn pale and then return to its original color. This is explained by the fact that angiomas consist of many tiny vessels. The mechanism of their occurrence is also not fully understood. Only one thing is clear - unlike ordinary moles, their occurrence is in no way connected with genetic reasons. Vascular moles have a relatively low risk of malignant transformation.
Angioma – vascular mole
When and who gets moles?
Although nevi are popularly called birthmarks, in fact, most moles are not present in a person from birth, but appear much later, throughout life. 99% of children are born with an absolutely clean body, devoid of age spots. And the first birthmarks appear in babies in the first or second year. However, these moles are so small that they are often simply not noticed.
Most moles appear on the body during adolescence and before the age of 25. This feature is associated with the intensive production of sex hormones during this period. And old moles may increase slightly or change color during puberty.
However, even in adults, age spots can occur from time to time. And some spots can also disappear spontaneously. The total number of moles can reach hundreds, although usually there are much fewer of them - no more than a dozen. There are also people who have almost no moles. Women usually have more birthmarks than men. Light-skinned people also have more moles than dark-skinned people.
Thus, the appearance of new moles in various parts of the body is a process that is a normal phenomenon in the body. Usually it is not associated with any pathologies. Of course, if the number of moles does not exceed a reasonable limit. And the birthmarks themselves look standard and do not cause discomfort.
Causes of birthmarks
The reason for the appearance of new birthmarks on the body is largely unclear. What is known is that the amount of melanin in the body is regulated by melanotropic hormone produced by the pituitary gland. Consequently, if a new mole appears on the body, this fact is often a consequence of increased levels of this hormone.
What phenomena affect the level of melanotropic hormone? First of all, such factors include an imbalance in the endocrine system. In women, this condition occurs during pregnancy and childbirth, in the period preceding menopause. Women are more likely to experience hormonal changes. Perhaps this circumstance is the reason for the more frequent appearance of birthmarks in women.
In men, this process can be triggered by diseases or injuries of the testicles, resulting in increased estrogen production. Also, the reasons for fluctuations in the level of melanotropic hormone can be:
- stress,
- serious illnesses,
- pathology of the pituitary gland,
- viral infections.
Insect bites and abrasions are another possible cause of moles. This circumstance is due to the fact that wounds can get infected, which often leads to local accumulation of melanin.
New moles can also appear after exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays. Exposure to sunlight or other ultraviolet sources is accompanied by an increase in the level of melanin in the skin and the release of melanocytes to the surface. The sun's rays can not only lead to the appearance of new nevi, but also to the enlargement or degeneration of old ones. It is possible that other types of radiation, such as x-rays, contribute to the appearance of moles on various parts of the body. Such radiation can affect the body, for example, during medical procedures.
The causes of angiomas are dysfunction of the liver, intestines, and pancreas.
What to do if new birthmarks appear?
If one or two moles appear on the body in a place where there were none before, this is not yet a cause for concern. True, here you need to pay attention to the shape, color, size of the spot and accompanying symptoms. If the mole has the correct shape and uniform color, does not hurt, is not inflamed and does not bleed, then most likely it does not pose a danger. But a change in shape, color or increase in existing moles should be alarming.
If there are reasons for concern, or the nature of the formation is unclear, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. The fact is that some birthmarks can turn into malignant tumors - melanomas. The greatest danger is represented by dysplastic nevi. Although this happens infrequently, it still doesn’t hurt to be on the safe side. The main thing to remember is that you should not touch the mole or try to remove it yourself. This can lead to dire consequences.
Removal of common nevi is usually not indicated. The only exceptions are moles that protrude from the skin, the risk of injury to which is very high, moles that create psychological discomfort in the patient, as well as dysplastic nevi.
Why can there be many moles on the body, and are they dangerous?
The abundance of nevi in itself is not dangerous to health. However, they need to be closely monitored and regularly examined by a dermatologist. A doctor's examination is also required after a holiday in the southern resorts. Regular self-examination of the body is also necessary. If a new birthmark of an unusual shape appears on the body, or an old one has quickly grown and changed its shape, size and color, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Numerous moles on the body
People with an abundance of moles on their skin should remember that the sun is not only a friend, but also an enemy. The danger comes from the ultraviolet rays contained in the radiation of the star closest to us. When they come into contact with pigmented areas of the skin, they can cause their malignant degeneration. Therefore, it is necessary to limit the duration of sunbathing. In summer, you should not sunbathe during the most dangerous hours in the middle of the day, when the largest amount of hard UV rays reaches the Earth. And in a situation where the sun's rays fall on bare skin for a long time, it is necessary to use sunscreen to protect the body. Recently, there has been a thinning of the ozone layer in the atmosphere. This results in increased intensity of UV rays. It has also been established that people with pale skin are more susceptible to the negative effects of radiation than people with dark skin.
If a person has many nevi on his skin, then often only his genes can be to blame. It is known that the tendency to the abundant appearance of nevi can be inherited. Also, the appearance of moles is, to some extent, evidence of the biological processes of aging. Although, on the other hand, there is a theory that the abundance of moles reduces biological age by several years, and moles themselves are a protective factor for the body. According to popular belief, moles are a symbol of longevity and promote good luck. But another fact has been proven - the abundance of nevi increases the likelihood of developing skin cancer.
The content of the article:
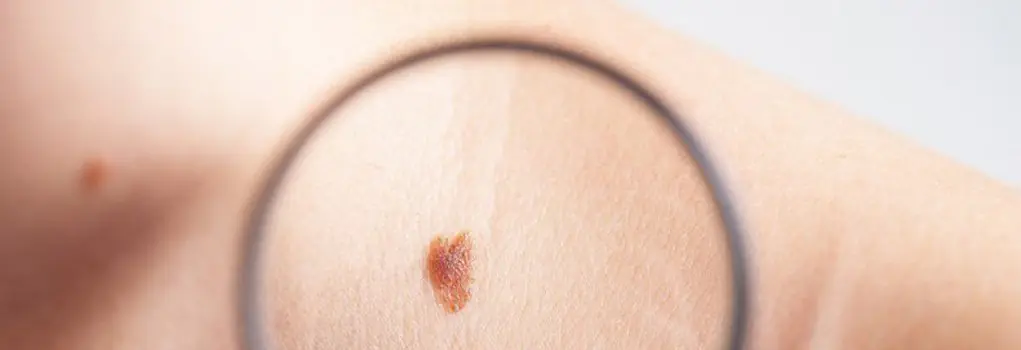
Reasons for the formation of moles
Moles, or as they are scientifically called, nevi, are formed in the upper layers of the skin when a large number of pigmented cells accumulate next to each other. Typically, such neoplasms begin to appear during the first year of a child’s life - in this case they speak of congenital spots, the appearance of which is embedded in the baby’s DNA, or during puberty against the background of hormonal changes.
The exact cause of the formation of a nevus on the body is very difficult to establish. If we exclude the hereditary factor, due to which moles are already noticeable in infants, a hormonal surge in the body can provoke the appearance of new spots. For this reason, new spots are especially noticeable during pregnancy or menopause in women, with certain diseases of the thyroid gland, etc.
The frequency and duration of sunbathing affects the number of nevi, because it is under the influence of ultraviolet radiation that the melanin pigment appears. By the way, in many cases it is sunburn that provokes the degeneration of a benign mole into a malignant one.

Red moles - most often noticeable in the form of small red dots - are evidence of pathological branching and growth of the circulatory system, but they do not pose a health hazard. Such nevi can appear and disappear on their own.
Stress can also trigger the formation of moles - it has long been proven that strong negative experiences also change the body’s hormonal system, which directly affects the appearance of any neoplasms. Other reasons may be any radiation or x-ray exposure, viral infections, or unfavorable environmental conditions.
Types of moles on the body
Experts distinguish moles depending on their size, color, shape, and location on the skin. Based on all these parameters, the following types of nevi can be distinguished:
- Hemangiomas are vascular moles of bright red or burgundy color, which can have different sizes, but rarely exceed 2 mm in diameter. They are located either in the epidermis itself or rise above it.
- Lentigo is a uniform pigment spot, the color of which is slightly darker than freckles.
- Flat moles are neoplasms located in the dermis itself or slightly rising above it. Their size varies within 10 mm, localization extends mainly to the palms, soles and genital area, and the color range ranges from yellowish-brown to black.
- Convex moles are brown nevi that rise above the skin. The surface can be either absolutely smooth or uneven. Among them there are hairy formations.
- Dysplastic moles are nevi of various shapes, exceeding 10 mm in diameter. Such formations are distinguished by reddish tints and blurred edges, are usually inherited and are located on the buttocks and chest.
- White moles are nevi that have an almost transparent color and sometimes a white edge. The colorlessness of such neoplasms is due to an insufficient amount of melanin at the site of localization. They can usually be seen on the scalp.
- Large pigmented moles are brown or almost black formations over 1 cm in diameter, localized either in the epidermis or rising above the skin.
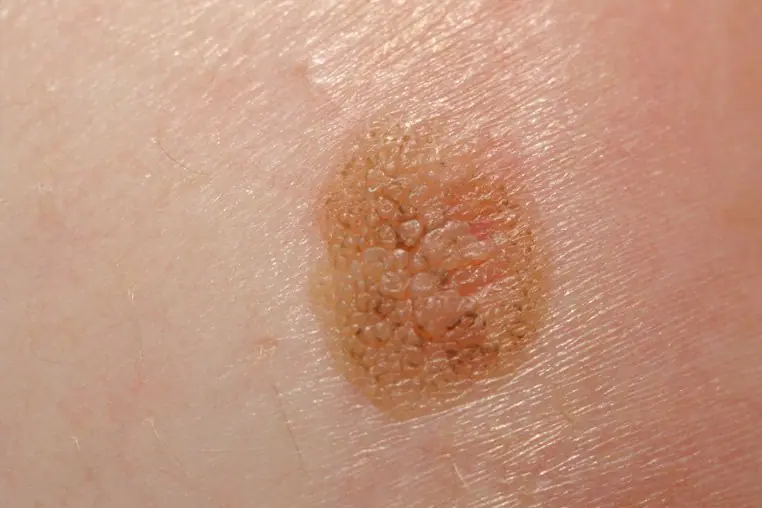
According to statistics, it is large moles that more often degenerate into malignant formations, so they should be constantly monitored.
Moles as a signal of dangerous diseases
Moles are considered benign formations, which, under the influence of certain factors, can cause the development of such a dangerous cancer as melanoma.
According to statistics, 30% of melanomas develop in the area where nevi are located.
Factors contributing to the degeneration of moles into malignant ones:
- Ultraviolet radiation - scientists have repeatedly stated the danger of direct sunlight for the skin in general and pigmented spots on it in particular. This is also confirmed by statistics, according to which residents of southern countries more often suffer from melanoma, and it manifests itself in open areas of the body.
- Hormonal imbalance - hormones control overall health, including the formation and degeneration of nevi. Not always their imbalance in the body leads to melanoma, but the fact that moles begin to transform into malignant ones during a hormonal surge has been confirmed.
- Injuries - according to oncologists, the transformation of nevi in almost half of the cases is associated with injury to either themselves or the skin around them. In this case, both deep wounds and seemingly insignificant scratches can cause mutation.
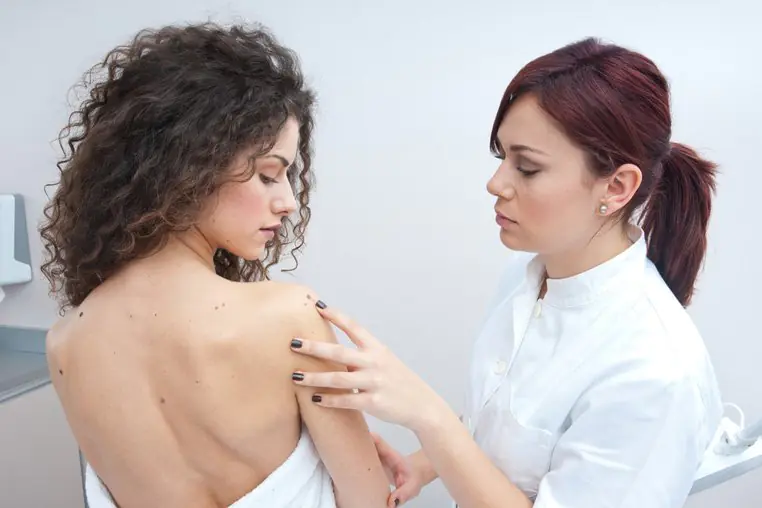
For this reason, hanging moles or nevi in places where they are easy to touch are recommended by dermatologists for removal.
Which moles are dangerous:
In order to prevent the development of melanoma, experts came up with the AKORD system, which helps ordinary people not to forget the main signs of dangerous moles and to take care of their health in a timely manner. ACORD is:
— Asymmetry – both parts of nevi, especially large and dark ones, must be symmetrical with each other, since asymmetry is a sign of degeneration of a mole;
— Edge – uneven edges of pigmented spots should also be a sign of concern, especially if they are wavy or jagged;
— Coloring – the color of a healthy mole is usually constant, so any darkening of the nevus is a reason to consult a doctor;
— Size – moles of about 10 mm or more should always be under the supervision of a specialist, since the risk of their mutation is especially high;
— Dynamics - any changes in moles, be it peeling, cracks, enlargement, itching or fluid secretion, may indicate the development of a malignant neoplasm.
It is important to note that the listed symptoms are not always 100% indicative of oncology, sometimes this can be the body’s reaction to sunburn or hormonal imbalance, but it is always better to make sure there is no danger, since melanoma is considered one of the most aggressive types of cancer.
Very often, to be on the safe side, doctors advise removing moles that have a high chance of degenerating based on external signs, as well as those nevi that can be accidentally injured by hands, clothing, a comb or a razor. It is better to get rid of them from a doctor, and not from a cosmetologist, who is not able to conduct the necessary preliminary studies of tumors.
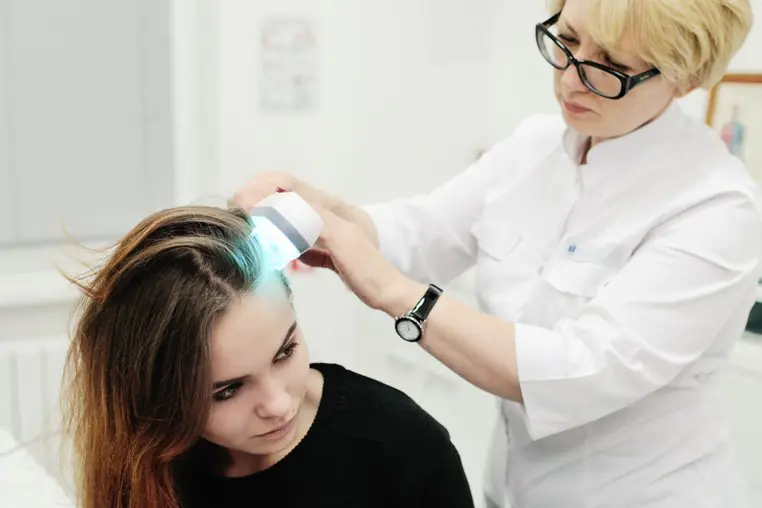

As methods for removing moles, modern medicine offers: surgery, burning with a laser or liquid nitrogen, as well as electrocoagulation. Their choice depends on the specific situation and problems with nevi.
The meaning of moles on the body
Ancient Tibetan and Indian practitioners believed that all lines and spots on the body have their own meaning. And moles were studied especially carefully. Thus, it was believed that moles on a person’s neck indicate the fickleness of unbalanced nature, rapidly changing principles and tastes, which especially concerns the female half.
Markings on the palms are usually characteristic of extraordinary individuals; they indicate great willpower and the ability to even change fate with due effort.
Moles on the chest appear more often in people whose lives are always full of different events, both positive and negative. But at the same time, their owners always maintain a positive attitude and can find a way out of any situation.
In ancient practices, the stomach is the basis of a person’s foundations, so moles on it can mean self-love, self-indulgence, and even some kind of selfishness.
A spot on the navel is a sign of wealth, and for the female half it is also a sign of good luck in love affairs.
Nevi on the face are of particular importance. Thus, a mole on the chin reveals the vulnerability of nature, above the upper lip it declares independence, and between the eyebrows indicates good intuition. For women, a mole near the lips can mean some frivolity and great sexuality of nature, but a man with such a mark, on the contrary, embodies modesty and a penchant for one love for life.



