
- What are condylomas
- What do papillomas look like?
- What is the difference
The difference between papilloma and condyloma is the peculiarities of the formation of benign growths on the body, depending on the type of virus that caused them. Both types of tumors are the result of HPV activity in the body. Essentially, this is a pathological growth of epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes, which leads to the formation of growths.
What are condylomas?
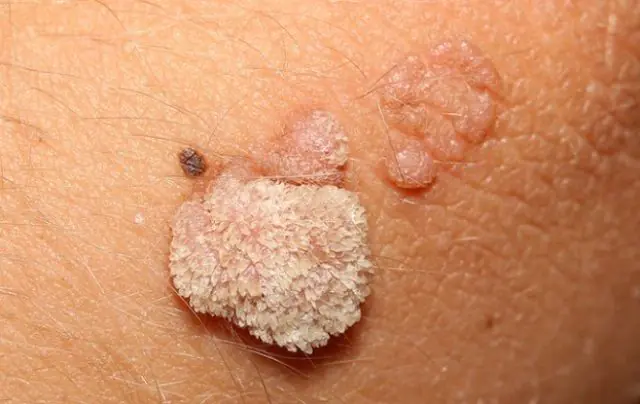
The photo shows genital warts
Condylomas are neoplasms on the human body caused by the activation of papillomavirus in the body. Viruses 6, 11, 16, 18, 54, 56, 39, 73 strains provoke the appearance of condylomas.
Among the above pathogens there are both oncogenic and non-oncogenic types. That is, the risk of developing cancer due to the degeneration of condylomas into malignant tumors is approximately the same as in the case of papillomas.
The strains of the virus responsible for the appearance of condylomas are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. The pathogen penetrates into damaged areas of the mucous membrane during unprotected intercourse. Condylomas often form in these areas.As a rule, condylomas, unlike papillomas, are localized on the genitals of men and women. These growths are like a cluster of small papillae and resemble cauliflower.
Condylomas are divided into 2 types:
- Pointed. They are also called “lobed”. They look like papillae with sharp tips on a thin stalk, through which they are attached to the genital mucosa. Usually formed in groups.
- Wide. In fact, these are not always manifestations of HPV. These condylomas may be a symptom of secondary syphilis. They have a wide base and a flattened top. Also, flat condylomas form on the internal genital organs of women, for example, on the cervix. In this case, they do not stick out, but grow into the deeper layers of the mucosa. If they are detected, the woman’s condition is assessed as precancerous and requires close attention and further diagnosis and treatment.
Genital warts are the most common. They are localized on any mucous membrane, but most often on the genitals of men and women, in the corners of the mouth, inguinal folds, and sometimes in the armpit area. “Favorite” places for condylomas are those that are subject to the greatest friction with clothing or linen.
The size of condyloma is 2-15 mm. The shade is practically no different from healthy mucous membrane. Sometimes the growths can acquire a brighter color - pink, reddish, gray.
Condylomas and papillomas have many differences, but the main thing is that condylomas cause more discomfort to the patient, since they are more often damaged, ulcerated and can cause severe inflammation. Therefore, when condylomas are detected on the mucous membranes, doctors recommend removing them by any surgical method, since conservative treatment in this case is powerless.
What do papillomas look like?
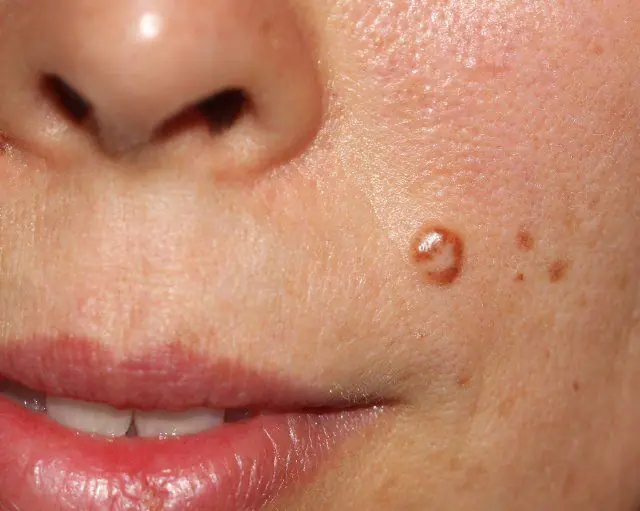
Photo of papilloma
Papillomas are another type of benign neoplasm on the skin of men and women infected with the virus of the same name. HPV, which is responsible for the appearance of these growths, can be transmitted through sexual contact, household contact, and also during the process of delivery from a sick mother to a baby.
These tumors usually affect the skin. Most often they accumulate under the armpits, on the neck, face, and limbs, which is how papilloma differs from condyloma. Depending on the variety, these growths can blend in color with the epidermis or differ by 1-2 shades.
There are such types of papillomas:
- Filiform. The most common group of papillomas. They resemble round or elongated papillae, which are attached to the skin by a thin stalk. Soft in structure and painless. They can gather in groups.
- Flat. Their second name is “youthful”, since they are common among young people and are the result of a rapid hormonal surge. They protrude slightly above the main surface of the skin and have a rounded shape with a smooth or slightly rough keratinized tip. As a rule, they occur on the face and hands and often go away on their own after puberty.
- Common (vulgar) warts. They are located on the rough skin of the feet or hands. They protrude slightly above the skin and are 2-15 mm in diameter. Round in shape and sometimes painful.
Threaded papillomas can often be injured due to their localization in areas of friction between clothing and skin. Therefore, doctors recommend removing them. In addition, some papillomas that are caused by an oncogenic strain of HPV can turn into malignant tumors.
How do papillomas differ from condylomas?
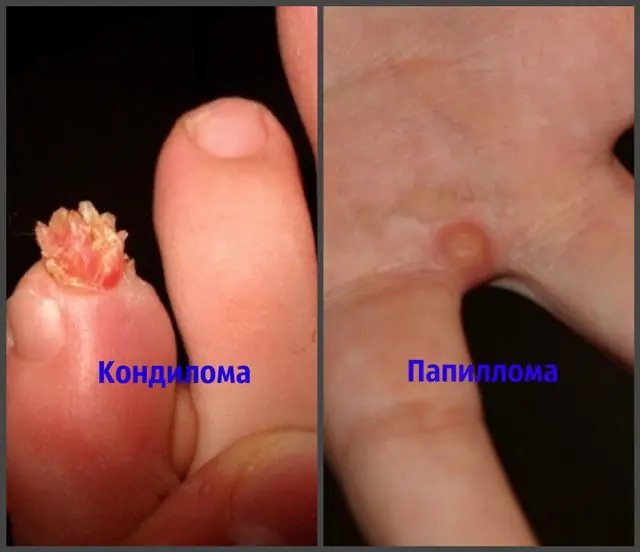
The main similarity of these neoplasms is the root cause of their formation on the human body - HPV. However, it is important to know how to distinguish papilloma from condyloma in order to select the appropriate treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Let's look at the main differences between papillomas and condylomas:
- Virus strain. These neoplasms are caused by different types of the same pathogen. Condylomas are the result of the activity of 6, 11, 16, 18, 54, 56, 39, 73 strains. All other types of viruses are responsible for the development of papillomas.
- Routes of infection. You can become infected with HPV in various ways. But, as a rule, condylomas appear due to unprotected intimate contacts and their appearance is associated with sexually transmitted diseases. Strains of the virus that cause papillomas can also be transmitted through sexual partners, but most often this occurs through household contact.
- Localization of neoplasms. If you find it difficult to figure out the difference between papillomas and condylomas, then pay attention to the place where the tumor has grown. Condylomas are lesions of the mucous membranes of the genitals, less commonly the oral cavity. Very rarely they form on the armpits. Papillomas affect the epidermal integument.
- Contagiousness of growths. Condylomas, unlike papillomas, are transmitted much more easily. The viruses that cause condylomas are more highly contagious than those that cause papillomas.
- Appearance. Condylomas often grow on the mucous membrane in groups, forming clusters similar to cauliflower or broccoli. Papillomas can be single or grouped, but rarely merge together.
- Need for treatment. Both condylomas and papillomas require careful monitoring by a doctor. But if papillomas of non-oncogenic types, as a rule, cause only aesthetic discomfort, then condylomas are more dangerous, since they are more easily injured and inflamed. And since they are located on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, which is the difference between papilloma and condyloma, insufficient hygiene in this area can lead to infection of the growths and suppuration.
- Read also: the difference between polyps and papillomas
What is the difference between papilloma and condyloma - look at the video:
Photos of the differences between condylomas and papillomas can be found on the Internet. However, you should not self-diagnose. It is recommended to undergo a full examination to find out the cause of the growths. In addition, some neoplasms are localized on internal organs, and only a doctor can identify them during special diagnostics.
- Related article: What is the difference between a wart and a papilloma



