- Common causes of all types of warts
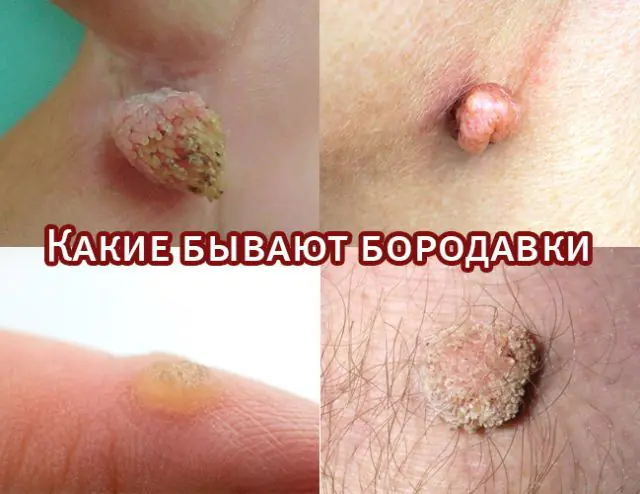
- Types of warts on the skin: description and photo
- Common warts (vulgar)
- Juvenile warts
- Palmoplantar
- Senile warts
- Thread-like formations on the skin
- Genital warts
Wart (Verruca) can also be called Wart, and in the plural - Verrucae. Basically, it is a benign formation on the skin, which is of viral etiology. This skin formation looks like a papilla or nodule. Various viruses can cause warts, which are called human papillomatosis, abbreviated as HPV. This infection can be transmitted through the belongings of an infected person or through direct contact with a carrier. But sometimes the pathogen exists perfectly in the affected human body, without revealing itself, but it can be transferred to another carrier and develops in his body and appears as a wart formation.
Common reasons for the formation of all types of warts on the skin
Factors that contribute to the formation of warts on the human body can be:
- general decrease in immunity or a particular organ;
- mental disorder of the nervous system and constant stress;
- vegetative neurosis or vegetative dystonia, which occurs in cases where a disease of tissues or organs occurs due to damage to both the dynamic and functional nervous system responsible for vegetative processes;
- insufficient blood supply to small capillaries, causing bluish skin and acrocyanosis;
- excessive and constant sweating on the hands and soles.
Typically, a wart is a raised area that protrudes above the skin. It can range from 1-2 mm to 1.5 cm, while the size directly depends on the location of the papillae and their variety. If several wart nodules merge into one tumor, it takes on a conical or hemispherical shape, having a wide base. Over time, the color of the wart, at first indistinguishable from the skin tone, can take on darker colors, such as brown or even black. But such transformations occur due to the fact that the surface of the warty formation is rough and dirt easily sticks to it.
Types of warts on the skin: description and their symptoms
Almost 90% of the world's population suffers from problems associated with warts, and on average such formations are observed in 10% of patients of childhood or adolescence. Often their warts appear and go away spontaneously, without any outside intervention. Typically, such skin papillae do not cause pain, and only some cause cosmetic or physical discomfort.
Important! Both people and animals can transmit HPV.In general, when treating warts, the prognosis is favorable, but occasionally the recurrence of such nodular skin formations, so-called relapses, is possible. Approximately 50% of warts can disappear on their own, but if it happens that you cannot diagnose a formation on the skin yourself, then it is better to consult a specialist - a dermatologist. Removal is recommended if there is obvious discomfort (aesthetic or walking discomfort, bleeding or pain).
The manifestations of HPV are quite diverse and only some appear in the form of warts, but doctors distinguish the following types: ordinary, juvenile, palmoplantar, senile, filiform and genital.
1. Common warts
The photo shows a common wart on a finger
They are also called warts vulgaris. They are represented mainly by nodules of a specific type, characterized by a fairly high density (which allows them to be felt with your fingers) and a grayish or yellow-brown tint, but they often have a normal (flesh) skin color. There are cases when a large number of common warts are formed. The surface has a slight roughness. The diameter of vulgar warts can vary in the range of 3-10 mm, that is, their size can reach the size of a pinhead to a pea. They rise slightly above the skin. The concentration of such nodules is on the back of the hand or fingers, face (red line of the lips) or very rarely they form on the oral mucosa. The largest among them is the “maternal” papule. It is curious that if such a wart is removed, the remaining nodules may gradually disappear.
Among all patients, up to 70% suffer from common warts, but they are mainly detected in children and adolescents. If a lot of warts form nearby, they can merge into a formation of specific shapes, resembling a tumor. Such raised nodules do not cause pain to the patient, but this does not guarantee that if they are subjected to injury (especially if we are talking about regular exposure to the wart), there will be no likelihood of inflammatory processes, which in turn will lead to a feeling of pain. Vulgar warts can often disappear on their own. The reason for their appearance is a decrease in immunity and skin microtraumas.
2. Juvenile warts
These skin nodules are called flat warts. Affects up to 4% of all patients. Such nodules on the skin have a diameter of 0.5-3 mm. Juvenile warts are distinguished by their rounded shape; several of them form side by side. If the color of the skin is normal, then such nodular formations practically merge in shade with it, often acquiring a yellowish-brown tint or having a bluish tone. Their surface is characterized by smoothness, and mainly the places where they are concentrated are the face and the back of the hands, but occasionally juvenile nodules are observed in the area of the forearms and shins. It happens that a teenager can detect such nodules on the mucous membranes.
A peculiarity of juvenile warts is that their number is usually multiple. The patient often does not experience any special sensations. Such warts occur in teenagers or young adults, usually due to decreased immunity or lack of vitamins, stress or colds. The cause is also increased sweating, when the skin is constantly in a moist state, severe skin irritation or minor injuries, cuts, abrasions or scratches.
Infection with this type of virus usually occurs at the age of 3-5 years, but symptoms may not appear until the person reaches adolescence, that is, after 10 years. If timely medical treatment is not carried out, then such flat warts become quite numerous and can cause aesthetic and psychological problems.
- Read about injection solutions for removing flat papillomas
3. Palmoplantar warts
Often found under the name horny warts. The location of such papules is clear from the name, that is, most often they appear on the hands and feet (legs). They affect up to 34% of young people and adult patients. Palmoplantar warts look like dense plaques or nodules with a horny coating. Their surface has a grayish tint and therefore many people mistake them for a simple callus, callus or horny syphilitic papule of the sole. But an important difference and, accordingly, characteristic features of such warts is that there are growths in the form of papillae with a reddish color, located in its very central part. Basically, it is almost impossible to see them only by removing the upper stratum corneum of the skin (such plaque is easy to crumble). These skin papillae have a succulent appearance and can bleed, causing pain, especially when walking.
The cause of palmoplantar warts is wearing uncomfortable and tight shoes, shoes made of non-breathable (rubber) materials, and lack of mittens in the cold season. All these factors contribute to a lack of blood supply to the vessels and impaired blood flow. The types of these warts do not like when the patient is characterized by increased sweating; the growth of such warty formations occurs quite rapidly and then they are difficult to treat. Read about traditional methods of treating warts.
4. Senile warts
This type of wart is called seborrheic wart or keratoma. It is a benign formation that occurs in patients whose age begins at 40 years and does not have a viral etiology. A characteristic feature of senile warts is their reduced growth rate, which can even last for decades. Usually, at the very beginning, a small speck of brown color forms on the skin. Then, over time, it begins to grow, often reaching 6-10 mm in diameter. The surface of senile warts is covered with crusts that are permeated with sebum - seborrheic scales. Such crusts are removed quite easily and under them growths in the form of papillae are found.
But when the final stage of wart development is reached, that is, its growth has completed, such a nodule already rises slightly above the skin, taking on a rich shade - mostly dark brown, grayish and even black. The crusts that covered the surface become compacted and cracks begin to cut through them. The concentration of such warts is in areas of the body hidden under clothing, although in some patients, senile nodules form on the surface of the face, arms and legs, on the neck and on the hairy area of the head.
It often happens that in fairly elderly patients, age-related nodules begin to merge into one tumor. It is important at this stage that the dermatologist accurately distinguishes seborrheic keratoma from a pigment spot called Clark's diplastic nevus, which also has the form of a warty formation with a diameter exceeding 5 mm and is characterized by an intradermal accumulation of melanocytes. This disease can develop into melanoma, that is, a malignant tumor. But there are cases when a senile wart can degenerate into melanoma.
5. Filiform warts
This type of wart on the skin is also called in medicine papillomas or acrochords. People who have crossed the 40-year mark suffer from such formations on the skin, but most often elderly patients. It is important that they are promptly distinguished from molluscum contagiosum. Filiform warts are papules that are soft to the touch and vary in color from flesh-colored to dark brown. Occasionally, a small “leg” may be present. The places of their formation on the surface of the neck, the skin of the eyelids or the armpit, can be found in the groin area and in women under the mammary glands.
Typically, a filamentous wart varies in size between 1-4 mm, but can reach 3 cm or more in diameter. Since there is a feature of self-infection (or as it is also called autoinoculation), it is confirmed that such a wart arose on the human body during a viral infection, which can be combined with diabetes mellitus or the patient’s weight is too high (obesity), and can occur during pregnancy or when a woman reaches menopause. The last two factors indicate the presence of a hormonal component of the disease. Acrochords differ from other types of warts in that they can easily spread to adjacent skin and merge with each other to form tumors. Recurrences are also observed after removal of such nodules.
6. Genital warts
They are called in dermatology pointed condylomas or genital warts. This type of wart formation is highlighted in a separate section, since they can form at the entrance to the vagina, near the coronary groove of the penis, near the anus, and the place of their formation can also be the internal areas of the foreskin. Occasionally, the patient may find them in the folds of the inguinal-femoral part, near the mammary glands or near the hollows of the armpits. Pointed warts look very much like a cockscomb or cauliflower, as they appear in large numbers, they rise slightly above the surface of the skin and practically blend in with its color or take on a dark brown tint. May cause pain during sexual intercourse or during bowel movements.
Infection occurs due to HPV, but intimate warts are mainly transmitted through sexual contact. Occasionally, specialists or patients may find such formations in the oral cavity. It is important for a dermatologist to distinguish condylomas from diseases with similar symptoms, such as secondary syphilis, which causes condylomas lata. The latter are more dense and have a wide, hard base.
Video about the types of warts (papillomas): simple, plantar, flat, pointed, filiform, senile: (said by a practicing dermatovenerologist: Makarchuk Vyacheslav Vasilyevich):
[media=https://youtu.be/wxiwfKqRMCg]
Watch the video from the program “Live Healthy!” removing warts and moles at home: