If you experience itchy skin all over your body, the cause may be a parasitic infection, fungus, or some other disease. Most cases of such manifestations are associated with a skin reaction to allergens. Such manifestations are quickly eliminated if the provoking factor is identified and removed. Itching sensations due to diseases are much more difficult to remove.
What is itchy skin
Human skin is penetrated by billions of nerve endings, which are very sensitive to all sorts of irritants: vibration, touch, chemical or thermal effects. A crawling insect, an insect bite, the touch of a feather, a cobweb, or a hair can cause a desire to itch, burning, tingling at the site of irritation: you want to quickly remove this unpleasant sensation by scratching the itchy skin.
Generalized itching - unbearable discomfort in the superficial layers of the dermis - can cause some diseases of the internal organs, allergic reactions due to dermatitis. Among the symptoms of dermatological diseases, skin itching dominates, but scratching syndrome of the anogenital zone, conjunctiva, trachea, pharynx, nose, and oral mucosa often occurs. There is a distinction between itching of the whole body without rash and with rash.
Body itching without rash
Itching all over the body without rashes can occur due to the following diseases:
- Kidney: chronic failure.
- Liver, gallbladder, pancreas: cancer of the head of the pancreas, biliary cirrhosis, hepatitis, bile stagnation, obstruction of a large bile duct, increased bile salts in the blood, sclerosing cholangitis, obstruction of the duodenal papilla by a neoplasm or stone.
- Neuroendocrine: hypo- and hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, carcinoid syndrome, diabetes mellitus, symmetrical erythrocyanosis.
- Hematological (blood diseases): leukemia, paraproteinemia, mastocytosis, lymphogranulomatosis, iron deficiency anemia, polycythemia vera, lymphomas, multiple myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia.
- Neurological: brain tumor, multiple sclerosis, brain abscess, cerebral infarction.
- Paraneoplastic syndrome: visceral carcinoma, Sjogren's disease.
- Rheumatological: dermatomyositis.
- Mental: depressive states and psychoses.
- Infectious and parasitic: parasitosis, HIV.
- Other conditions: age-related changes (senile), pregnancy, alcoholism and hangover.
Rash and itching on the body
When multiple changes occur on the mucous membrane and skin that differ in color, texture, and appearance from normal skin, they indicate a rash. The rash can affect the arms, legs, face, stomach, and chest. These may be primary symptoms - pustules, redness, spots, goosebumps, blisters, pimples, blisters. As the disease progresses, the rash is replaced by secondary elements:
- Loss of natural skin color (discoloration, darkening).
- Erosions and ulcers are the result of opening an abscess with a violation of the integrity of the skin with the capture of subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Peeling - scales of dead epidermis.
- Crusts are the dried surface of weeping erosion, ulcers, and opened blisters.
- Scratching – superficial or deep abrasions.
- Lichenification – thickening, strengthening of the skin pattern.
It is not worth making a diagnosis on your own, guided by visible signs and information you have read. In case of any suspicious manifestations, you should consult a doctor to identify the underlying internal pathology that caused the scratching. A rash and a strong desire to scratch on the body are accompanied by diseases such as:
- chicken pox;
- postherpetic neuralgia;
- rubella;
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- herpes;
- meningococcal sepsis;
- hives;
- acne;
- fungal infections;
- psoriasis;
- scabies due to infection by microscopic parasites.

Why does my whole body itch?
When the body itches in different places, it is necessary, first of all, to determine the cause of this condition. Perhaps this is a consequence of fungal, allergic, inflammatory skin diseases, pathologies of internal organs, mental disorders and neuropathic diseases. Since there are so many causes, it is important to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the body to determine the root cause.
Allergy
Allergies in the 21st century have become the scourge of humanity. The entire population of the planet suffers from this disease to one degree or another. Allergies manifest themselves in the form of swelling, rashes, scratching, which vary in severity - from light scratching to scratching with the appearance of blood. With allergies and dermatitis, a large amount of histamine accumulates in the skin - a substance that causes scabies, tissue swelling, and dilates blood vessels. Therefore, itchy areas on the skin appear swollen and red.
Allergic itching is eliminated with antihistamines, but then the allergen should be identified and eliminated. A more serious neuroallergic disease is neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis, which is characterized by uncontrollable, unbearable localized itching. This disease develops from childhood and subsides a little during puberty, but later recurs again. Treatment of diffuse neurodermatitis is long and complex.
Stress
A common cause of itching throughout the body is the development of psychogenic conditions: mental trauma, overstrain of the nervous system, stress, when a person does not control hand movements and constantly scratches and rubs the skin. At the same time, the desire to scratch under stress does not weaken, but, on the contrary, can only intensify. Often, against the background of neuroses, periodic wandering itching occurs, when it is impossible to determine a specific place. It is possible to avoid attacks or reduce their intensity if you eliminate the factors that cause stress.
Seasonal itching
Patients who complain of exacerbation of scabies attacks in spring or autumn can be confidently diagnosed with VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia). This is due to a lack of vitamins in the body. Vitamin therapy, which should be prescribed by the attending physician, will help eliminate the symptoms. If your whole body itches in winter, you should go to the doctor and find out the reasons for this condition.
What diseases cause the body to itch?
Itching throughout the body can occur in various diseases, with different symptoms:
- Diffuse neurodermatitis. Symptoms: severely itchy areas of the skin, roughness, dryness and roughness of the skin at the affected area.
- Atopic dermatitis. Symptoms: redness, desire to itch with the formation of wounds and crusts. The face, neck, legs and arms, and abdomen are affected. It happens due to food allergies and dysbacteriosis.
- Contact dermatitis. Symptoms: local itching, redness, blisters, which eventually open and are replaced by ulcers. Locations: hands. Causes of appearance: allergens, dyes, medications.
- Hives. Symptoms: redness, swelling in strictly localized areas of the skin. In more severe cases, signs may include angioedema and anaphylactic shock. As a rule, itching with urticaria occurs on the abdomen, large joints, and the outer side of the palm.
- Fungal infection. Symptoms: the body itches, hair falls out with ringworm, suppuration of the skin with scab, peeling with fungal infection of the feet, redness in the folds of the skin and in the groin.
- Pediculosis (lice). Symptoms: itchy scalp, presence of nits (lice larvae), small bloody crusts, signs of bites on the neck.
- Scabies. Symptoms: scabies itches between the fingers, on the wrists, on the stomach, in the groin and gets worse at night. Characterized by localized symptoms with distribution throughout the body.
- Pruritoceptive. The cause is insect bites (mosquitoes, mosquitoes, wasps, hornets, ticks, bedbugs, fleas, bees, spiders). Symptoms: redness, swelling, strong desire to scratch at the site of the bite.
- Psoriasis. Symptoms: inflamed, reddened lesions with white scales of varying sizes. Areas beyond the psoriatic plaques may itch. The disease is chronic and difficult to treat.
- Anal. Symptoms: unbearable desire to scratch the itchy area. The desire to scratch may not be associated with any disease and can be explained by poor hygiene, but it can be a consequence of certain diseases: parasites (pinworms), erythrasma, hemorrhoids, thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, proctitis, diabetes.
- Genital. Symptoms: in women – the mucous membrane of the labia and vagina itch; in men - the scrotum and head of the penis. Causes: candidiasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, bacterial vaginosis, colpitis, vulvar kraurosis (vulvar atrophy), in men - balanoposthitis (inflammation of the foreskin and head of the penis).
- Scalp. Causes: seborrhea, pediculosis, lichen. As a rule, it develops with dry skin.
Types of skin itching
There is the following classification according to the frequency of relapses and intensity of manifestation:
- Spicy. It is a consequence of pathology in the body.
- Local. It has biological causes - bedbugs, ticks, etc. and is felt in a certain place.
- Generalized. Unpleasant manifestations throughout the body for various reasons. Can be observed in liver, endocrine, dermatological, hematological, neurogenic diseases, oncology.
- Chronic. It occurs for no apparent reason and indicates dermatosis and systemic diseases during an exacerbation.
What to do if your whole body itches
Considering that there is only one itching, but there are many causes, its treatment must be approached differently. What to do if your whole body itches? You can use ointments and creams that can relieve discomfort, but if the causes lie in liver disease or endocrine system disorders, then self-medication with local remedies can only aggravate the problem and complicate further treatment. Indeed, in this case, itching on the skin is just the tip of the iceberg, under which lies a serious illness, possibly fraught with tragic consequences.
Diagnostics
Determining the root cause will require diagnosing the itchy areas. First contact a dermatologist to prescribe tests and a detailed examination. If the dermatologist finds it difficult to name the cause, consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist, allergist, gastroenterologist and other specialists will be required. Principles of treating itchy skin:
- eliminating the cause;
- local treatment;
- systemic treatment.
Drug treatment
Depending on the reasons that caused the unpleasant symptoms, treatment for itching of the body skin is prescribed. For allergic scratching, antihistamines are prescribed: Zyrtec, Loratidine, Erius, Zyrtec, Suprastin, Tavegil. Additionally, it is recommended to take sedatives: Novo-Passit, valerian, mint tea, motherwort tincture, since the constant desire to itch disrupts sleep and makes the patient irritable. Complex manifestations are treated only under the supervision of a doctor.
However, this will take some time, and you want to relieve the itching as quickly as possible. Therefore, there are general recommendations:
- The diet should not contain salty, hot, spicy foods. It is undesirable to drink strong tea, coffee, and alcohol.
- If an elderly person has body itching (senile, worse in the evening and at night), then iodine preparations will alleviate the condition.
- Take warm baths with sea salt.
- Wipe the skin with calendula tincture in alcohol, lubricate with menthol-based antihistamine ointments.

Folk remedies
Along with drug therapy, folk remedies for body itching are used:
- A quick effect is achieved by taking baths with decoctions of plants: nettle, chamomile, mint, celandine, pine needles.
- Pruritoceptive (insect bites) are removed with coconut oil baths. To do this, dissolve 50 g of oil in a water bath and pour into warm water. The procedure time is 15 minutes.
- Lemon juice works great for itching, but it should not be applied to areas with damaged skin.
- Vaseline will help quickly relieve itching, as it will additionally moisturize and soften.
- To soothe irritations, you should use basil. It contains vitamins A, C, P, which are very important for skin health. You need to wipe the irritated areas with a clean fresh leaf or prepare a decoction of basil and make lotions.
- Apple cider vinegar and celandine are used as applications (do not use celandine for chemical or sunburn).
How to treat body itching
If a diagnosis is made, the disease that became the cause is determined, the appropriate medicine is prescribed for itching of the body skin:
- For renal itching: UVB therapy, Cholestyramine, activated carbon, Thalidomide, Naltrexone, Ondansetron, Capsacin cream, Tavegil.
- Itching due to cholestasis is treated with ursodeoxycholic acid, Cholestyramine, Phenobarbital, Rifampicin, Naloxone, Naltrexone, Nalmefene, Fexadine, Trexyl, Tavegil.
- Endocrine diseases: skin moisturizing, hormonal medications, compensation for diabetes mellitus are necessary.
- Hematological diseases: iron supplements, Aspirin, Cholestyramine, Cimetidine.
- Senile (senile): drugs with a calming effect (sedatives).
Local treatment
Local treatment includes treatment of the skin surface in areas of inflammation. These can be compresses, lotions of 3-5% vinegar, talcum powder, morning and evening hygiene. Among the medications, ointment is effective:
- Lokoid;
- Triderm;
- Ultraproct;
- Belosalik;
- Baneocin;
- hydrocortisone ointment (has a lot of contraindications).

Antihistamines
In the treatment of diseases with manifestations of itching, drugs that block the production of histamine are often used. Antihistamines:
- Atarax. The active ingredient is hydroxyzine hydrochloride.
- Berlicourt. Prescribed to eliminate any signs of allergies. The active ingredient is triamcinolone.
- Desazon. The active ingredient is dexamethasone.
- Diazolin. Prescribed for psoriasis, eczema, urticaria, insect bites.
Etiotropic therapy
This is a treatment aimed at eliminating a microbial, viral, bacterial, infectious pathogen. All antibacterial drugs (antibiotics), sulfonamides, nitrofuran drugs are etiotropic. Etiotropic agents include interferons, antidotes, immune globulins, probiotics, bacteriophages, and anthelmintic drugs. Etiotropic therapy drugs are used for complications of hereditary diseases, poisoning, and herpetic infections of various organs.
How to remove body itching at home
Treatment at home is aimed at eliminating the symptoms, but you need to work with your doctor to combat the cause of the strong desire to scratch the skin. As temporary help you can use:
- Burdock roots. You need already dried roots to then obtain the powder using a coffee grinder. Pour 2 tbsp into a saucepan. l. powder, pour 1 liter of water. Cook for half an hour. When it cools down, you can make gauze compresses by applying to the irritated area. The effect should occur within half an hour.
- Alcohol tincture of elecampane. You can prepare it at home, for which you take 1 tbsp. l. finely chopped roots, pour them into a suitable dark glass bottle, add 50 ml of alcohol. The tincture is prepared for 10 days, after which you need to make an aqueous solution with the tincture and wipe the itchy skin. According to people's reviews, the effect occurs immediately.
- Needles. You will need young buds and pine needles in the amount of one glass. Pour a liter of boiling water over them and simmer over low heat for 20 minutes. Wash with the cooled broth, wipe the skin, make compresses and lotions. The result is felt quickly.
The symptom of itching a certain part of the body is called pruritus in medicine. It, like pain, is an attempt by the body to convey to a person’s consciousness that there is a problem in him that requires an urgent solution. To some extent, itching can be called a protective reaction, since such mechanical stimulation of the pathological focus helps to shake off parasites, poisonous plants or stinging insects.
Often itching is caused by individual intolerance to some substance that gets either on the skin or inside the body - through the mouth or by injection. It can occur due to thermal, mechanical or electrical stimulation of skin receptors. The symptom also indicates an excess of substances in the blood other than histamine, which appears during allergies. Some of these diseases can be life-threatening.
Where does the itching sensation come from?
The imperative desire to scratch an area of skin occurs when blood with a high concentration of dissolved substances flows to the pain receptors (nociceptors), spread out in the form of a network under a layer of epithelial cells:
- histamine and/or histidine. These substances are formed in excess by immune cells when certain – specific to each organism – foreign proteins enter the body;
- bile acids produced in the liver. They enter the skin cells and cannot leave them when a condition such as cholestasis develops - when bile cannot completely enter the duodenum and is forced to stagnate in the cells of the liver and biliary tract;
- serotonin is a substance formed from an amino acid, which, when released, leads to a significant contraction of smooth muscles located in blood vessels and internal organs. This is a neurotransmitter, that is, a chemical compound that allows communication between nerve endings (the signal passes from nerve to nerve not like electricity, but rather like a bubble with a chemical substance, depending on the structure of which the activity of a neuron can be inhibited or activated). Its structure is very similar to the psychoactive hallucinogen LSD;
- cytokines – molecules that enable “communication” between immune cells;
- endorphins – natural pain-relieving molecules;
- nitrogenous wastes that accumulate in the blood during kidney disease;
- some other bioactive substances: thyroid hormone calcitonin, pancreatic enzymes (trypsin, kallikrein), VIP neuropeptides and substance P.
Since each person’s body has its own characteristics, no direct connection has been identified between the concentration of the above substances and the severity of the need to perform mechanical stimulation. Thus, severe itching in one individual may accompany the initial stage of renal failure, while in another it will not appear even with the terminal stage of uremia.
Only the skin and those mucous membranes, the layer of epithelial cells in which is in contact with the external environment and is located near the skin: gums, tongue, genitals, are “subject to itching”. The signal from the pain receptors located underneath them travels along type C and A-delta nerve fibers, reaches the spinal cord and, together with its structures, is delivered to the brain, to its sensitive zone.
Itching can be of a different nature: from a mild “tickling” to severe, painful. Its nature dictates to a person how to “process” its localization:
- scratch: this is more typical for skin pathologies such as neurodermatitis or eczema;
- rub gently: inherent in lichen planus;
- cool (typical for acute urticaria).
However, a diagnosis cannot be made based on these characteristics alone. In determining the cause of itchy body skin, the following are important: 
- its localization;
- the condition of the skin at the site of such sensations;
- conditions for the appearance and relief of itching;
- additional symptoms.
Let’s consider the combination of these factors to make it easier to get examined and choose exactly the specialist who can quickly alleviate your condition.
Types of itching
The prevalence of the symptom is the main criterion from which the diagnosis of the cause of skin itching begins. Based on this measure, pruritus (the so-called itching in medicine) may be:
- Localized (a person can indicate a specific place where itching is felt).
- Generalized (throughout the whole body, not necessarily at the same time).
Generalized itching
- Diseases of the liver and biliary tract: hepatitis, cirrhosis, pancreatic cancer, cholestasis of pregnancy, giardiasis.
- Kidney failure.
- Presence of worms in the intestines.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Gout.
- Diabetes.
- Hypovitaminosis A.
- HIV infection.
- Oncological diseases: stomach cancer, multiple myeloma, erythremia, iron deficiency anemia, leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Mental illnesses: depression, phobias, mnemoderma (itching associated with the mention of biting and stinging parasites).
- Senile itching.
- Itching when going up to altitude.
- Associated with neurological diseases: brain tumors, multiple sclerosis.
- Seasonal itching.
- For systemic pathologies, for example, periarteritis nodosa.
Localized itching
| Localization | Causes |
| On the face |
|
| On the head |
|
| In areas subject to friction | Bullous pemphigoid |
| On the crooks of your wrists | Atopic dermatitis, lichen planus |
| In the anal area |
|
| In the genital area |
|
| In areas covered by clothing most of the year | T cell lymphoma |
| On the back, on the hips | Folliculitis |
| On the knees | Atopic dermatitis |
| On hands | Scabies |
| Anywhere | Neurodermatitis, eczema, contact dermatitis, insect bites |
Itching accompanied by changes in the skin
This symptom indicates pathologies that are within the competence of dermatologists. That is, local changes are accompanied by skin diseases that are less dangerous than systemic diseases.
Diseases accompanied by redness of the skin
Itching and redness of the skin are more typical for inflammatory or allergic diseases. This:
- Contact dermatitis: irritation and itching located in the area that came into contact with the allergen. The boundaries of redness are clear. To diagnose, you need to remember what new places you have been to, what new household chemicals you started using, what clothes or accessory you put directly on your skin. So, redness in the armpits may be associated with wearing a new woolen sweater/dress or clothes that are familiar, but washed with a new powder. And itching of the skin of the hands - using a new cream or other chemical product. A characteristic feature of this disease is the complete disappearance of symptoms after the allergen ends.
- Atopic dermatitis is a disease that most often affects children, but atopic dermatitis can also occur in adults. Its causes are an allergen, most often taken orally with food. In children, redness is located mainly on the skin of the face (on the cheeks), the flexor surface of the knees and elbows. In adults: the face is excluded, wrists, knees and elbows may turn red - on their bends.
Combination of itching and rash
If such blisters protruding above the cover appear after mechanical friction of this area - dermographic urticaria
| Disease | Type of rash | Localization, features |
| Contact dermatitis | Redness with a clearly defined border; there may be blisters at the top of the redness | Anywhere. Can recall contact with clothing/accessory/chemical |
| Redness that has a border, protrudes above the skin level, and tends to merge with each other, similar to a mark left by a nettle. | Anywhere | |
| Bullous pemphigoid | Initially, redness rises above the skin, after which a bubble of tense properties appears in this place | In places where friction occurs with clothing or accessories (bag belt, watch belt) |
| Eczema | At first there is redness and swelling, which have a clear shape, then bubbles appear, some of which open, and crusts develop in their place. Elements of several stages are observed in one place (redness, blisters, crusts) | Symmetrical areas of skin, most often on the extremities (especially the upper ones), as well as the face |
| Limited neurodermatitis | Dry plaques, around which there may be red spots that do not have clear boundaries with healthy skin | On the sides of the neck, in the folds |
| Neurodermatitis diffuse | In adults - dried spots on the skin, surrounded by a reddish rim, without a sharp transition to healthy skin | Eyelids, feet, lips, hands. May be all over the body. |
| Swelling and redness, swelling and peeling, there may be red rashes, blisters or crusts on top | In children - after the introduction of complementary foods - on the cheeks, collar area, upper limbs | |
| Small spots of various shapes protruding above the skin, shiny | At the 2nd year of life, located in the area of the folds | |
| T cell lymphoma | Red rash on the skin, accompanied by itching, oval | In places not exposed to sunlight |
| Lichen planus | Violet, polygonal shaped polygonal polygonal granules with scales that rise above the healthy cover | Flexion surface of the wrists |
| Folliculitis | Bubbles and pustules | Hips, back, chest |
| Psoriasis | Silvery plaques with peeling on top | Extensor surface of the extremities, itching of the scalp and neck, palms and soles |
| Scabies | Paired black dots are visible | Arms, armpits, stomach, genitals |
Combination of itching and skin peeling
Itching accompanies peeling of the skin in the following cases:
- The outcome of an allergic reaction, which manifested itself as urticaria. The allergy could be caused by:
- products;
- medicines;
- animal saliva;
- household and other chemicals;
- insect bites;
- cosmetics.
If the itching is accompanied by a burning sensation
Burning and itching most often occur at the site of skin inflammation. This may be a reaction to mechanical irritation when shaving, using a depilator or waxing. Poorly healing inflammation in diabetes mellitus is also possible, which burns due to the pH of the tissues changing as a result of this metabolic disease. Burning and itching may be accompanied by diseases of the veins of the lower extremities - then the skin may be swollen, slightly bluish, but without any visible rash.
A combination of these two symptoms can develop in a person when a rash appears (see the corresponding section) - as an individual reaction to eczema, neurodermatitis, urticaria or other dermatitis.
Other symptoms that may indicate the cause of itching
The symptom may also indicate systemic diseases:
- With cholestasis, in addition to itching, yellowness also occurs, if not of the entire skin, then of the whites of the eyes. Itching more often appears in places that rub with clothing, intensifies at night;
- the smell of urine from the body, dry skin sprinkled with white “powder” and its itching, a change in the amount or color of urine indicates kidney failure;
- itching of the skin after taking a warm bath/shower is characteristic of erythremia, a pathology when the number of red blood cells is significantly higher than normal.
However, if the skin itches for some time after swimming (shower, bath) only during the heating season, it is possible that the skin reacts this way to “technical” hot water in the tap, containing various harmful impurities. If itching is felt after swimming and in the summer, perhaps the reason is that the water is very hard, with a high content of chlorine.
Itching without other symptoms
When itching appears, and there is no dryness, no “powder”, no spots, or any changes in color on the skin, it may be:
- disease of the hematopoietic system, in particular lymphogranulomatosis. You need to consult a therapist who will palpate a person’s lymph nodes, prescribe and interpret a hemogram and other blood tests, and refer you to a hematologist or oncologist;
- senile itch, which appears after 60 years of age for an unknown reason. But, even if you fit into this category, you need to rule out more serious diseases;
- mental or neurological diseases, the symptoms of which you may not notice;
- population of the intestines with helminths, which can be excluded by analyzing stool for their eggs, as well as blood tests for antibodies to worms. Prescribing such a diagnosis is the job of an infectious disease doctor (he can be found in the clinic in the office with the abbreviation “KIZ”).
In any case, you may not notice the symptoms that a qualified doctor will pay attention to, so if itching occurs, contact him.
Treatment
Treatment for itchy skin is prescribed after an examination, the purpose of which is to identify the cause of this condition. The main tests that will help clarify the ethology will be:
- general urine and blood tests;
- blood glucose;
- skin scraping to identify fungi;
- liver and kidney tests (blood);
- test for occult blood in stool;
- detection of helminth eggs in feces.
While the tests are being performed, to alleviate the symptoms of itching - if there are no signs of renal or liver failure, which the doctor must tell you about - antihistamines are prescribed: "Eden", "Fenistil", "Diazolin", which do not cause drowsiness, or more powerful drugs, but with this effect (“Suprastin”, “Tavegil”).
For a localized lesion, an antiallergic ointment for skin itching can be used, for example, Sinaflan, Akriderm, Apulein, hydrocortisone ointment or other corticosteroids. Sometimes other local drugs of non-hormonal origin are prescribed - “Prograf” or “Elidel”.
If itching is caused by cholestasis, bile acid-absorbing drugs have been used successfully. When the cause of the symptom lies in a blood disease, specific drugs are used - monoclonal antibody inhibitors. Psoriasis is treated by combining local and systemic medications that normalize skin cell division.
In case of extremely severe itching, weak opiates are prescribed, and treatment is supplemented with hirudotherapy, ultraviolet irradiation of the skin and acupuncture.
Thus, the causes of itching of the scalp and body are varied. Most often, these are various allergic reactions both to a substance that has entered the body and to a substance that has touched the skin. But there may also be life-threatening kidney diseases, liver diseases, or even blood diseases. To clarify the cause and select treatment, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Itching is not a disease, but only a symptom. According to doctors, the body cannot itch without a reason. Most often, the reason that the body itches is some kind of disease, even if peeling, dryness and itching go away for no apparent reason.
It is necessary to understand the reasons before starting treatment. Itching is dangerous because the patient can scratch the skin, which will lead to inflammation, infection and dehydration.
Skin diseases
The most common cause of itching is skin diseases. An inflammatory process appears, which is accompanied by itching.

Most often occurs due to hereditary predisposition. Stress, anxiety and poor living conditions are also prerequisites for the development of dermatitis.
Eczema
An inflammatory skin disease that causes blistering and burning. Also characterized by redness and itching. When scratching the blisters, erosions appear that turn into crusts.
Most often appears on the hands and face. It occurs in a chronic form and is accompanied by respiratory tract infections, as well as metabolic disorders.
Dermatophytosis
The answer to the question of why the body itches for no apparent reason may be the disease dermatophytosis. It is caused by fungi that live in the soil, the body of animals and humans.
Fungi penetrate into the upper layers of the skin, decompose proteins and feed on decay products. Dermatophytosis can occur on the scalp or body, on smooth skin, and on the nails.
Lichen
A skin disease that is caused by fungi or viruses. Most often develops after direct contact with an infected person or animal. There are several varieties: pink, cutting, weeping, girdling.
Most often appears on the scalp. The affected area becomes bright red, flaky and itchy. The main factor in contracting lichen is a weakened immune system.
Pediculosis or human lice infestation
The main factor of infection is unsanitary living conditions. Lice can be contracted in villages and villages, from people without a fixed place of residence.
Pediculosis is an ancient disease that most often occurs as an epidemic. You can become infected with it in a military barracks, children's camp, or school.
Blood-sucking parasites cause a lot of trouble. Their bites cause severe itching, but the main danger is that they carry typhus. Lice live on the scalp or pubic area.

Important point! To avoid becoming infected with lice, do not use other people's combs and do not give yours to anyone. Also be careful about the cleanliness of your pillows, and try not to sleep on a shared bed.
Note! You can only get lice from other people. Other types of lice live on the body of animals, which are not dangerous to humans.
Psoriasis
A type of scaly lichen. Inflammation is caused by the body's immune cells. The disease is characterized by red, dry spots that are covered with a white coating.
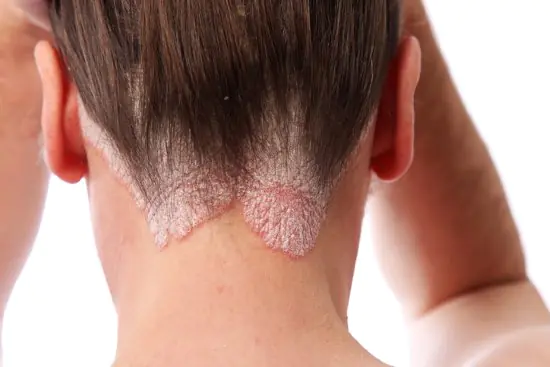
Most often they appear on the bends of the elbows, on the head, and lower back. They can also affect other parts of the body, as well as the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Factors that cause psoriasis: heredity, infections, HIV, certain medications.
Scabies
A disease caused by parasites. Scabies mites feed on the upper layers of human skin. The first sign of the disease is blisters in the interdigital folds. They itch a lot, the itching gets worse in the evenings.
Scabies can be contracted from contact with a sick person, through bed, clothing, and household items. In this case, the incubation period of the disease can last up to 4 weeks.
Hives
An allergic disease characterized by a red rash. The patient may scratch it vigorously, which only aggravates the disease. Often accompanied by Quincke's edema.
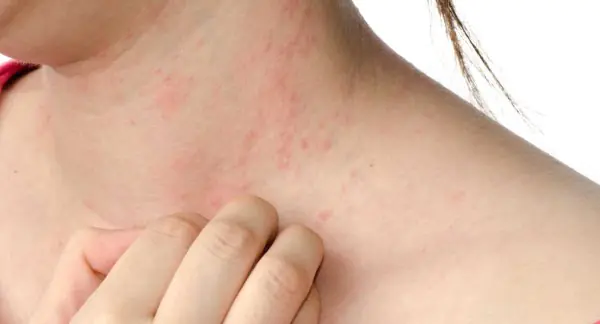
Causes may include food allergens, digestive disorders, insect bites, and hypothermia. With disorders of the kidneys, liver or intestines, urticaria takes a chronic form.
Xerosis
Abnormal dry skin. This is a consequence of severe itching or infectious diseases. The skin becomes rough, peels, itches, and turns red.
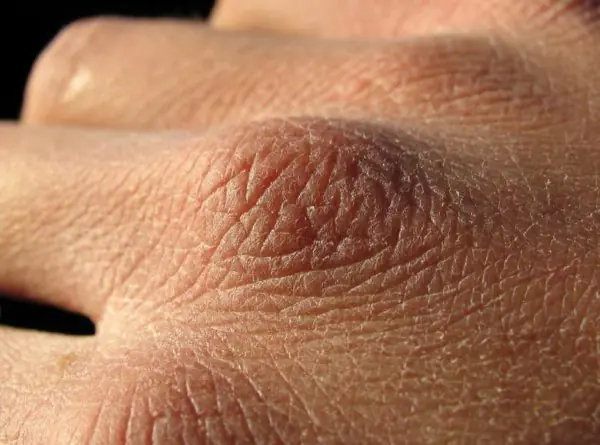
Xerosis can be a symptom of other disorders: psoriasis, dermatitis, eczema, seborrhea.
In addition, xerosis is caused by cirrhosis of the liver, hepatitis, and renal failure.
It may be caused by a cancerous tumor. When xerosis appears, it is especially important to examine the internal organs.
Systemic diseases
Systemic diseases are diseases of internal organs that may be accompanied by itchy skin. To accurately diagnose a particular disease, listen to other symptoms and consult a doctor.
| Why the body itches for no apparent reason is a disease | Nature of itching | Other symptoms |
| Allergy | Most often accompanied by the skin diseases listed above. The patient suffers from severe itching throughout the day. | Skin rash, digestive disorders. |
| Cancer | Body itching may occur after swimming. Most often, itching is localized in the lower extremities. Itching is the first symptom of cancer, after which others appear. | Skin rashes, spots, swelling of the limbs and face. |
| Cholestasis | Itching and skin rashes indicate problems with the gallbladder. The skin may turn yellow. The skin reaction occurs due to the accumulation of bile in the bile ducts. | Jaundice, nausea, weakness, pain in the right hypochondrium. |
| Diabetes | Due to excessive accumulation of sugar in the blood, peeling and itching of the skin, dryness and deterioration of its condition appear. Scratching can lead to infection with infectious and viral diseases. | Thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, weight loss. |
| Anemia | The itching is not permanent; most often it is localized to a specific area of the body. Skin burning may occur. | Weakness, headache, appetite disorder, exercise intolerance. |
| Multiple sclerosis | In cases of nervous system disorders, the skin may experience itching and burning. Other unpleasant sensations also occur: tingling, numbness, and decreased sensitivity. | Photosensitivity, impaired color perception, hand tremors, changes in gait, instability, frequent urination or retention, sexual dysfunction. |
| Thyroid diseases | There is dryness, flaking and itching of the skin. The skin of the hands and face is most often affected. You can soften the symptoms with moisturizing creams and oils. | Rapid heartbeat, anxiety, irritability, weight loss or gain, sweating, depression. |
| Liver diseases | Any of the liver diseases affects the external condition of the skin. When there are parasites or toxins in the liver, itching is observed, localized mainly on the hands and face. | Jaundice, pain in the right hypochondrium, burning skin. |
| Kidney diseases | Most often, itching occurs in the genital area, this indicates an inflammatory process. With kidney failure, skin diseases may develop, which are accompanied by itching and rashes on the skin. | Swelling, pain in the kidney area, blood in the urine, urination problems. |
Why the body itches for no apparent reason - the answer may lie in diseases of the internal organs.
Most often, this is not the only symptom and the disease can be diagnosed by other symptoms. But it is best to immediately consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and make the correct diagnosis.
Other common causes of itching for no apparent reason
Itchy skin is not always caused by serious illnesses. This may be a consequence of stress, age-related changes in the body, or a reaction to allergens and medications.
Infection with immunodeficiency virus
HIV does not manifest itself in the body for a long time, and the infected person may not be aware of the disease. But he has signs that indicate immunodeficiency. Skin signs are:

Fungal and viral diseases are accompanied by itching. Most often, herpes affects the mucous membranes, which are very itchy at the initial stage of the disease. Eczema can occur on the hands and face.
Mental disorders: psychogenic itching
Our body is sensitive to stress and anxiety. It often responds with redness in certain areas, itching, and chest pain. If you are sure that you are healthy and there can be no other reason for the itching, try to be less nervous and the itching will go away.
Allergic skin itching in adults and children
Food allergens cause irritation of the intestinal walls, which immediately affects the skin. Rashes and itching appear. Allergies to cosmetics, shampoos, soaps, and cleaning products may also occur. It is recommended to find the cause and not come into contact with this reagent.
Seasonal itching
For no apparent reason, the body may itch in the fall and spring in patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia. Why this happens cannot be said with certainty. Most likely, this is due to a lack of vitamins in the diet and weather changes.

Dehydration
If your body itches, but there is no visible reason for it, it may be a consequence of dehydration. It is difficult to say why this condition occurs. The reason may be insufficient fluid intake or a large loss of fluid if you were in extreme conditions.
Senile or senile itching
In old age, the body undergoes many changes: metabolism changes, the skin becomes thin and dry, the functioning of the sebaceous glands is disrupted, and cell renewal slows down.

This leads to unpleasant consequences: irritation, peeling, and itching. The skin of the face most often suffers, as it is thinner and more sensitive.
Note! Over many years of life, the body accumulates stress, allergens, and diseases, which can make the body itch. Even if it seems to you that there are no visible reasons, this is not so. That is why you need to take care of your physical and mental health from a young age.
Parasite infestation
Itchy skin can be caused by parasites such as scabies mites and demodex mites. The parasite does not necessarily have to live under the skin. Even worms and roundworms can cause skin rashes and itching.
Most often, antibacterial agents and antipruritic ointments are prescribed to get rid of them. Remember that self-medication with ointments alone will not bring results; you need to identify the cause and treat it.
Menopause
During menopause, women's hormonal levels change, which affects the condition of the entire body. In addition to changes in the sexual sphere, you will feel a change in the condition of your skin and hair. This may include the body itching for no apparent reason.
Why you shouldn't be afraid of it: As soon as the hormones return to normal, the itching will go away. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, use moisturizing creams.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy
Pregnant women often have itchy breasts and stomach. These are normal phenomena, as the body is undergoing restructuring. Other parts of the body may also itch.
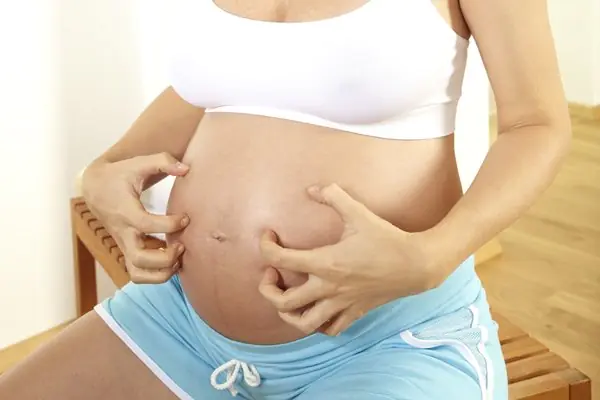

This should be treated carefully, as itching indicates allergies or diseases of the internal organs. See your doctor to determine the cause of the itching.
Itching of the body as a result of taking medications
If you are being treated with pills or folk remedies, itchy skin may be a side effect. Read the instructions before diagnosing yourself differently. It is best to replace the medicine that makes your body itchy with a similar one.
Itchy skin can be caused by skin diseases, diseases of internal organs and some other reasons. If you have other symptoms besides itching, consult your doctor.
If there are no apparent reasons, eliminate stress and anxiety from your life, and the itching will go away.
Why the body itches for no apparent reason:
Causes of skin itching:
">



