
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Treatment
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
Folliculitis is an infectious purulent disease that can be transmitted from one person to another through household and contact contact. The disease especially often affects children, since their immunity is not yet fully formed, and the body cannot fully fight the infection. In addition, children's skin is soft, moist and loose, which facilitates the rapid entry of infection. In adults, the immune system and natural skin microflora prevent infection, although they do not guarantee protection.
Symptoms of folliculitis, which is transmitted from person to person
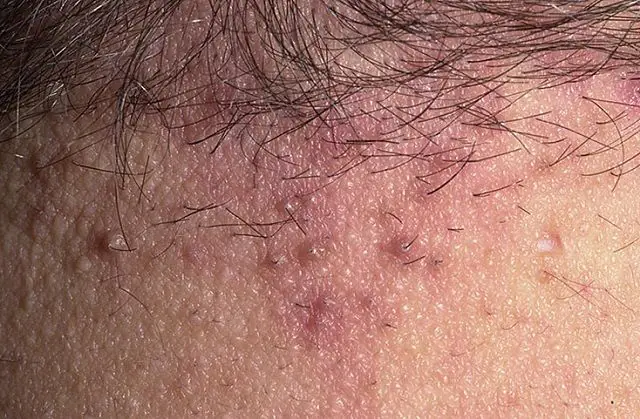
In the photo there is folliculitis on the back of the head
A slightly painful, dense, cone-shaped nodule of bright red color appears on the human skin at the base of the hair. After a few days, an abscess develops in its center, which, when dried, forms a crust. When it falls off, there are usually no traces left. In most cases, folliculitis is mild and does not pose a threat to life, but in some cases complications may develop. This usually occurs in the absence of proper treatment, rules of personal hygiene and insufficient immune defense of the body. Then the inflammatory process can go deeper, affecting the entire follicle, and not just its upper section.
The disease has favorite areas of localization - parts of the body with an abundance of vellus hair. For this reason, folliculitis often affects the sites of germination of the hair follicle through which hair passes: the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, scalp, forehead, nose, cheekbones.
- See also symptoms of folliculitis decalvans
Reasons why folliculitis is transmitted from person to person
Since folliculitis is an infectious disease, it can be caused by various types of pathogens: fungi, bacteria, herpes viruses. At the same time, the likelihood of developing the disease increases against the background of other factors, which are divided into two groups: internal (endogenous) and external (exogenous).
Endogenous (internal) reasons:
- Metabolic diseases, diabetes, anemia.
- Circulatory disorders and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Long-term chronic infections.
- Liver diseases.
- Decreased immunity, especially against the background of HIV infection.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Lack of vitamins, in particular A and C.
- Acute infectious processes of viral and bacterial origin.
- Lack of adequate nutrition, especially a decrease in the amount of protein consumed.
- Treatment with immunosuppressants.
Exogenous (external) causes:
- Skin injuries - abrasions, cuts, scratches.
- Improper skin care.
- Regular contamination of the skin, for example, when working in unfavorable conditions and coming into contact with hazardous chemicals without skin protection.
- Incorrect or untimely application of occlusive dressings.
- Climatic conditions (temperature changes, high humidity, high and low ambient temperatures).
- Hypothermia.
- Wearing tight-fitting, tight-fitting synthetic fiber clothing.
In addition to the above reasons that contribute to the occurrence of folliculitis, people with AIDS are at risk. They may develop eosinophilic, herpetic or fungal folliculitis. People infected with syphilis develop syphilitic folliculitis (a contagious infectious disease), which cannot be eliminated without treating the underlying disease.
Viral damage to hair follicles can develop during long-term use of antibiotics. This treatment leads to disruption of normal microflora and dysbacteriosis, which provokes the appearance of skin diseases caused by gram-negative bacteria, for example, E. coli. Such infections are often resistant to antimicrobial drugs because they begin to multiply during the action of the antibiotic and have developed resistance.
No less dangerous is staphylococcal folliculitis. In this case, the method of infection is usually airborne or contact.
Also, the development of folliculitis is facilitated by disorders in the body (periodontal disease, gingivitis, caries, obesity, chronic tonsillitis), which, although indirectly affecting, prevent resistance to skin infections, especially with weakened immunity.
- See also causes of staphylococcal folliculitis
Treatment of folliculitis, which is transmitted from person to person
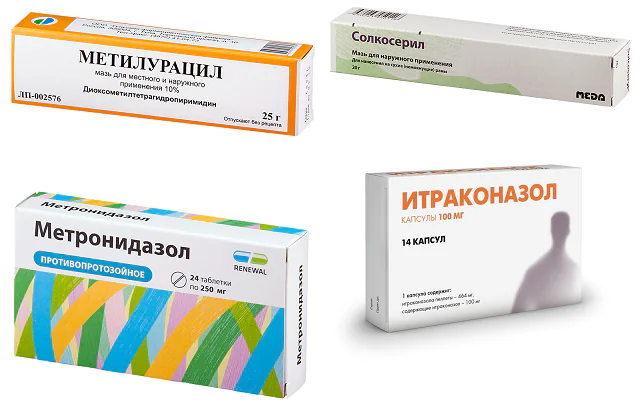
Since folliculitis, which is transmitted from person to person, can occur against the background of various factors, the first step is to determine the cause of the disease and eliminate it. Treatment of folliculitis is carried out simultaneously with the treatment of concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency, HIV). Therapy must be appropriate to the etiology of the disease.
For staphylococcal folliculitis antibiotics are prescribed based on the results of bacterial cultures. Mostly Amoxiclav is prescribed. For local treatment, a solution of Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, salicylic alcohol or alcohol tincture of propolis is suitable. After the purulent contents are released, ointment with the antibiotic Methyluracil or Solcoseryl is applied to the affected areas.
For eosinophilic folliculitis, which appears as a result of HIV infection, there is no specific therapy. It is important to start treatment on time, the method of which depends on the type of disease:
- Steroid cream will reduce discomfort.
- Antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs will relieve inflammation.
- Antiretroviral therapy will improve weak immunity.
- Calcineurin inhibitors will reduce the immune system's response to inflammation.
- Metronidazole tablets are used for secondary infection.
- Antihistamines are indicated for severe itching.
- Itraconazole is an antifungal drug.
For bacterial folliculitis in the initial form of the disease, the affected area is treated with alcohol solutions (fucorcin, brilliant green, 2% camphor or salicylic alcohol). In case of deep damage, the pustules are opened, the pus is removed, the affected area is treated with the above alcohol solutions and antibacterial drugs are prescribed: ointments (Zinerit, Lincomycin, Erythromycin, Epiderm, Dalatsin-T) and tablets (Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Cephalosporin). If the disease has become chronic, antibiotics of the tetracycline group with a bacteriostatic effect (Oxycort) are prescribed.
For syphilitic folliculitis, which appears against the background of syphilis, treatment begins with the main pathology, since the rash will not go away until syphilis is cured. Antifungal drugs (Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Terbinafine ointment), antibiotics and antibacterial therapy are prescribed as maintenance therapy. The lesions are treated with antiseptics (salicylic or boric alcohol).
For fungal (candidal) folliculitis antifungal drugs are prescribed (Fluconazole, Ketoconazole or Itraconazole tablets). The emphasis in treatment is on external treatment of the affected surface: brilliant green, methylene blue, boric and salicylic alcohol, furatsilin solution. Skin lesions are treated with antifungal ointments or gels (Clotrimazole, Amphotericin, Bifonazole, Nizoral, Nystatin ointment). If the cause of its occurrence is another disease, then treatment of pyoderma begins after the underlying disease has been eliminated.
For herpetic folliculitis, which causes the herpes virus, infection occurs through skin injuries (abrasions, scratches, excoriations). The main antiviral drug is Acyclovir, Valtrex or Famvir. Pustules are also treated with salicylic alcohol, brilliant green or Acyclovir 5% ointment. Itching is relieved with antiallergic drugs (Suprastin, Claritin, Lomilan). If a bacterial infection is associated with herpetic folliculitis, local antiviral and antibacterial drugs are prescribed that dry the skin and relieve inflammation (Methyluracil, Betadine, Miramistin, zinc ointment).
For any form of folliculitis, in addition to the above therapy, it is necessary to strengthen the body’s immune system, especially if immunodeficiency is diagnosed. It is brought back to normal with Vitaferon, Timalin or Immunal. Also, to improve immunity, include in the diet foods containing vitamin C, fresh vegetables and fruits rich in amino acids and antioxidants. Preparations with echinacea and aloe juice help increase the body's defenses.
In combination with medications, after stopping the acute inflammatory process, non-drug therapy has proven well: irradiation with ultraviolet rays, polarized light, ultraphonophoresis, laser therapy, dermabrasion.
Also, during the treatment period, the patient must maintain proper nutrition. The diet menu should contain large quantities of vegetables and fruits, rich in plant fiber, as well as protein foods. Limit the consumption of fats, sweets, baked goods, spicy, hot and salty foods. Canned and smoked products are excluded. Maintain a drinking regime, especially during exacerbation of the disease. During the day, drink 2 liters of water, including a glass in the morning after waking up and in the evening before bed.
- Read also about the treatment of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Folk remedies for the treatment of folliculitis, which is transmitted from person to person
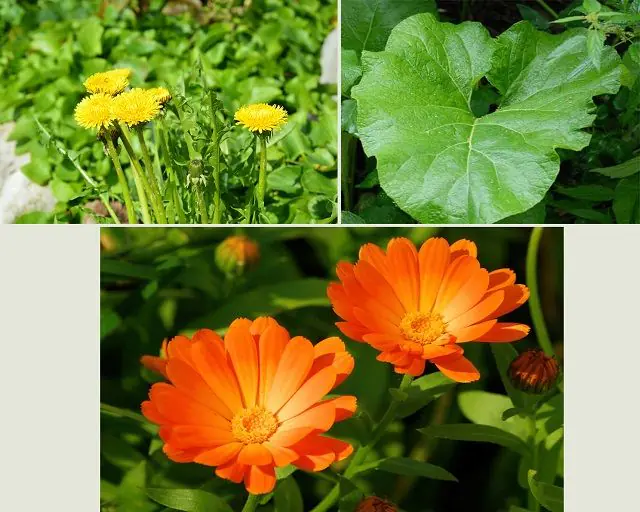

Traditional medicine has successfully proven itself in the treatment of folliculitis. However, before using it, you should first consult with your dermatologist. The most common and effective methods are as follows.
- Crushed dry dandelion roots (1 tbsp) are boiled for 10 minutes in 1 liter of water. The broth is infused for 2 hours, filtered and drunk 2 times a day.
- Burdock (2 tablespoons) is boiled for 10 minutes in 1 liter of water, left for 1 hour, filtered and consumed 2 times a day.
- Calendula leaves (5 g) are boiled in 200 ml of water, left for 20 minutes, filtered and treated with affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day.
- Spine root (50 g) is boiled for 30 minutes in 0.5 liters of water, infused for 1 hour, filtered and used for compresses.
- Chamomile leaves (20 g) are boiled for 20 minutes in 200 ml of water, filtered and applied to the affected areas 3-4 times a day.
- Tea tree oil is applied to the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day.
- Fresh woodruff leaves are ground to a pulp and applied to the site of the abscess under a medicinal bandage 2 times a day.
See also folk remedies for the treatment of herpetic folliculitis.
Prevention of folliculitis, which is transmitted from person to person

As a preventative measure, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene:
- When taking a shower, wash with laundry soap.
- Wash with antibacterial soap.
- Do not use harsh soaps or scrubs for washing and bathing. This will increase irritation and itching.
- Do not use other people’s hygiene products (washcloth, towel, clothes).
- Thoroughly disinfect skin care items.
- Get rid of expired and open medications, and open new ones after completing the course of treatment.
- Wear clean clothes every day.
- Change bedding in a timely manner.
- Do not visit swimming pools, saunas or swim in open water.
- Do not take hot baths.
- Do not shave the affected area, as constant shaving worsens the condition.
- Upon contact with a patient, immediately carry out antiseptic treatment of the skin and change underwear.
- Monitor your diet.
- Do not wear tight or tight clothing, as the friction of tight clothing carries infection and causes itching.
- Do not touch the affected area with your hands to avoid transferring bacteria.
Read also about preventive measures for pseudomonas folliculitis.
Video of what folliculitis looks like:
[media=https://youtu.be/3bF4wShzGQU]
- Related article: What is folliculitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment



