Indirect cardiac massage is performed to restore heart function and blood circulation. As a rule, mechanical action is carried out after cardiac arrest to restore its vital activity, as well as maintain continuous blood flow. Absolutely all cases of stopping are indications for use.
What are the signs in case of sudden cardiac arrest:
- Loss of consciousness
- Sharp pallor of the face
- Stopping breathing
- Disappearance of pulse in the area of the carotid arteries
- The appearance of rare, convulsive breaths
- Dilated pupils
Closed cardiac massage should be performed until independent cardiac activity is restored. Signs of independent cardiac activity are:
- Appearance of pulse
- Reduction of pallor and cyanosis
- Constriction of pupils
Rules for external cardiac massage
As soon as a person’s breathing and cardiac arrest are detected, regardless of the cause, a closed massage technique must be performed. But it is worth keeping in mind that a lot will depend on the correct execution of the techniques. Untimely and incorrect technique may be ineffective.
The procedure is performed by rhythmically pressing the heart through the chest. Pressure occurs on the relatively mobile part of the sternum, which is located below. It is behind her that the heart is located. What happens in this case: blood is “squeezed” out of the heart cavity into the blood vessels. Sufficient blood circulation in the absence of heart function can be achieved by 66-7 pressures per minute.
When carrying out the procedure, the victim must be laid with his back on a hard surface, the chest is exposed and the body is freed from compressive things (belt, suspenders, etc.). Human. The person providing assistance should stand in such a way that it is convenient for him to bend over the victim. If the victim is located at a higher level, the person being massaged should stand on a small chair; if, on the contrary, at a lower level, it is necessary to kneel.
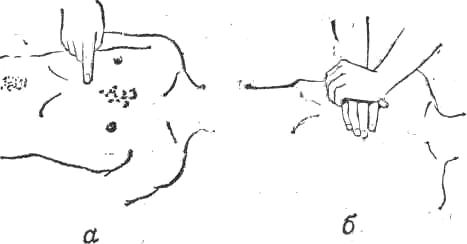
Indirect cardiac massage technique
The first step is to determine the place where the thrusts need to be performed. The point is located in the lower third of the sternum. The person being massaged should place the upper edge of the extended palm there, and place the other hand on top, as shown in the figure. The body tilted forward helps slightly when applying pressure. The pressure itself should be carried out in quick bursts so that the sternum goes down 3-4 cm. The pressure force should be concentrated in the lower part of the sternum. If you apply pressure to the upper part, a fracture may occur, since the upper part is immovably attached to the bony ribs. You should also avoid pressing on the ends of the lower ribs, as this can also lead to their fracture.
Do not apply pressure to the soft tissues located below the chest. This can lead to damage to the internal organs located there. This is, first of all, the liver. The shocks are repeated approximately once per second. If the person being massaged has an assistant, the second person must perform artificial respiration.
Artificial respiration is carried out by blowing air into the patient's mouth. Ventilation and indirect cardiac massage are performed to provide oxygen to the body in the absence of heart function. Due to the fact that it is difficult to expand the chest through pressure, artificial respiration is carried out in specially designated pauses, which are performed after 4-6 pressures.
Execution technique
- All restrictive clothing must be removed from the victim’s body.
- Clear your mouth of dirt, vomit and other contaminants.
- The victim's head should be tilted back as much as possible.
- The lower jaw needs to be brought forward.
- Take a deep breath and exhale into the victim’s mouth. If possible, you need to exhale air through gauze or a scarf, after making a hole of 2-3 cm.
- The victim's nose must be pinched.
If you have performed the massage technique and artificial respiration correctly, the victim should display the following signs:
- The appearance of independent signs of breathing
- Improved complexion, appearance of a pinkish tint
- Constriction of pupils
It is by the degree of constriction of the pupils that one can judge how correctly the ambulance was carried out. Small pupils indicate sufficient oxygen supply to the brain. Dilation of the pupils, on the contrary, indicates a slowdown in oxygen supply to the brain. If you notice this, you need to take effective measures to revive it.
The above technique should be carried out until the heart begins to work independently and signs of breathing appear. If slightly weak signs of breathing and a barely perceptible pulse appear, do not stop artificial respiration.
The restoration of heart function is judged by the appearance of the victim’s own regular pulse. If the victim has no pulse or heart rhythm, but has spontaneous breathing and narrow pupils, this indicates cardiac fibrillation. In this case, all measures to revive should be continued until the doctor arrives. Even a short-term cessation of revitalization measures (1 minute or less) can lead to irreparable consequences.



