All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical research. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
The mortality rate from burns is quite high, so every person needs to know what to do in case of a burn in order to prevent negative consequences. In addition, an approximate classification of burns and first aid methods should be provided.
Burns are divided into thermal, i.e. as a result of exposure to steam, hot water, fire, and chemicals. Received as a result of contact with chemicals on the skin.
First-degree burns affect the top layer of skin and are considered the least dangerous injuries. With a first-degree burn, the skin turns red and there is slight swelling. If the burn occupies more than 25% of the area (in an adult), then the injury is considered severe.
In case of a thermal burn, it is necessary to eliminate the source of high temperature (fire, steam, hot water) and, if possible, cool the affected area with cold water for several minutes. If a chemical comes into contact with your skin, rinse the affected area well with cool water. After this, the affected area is treated with a special anti-burn agent (panthenol, etc.) and covered with a sterile bandage (plasters, alcohol solutions cannot be used). As a rule, with first-degree burns, recovery occurs within 7-10 days; chemical burns take a little longer to heal.
In second-degree burns, in addition to redness, watery blisters appear. Blisters need to be pierced only in hospital settings to prevent infection. The affected area should not be treated with oils or ointments, as this creates a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. For second-degree burns, cover the affected area with a dry bandage and seek medical attention. If the affected area is not large, you can apply a special product to the wound. Typically the recovery period takes 10-14 days.
Any burns to the respiratory tract are considered second degree burns.
With third and fourth degree burns, the skin and muscle tissue are significantly damaged; if most of the skin is burned, death is possible. Often such burns cause shock in a person.
When transporting a victim independently, it is important to minimize the contact of burned areas with a non-sterile surface.
Treatment of burns in this case is carried out only in a hospital, and the sooner a person receives qualified medical care, the better. In some situations, skin graft surgery is necessary. Before the ambulance arrives, you can give the victim painkillers and plenty of fluids.
What to do if your skin is burned?
The first thing to do if your skin is burned is to rinse the affected area under cool running water. In the case of a thermal burn, this will help cool the surface of the skin and prevent further damage. In case of a chemical burn, water will help wash away the remaining substance from the surface of the skin and stop the burning effect.
Further, if the burn is not significant, it is recommended to apply a cream or ointment that restores the epidermis (Panthenol, Bepanten) to the affected area. In case of severe burns, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
What to do if your hand is burned?
A hand burn is the most common injury. Typically, such burns occur when touching an iron, fire, boiling water, or when handling chemicals carelessly. Treatment depends on the strength and area of the lesion. What to do if your hand is burned first is to cool the burnt surface or wash off the remaining chemicals. Further actions depend on how badly your hand is burned. If the burn is not severe, then you can use Panthenol, Bepanten, etc. If most of the arm (or the entire arm) is affected, you must call an ambulance.
What to do if your finger is burned?
A burn to a finger, like any other part of the body, requires immediate first aid. First of all, this is cooling the finger or washing off the remaining chemicals. You need to hold your finger under running cold water for quite a long time until the pain begins to subside. After this, if necessary, blotting with a clean, dry cloth, apply a skin regeneration agent with an anti-inflammatory effect (Bepanten, Panthenol, Levomekol) to the affected finger. For deep burns, consult a doctor.
What to do if your leg is burned?
What to do if your leg is burned depends on several factors (depth of injury, area of burn, etc.). With any burn, it is important to provide assistance in the first minutes, i.e. rinse the affected area with cool water (in case of a thermal burn, this will help cool and reduce pain, and in case of a chemical burn, remove the remnants of the drug that caused the burn).
After first aid, for minor burns (without blistering), an anti-burn agent with wound-healing and anti-inflammatory properties (panthenol, solcoseryl, etc.) should be applied to the affected area.
Deep burns should be treated under the supervision of a specialist.
What to do if your face is burned?
With facial burns, many people ask the question of what to do in case of a burn in order to get rid of the marks as soon as possible.
For deep and severe lesions, it is not recommended to apply bandages with ointments or creams to the face, as this may prevent specialists from assessing the depth of the burns. When transporting to the hospital, you can cover your face with a light, dry gauze bandage to avoid exposure to external irritants.
Hospital treatment is only necessary for deep burns, as damage to the eyes or respiratory system is possible.
Treatment of minor burns is carried out at home according to the recommendations of a doctor.
For thermal burns of the facial skin after cooling the skin, it is recommended to treat the wound with cooling creams and disinfectant ointments. If there are no blisters, you can lubricate the affected area with rubbing alcohol. Treatment of minor burns is carried out in an open or semi-open manner (short-term application of compresses with medications).
What to do if you have an eye burn?
Eye burns can occur for various reasons: exposure to high temperatures (steam, boiling water, fire, etc.), ultraviolet radiation, infrared radiation, exposure to chemicals on the mucous membrane of the eye.
In case of an eye burn, it is necessary to quickly provide first aid to the victim, after which you must wait for an ambulance or go to the hospital yourself.
The first thing to do if you have an eye burn is to rinse with plenty of running water. The use of any neutralizing solutions is not recommended, as unpredictable reactions are possible. To treat burns, a specialist prescribes painkillers and antibacterial ointments, drops, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures.
What to do if your tongue is burned?
Tongue burns are common in everyday life. Usually there is a mild degree of damage, with redness and slight swelling, which occurs due to too hot food and drink. Chemical burns of the tongue mucosa are less common. It is extremely rare that burns occur due to radiation or electricity.
What to do if your tongue is burned is a question that interests many. So, in case of a burn, you should rinse your mouth generously and for a long time with cold water, after which you can treat the affected area with a weak solution of furatsilin. If blisters appear on your tongue, it is recommended to seek medical help (surgery may be required).
For chemical burns, after copious rinsing, painkillers and treatment of damaged mucous membranes with anti-inflammatory agents (sodium tetraborate) are recommended. After a few days, you can use traditional medicine (honey, fish oil, rosehip oil, sea buckthorn). For speedy healing, you should not eat foods that irritate the mucous membrane (citrus fruits, salty, sour, spicy foods).
What to do if your lip is burned?
Lips are the most delicate part of the face. Burns can be thermal (boiling water, hot objects, etc.) or chemical. What to do if your lips are burned practically does not depend on the type of injury; in the first minutes after the injury, you must thoroughly rinse the affected area with running water (the exception is burns with quicklime, which absolutely cannot be washed off with water).
Chemical burns should be treated with neutralizing solutions, then treated with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing agents (panthenol, rescuer, solcoseryl).
If blisters or ulcerations appear, an antiseptic must be applied before eating. You should also avoid spicy, salty, and sour foods during treatment.
What to do if your throat is burned?
What to do if you have a throat burn depends on what caused the burn. After gargling with cool water, in case of a chemical burn, you need to neutralize the effect of the substance that caused the burn (soda or diluted acetic or citric acid). In case of thermal damage to the mucous membrane of the throat, after rinsing with cool water, you can give a drink (or inject) an anesthetic (Novocaine). After providing first aid, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
What to do if your palate is burned?
The first thing to do when the palate is burned is to try to alleviate the condition of the victim. Regular cool water is a good pain reliever; you need to rinse your mouth until the condition improves (the burning sensation and pain stop). After this, it is recommended to use anti-inflammatory drugs (sodium tetraborate). Honey, which is a natural anti-inflammatory, healing agent with an antibacterial effect, also has a good healing effect.
What to do if your gums are burned?
A gum burn can occur not only due to high temperatures (hot food, etc.), but also when chemicals come into contact with the gums (for example, during dental treatment).
It is quite difficult to determine what to do in case of a gum burn on your own, since only a doctor can assess the extent of the injury. In case of a burn, it is necessary to provide first aid to the victim: reduce the effect of the burning substance (remove the remaining chemicals from the oral cavity), give an anesthetic (for severe pain), rinse the mouth.
Further actions depend on the extent of the injury. Minor injuries are treated by rinsing with solutions with an antiseptic effect (furatsilin) and healing agents (sea buckthorn oil). In addition, rinsing the mouth with herbs (chamomile, St. John's wort) can be prescribed to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. Treatment of more severe burns is carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
What to do if you have a scalp burn?
What to do in case of a head burn also depends on the extent of the damage, the cause of the injury, etc. A scalp burn can occur from prolonged exposure to the open sun without a hat, or from exposure to chemicals (hair dyeing at home, applying masks to the scalp, etc.). A scalp burn can also be caused by radiation therapy or a hot object.
In case of a chemical burn, it is necessary to rinse the hair well and remove any remaining substance; in case of sunburn (after cooling with cool water), it is recommended to use sunburn creams; in case of thermal injury, the victim must be taken to the hospital as quickly as possible.
Self-treatment of scalp burns is not recommended, as this can provoke negative consequences (baldness, infection, etc.)
What to do if you have a blister from a burn?
The formation of blisters on the surface of the skin indicates deep tissue damage; in this case, burns are classified as second degree of severity, i.e. posing a threat to life. Bubbles can form immediately after a burn or after some time. Typically, blisters appear on the skin after burns from boiling water or after excessive tanning. Such burns are very painful; in addition, the general condition after the injury can significantly worsen.
Piercing or in any way damaging the resulting blisters is something that is strictly prohibited to do in case of a second-degree burn. Only a specialist can decide to open the bladder in case of suppuration (infection and inflammation). An autopsy is performed only in a hospital.
Treatment of burns with the formation of blisters is carried out independently only when the affected area is no larger than the palm (treatment with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing agents); in other cases, hospitalization and treatment in a hospital are required.
What to do if a child has a burn?
Burns in a child require urgent care. The effectiveness of burn treatment in this case depends on timely first aid.
What to do if a child is burned depends on the severity of the injury. If the burn is not large, you should immediately rinse it with cold water, apply a cool compress, treat the wound with a special product (panthenol, furatsilin ointment, Boro-plus, Rescuer), and if necessary, apply a bandage. If it is difficult to treat the wound, you can soak gauze with anti-burn agent and apply it to the affected area (change 2-3 times a day).
You should urgently call an ambulance if the affected area turns purple, becomes blistered, or clothing sticks to the burned area. For minor burns, when treatment can be carried out independently, it is recommended to use natural-based preparations (with aloe, honey, sea buckthorn oil).
What should you do in case of a burn?
The first thing to do in case of a burn is not to panic. If the burned area occupies no more than 10%, then the burn poses virtually no threat to life. It is recommended to immediately rinse the burn under water. In case of a thermal burn, this will help cool the surface and prevent damage to the deeper layers of the skin. In case of a chemical burn, running water will help remove any remaining substance so as not to damage deep tissues.
If the burn is minor, but with the formation of blisters, you need to ensure that inflammation does not start. An infection in the affected area may be indicated by a cloudy yellowish liquid in the blister or redness around it. In this case, you need to urgently seek medical help.
Severe, numerous and extensive burns, as well as burns of mucous membranes, require urgent medical attention. Before the ambulance arrives, you can wash the affected area with cool water and cover with a dry, clean bandage.
How to bandage a burn?
Dressings for burns are necessary to prevent dust, infection, etc. from entering the wound and not causing severe inflammation (suppuration).
The bandage on the burned surface should not be tight, so as not to further injure the inflamed areas and not impair blood circulation (otherwise, tissue death is possible). Also, the bandage should be well fixed on the wound.
If necessary, the gauze bandage can be impregnated with medicine (furatsilin solution, novocaine).
What to do in case of a burn and how to bandage the wound are the first questions that arise with this type of injury.
First of all, it is worth noting that dressing should only be done with clean hands, a sterile napkin should be applied to the wound, then carefully secure it to the damaged area with a bandage (not too tightly).
What should you not do for burns?
What not to do in case of burns is an important question. As a result of incorrect actions in case of such injuries, the process of healing and tissue restoration may increase, in addition, serious consequences are possible (inflammation, suppuration, etc.).
So, immediately after a burn, you cannot treat the affected area with fat (vegetable oil), brilliant green, iodine, or alcohol (for deep tissue damage). Such actions can aggravate the situation and prevent specialists from determining the extent of the burn, which will lead to initially incorrect treatment. You should also not use ice to cool the damaged area, as this can cause frostbite to the tissue.
If blisters appear, you should not open them yourself (puncture, comb, etc.), as this can lead to infection and severe inflammation.
What to do after a burn?
When a burn occurs, not only the burned area of the body suffers, but the entire body as a whole. With burns that occupy more than 15% of the body surface, a significant deterioration in the general condition (burn disease) is possible, so it is better to spend some time under the supervision of specialists.
What to do in case of a burn and after it depends on the severity of the injury. For a minor burn, it is recommended to regularly treat the wound with special products; if necessary, change the bandage 1-2 times a day and follow a gentle regimen.
Severe and extensive burns require hospitalization.
It is important for everyone to know what to do in case of a burn and how to provide first aid, since these injuries often occur not only at work, but also at home. Domestic burns occupy a leading position among all types of injuries, especially among young children. In such a situation, the main thing is not to get confused and provide first aid in a timely manner, which will help not only alleviate the victim’s condition (reduce pain), but also make the recovery process easier and faster.
It is important to know!
Peeling is a procedure that helps exfoliate dead skin cells, thereby improving its condition and rejuvenating it. To carry it out, weak acidic solutions are used (usually glycolic or trichloroacetic).
Burns are considered the most dangerous injuries to the skin, because not a single skin is affected, and the whole body feels bad at this moment. Burns have a particularly negative effect on the functioning of the kidneys and heart, disruptions in metabolic processes occur, an increase in body temperature, manifestations of vomiting, etc. are observed. How to behave in case of a burn, how to provide first aid to the victim? Indeed, often the further condition and full functioning of the human body, and often his life, depend on timely and correctly provided first aid.
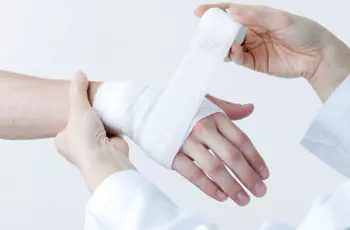
First aid for burns.
A burn should be understood as traumatic tissue damage caused by exposure to thermal and chemical factors. High-temperature burns usually occur during a fire, or at home when coming into contact with hot objects and boiling liquids (oil, water, etc.). A chemical burn can occur when alkali, acids, or salts of heavy metals come into contact with the skin. It is burns that take second place among the causes of death, and often a person dies due to the lack of first aid or basic ignorance of the basics of its provision by those who are nearby at the time the victim receives a burn. That is why absolutely every person should have basic knowledge and skills in providing first aid for burns, and be able to classify them according to the degree of skin damage.
If you receive a burn, you must call an ambulance and take some actions yourself to alleviate the victim’s condition:
- Eliminate the damaging factor, remove remnants of hot clothing.
- Cool the burned areas of the skin (cold or even ice water) for ten to twenty minutes (prolonged cooling is fraught with vasospasm, impaired blood circulation), this will reduce the depth of tissue damage and reduce pain. Cooling of damaged tissues can only be done in the first two hours after a burn.
- Anesthetize, then apply a sterile bandage or, in case of large areas of skin damage, wrap the victim in a clean sheet.
- For first-degree burns, you can use special burn remedies. If a child is burned, the treatment of his skin will require special attention. Antiseptic treatment is the main aspect in the treatment of a child's burn. Parents are wondering what to use to treat a raw, blistered wound to achieve a disinfecting and restorative effect while relieving pain. You can forget about brilliant green and iodine, since these products have too aggressive an effect on the delicate children's skin. Therefore, today pediatricians prescribe antiseptic drugs that contain silver salts. One of these is Sulfargin, the drug accelerates the healing process, protects against bacteria and is suitable for children's sensitive skin.
In case of burns, it is strictly prohibited:
- lubricate the damaged surface with vegetable oil and starch;
- use alcohol-containing preparations, iodine, etc.;
- cut the skin or artificially open “blisters”;
- clean the wound yourself from remnants of clothing, etc.;
- apply ointment for burns;
- use urine as a healing healing agent.
Classification of burns, first aid for thermal burns.
There are four degrees of burns:
First degree burns.
This category includes burns resulting from contact with hot (up to 50-70 degrees) objects and liquids (water, oil, steam, iron). Since the affected area affects only the superficial layers of the skin, first-degree burns are the least dangerous. With this degree of tissue damage, redness, swelling, severe burning and pain symptoms are observed. In this situation, it is necessary to cool the burn area and treat it with Panthenol. For this degree of burns, folk remedies can be used in treatment. Usually, after a few days, all this goes away, the skin begins to peel off, and after healing, pigmented areas remain. If the damaged surface of the skin due to a burn is more than 25%, a serious injury has occurred, therefore, before the doctor arrives, first aid must be provided, following the steps described above.
Second degree burns.
Such a burn is diagnosed when the skin comes into contact with a temperature of 70-100 degrees. This also includes any kind of burns of the respiratory tract. In addition to extensive redness of the skin, blisters or blisters filled with serous fluid appear immediately or several hours later. After the blister breaks (independently, not mechanically), redness of the skin persists. Recovery usually occurs within about two weeks, but this is only if infection does not occur.
In case of damage of this degree, you should not lubricate the burn area with ointments or oils, as well as resort to traditional medicine recipes. Despite the pronounced effect of reducing the manifestation of pain, these drugs provide an excellent breeding ground for the development of bacteria and infections, which in the future seriously complicates the situation, interfering with the recovery processes. If the victim receives burns, they should call an ambulance, and while help is coming, apply a dry and always sterile dry bandage. The healing process can take up to fourteen days. Any damage to the respiratory tract due to a burn is classified as a second degree burn.
Burns of III and IV degrees.
Third- and fourth-degree burns result in severe destruction of skin and muscle tissue; with large areas of damage, fatalities are often observed. Victims of this degree experience so-called burn shock, when at first they experience excruciating and unbearable pain, and then completely lose the ability to realize or feel anything. At the same time, blood pressure decreases and the pulse weakens. This happens with oil, steam, or boiling water burns of the second degree with 30% of the body surface affected, or with third-degree burns of 10% of the body surface. Scabs and deep ulcers remain on the damaged areas, and after final healing, scars remain. There are cases of disability.
In the fourth degree, charring of the skin is observed, skin, fiber, bones, and muscles are destroyed. Victims may not experience pain (which often happens) because the nerve endings are damaged. As a result, doctors are often forced to amputate limbs. If extensive burns are observed, the victim should be hospitalized immediately. Under no circumstances should you try to remove stuck clothing from your skin on your own.
If the victim is unable to move independently and has to be carried, it is necessary to ensure protection of the damaged areas of the body on any surfaces. In this situation, an ambulance is immediately called, the victim is given pain medication and provided with plenty of fluids.
What to do if you are burned by boiling water?
- Remove clothing that has been exposed to boiling water.
- Determine the degree of skin damage (human palm – 1%). If damage exceeds 10% (ten palms), you should consult a doctor.
- Treat the injured surface with Panthenol.
- If the burn is on the arm, it must be kept elevated to reduce swelling.
- For first or second degree burns, apply a sterile cloth soaked in cold water to the damaged areas. Change every few minutes (no more than twenty minutes and only while maintaining the integrity of the skin).
- If blisters appear, do not try to pop them.
What to do if you are burned by steam.
- Cooling the damaged surface after first removing clothing.
- If more than 10% of the body is damaged, consult a doctor.
- Do not apply oil to the burn site, open the blisters or touch them.
What to do if you get an oil burn?
- Soak the area where the oil has come into contact with cold water until completely cooled.
- If the area of the burn with oil is more than 1% or the oil gets into the eyes, you must urgently call an ambulance, and until then apply a sterile wet bandage. You can pre-use analgesics (for the eyelids): solution of novocaine (4% - 5%), lidocaine, albucid (10% - 30%), chloramphenicol (0.2%).
What to do if you are burned by an iron.
- Apply oil or glycerin to the affected area.
- Add finely grated beets, or cabbage, change every ten minutes.
- Cool the injured area of skin with water and sprinkle with baking soda.
- You can lubricate the burn with a raw chicken egg.
If the burn results in blisters, it is better to abandon the methods described above and consult a doctor.
Treatment of chemical burns.
Chemical burns are treated taking into account the damaging substances. Of course, first aid is to call an ambulance. Then the victim’s clothing is removed or torn at the site of injury, and the substance is removed from the skin. To do this, wash the surface with a strong stream of cold water for twenty to thirty minutes. If the burns were caused by quicklime, you cannot cool the surface of the body, since when it comes into contact with water, lime has the opposite effect, burning even more. If the damaging substance is sulfuric acid, it is first removed with a dry cloth (after putting on protective gloves), and only then the area is washed with cold water. After this, apply a dry bandage to the damaged surface.
In such cases, medications should only be prescribed by doctors, since the reaction of damaging substances with medicinal compounds can be very unpredictable. If the substance that caused the burn is known, for example, acid, then the wound can be pre-treated with a two percent solution of baking soda; if it is a caustic alkali, then the wound should be treated with water with the addition of boric acid or a few drops of citric acid. After this, be sure to apply a dry and clean bandage.
Any healing agents should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Typically, such burns take a very long time to heal, and therapy can be internal or external. To alleviate the condition of the victim, accelerate healing processes, cool and moisturize the skin at the site of injury, aloe vera is used (applied). Vitamin E is also used on diseased areas for healing and scar resorption. For internal treatment, vitamins E in capsules, C, A, B are used.
Folk remedies for burns.
As previously noted, traditional medicine is relevant only in cases of first-degree burns, that is, with minor damage to the skin.
You can apply compresses from raw potatoes, pumpkin or carrots. Any of the vegetables is rubbed through a grater, applied to the affected area and secured with a sterile bandage. This dressing should be changed every ten to fifteen minutes.
Lotions made from a decoction of coltsfoot, rose hips, and oak bark are very effective in reducing pain and redness. Brew according to the instructions on the box, moisten the gauze and apply for fifteen minutes, then replace the bandage.
Dairy products are great for pain relief. Three times a day for half an hour you can make lotions with kefir or sour cream.
Honey, due to its high bactericidal properties, has long been used in folk medicine to treat minor burns, reduce pain and accelerate regeneration.
Be careful and vigilant when handling hot appliances, liquids and chemicals, and if burns occur, follow our advice.
Injury from boiling water, steam, hot water, or hot kitchen utensils is a common household injury, in a fifth of cases children suffer - an electric kettle boils on the table, the child pulls the cord and knocks it over. What to do if you are scalded, what first aid to provide? Timely actions will help avoid long-term treatment.
Types of burns
First degree. Redness of the skin, sometimes swelling, small blisters - this happens if you are exposed to the sun too much.
Second degree. When affected, large transparent blisters form.
Third degree. The skin becomes dead, the high temperature penetrates the muscle and nerve tissue, blisters with cloudy contents. Skin grafts are usually required.
Fourth degree. The skin is charred, the thermal effect reaches the bones.
You can treat first and second degree burns at home. In all other cases, it is necessary to contact a specialized burn center, trauma center or intensive care unit of a hospital as quickly as possible.
For first and second degree burns, it is necessary to assess the affected area. It can be easily identified by the palm, the area of which is approximately one percent of the area of the skin. If the lesion is the size of your palm or larger, be sure to see a doctor, especially when the skin peels off.
It is necessary to provide first aid and call an ambulance, even in the case of first or second degree damage. If after a day or two swelling appears, redness increases, and the temperature rises, in order to prevent infection, you should also consult a doctor.
If the area of thermal damage is 10-15% of the skin or more, a burn disease is diagnosed.
First aid
Remove wet, hot clothing as soon as possible, as boiling water continues to burn. It is especially important to act quickly in the case of synthetic fabrics. You can cut clothes before they stick to your skin.
Remove clothes carefully to avoid blisters. It is forbidden to pierce them - this can lead to infection in the wound.
Place the scalded area under cold water or in a container with cold water. The coolness will relieve pain and slow down the spread of the burn. To reduce swelling, hold the burned area up.
When providing first aid, you can also use sheets and towels moistened with cold water for cooling.
After 15-20 minutes, dry the burn site and cover with a loose sterile bandage.
First degree lesions can be wiped with cologne and vodka. You should not use iodine or brilliant green - if you have to see a doctor, it will be more difficult for him to determine the degree of thermal damage.
Do not apply oil or fat to the burned area - the film prevents heat transfer.
Pharmacy remedies for burns
In case of a 1st or 2nd degree burn with boiling water, first aid is provided with Panthenol, Olazol, and Solcoseryl ointment.
Panthenol is used to treat skin damage - thermal burns, including sunburn, as well as abrasions and cracks.
Olazol anesthetizes, inhibits the growth and reproduction of microorganisms, improves and accelerates healing.
Solcoseryl gel or ointment is used to help after scalding with boiling water, to treat thermal injuries, and also if you happen to get sunburned.
The most convenient remedies for burns are in aerosol packaging.
Anti-burn gel wipes cool, anesthetize and localize the lesion, destroy microbes, and are easy to remove when replacing.
When providing first aid, it is forbidden to cover the burned area with an adhesive plaster - it will be painful to peel it off later.
For pain relief, take Analgin.
If the skin peels off, treat the affected area with a non-alcoholic antiseptic solution and cover the wound with a sterile bandage or gel pad.
How to treat a burn
When scalding with boiling water, grated raw potatoes help:
- Place the paste, apply it to the affected area, and secure with a bandage.
Replace as soon as the mixture warms up.
For a thermal burn, first aid is provided by a leaf of fresh cabbage:
- Attach the sheet to the affected area.
After a few minutes, the pain disappears or is significantly reduced, and after another half hour it completely disappears. Cabbage leaf is also effective for bruises and sprains.
Heat damage is treated with potato starch:
- Sprinkle the scalded area with a thick layer, cover with cotton wool, and bandage loosely.
Aloe vera helps cure burns:
- Cut the skin off the leaf and place it on the affected area for 12 hours.
- Grind the leaf into a paste, apply to the affected area, secure with a sterile bandage.
How to remove a burn with folk remedies
In order for a thermal wound to heal as quickly as possible and not leave a mark on the skin, timely correct treatment is required.
Getting rid of burns with propolis and St. John's wort:
- Cool 20g of propolis in the freezer, grate and pour a glass of medical alcohol. Leave for 10 days, stir every day, and strain when finished.
- Pour 500 ml of unrefined sunflower oil into 4 tbsp. St. John's wort flowers, leave in the sun for 14 days, stir once a day, mix with the prepared propolis tincture.
Apply the product to gauze, secure it to the wound with a bandage, change the bandage every 4 hours.
Treatment for scalding with onions:
- Finely chop the onion, mix with 20 blossoming dandelion flowers, pour in a glass of unrefined sunflower oil, simmer over low heat for twenty minutes, strain.
Lubricate the thermal wound as often as possible. Store burn ointment in a cool, dark place.
- Dissolve potassium permanganate in water to achieve a pale pink color.
Apply a gauze bandage to the burned area and periodically moisten it with the prepared solution. Replace the gauze once a day.



