The formation of moles on the eye is rare, but it is possible. They are formed due to accumulations of melanin and are created on any anatomical areas, including in the eye. The formation is of exactly the same nature as on the shoulder or arm. However, this area causes reasonable concern and concern, so it needs to be monitored and observed by a doctor.
Causes
A mole can appear in infants, adults and the elderly. In this case, the ocular nevus can be localized on the iris, on the white or on the cornea. In some cases, the mole is not visible and can only be detected using an ophthalmological microscope.
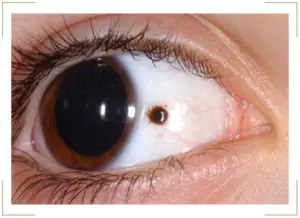
As a rule, a birthmark is visible from the side. It has a darker pigment composition. Therefore, the nevus is very noticeable in people with light eyes. To understand why it is dangerous, you need to understand the reasons for the formation:
Congenital feature
Then the pupil and white will have a nevus from the first days of the child’s life. In newborns, this spot is often small in size. But over time, the eye changes color and it grows. Moreover, its increase is very intense.
| Congenital nevus does not pose a threat to vision. It does not interfere with visual function and does not affect the functioning of capillaries. |
Acquired nevus
In this case, the mole appears throughout life. And this can happen at any moment. After all, the conjunctiva and the eye are exposed to different influences throughout life. Moreover, such effects can be directed not only directly to the conjunctival region. This is caused by severe stress, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and so on. In any of the above cases, there is a possibility of a birthmark appearing on the eye.
Types of moles in the eye
Typical nevus
Located on the iris of the eye. This area is also called the conjunctiva. Such moles are small spots with a diameter of several centimeters. As a rule, they have a clear shape and edges. The color of the nevus is often brown. 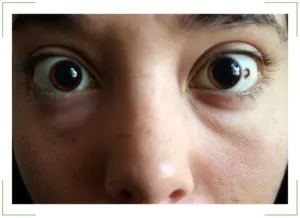
Atypical nevus
It may be colorless and located on the inner surface of the iris, where it is not visible. Accordingly, it is invisible from the outside. The initial nevus is also small in size. At the same time, they may not change during a person’s life. But when the mole enlarges, the subsequent stage is expressed by a more extensive nevus. It begins to take up a lot of space and switches to protein.
Conjunctival nevus
Covers the previous two types. Since this is the iris of the eye, the moles that are located on it are conjunctival nevi. This type of spots is further divided into cystic and vascular.
Thus, cyst-shaped ones do not have a pronounced color and are honeycomb-like formations. Meanwhile, capillary ones are created from small blood vessels. That's why they have a pale pink or red color.
Choroidal nevus
It is located inside the eye and is invisible to others. Actually, the choroid is a collection of vessels located on the inner surface of the eyeball. Therefore, a nevus can only be noticed during an examination. Such formations may have a constant shape and size, but there are times when they change.
Stationary and progressive nevus
| The appearance of a mole in the eye does not mean a risk of developing cancer. This sign can be completely safe. Moreover, the nevus does not affect visual acuity or eye function in any way. |
Nevus is not considered a disease. This is an education that every person has. It’s just that moles are usually located in other anatomical areas. For example, on the back, arms, and so on.
In this case, the nevus can grow over time. Such formations are called progressive. They change size and shape, gradually increasing. Often, growth occurs at a very rapid pace. So, in one year a mole doubles in size.
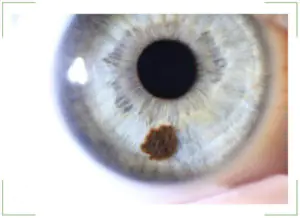
If any other spot begins to grow, this indicates a potential cancer threat. But this principle does not work regarding nevus in the eye. It is important to clarify the situation. An increase in the size of the spot does not mean that the mole is turning into a malignant formation. The risk of developing cancer remains throughout the entire period of existence of the nevus in the eye. Therefore, when a mole appears, it is necessary to consult a doctor, undergo an examination and monitor the dynamics of its condition.
What is the danger of pigmented nevi in the eye?
As stated above, education does not pose serious consequences for vision. They do not obstruct vision, do not narrow the field of vision, or impair its sharpness. At the same time, birthmarks do not cause any discomfort to a person.
The only threat is the likely development of the nevus into a malignant cancer. Therefore, many consider it necessary to treat and remove moles in the eye.
Symptoms of nevi
The main sign is that the stain is noticeable to others and to the person himself. The nevus can be located around the entire perimeter of the eye, this does not play any role.
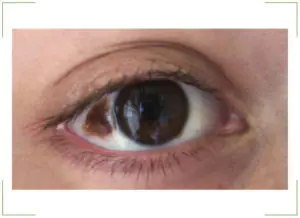
The only symptom of a birthmark is a change in corneal pigmentation or protein. The appearance of small spots and clusters in the form of bubbles indicates the initial stage of the nevus. If such formation causes concern, you should contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination. It is impossible to be sure in any other way what type of nevus it is.
Diagnosis of formations
Detection of a birthmark is carried out using special equipment. After all, it is necessary not only to study the cornea or pupil. The doctor must look inside the eyeball, examine the fundus, and so on. Therefore, various techniques are used:
Ultrasound diagnostics
It is a well-known ultrasound examination. Only the patient's eye is the object. Using this technique, it is possible to identify accumulations of melanin in certain parts of the eye. This test is very accurate and provides a complete picture of what is happening inside the visual organs. There will be no hidden areas, which is very important for further treatment of nevus;
Angiography
This is a type of x-ray examination. It is necessary for studying and assessing the condition of blood vessels. As stated above, a nevus can form directly on a collection of blood vessels in the eye.
During the examination, it is recommended to use both methods. They complement each other perfectly and give an accurate picture of the development of the birthmark. A lot of information can be obtained by studying the nevus over several years.
Treatment methods
This phenomenon is not a disease. This is a condition of the eye in which there is an accumulation of pigmented formations. They form a nevus. It cannot be affected by medications or physiotherapeutic methods. The mole will not disappear from this.
Only birthmark removal is used. It can be removed using laser technologies, with local anesthesia, without placing the patient in a hospital.
| Such technology is safe and does not involve the risk of worsening the patient’s condition. |
Forecast
In the vast majority of cases, even if a mole grows, it remains safe and does not affect health. However, it can always be removed using a laser, thus eliminating the risks.
Can a nevus turn into cancer?
Theoretically, any mole can turn into cancer. And nevus is no exception. However, it is not a disease in itself. But in order to eliminate the risk, the formation should be removed.
Prevention of cancerous transformation of eye nevi
It is impossible to predict the growth of a nevus into a cancerous tumor. There is such a risk, although it is extremely insignificant. It is impossible to exclude such a case with the help of medicines, drops or traditional medicine potions. Therefore, the only option is to remove the nevus immediately after detection.
Most Caucasians have moles (nevi). Pigment spots form on the body, face and even the eyeball. Nevi differ in shape, color, size, and location. A mole in the eye occurs in people belonging to different age groups. Nevus tumor is found in adults, elderly patients, adolescents and young children. Eye moles are benign.
Causes
Moles in the eye are formed under the influence of melanocytes - cells containing pigment. Melanin, accumulating in tissues, gives them a certain color. The color of skin, hair, iris, and birthmarks depends on this substance.
The following factors lead to the formation of nevi in the eye:
Light-skinned people are at risk. Their epithelial tissues contain a small amount of melanin. The likelihood of mole formation decreases with a sufficient concentration of pigment in the skin cells.
Types of moles in the eye
There are 2 types of birthmarks in the eye:
- Vascular moles. Red nevus spots and hemangiomas appear when blood or lymphatic vessels are damaged.
- Non-vascular (pigmented) moles. Neoplasms develop from melanocytes. The spots are colored brown and black. There are no blood vessels passing through them.
Among pigmented nevi there are:
By nature, ocular nevi are:
- benign;
- malignant.
Based on location, there are 2 types of moles in the eye:
- Nevus of the conjunctiva. The spot forms on the mucous layer of the eyeball. Such moles are easy to notice. The unusual pigmentation on the protein itself catches the eye of people around it.
- Choroidal nevus. The doctor identifies the spots by examining the patient using specialized equipment. Moles appear in the deep layers of the eyeball.
The ICD 10 code for an ocular mole is assigned depending on the type of neoplasm: D31-36.
Conjunctival nevus
Vascular moles that appear on the conjunctiva cover the entire thickness of the mucous layer in the eye. New growths of pink and red shades are formed from capillaries.
Pigmented nevus of the conjunctiva occurs when there is an excessive concentration of melanin on the mucous membrane of the eye. The spots are colored brown and black.
Cyst-shaped nevi that appear on the conjunctiva are formed from lymphatic vessels. They are cystic formations, the internal cavity of which is filled with colorless exudate. The outgrowths from the inside look like a honeycomb.
In stationary conjunctival nevi, the shape and size are unchanged. They are benign and do not threaten health or life. Such growths are not treated or removed. The doctor simply observes the dynamics of the tumors. For preventive purposes, the doctor examines such patients once a year.
Progressive birthmarks constantly change:
- increase in size;
- transform, take on different shapes;
- compress the vessels.
If the need arises, the doctor insists on removing the transforming birthmark. The mole is removed using microsurgery methods or laser.
Treatment of progressive nevus is carried out in the following cases:
- if dystrophic changes appear in the retina or epithelial tissues with pigmentation;
- tissue detachment occurs.
Choroidal nevi
Birthmarks can form on the vascular membranes of the eyes. Such outgrowths are formed from vascular cells.
Birthmarks on the choroid appear during periods of hormonal changes. Outgrowths appear singly and do not form groups. Usually a mole forms in one eye. Bilateral lesions are quite rare.
Choroidal birthmarks, like iris nevi, are divided into stationary and progressive. Stationary growths are benign.
Progressive spots transform: they take on different shapes and grow. Large tumors limit vision, impair vision, and compress blood vessels. In this case, patients focus on the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
Locations
Birthmarks form in different areas of the eye:
- external and internal areas of the protein;
- tearful month;
- semilunar fold;
- iris or retina;
- limbo.
Location of conjunctival nevi
An ocular nevus forms on the inner and outer parts of the conjunctiva. Birthmarks are detected on the inner corner of the eye, the periphery of the cornea, the lacrimal month, and the semilunar fold. Sometimes neoplasms appear on the inside of the eyelid. Although moles are located near the pupil, they do not block the view or impair vision.
Localization of choroidal nevi
- on the back of the eyeball;
- on the fundus;
- at the ocular equator.
The spots are invisible to others; they are discovered by a doctor who performs diagnostics using specialized equipment. But an ophthalmologist is not always able to identify a nevus of the choroid of the eye. Diagnosis is difficult if the tumor lacks pigment.
Color and size
Eye birthmarks vary in size and color.
Conjunctival moles
The color of conjunctival nevi is influenced by the cells from which the tumor is formed. The color of the spots varies from pink to black. Some moles do not develop pigmentation. With a sharp hormonal surge, the color of the nevi changes. In some people, tumors become discolored as they age.
The shape of such pigment spots is flat, with clear outlines and a velvety surface. The size of the iris in diameter reaches 4 mm.
Choroidal moles
The outgrowths that arise on the choroid have a flat shape with pronounced outlines. They are clearly visible when examining the patient. The spots are painted in dark colors. If moles do not contain pigment, they cannot be seen. The size of the growths in diameter reaches 6 mm.
What is the danger
Eye moles do not manifest themselves for many years and do not cause a person any discomfort. However, when certain factors come together, they begin to undergo transformation. Progressive nevus is the most dangerous type of eye mole. Changing pigment spots cause:
- deterioration and loss of vision;
- degenerate into a cancerous tumor - melanoma.
After discovering a birthmark, you should regularly visit an ophthalmologist. This will prevent the development of melanoma. In case of negative dynamics, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen or decide to remove the nevus.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following complications occur:
- a mole makes it difficult to see;
- the quality of vision decreases;
- a foreign body is felt in the eye;
- the size and color of the spot changes.
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. A nevus in the eye transforms into cancer in 1 patient out of 500. Close attention must be paid to the spots:
- the thickening of which has reached 2 mm;
- with subretinal exudate;
- with orange pigmentation;
- located on the posterior disc of the eyeball.
Removal
Before removing a nevus in the eye, the doctor determines the nature of the neoplasm. Interfering birthmarks can be removed in several ways. The ophthalmologist chooses the method of excision of a dangerous tumor. Patients are given:
- electroexcision followed by plastic surgery of affected tissues;
- microsurgical operation;
- laser excision.
With progressive choroidal nevus, the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account. Treatment tactics are influenced by:
- localization of the birthmark;
- tumor growth rate;
- age and condition of the patient;
- accompanying pathologies.
Progressive growths are removed using traditional microsurgery techniques or laser coagulation. Hard-to-reach moles are removed with laser. Removing problematic moles allows you to avoid the development of a cancerous tumor, the transformation of a nevus into melanoma.
In a child, a nevus is treated as a last resort when the eye mole grows rapidly.
Progressive medical technologies prevent the degeneration of eye nevi into cancerous tumors. Thanks to them, it is possible to preserve vision and health. The main thing is to seek medical help in a timely manner and undergo regular preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist.
There are moles on every person's body. But sometimes they appear in completely unexpected places, for example, in the eye area - on the eyelids, conjunctiva and even on the eyeball.
What does a brown birthmark mean in ophthalmology?
Brown birthmarks on the body are areas of accumulation of melanin, produced by a concentration of special cells called melanocytes. But the usual moles (nevi) may well appear on the mucous membranes, although such localization is not too typical.
Moles in the eyes, as ophthalmologists say, are more often observed in patients with fair skin. They are often congenital, but can also appear in adults. If a nevus is located on the surface of the right or left eyelid, under them or on the front of the eyeball, it is clearly visible to the person himself, but most often such areas of darkening are localized on the back surface of the eye, and therefore can only be detected by chance - during an examination or if there is certain complaints associated with their growth.
Today, doctors do not know the exact reasons for the formation of a mole in the eye area. However, doctors suggest that such pigment formation may occur due to:
Also, melanin migration can be a consequence of X-ray radiation, inflammatory processes and injuries.
The appearance of a brown spot on the eyelid or on the eye itself means that you need to consult an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. Most often, moles of this localization are not dangerous, but they require some medical supervision.
Localization
Nevi on the eye can occur in a wide variety of areas in this area. Doctors detect them on:
- Choroid (choroid).
- Retina.
- Conjunctiva.
- Iris.
- Centuries, etc.
The most common types of nevi in ophthalmology are formations on the eyelids and choroid.
Choroidal nevus
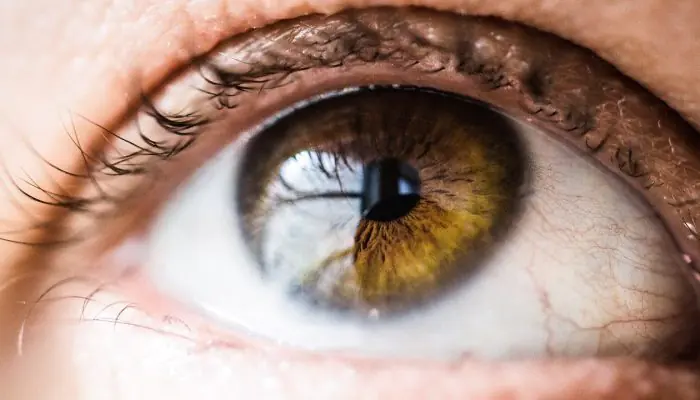

Such neoplasms are usually localized outside the equator of the eyeball, in the posterior part of the fundus. But sometimes they are found directly in the equator region or in the preequatorial region. At an early stage of its occurrence, such a nevus is located in the superficial layer of the choroid, and subsequently can spread deeper. A standard neoplasm of this type is different:
A typical choroidal nevus does not impair the quality of vision in any way. However, such a neoplasm can also be progressive in nature, which manifests itself:
- Tendency to grow and change shape. Such a spot has unclear boundaries and may have a non-uniform color.
- Development of dystrophic changes in the adjacent retina.
- Compression of choroidal vessels.
- Decreased quality of vision, the appearance of spots before the eyes and distortion of the picture.
Sometimes doctors also diagnose atypical choroidal nevi, which do not contain pigment or are surrounded by a zone of atrophy of the choroid, which has a paler color.
Progressive and atypical choroidal nevi are considered potentially dangerous in terms of malignancy. Only a doctor can identify the tendency of a formation to grow based on dynamic observation.
Melanosis of the conjunctiva
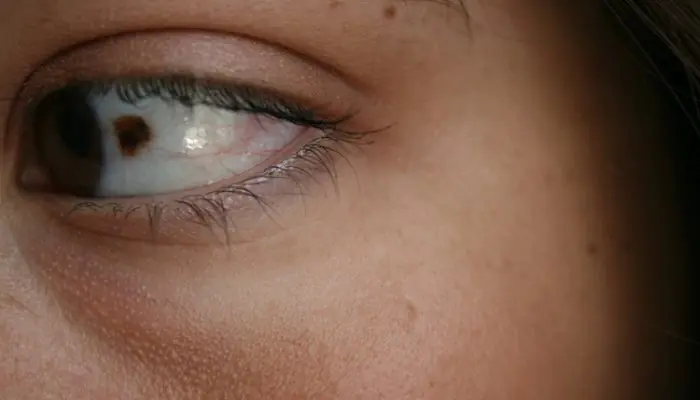

The term “conjunctival melanosis” is used to refer to a variegated diffuse nevus that does not have clear boundaries and is located directly on the conjunctiva in the limbus (the place where the cornea connects to the sclera). This neoplasm is quite rare, mainly in people with white skin color. Manifestations of melanosis may disappear or reappear.
If this condition is primary, patients are strongly advised to be constantly monitored by a doctor to eliminate the risk of cancer. Secondary neoplasms of this kind often occur in two eyes at once; they are not prone to proliferation and cannot transform into cancer.
Pigment marks on the retina
Typically, in the context of retinal nevi, neoplasms of the choroid, which is a structural part of the retina, are considered. But in fact, nevi can also appear in other areas of such tissue. Usually they can be detected only by chance - during a routine examination or if the patient has any complaints, including those related to the growth of a nevus. In general, such moles have all the same features as other similar formations in the eye.
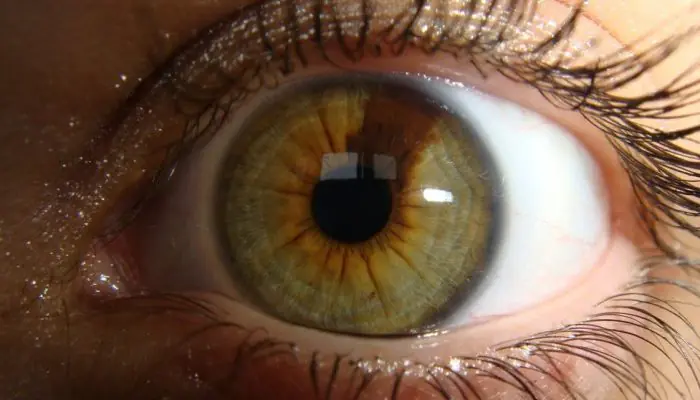
On the iris
The human iris is the anterior choroid, which contains several layers of pigment cells. The color of the eyes depends on their number and location. In principle, the iris can be compared to spongy tissue, inside of which there are many bridges and vessels. Different types of nevi may also appear in such an area:
Vascular and cystic nevi can cause a feeling of speck in the eye. And when they increase in size or darken, such neoplasms can impair the quality of vision.
Having discovered a mole on the retina, there is no need to panic. Such a neoplasm is most often benign in nature, but it must be shown to a doctor.
On the eyeball
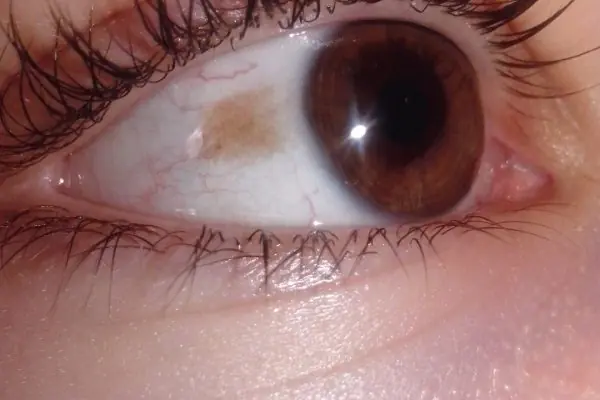
The eyeball is the spherical body of the eye, and the iris, cornea, retina, and pupil are its constituent components. But usually, when we talk about nevi on the eyeball, we mean accumulations of pigment on the most visible white part of the eye. This situation does occur, although it is quite rare. Spots on the eyeball that look like a mole can also be various types of tumors.
Does it happen on the pupil?
The pupil is the hole inside the iris of the eye through which light rays penetrate into the eye itself. Just from this definition it becomes clear that in principle nevi cannot form on the pupil itself. Areas of pigmentation can be observed on the iris, and this situation is quite normal. And visible changes in the pupil area are defects of the cornea or anterior chamber of the eye. Only a doctor can identify what exactly they are.
On the lower or upper eyelid near the eyelashes
Moles and birthmarks can appear in a variety of areas of the eye, including on the skin of the eyelids where eyelashes grow, directly under the eye, and even in the area of the lacrimal sac. The color of such neoplasms depends on the type of melanocytes and the intensity of pigment production. Moles can be light brown, reddish and even very dark, almost black. All of them require diagnosis by an ophthalmologist, but most often flat nevi that are not prone to growth do not need any targeted treatment.
Location of two nearby
Nevi can appear in the structures of the eye either individually or in groups. A pair of adjacent pigmented neoplasms requires especially close attention, since large nevi can lead to limited vision, causing a local “shadow” to appear in front of the eyes. But here, of course, it matters where they are localized. Definitely, if moles are small and do not tend to grow and merge, they do not have any effect on the quality of vision.
Paired nevi can appear on their own, for example, after severe stress or illness. There are cases when such neoplasms also disappeared without a trace.
Diagnostics
To identify moles on the eyes and monitor their development, the patient must be regularly observed by an ophthalmologist. Even if you are in perfect health, it is worth visiting such a specialist once a year, because preventive visits allow you to promptly identify and correct possible problems. To diagnose nevi, a doctor can use the following methods:
- Visual inspection.
- Ophthalmoscopy. With this type of examination, the doctor examines the fundus of the eye using directed light. Ophthalmoscopy allows you to see pigmented neoplasms, track the dynamics of their growth, possible changes in shape and color, and also detect germination into other layers.
The necessary diagnostic measures are determined by the doctor on an individual basis. Sometimes, to monitor a nevus, only periodic photographic recording of the fundus picture and regular ophthalmoscopy are required.
Treatment
The mere presence of a nevus in the eye is not an indication for targeted treatment. After the initial detection of a neoplasm, it is necessary to monitor its condition three times once a month, then preventive examinations are performed every six months.
Directed therapy is necessary for:
- Active growth of nevus.
- Darkening of the mole.
- The occurrence of discomfort and/or visual impairment.
Such signs become a clear indication for removal of a mole on the eye. It is worth considering that a nevus of this localization, in the absence of therapy and active growth, can lead to irreversible visual impairment and even degenerate into cancer - melanoma. Malignancy of a mole in the eye is a very rare complication, and its occurrence can be completely avoided with regular visits to the ophthalmologist. If cancer does develop, the patient usually has to have the affected eye removed.
How is removal carried out?
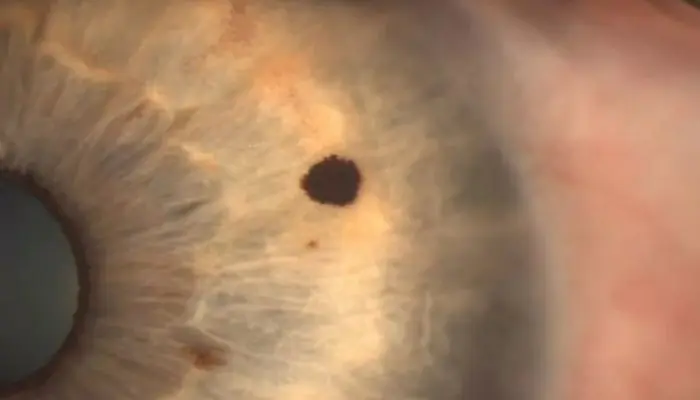
To get rid of a mole on the eye, doctors can offer several different surgical methods:
- Electroexcision. In such a situation, the tumor is removed using a small electric scalpel. This device makes it possible to make a precise and neat cut, then the existing defect is replaced with tissue. After electroexcision, no major hemorrhages are observed on the eye; such an intervention is also considered painless and allows recovery within a short time.
Methods for removing moles on the eyes are selected on an individual basis. Each intervention method has certain contraindications that must be taken into account when choosing therapy.
Can I take vitamins?
The use of various vitamin preparations cannot affect the development of nevus or contribute to its disappearance. However, doctors warn that using multivitamin preparations simply for preventive purposes may not be beneficial or even harmful to health. Some products of this type can lead to an overdose of certain vitamins, which, in turn, is fraught with health problems.
Therefore, even if you are in perfect health, it is better to consult a doctor before taking vitamin supplements.
Prevention
To avoid pigmentation in the eyes, doctors recommend:
- Protect your eyes from ultraviolet radiation, in particular, use high-quality sunglasses and wear hats with a visor.
- Avoid exposure to the sun at noon (11 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
- Do not self-medicate and in case of any disturbances in the functioning of the visual apparatus, seek medical help.
The most effective method of preventing any ophthalmological diseases is regular visits to an ophthalmologist.



