Medical expert article
Absolutely everyone has moles: it’s just that some people have more of them, while others have several. There is nothing strange in the appearance of such pigment spots. The mole grows slowly, in proportion to the growth of the body, without causing discomfort or unpleasant sensations. But if the growth of a mole has sharply accelerated, it has changed its color, or began to remind itself of itself with tingling or pain - this is already a reason to worry.
Why does a mole grow and what to do? A lot is known about moles and nothing is known: this opinion was expressed by one of the domestic dermatologists. Indeed, there are many beliefs and even superstitions around the notorious spot. Grandparents are absolutely sure: it is absolutely forbidden to touch birthmarks. Surgeons insist: the sooner a mole is removed, the better. Who is right?
We hope that our article will help you get answers to the most common questions regarding this topic.
ICD-10 code
Reasons for the growth of a mole
As a rule, as a person grows, moles on his body also grow. Moreover, their number is also increasing.
An increase in the size of the birthmark in proportion to the size of the body is considered normal. The number of moles increases depending on the presence of favorable factors:
- infectious skin diseases, inflammatory elements on the skin surface;
- hormonal changes, both physiological and pathological (for example, the period of puberty, the period of bearing a baby, menopause, etc.);
- excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- regular mechanical damage to the skin and birthmarks (elements of clothing, razors, accessories, etc.).
The growth of a mole is considered relatively safe when the spot grows up to 2 mm per year. If the size increases sharply or too quickly, then the onset of a pathological process can be suspected. In addition to size, such processes are accompanied by thickening of the formation, change in color, sometimes itching or tingling sensations, bleeding or peeling.
[1], [2]
Pathogenesis
To date, the pathogenesis of mole growth has not been fully determined. Only theoretically, a number of possible exogenous and internal reasons are identified that stimulate a mole to appear and grow.
Many scientists do not deny the genetically determined appearance of moles. In addition, the level of production of melanin, a pigment substance produced by melanocytes, is controlled by melanostimulating hormone. Violation of this control can occur with diseases of the central nervous system or liver, with dysfunction of the ovaries, adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
However, the majority of moles grow as a result of excess UV radiation and a failure of the antioxidant protection of the skin. For example, ultraviolet light directly stimulates the production of melanin by melanocyte cells. Moreover, the more intense the radiation and the longer the exposure to UV, the more melanin is produced. If irradiation occurs against the background of weak antioxidant protection of the skin, then the growth of the mole is almost guaranteed.
In addition, the following factors increase the defenselessness of the skin:
- decreased synthesis of glucocorticoids;
- inflammatory diseases of the skin;
- suppression of hyaluronic acid synthesis;
- frequent or incorrect peeling procedures;
- laser and photoprovoking procedures;
- natural skin aging;
- injuries, skin burns;
- hormonal disorders and shifts;
- the influence of certain medications (oral contraceptives, chemotherapy drugs, etc.);
- liver dysfunction.
[3], [4], [5], [6], [7]
Symptoms of mole growth
Moles are never the same. They can be different in color (from beige to dark brown), in convexity (flat, convex, hanging), in location and shape.
The growth of a mole within 2 mm per year without changing color and in the absence of unpleasant sensations can be considered normal. The first signs of pathological growth of a mole, which you need to pay special attention to, are usually the following:
Normally, the birthmark is symmetrical. If the shape of the spot does not correspond to this sign, then it is better to consult a doctor.
Normally, the mole is clearly defined, not blurred, without ragged edges.
The color of the formation is normally always uniform and homogeneous. Pathology may include blackening, redness of the mole, the appearance of dots, veins, etc. in its structure.
Spots that are large in diameter are always more prone to degeneration. Formations with intensive growth are especially dangerous.
- Dynamic development of a mole.
With age, moles on the skin may appear or disappear. And this will not always be considered a sign of disease. What you should be wary of:
- rapid growth in the size or number of moles;
- sensation of itching, tingling or pain in the mole;
- superficial peeling;
- bleeding, cracks appearing.
The most common questions related to mole growth
- The child has moles growing on his body. This is fine?
Sometimes a child may be born with existing birthmarks. Most often this happens in babies with fair skin or in premature babies. There is nothing wrong with this: moreover, it is believed that congenital nevi are less likely to degenerate into a cancerous tumor than those that appeared in adulthood.
If birthmarks occur in a child with age, then you just need to monitor them and follow some precautions to avoid complications. Most moles are genetically determined and are not something to be afraid of. It is good if such a child is periodically examined by a dermatologist.
- I have dark moles and even a few red ones. I recently noticed that a red mole is growing. Is it dangerous?
The red spot is most often not a mole, but a hemangioma - a collection of blood vessels. Usually such formations are not touched at first, but their growth is observed over time. The fact is that sometimes hemangiomas can even disappear on their own.
In any case, with a growing red mole, it is better to see a surgeon or dermatologist.
- During pregnancy, many moles appeared, and one mole grows and itches. Should I be worried about this?
Indeed, pregnant women often experience increased growth of moles and the appearance of new ones. This is due to a radical hormonal change inside the body, because the amount of certain hormones increases thousands (!) of times. The situation can get even worse if a woman has problems with the thyroid gland.
The growth of a mole in a pregnant woman is not always a disease. But if the formation itches, or other pathological changes appear, which we wrote about above, then consulting a doctor should not only be mandatory, but also urgent.
- What to do if a hanging mole grows on a stalk?
The growth of a hanging mole is no different from the growth of any other birthmark. If the increase is insignificant and there are no other signs of degeneration, then you should not panic. Otherwise, doctor's intervention is mandatory.
- I recently noticed that a black mole is growing on my body. At the same time, all other moles are lighter. What could it be?
A black mole contains a larger amount of pigment, and is therefore considered more dangerous in terms of cancerous degeneration. The owner of such an education must carefully observe and record any slightest modification of the spot. It’s even better if a doctor does it.
- New moles are constantly growing. Is this considered normal?
As we have already said, the growth of a mole can be associated with many reasons. Therefore, the appearance of new pigment formations is quite understandable and is considered a variant of the norm. Some people have thousands of moles on their body, and yet they are completely healthy. Another issue is that a person with a large number of birthmarks is more susceptible to developing cancerous tumors. For this reason, such people are advised to visit a dermatologist regularly for diagnosis.
- If a raised mole grows but its color does not change, should you panic?
If the growth of a mole is intense, exceeding 2 mm per year, then you really should panic. More precisely, do not panic, but consult a doctor for advice and diagnosis. If the increase is small and there are no other negative signs, then there is most likely no reason to panic. For more accurate information, you should still see a doctor.
- A flat mole grows in diameter: is it possible to remove a flat mole? And is it necessary to do this?
A flat mole is removed in the same way as other, for example, convex, formations. If a spot bothers you, then it is undoubtedly advisable to get rid of it. And the sooner this is done, the better.
- I have never had many moles on my body. But I heard that moles grow the most during pregnancy. Does this happen to all women?
This occurs in the vast majority of women, depending on their genetic predisposition. That is, some may have several additional formations, while others may have several dozen. Both the first and second cases are a variant of the norm.
[8], [9]
Complications and consequences
The main complication of a birthmark is its degeneration, or malignancy. But not all moles are reborn. Most often, nevi with a diameter of more than 20 mm degenerate into cancerous tumors. The percentage of malignancy ranges from approximately 5 to 15%.
Birthmarks located in the facial area, as well as people with a large number of pigmented formations on the body (more than 2 dozen), are especially at risk.
[10], [11], [12], [13], [14], [15]
Diagnosis of mole growth
How is mole growth diagnosed?
First of all, the doctor will examine the disturbing birthmark and make certain conclusions: is the formation different from other similar pigment spots, are there signs of malignant degeneration.
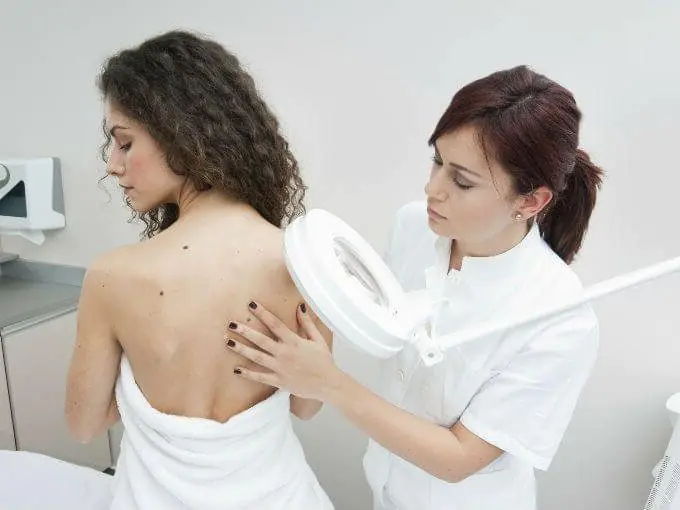
The next step is instrumental diagnostics, the most informative representative of which is dermatoscopy.
Dermatoscopy is used to visualize structural changes in the skin. The procedure is carried out using a dermatoscope, consisting of a magnifying glass, a light emitter, a transparent plate and a special gel-like substance, which is applied to the skin in places of contact with the device. Due to this, light is reflected from the rough surface of the skin. A dermatoscope allows you to distinguish benign moles from malignant cancerous growths. This procedure is a good alternative to a skin biopsy, which is the removal of a tissue element from a suspicious nevus.
Tests are carried out after direct removal of the birthmark. The mole is sent for histological analysis, which can confirm or refute suspicions of malignancy.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with cancerous tumors, melanomas, papillomas, hemangiomas.
[16], [17], [18], [19], [20], [21]
Who to contact?
Treatment for mole growth
What to do if a mole grows? If you notice a gradually growing birthmark, then you need to follow the following recommendations:
- pay attention to the symmetry of the neoplasm;
- make sure that the boundaries of the spot are smooth;
- observe the color change;
- periodically monitor the growth of the mole in millimeters, carefully recording the indicators;
- Having the listed observations in hand, you should visit a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact if a mole grows? You can contact a dermatologist, an oncologist, a surgeon: all these specialists can help with the problem and stop the growth of the mole.
Is it possible to remove a growing mole?
Removal of growing moles can be done in different ways, more or less effective. If the question is whether to remove a birthmark or not, then the answer from experts is clear: of course, remove it.
We list the main removal methods that are practiced in most medical institutions.
- The method of cauterization with liquid nitrogen is not the most effective method, because in most cases only the protruding surface of the formation is removed, while the tissues located deeper remain.
- The cryodestruction method is freezing a mole, similar to cauterization. After cryodestruction there is also a risk of relapse.
- The electrocoagulation method is the use of electric current in combination with local anesthesia. Before the advent of laser technology, the latter method was considered the most effective.
- Surgical treatment – removal of the pigmented tumor using a scalpel. It is used for large or deep moles that cannot be removed in any other way. The method is traumatic, but effective. A small scar remains at the site of the intervention.
- The laser method is currently considered the most acceptable for high-quality mole removal. The depth of penetration of the laser beam is determined by the doctor: it is easy to control so that the formation is completely removed. In this case, healthy tissues are practically not affected, and a small mark remains at the site of the birthmark, like a burn, which over time becomes almost invisible.
Advantages of laser removal:
- the method is absolutely bloodless;
- no scar tissue is formed after removal;
- healthy nearby tissues are not damaged;
- the risk of complications is extremely minimal;
- the operation takes place quickly, within 10-15 minutes;
- removal can be performed in any area of the body.
Disadvantages of the laser procedure:
- It is impossible to remove large moles.
The doctor decides which method to choose. However, the patient's opinion must also be taken into account. You should take into account the size of the birthmark, its condition, the condition of the patient as a whole, the depth of growth of the birthmark, as well as some other individual characteristics.
What if a mole grows again after removal?
Sometimes a mole grows again, in the same place. This can happen if the tumor is removed incorrectly and incompletely. That is why, when choosing a method for removing a mole, you need to check with your doctor whether there is a risk of recurrence. If there is such a risk, then it makes sense to choose another method, even surgical intervention.
In addition to the correct selection of the removal method, it is also important to choose wisely the specialist who will carry out the procedure. It is unacceptable to remove moles in beauty salons, from people who do not have qualifications or even medical education. You should not use peelings, photodestruction, or laser skin resurfacing to get rid of a growing mole. All these procedures are aimed only at superficial effects, which sooner or later only aggravates the situation with birthmarks.
Will medications help if a mole grows?
Some doctors prescribe medications for the growth of a benign mole: mainly, these are vitamin preparations that contain substances important for the body (vitamins, amino acids, etc.). The essence of their purpose is that often the massive appearance and growth of moles can be provoked by a person’s deficiency of certain substances. The use of such therapeutic and prophylactic drugs is justified in most cases. But it should be noted: formations that have already arisen after taking the drug will not disappear anywhere. Treatment will only help prevent the growth and increase in the number of age spots.
- AEvit is a combination of vitamins A and E in one preparation. AEvit is taken for up to one and a half months, 1 capsule per day with food.
- Vitamin C is an extremely important vitamin for the body. Take it 0.05-1 g per day.
- Methionine is an essential amino acid, which is necessary, first of all, to normalize liver function. Methionine is prescribed orally, approximately 1 g up to 4 times a day, half an hour before meals. Treatment should be continued for up to 1 month, or in short 10-day courses.
- Riboflavin is a vitamin that regulates oxidation and reduction processes. Tablets are taken for one and a half months, 0.005-0.01 g up to 3 times a day.
- Skinoren is an anti-pigment cream that inhibits the growth of abnormal melanocytes. Use as an external agent, lightly rubbing into the pigment spot area twice a day.
- Folic acid is a vitamin substance that belongs to the B vitamins. It is actively involved in metabolic processes, as well as in the production of amino acids. The drug is used in amounts from 20 to 50 mg per day. During pregnancy, the dosage of the medicine is determined by the doctor.
Traditional treatment and mole growth
Treatment with herbs and other folk remedies is very popular: drugs prepared in traditional ways are usually available and have few side effects. However, is it possible to use such remedies when moles are actively growing?
To be honest, if there is a danger of degeneration of a birthmark, any delay can cost serious consequences. Therefore, doctors definitely do not recommend taking risks, but immediately removing the tumor.
Only in extremely rare cases, when the birthmark is small, shallow and 100% benign, is it permissible to use folk remedies, but only after consulting a doctor.
- Fresh celandine juice is applied to the mole in the morning and evening until the formation disappears on its own.
- Cut a raw potato and rub the clean cut onto the stain, after which the potato is thrown away.
- Grind a clove of garlic, pour vinegar over it and knead the dough with the addition of flour. Place a cake of this dough on the birthmark, fix it with a band-aid and do not remove it for 2-3 days. If after the first procedure there is no effect, then it can be repeated.
- Apply freshly picked iris leaves under the bandage.
- Apply grated rosehip flowers several times a day.
- Place a drop of vinegar essence on the birthmark once a day.
You need to be extremely careful with traditional methods of destroying moles. It is better if the treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
[22], [23], [24], [25]
Homeopathy for a growing mole
Homeopathic treatment of birthmarks is not very common, since there are not many drugs that can help in this matter. One of the representatives of such homeopathic remedies is Nitricum Acidum - nitric acid, which is active against erosive, ulcerative skin lesions, cracks, warts, rashes and benign formations.
The drug is prescribed individually. The most commonly used homeopathic treatment regimen is: up to 10 drops of the product twice a day before meals.
There is quite a bit of information on the Internet that the rapid growth of a mole is a sign of its malignancy.
If you take this information literally, you can very easily suspect melanoma. The time has come to clarify what rate of growth of a mole is dangerous and what is not.
Why does the mole grow?
If you examine the tissue of a mole under a microscope, you can see that it consists of special cells - nevus cells.
These cells can divide under the influence of various factors. The most common ones are sunlight and pregnancy.
If the number of nevus cells increases as a result of division, we see the growth of the mole.
If a mole grows, is it melanoma or cancer?
As we have already found out above, cell division in a mole is a normal phenomenon. Moreover, from my practice I have found out that almost all moles can increase during a person’s life. At the same time, it remains unclear - after all, cells of malignant tumors are also prone to rapid division and growth.
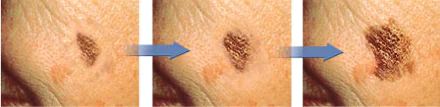
Unfortunately, without a microscope, we will not be able to determine by eye whether growth is associated with the degeneration of a mole. To find out this, a histological examination after removal of a mole is well suited. However, there is a less accurate, but simpler method - read on about it.
How to distinguish malignant growth of a mole from normal one?
First: almost every mole on our body can grow at a rate of about 1-2 mm per year. In my opinion, such a rate of increase should not raise suspicions among the oncologist.
There are rare types of melanoma (lentigo melanoma) that can grow very slowly. More on them later. For now, I’ll just note that in most cases, this tumor grows quickly. Its increase often occurs at a rate of 1-2 cm over six months to a year.
Second: when answering the question “is it melanoma?” You always need to analyze the complex of symptoms. Rapid growth alone is rarely enough to cause serious suspicion. This is because lentigo melanoma can grow very slowly, sometimes over decades. At the same time, it will definitely reveal itself by the presence of other signs or during dermatoscopy. The benign nature of a mole will be confirmed by its smooth edge, symmetrical shape, hair on the surface, and its existence for 5 years or more. In favor of malignancy - “geographical” edge, asymmetry along two axes, bleeding without trauma, etc.
How to accurately determine whether a mole is growing or not?
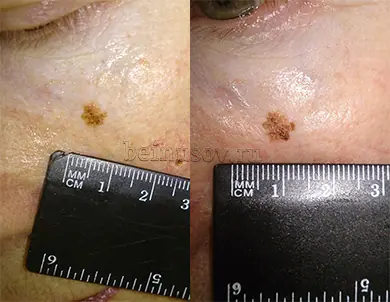
Sometimes it may seem that the mole that we have been carrying all our lives has grown in size. Sometimes it may seem that it has increased greatly. Unfortunately, the words “seems to have increased” will not help the doctor make a diagnosis. Accurate data required. There is an easy way to get them:

- Take a good photo of the mole against the background of a ruler with millimeter divisions. It's better to use a camera with a flash in macro mode. The photo must be taken by another person.
- If you have the slightest doubt about the size of the mole, you need to attach a ruler to it and compare the size with that in the original photo.
Summary or briefly about the main thing:
If your mole has enlarged, wait a minute to sound the alarm. First, answer the question: does the mole grow faster than 1-2 mm per year? If the rate is not higher than indicated and there are no other symptoms of melanoma ("geographical" edge, asymmetry along two axes, bleeding without injury, etc.), then most likely everything is fine with the mole. At the same time, if there is even the slightest doubt about the correctness of your conclusions, the oncologist should say the last word during an in-person examination.
If you still have questions, the following will help you:
In the human body there are cells responsible for skin color. They are called melanocytes. A mole (nevus) is an accumulation of such cells in one area. These formations come in various colors, shapes and topography. They appear both at birth and throughout life. Most often, moles do not cause any discomfort or health problems. However, recently, nevi of an oncological nature appear quite often. Even congenital benign formations can degenerate into cancer. There are quite a few reasons for this. A mole or nevus should be monitored periodically. When it changes color or shape, you should urgently consult a doctor. If there is such a formation on the body, then it cannot be injured. When taking a bath, it is better not to use a washcloth where moles grow. Often people are unhappy with the presence of such a cosmetic defect and try in every possible way to get rid of it. It is completely unacceptable to engage in such procedures at home. If the mole really looks bad, it is better to visit a medical facility. There, experienced doctors will help solve the problem without harm.
Types of moles
Main types of moles:
- Pigmented - can be light or black, small or very large. The main difference from the rest of the skin is the color.
- Vascular (hemangiomas) are pink or red formations with a bluish tint. They lighten when you press on the surface.
- Warty - raised, lumpy. Most often burgundy or pink. Sometimes they are flesh-colored.
Regardless of the group, they can all be benign or vice versa.
There are many nevi, each of which has its own medical name:
- blue moles;
- Sutton moles;
- complex moles;
- intradermal moles;
- giant pigmented moles;
- dysplastic nevi.
Sometimes it happens that hair grows from a mole. This is not some kind of alarming symptom. The most important thing is not to pull them out, so as not to injure the formation itself.
Reasons for the degeneration of a nevus into cancer
Often, most moles do not pose any danger. This requires a certain push. The most common causes of mole degeneration:
- Hormonal imbalance - during hormonal changes, skin cells change. It is necessary to carefully monitor nevi during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. If a mole begins to grow, you should definitely consult a doctor.
- Excessive sun exposure is a major factor in the development of skin cancer. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation promotes cell degeneration. It is very important, while in the sun, to minimize the likelihood of developing burns; they greatly weaken the skin’s immunity and cause irreversible changes in it. Particular care must be taken to hide from the sun the places where moles grow.
- Trauma - Many people take moles on their body lightly. Few people know that injury to such a benign formation can quickly degenerate into cancer. Places where moles grow should not be rubbed with a washcloth. They should not be squeezed out or pulled with thread. If the mole still bothers you greatly, it is better to consult a doctor.
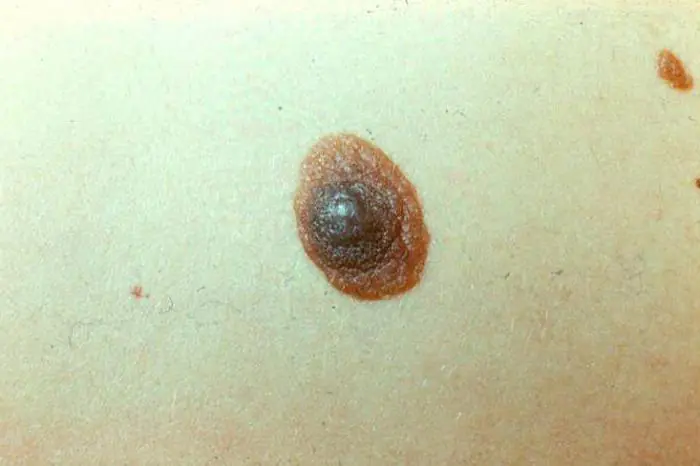
Dangerous moles
Why moles grow and how safe they are is of concern to many. You need to be very careful about them. Any changes in appearance should alert you. Periodically, congenital moles, under the influence of certain factors, can turn into cancer. The main thing here is not to miss the first symptoms. In the early stages, these diseases are easily treatable. The number of recovered people is almost 100%. In later stages, the prognosis is less optimistic and the disease can be fatal. You need to go to the hospital if a mole is growing very quickly. The doctor will tell you what to do in this case.
Symptoms of mole degeneration:
- changes in size, color;
- inflammation around the mole;
- its elevation above the surface of the skin;
- change in structure, varnish mole;
- discomfort associated with itching;
- formation of nodules, hardening;
- blurring of contours.
As for new moles, you should treat them even more carefully. Any new skin lesions larger than 0.5 centimeters require medical supervision. You should also go to the hospital immediately if a mole is growing rapidly. Not many people know which doctor to go to. Oncologists treat these diseases.
Safe moles
Most moles on the human body do not pose a health threat. Small congenital formations that are not compacted and have clear edges are completely harmless. They can degenerate into oncology only when exposed to certain factors. There is a certain type of benign nevi that can increase in size. Why moles grow is interesting to many. These types include hemangioma. This is a benign tumor caused by the accumulation of a large number of cells in the blood vessels. If the formation quickly increases in size, it is removed surgically. In most cases, treatment is carried out with hormonal drugs.

What moles need to be treated and how?
All suspicious formations on the skin require close medical supervision. Self-medication or removal at home is strictly prohibited. If the mole is benign and is a cosmetic defect, it is simply removed surgically. Laser therapy is also popular in this matter. With malignant tumors everything is more complicated. To begin with, many studies are carried out to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the stage. Then treatment is carried out. In the early stages, removal of the mole and further observation is sufficient. Advanced diseases are extremely difficult to treat. General chemical and radiation therapy is used. The prognosis may be unfavorable.
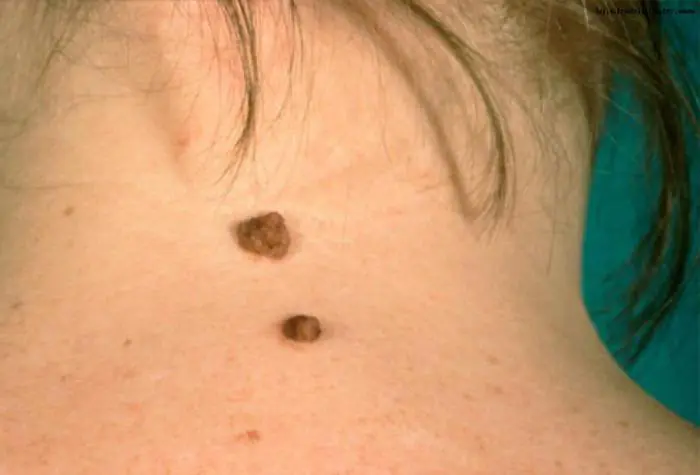
Complications after mole removal
In order to avoid complications after surgery to remove a mole, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions:
- treat the wound daily with an antiseptic solution;
- apply antibiotic ointment;
- Do not remove the crust from the surface of the wound yourself;
- Do not apply various cosmetics to the skin for 7-10 days.
As a rule, complete healing of the wound occurs after 3 weeks.
If a malignant mole has been removed, the patient must carefully monitor his body for a long time for new formations. If a relapse occurs, the patient is sent to oncology to continue treatment.
After removing ordinary moles and following all the doctor’s instructions, the risk of complications during this operation is minimal. If the size of the formation was large, scars and scars may remain, which can then be removed with a laser.
What not to do with moles
Any formations on the skin should be monitored. If the nevus does not manifest itself in any way for a long time, there is no need to worry. You should visit a doctor if new, suspicious moles appear. If existing ones begin to change, this also requires urgent medical consultation. When hair grows from a mole, under no circumstances should you pull it out or shave it off. This leads to injury, which can trigger the process of degeneration of the formation into oncology. To prevent a mole from causing problems, you must adhere to some simple rules:
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun;
- do not use a washcloth in places where moles accumulate;
- do not pull out hairs from them;
- Moles cannot be squeezed out or combed.
If the mole is injured, you should consult a doctor.

Moles in children
When moles grow on children's bodies, it causes a lot of worry for parents. The largest number of nevi in babies appear from birth to one year. Almost every child has small flat moles on the body. Require more attention:
- nevi more than 0.5 centimeters in diameter;
- elevated above the surface;
- with fuzzy edges;
- fast growing;
- changing color;
- itchy and inflamed.
If suspicious moles are identified, you should visit an oncologist.
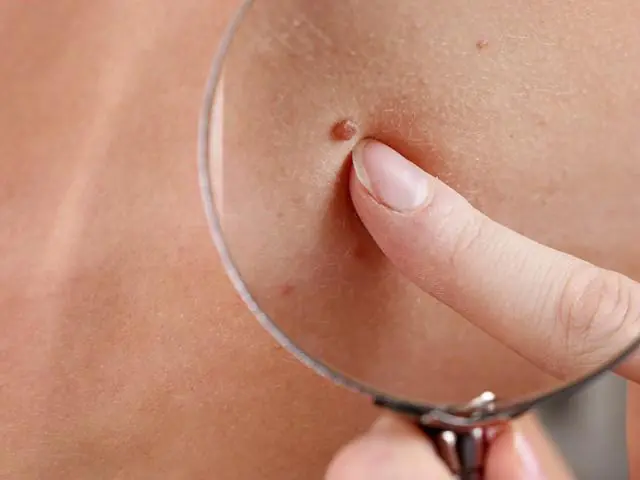

Folk signs about moles
Since ancient times, there has been a belief that a large number of moles portends a happy life for a person. By the place where moles grow, you can determine the nature:
- on the forehead - wisdom;
- on the cheeks and under the eyes - kindness and tenderness;
- on the cheekbones - courage, determination;
- on the scalp - a philosophical mindset;
- on the temple on the right - subtle intuition;
- on the ears - boasting;
- in language - such people are overly talkative;
- on the neck - high intelligence;
- on the shoulders - a karmic sign of strong people who do not recognize authorities;
- on the stomach - hysteria;
- on the eyelids - sensuality;
- above the upper lip - deceit;
- on the nose - a sense of humor, frivolity;
- on the foot - vital energy;
- On the shins - ease of instep;
- on your knees - impatience;
- on the palms - a hermit lifestyle;
- on the elbows - inability;
- on the back - demandingness towards oneself and others.



