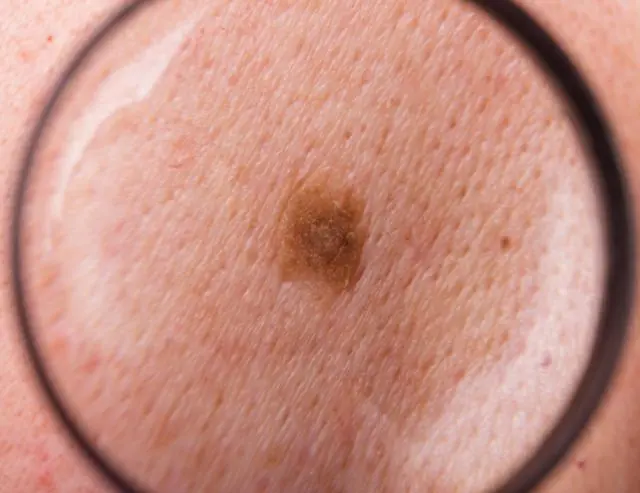
- Types of benign growths
- Features of appearance
- Moles
- Papillomas
- How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma
- What is the danger
The difference between a mole and a papilloma is a set of specific signs and symptoms that help identify a new growth on the skin. It is worth noting that both moles and papillomas are benign growths, but the reasons for their appearance are different. There are also visual differences between these neoplasms.
Types of benign growths on the body
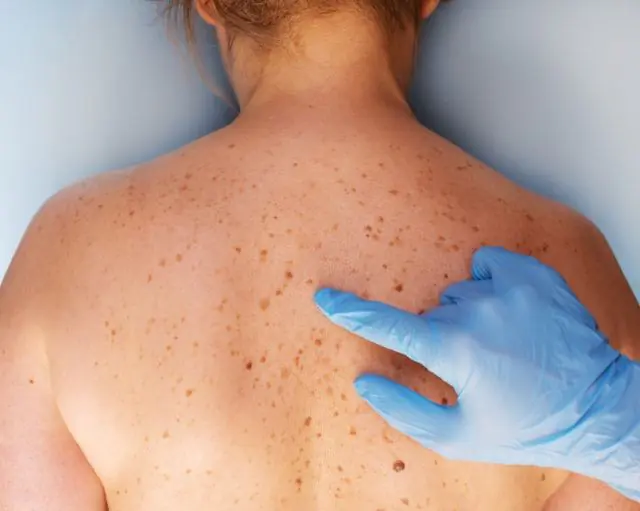
Benign formations are quite common on human skin. The first moles can appear on the body already in infancy. And some are formed even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. Papillomas are viral neoplasms that are initially also benign.
Both papillomas and moles can appear on any part of the epidermis, as well as on the mucous membrane. Also, these neoplasms can become malignant over time and under the influence of certain factors, that is, degenerate into malignant tumors. However, at the same time, there are some differences between papillomas and moles.
There are several main types of benign neoplasms on the body:
- Papillomas. They can have different shapes and structures. This is due to the strain of the virus that caused them. The most common are acrochords, which in appearance resemble thread-like outgrowths of the epithelium. Typically affects the armpits, neck, and chest. There are also flat papillomas and genital warts on the genitals.
- Moles. They are usually divided into two groups - moles themselves and birthmarks (nevi). Birthmarks, unlike moles, appear on the body even at the stage of intrauterine development. The following types of moles are also distinguished: borderline, intradermal, intradermal, basal, linear, blue, Seton, Ota. They come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes.
Read also: how to distinguish melanoma from papilloma?
Features of the appearance of papillomas and moles
The causes of occurrence are the main point why moles differ from papillomas. Visually, these neoplasms may be very similar, but their nature is completely different. Let's consider the mechanism of formation of moles and papillomas and what is the difference between them.
Why do moles appear?
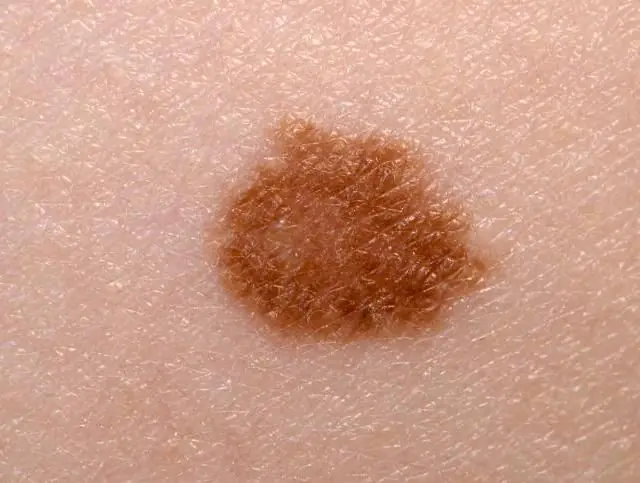
Photo of a mole
The reasons for the appearance of some moles on the human body, in contrast to papillomas, have not yet been fully elucidated. Concerning non-vascular moles, then they are epidermal cells in which a lot of melanin (skin pigment) has accumulated. Sometimes they can become malignant.
Vascular moles They are essentially a collection of small blood vessels. They can be convex or flat. Practically not prone to malignancy.

The main causes of moles:
- Genetic predisposition. Some nevi are inherited. This is especially true for large congenital birthmarks.
- Excess ultraviolet radiation. The sun's rays negatively affect human skin. They can cause the formation of new nevi, as well as their degeneration into oncological tumors.
- Hormonal surges. Potentially “dangerous” periods in this regard are periods of puberty, childbearing, severe stress and infectious diseases.
It is known that there cannot be two absolutely identical nevi on the body. The first moles usually form at the age of 1-2 years. These are small formations scattered randomly throughout the child’s body. With age, their number may increase.
However, even before the baby is born, birthmarks may form. In this case, the baby appears with them.
Why do papillomas occur?
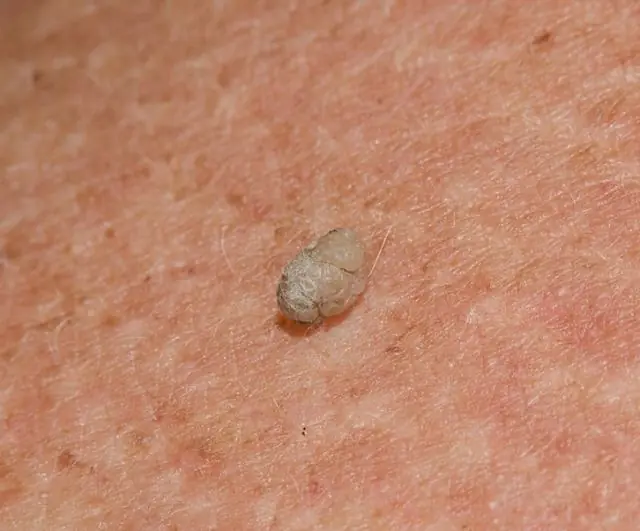
Photo of papilloma
Papillomas are sometimes called “hanging moles.” However, this is an incorrect name, since these neoplasms have little in common with moles. In addition, the main difference between a papilloma and a mole is that papillomas are acquired growths caused by the activity of the papilloma virus in the body. Moles are non-viral formations.
The only cause of papillomas is HPV. This pathogen, according to the latest data, is in the blood of about 80-90% of the world's population. There are many strains of this pathogen. Having affected the body, the papillomavirus begins to multiply in the upper layers of the epidermis and mucous membranes. Thus, it provokes pathological proliferation of the epithelium. This is how papillomas are formed.
HPV infection does not always cause the appearance of papillomas. Sometimes the virus remains in the blood in a passive state, without manifesting itself for years. A sharp hormonal surge, stress, and weakened immunity can lead to activation of the pathogen and the appearance of tumors.
How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma?
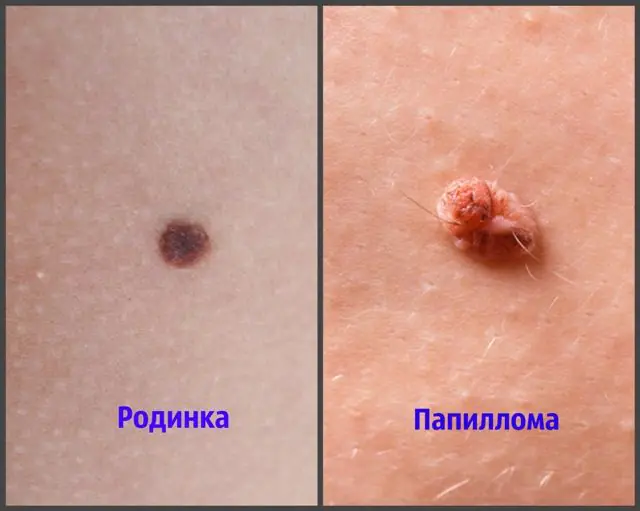
It is impossible to determine the presence of papilloma virus in the blood by eye at home. But if you still want to know how to distinguish a mole from a papilloma, then you can carefully study the neoplasm and establish its nature.
Let's look at the main visual differences below:
- Structure. In papillomas it is loose, the growth itself is soft and painless. Moles are distinguished by a dense and harder structure, they are quite elastic.
- Vessels. Papillomas have a wide vascular network that actively nourishes the growth. Therefore, when these tumors are damaged, severe bleeding occurs. Moles (if they are not red vascular) consist of epidermal cells and contain practically no blood vessels.
- Symmetry. If you are wondering how a mole differs from a papilloma, then study the shape of the growth. In papilloma, it is usually asymmetrical. Moles are usually round and more symmetrical.
- Localization. Papillomas most often affect the armpits, neck, and genitals. Sometimes they are localized on the mucous membrane. Moles are distributed throughout the body, but most of all on the arms and legs, face, and back.
- Shape and outline. Papillomas (even flat varieties) always more or less rise above the skin surface. They have rough, uneven outlines. Sometimes they look like broccoli florets. Moles, unlike papillomas, are usually smooth, slightly convex, and sometimes do not protrude above the surface of the skin.
- Hue. Papillomas can be flesh-colored, but during the development process they often change color from light to dark. Healthy moles do not change color over the course of life.
- Tendency to be passed on by inheritance. Papillomas are non-hereditary growths that can appear as early as a month after HPV infection. Moles are often passed on genetically.
- Discomfort. When papillomas actively grow, symptoms such as itching, burning, and redness may be present. Moles, unlike papillomas, never cause pain or any other sensations.
- Tendency to grow. Papillomas can grow in size and number, creating groups of neoplasms. Moles, if they are healthy, practically do not grow and do not change their size.
- Size. Single papillomas can reach sizes of 2-15 mm. Individual moles can cover a significant part of the skin - up to several tens of centimeters.
See also, what is the difference between nevi and papillomas?
What is the danger of moles and papillomas?
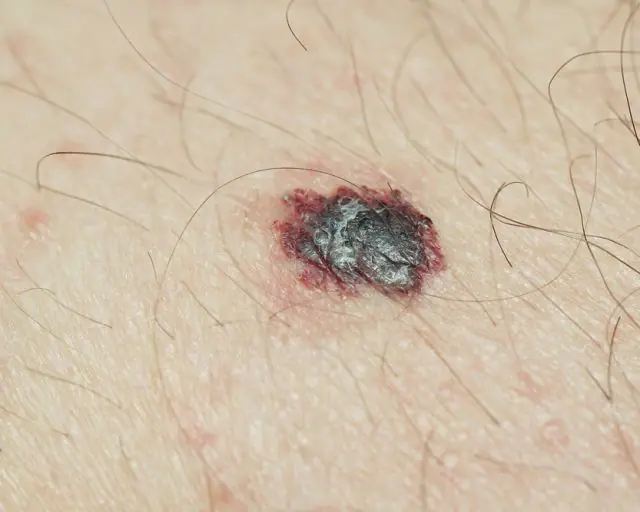
The photo shows what melanoma looks like
The main danger of benign neoplasms is the risk of their degeneration into malignant tumors. Both a mole and a papilloma can become melanoma.
The reasons that provoke malignancy of moles have not been fully studied. The risk of malignancy of papillomas depends on the strain of the virus that infected the person. Types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 52, 58, 59, 68 are oncogenic.
It is important to know not only how to distinguish a papilloma from a mole, but also unfavorable symptoms that indicate the onset of an oncological process in a neoplasm: an increase in the size of the growth, a change in color, the appearance of black spots, dots, pain, itching, bleeding, inflammation, suppuration, thickening , change in epidermal pattern.
Melanoma is an aggressive form of cancer that usually progresses quickly. Therefore, it is important to regularly examine tumors on the body in order to notice the first unpleasant symptoms in time. In this case, it is absolutely impossible to delay a visit to the doctor.
Also, moles and papillomas can be injured because they protrude above the surface of the epidermis. Papillomas are especially often damaged, since they usually grow in skin folds and places where clothing comes into contact with the body. Any damage to moles or papillomas requires consultation with a doctor. There are frequent cases of neoplasms degenerating into malignant tumors precisely after they are injured.
How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma - watch the video:
Photos of how to distinguish a mole from a papilloma can be found on the Internet. However, only a specialist can determine the exact cause of the appearance of a particular neoplasm after a visual examination and taking biological material for analysis. It is impossible to determine the presence of papillomavirus in the blood by eye.
- Related article: What types of papillomas are there on the body?



