In ancient times, people believed that birthmarks on a baby were signs of fate and predicted his future. Now scientists are considering more natural reasons for the appearance of such formations. Let's consider what factors influence the appearance of spots, and in what cases do they require removal? Why might a birthmark appear in a newborn?
Types of birthmarks
A child may have a wide variety of birthmarks on his body - smooth or covered with fluff, reddish or brown, convex or flat. The main types of birthmarks in newborns are nevi and angiomas.
What shade can nevi be?
Nevi are among the most common types of skin marks. They usually come in a variety of brownish shades, ranging from dark brown to pale. The basis of nevi are melantocytes. These epidermal cells contain melanin, a pigment that affects skin tone. It is necessary to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. Sometimes these cells are localized in one place, which leads to the appearance of a mole. Dark birthmarks indicate an abundance of melanin, while light ones indicate a lack of it.
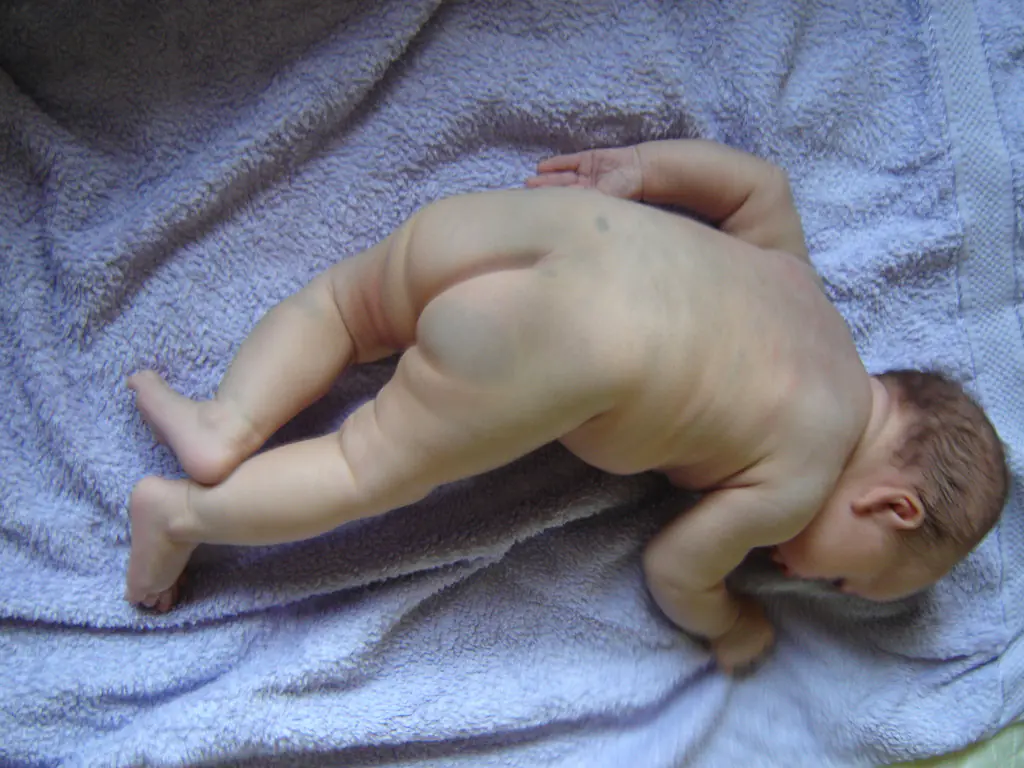
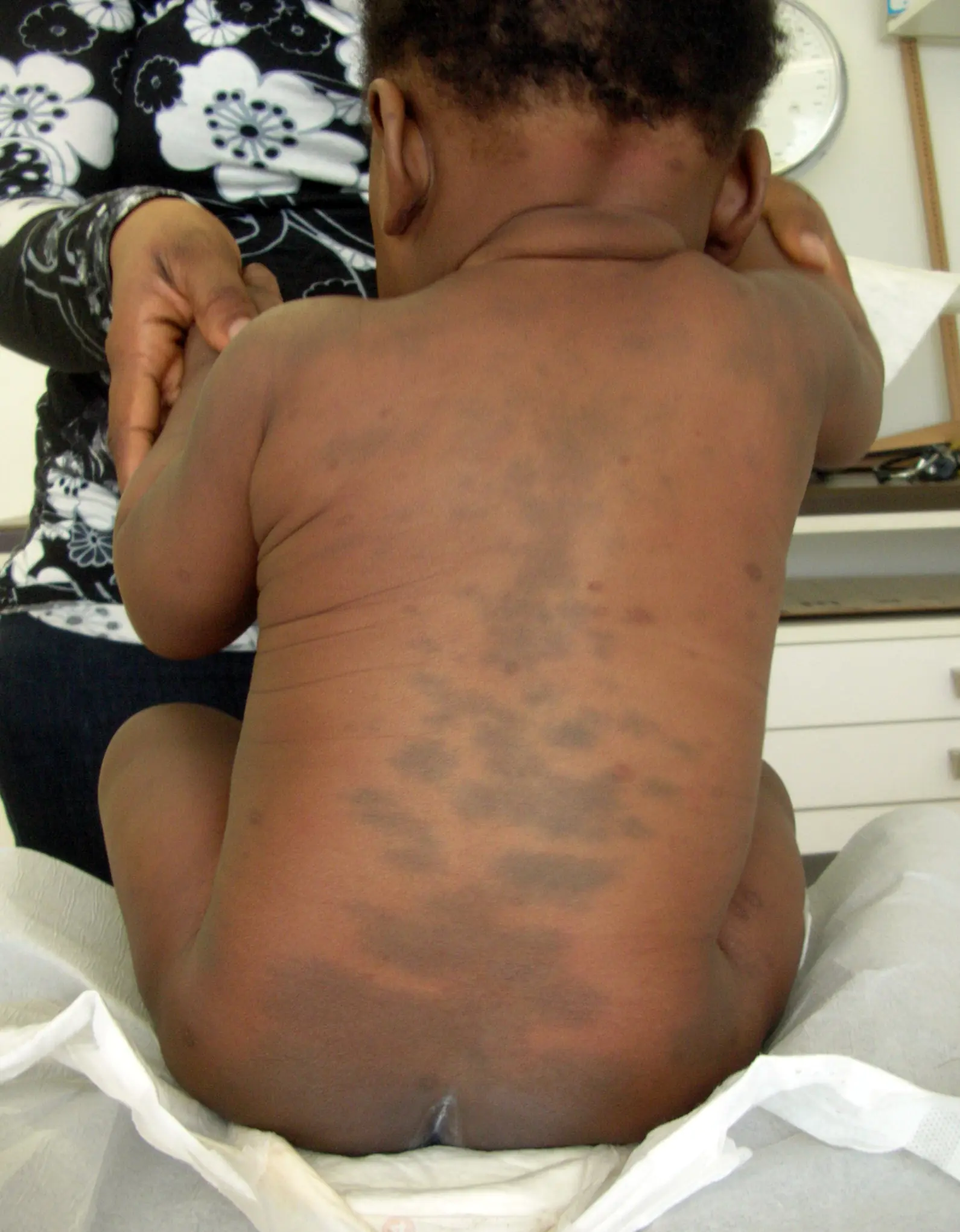
A Mongolian spot in a newborn should also not be a cause for concern for parents. It is also a place where melanin is concentrated and is a spot, or several spots of different sizes from 1 to 10 cm in diameter, blue, green or even black. The most common location is the baby’s lower back, mainly the tailbone or butt. Mongolian spots are safe, they do not cause any discomfort to the child and go away on their own before adolescence. This type of nevus is named so because of their frequent detection in Mongolian children (90%), Mongolian spots are also often found in Asians, representatives of the Mongoloid and Negroid races.
There are also white formations. These include anemic nevi that arise due to underdeveloped blood vessels.
They need to be distinguished from millet grasses - milia. The latter look like convex dots filled with whitish content. They are a type of skin rash. Anemic nevi are a congenital phenomenon, and they are easy to identify: you need to rub the spot. The surrounding skin will turn red, but the formation will remain white.
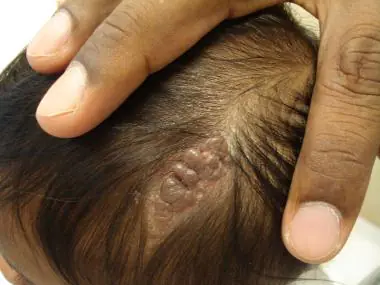
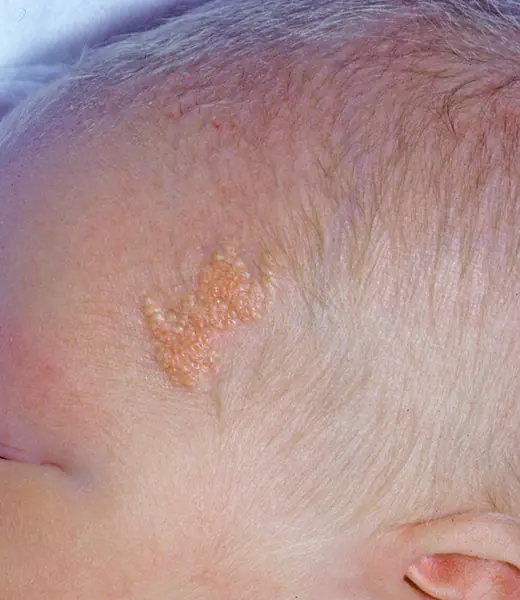
Light brown Jadassohn nevi indicate a congenital defect of the sebaceous glands. They are usually found on the baby's head, under the hairs. This occurs in 3 out of 1000 babies. It is recommended to remove it before adolescence, since in 10-15% of cases, they can subsequently develop into a cancerous tumor.
What if it’s a matter of blood vessels?
Another type of birthmarks is angiomas. They are of vascular nature. Congenital formations of small vessels on the skin are called hemangiomas. If such accumulations form in the lymphatic system, then they are classified as lymphangiomas. Even congenital, they appear externally only by the age of three.
In a newborn, only vascular hemangiomas can be detected. They are distinguished by a whole range of shades of red. Such formations are divided into several subtypes:
Strawberry (strawberry) hemangioma
These formations are convex, similar to red “berries”. They appear immediately after birth, usually on the face. The sizes can be different - from a millimeter to several in width. Strawberry hemangioma can increase in size, which is why it is dangerous, as it can affect the healthy tissues of the child.
Often this type of hemangioma stops growing, gradually brightens, shrinks and disappears completely by the age of 10.
Stellate (spider) angioma
It looks like a star with a bright base and “rays” extending from it. Most often it occurs on the child's neck. Disappears on its own in the first years of life.
Cavernous hemangioma
Loose, purple hemangioma, deeply embedded in the skin. It feels warmer to the touch than the surrounding epidermis. If you press, the baby will cry due to unpleasant sensations. This type of neoplasm requires treatment.
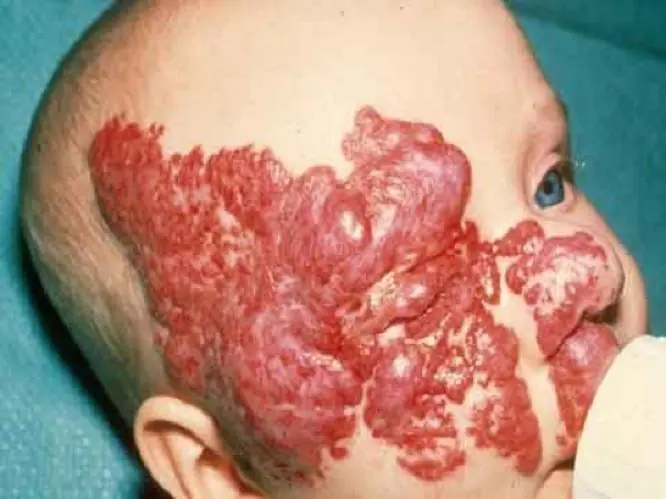
Flaming (fiery) nevus
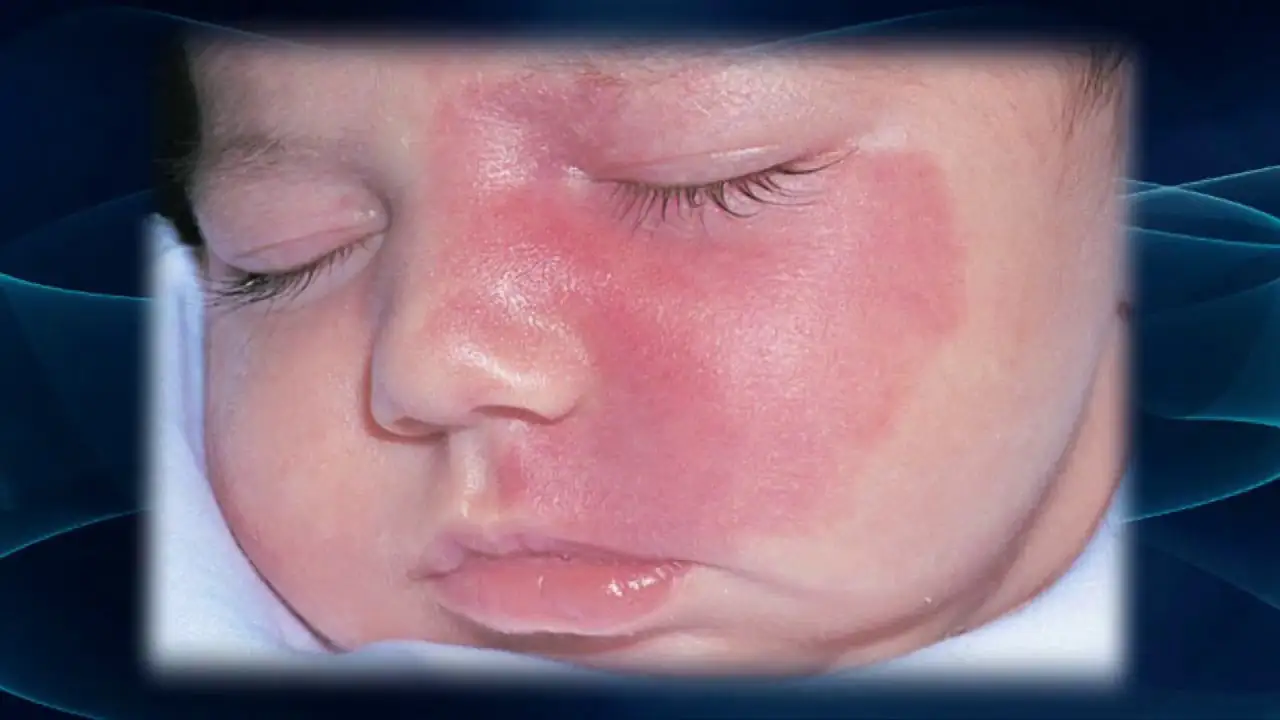
Looks like a red or purple stain from spilled wine. It can appear anywhere on the baby’s body. Such formations do not go away on their own. If they are not removed, they will remain for life. If the “wine stain” is in a visible place or continues to grow, it is better to take the trouble to correct the defect.
“Stork marks” (capillary hemangioma)
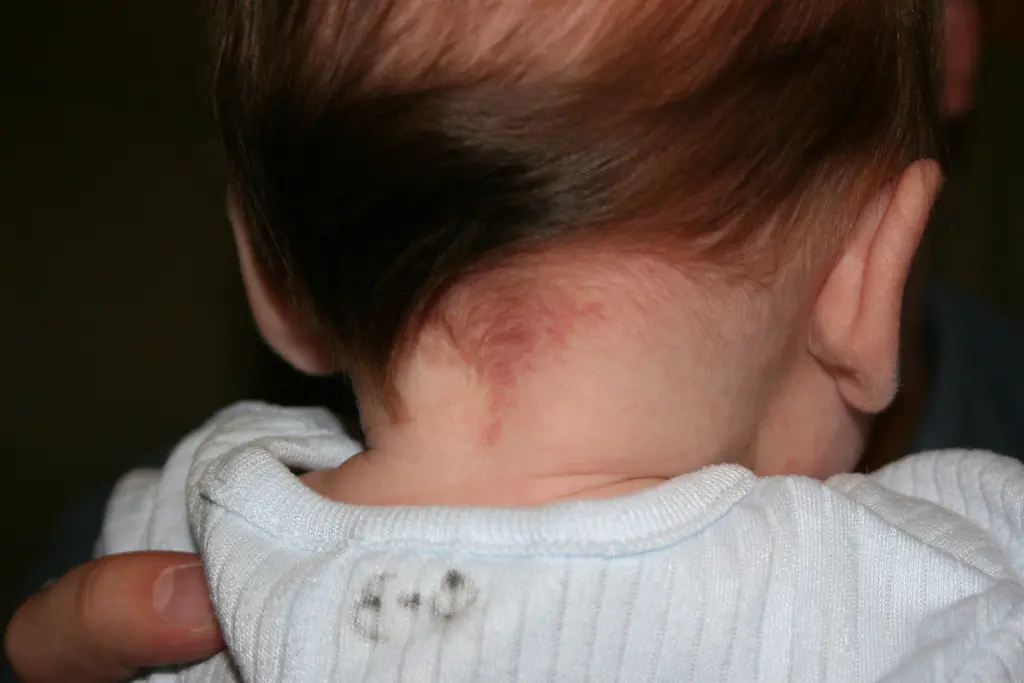
Such marks are also called “stork bites.” And if there is a mark on the baby’s forehead - “an angel’s kiss.” The formation is usually pink or red, but can also be orange, and resembles the mark of a bird's beak, which is how it gets its name. The formation is flat and does not rise above the skin. It is often found on the back of the baby’s head, in the neck area. When stressed, for example, when a baby cries, it acquires a brighter color. By the age of two, “stork marks” in most cases go away on their own.
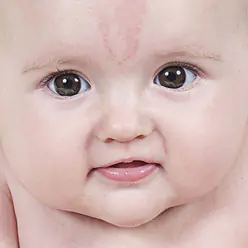
In addition to the above, there are other types of birthmarks. But they are much less common.
If you notice that a child’s hemangioma is increasing in size, immediately contact a specialist (surgeon). He will be able to assess the danger of the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment or removal of the tumor.
Causes of skin formations

The reasons for a birthmark in a newborn, of course, are not that his mother loved to pet dogs and cats, as the ancients believed. However, scientists cannot say exactly why such marks may appear. Only risk factors for their occurrence have been identified.
Why do birthmarks appear in newborns? This is affected by:
- Hereditary factor;
- Hormonal surges in the expectant mother;
- Exposure to toxic substances on the body of a pregnant woman;
- Bad ecology;
- Climate change;
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
But it happens that a birthmark appears in a newborn even without exposure to risk factors.
Birthmark on a baby: what to do?
Is your baby's birthmark small, smooth, does not grow and does not cause concern to the baby? Everything is fine, nothing to worry about. But you need to take the new growth seriously. Observe the nevus and notice whether the mark grows or hurts. If changes occur, you should visit a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist.
If a newborn has a birthmark on his body, several rules should be followed:
- Keep this area away from direct sunlight.
- Make sure that the baby does not scratch the area with the mark.
- Try to ensure that the nevus is never exposed to caustic substances, such as household chemicals.
In rare cases, marks on the skin can be fatal. Where can it appear? Under the influence of negative factors, a simple mole degenerates into a malignant formation - melanoma. Therefore, if the spot increases in size, you should urgently contact a specialist. If the formation is removed in time, there will be no health consequences.
Should moles be removed from babies?
It is recommended to eliminate formations in infants only if there is a danger to life. In babies, the immune system is not yet very developed, and any intervention can lead to serious consequences.
In what cases do doctors recommend surgery at an early age:
- The birthmark is very large;
- The formation rapidly increases in size;
- There are more than five marks, and they are concentrated in one place;
- The mole is located in a traumatic place (under the armpits, on the belt, on the skin of the eyelid, in the anus);
- Nevus interferes with the normal functioning of organs (on the hand, in the nose, in the eyes).
Particular importance should be given to those cases if a mole transforms - changes color or shape, grows, hairs fall out of it, it begins to bleed or itch.
How to get rid of formations?

The doctor may recommend one of the methods for removing nevi, depending on the size and condition of the formation, as well as the health of the baby:
Use of pharmaceuticals
Special medications are injected into the mole tissue to promote the death of overgrown cells. No anesthesia is required, but is not suitable in case of allergy to the active substances of the drug.
Using a laser
Excision of pathological tissues with a laser beam. It is quick and painless, but the procedure is not always possible for hard-to-reach areas.
Cryotherapy
Exposure of the mole to low temperatures. Suitable for eliminating small nevi.
Surgery
Removal of the formation using surgical instruments. It is used in cases where other methods cannot be used.
Carrying out the intervention under the supervision of a doctor, with preliminary examination of the tissues of the birthmark, reduces the likelihood of complications to zero. After removal of large formations, scars may remain. If they are located in a visible place, when the baby grows up, you can remove the scar using cosmetic procedures.
If you believe in fate, try telling your baby's destiny using moles. But pay attention only to happy signs:
- A mark on the baby’s cheek means love;
- A spot under the hair means high intelligence;
- Moles on the hands - to talents and good luck;
- Nevi on the back - to a life without worries;
- Mark on the leg - to hard work, calmness, confidence;
- A “sign” on the butt means success with the opposite sex.
As you can see, a mole is not a reason to panic at all. With the right approach, it will not be the cause of illness, but a happy sign that emphasizes the individuality of your son or daughter.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor.
Birthmarks and moles, medically called nevi, are brightly colored, often raised areas of skin that every child has from birth. Newborns have clean skin, but this does not mean that there are no new growths on it - they are simply not visible due to the weak coloring.
Clearly visible moles occur in 1% of infants, and in other children they gradually darken and appear by the age of 2-5 years. At this age, about 10 “marks” can already be seen on the body, but they continue to appear throughout life. What types of moles are there, are they dangerous, and how can you get rid of them?
Types and causes of birthmarks and moles in newborns
There are many types of nevi, but according to the nature of their occurrence they are divided into two groups:
There is no clear answer in medicine to the questions of where nevi come from and why babies are born with them. However, many years of observations have made it possible to compile a list of factors contributing to the formation of pigmented areas of the skin:
- heredity (often nevi of a similar shape and location are found in the mother or father of the child);
- prematurity of the baby;
- moles appear more often in girls;
- exposure of a woman to negative factors during pregnancy (for example, radiation, toxins);
- hormonal disruptions in the mother during the formation of the fetus;
- infections of the mother's genitourinary system.
In babies after birth, the appearance of a nevus may be due to several reasons:
- damage to the area of the dermis with a hidden nevus located on it;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- hormonal imbalance in the process of growing up;
- degree of pigmentation - in fair-haired children, moles form more often.
Pigmented nevi: what do they look like, are they dangerous?
Pigmented nevus is a papule or pigmented spot of nevus benign cells, located on the surface of the skin and has a relatively small size. Most often, such formation occurs in early childhood, but there may also be spots acquired throughout life.
Melanomic nevi (papillomatous, Mongolian spot, halonevus, etc.)
Pigment spots are formed under the influence of melanin - the more it accumulates, the darker the shade will be. There are several types of nevi that are often found in infants:
- Mongolian spot. It is typical for children of the Mongoloid race (90% of cases), but also occurs in representatives of the Negroid race (more details in the article: why do newborns sometimes develop a Mongoloid spot?). Formed in the lower back or on the butt, has a diameter of 1 to 10 cm and a color from gray to black. It does not affect the baby’s health and goes away until adolescence.
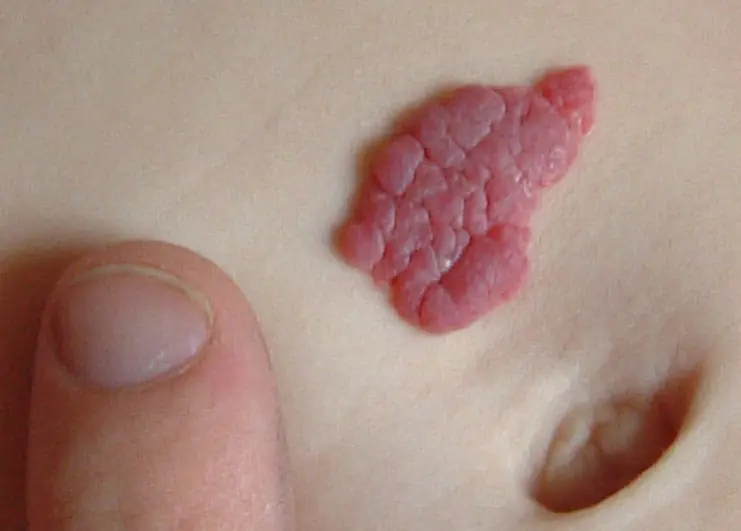
- Papillomatous nevus is a lumpy mole that protrudes strongly above the surface of the dermis and looks like a papilloma. Often located on the face, hands, under the hair on the head. The probability of degeneration into melanoma is almost zero.
- A halonevus is a benign mole that appears as a small, dark (darker than the surrounding epithelium) growth surrounded by a halo of discolored skin. It does not degenerate into cancer and disappears over time.
- Fibroepithelial nevus is a neoplasm up to 1.5 cm in diameter, located on a stalk. A benign mole, the shade of which varies from flesh to brown. Location: stomach, back and face (forehead, cheeks).
- Spitz mole. A harmless neoplasm that usually appears in childhood. It grows quickly, increasing to 2 or more centimeters in diameter. Localization of spots - cheeks, head and neck.
Melanoma-hazardous (borderline and giant pigmented, blue, nevus of Ota, dysplastic)
Skin cancer is possible even in an infant. Some age spots in newborns can become cancerous. Such neoplasms include the following types:
- A border nevus is a nodule with a clear border, raised above the skin and soft to the touch. It has a dark purple, brownish or black color and hair never grows on the surface. It is located in areas of skin injury - on the palms and soles. Often degenerates into an oncological tumor.
- A giant pigment spot is a neoplasm more than 14 cm in diameter. Often has hair follicles, in 50% of cases it turns into a malignant tumor.
- Blue, or blue nevus, is a formation with a characteristic dark blue color, which sometimes degenerates into melanoma. Most often it does not exceed 1 cm in diameter. It is localized on the feet, legs, hands and forearms, less often on the face.
- A dysplastic mole with a pink to brown coloration. Among these nevi there are dangerous species. If there are many spots or their number increases, they change - this is an alarming signal.
- Nevus of Ota is a blue spot or several merging spots that are located in the area of the eye, cheeks, and jaw. Sometimes it affects the nasal mucosa or the sclera of the eye. It rarely develops into a malignant neoplasm.
Hemangiomas: what do they look like, are they dangerous?
Hemangiomas, or vascular nevi, are spots that appear on the body due to abnormal proliferation of capillaries. They come in red or pink with a bluish tint. Infant angiomas form in the first weeks of life and increase in diameter over the course of a year, after which they resolve. 70% of neoplasms disappear by 7 years, and the rest disappear by 12. Their danger lies in bleeding - angiomas are easily injured.
Simple capillary (“stork mark”)
Such spots in newborns can be found on the back of the head, forehead or bridge of the nose. They have a color from orange to wine, sometimes appearing as a scattering of many small dots or specks. The size of the neoplasm reaches from 1.3 to 10 cm in diameter, and after its appearance it can increase. In the first few years of a child’s life, a hemangioma of this type, as a rule, becomes lighter in color and becomes noticeable only when stressed - crying, laughing, etc. This is an exclusively cosmetic defect that completely disappears by 5-9 years.
Strawberry angioma
In newborns, neoplasms are usually localized on the face and scalp. Angioma got its name because of its appearance - it is convex, red, berry-like, and after its appearance it can continue to increase in size. A birthmark is dangerous because, if it grows too much, it leads to an increase in the number of platelets in the blood and disruption of the functioning of the heart muscle.
"Wine Stain"
Capillary angiodysplasia, which is popularly called a port-wine stain, is an irregularly shaped area of red or burgundy color, most often located on the face (we recommend reading: why can spots appear on the face of a newborn?). Angioma is formed from dilated vessels, increases over the years and acquires a more saturated color. Sometimes bumps or nodules appear on it, and it reaches large sizes.
The reasons for the appearance of such spots are unknown. It is believed that this is an anomaly in the development of blood vessels that nourish the epidermis. Wine stains do not disappear, but they are not harmful to health either. They can be removed if they cause psychological discomfort to the child, but hemangioma tends to recur in the same place.
Birthmarks in newborns are a cause of concern for many caring fathers and mothers. Clear skin is much more common in babies. When do children get birthmarks? This may be a congenital pathology, or the spot may appear after a few years. But still, cases when babies are born with birthmarks are more common.
Possible reasons for the appearance
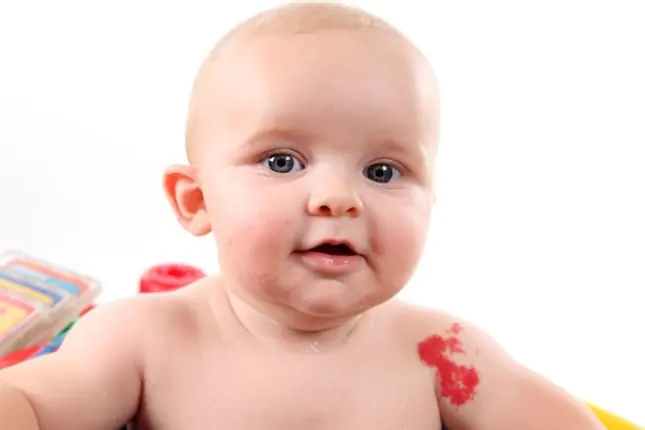

A birthmark in a newborn may appear on the back of the head, face, head or arm. The meaning of birthmarks and the reasons for their occurrence can be very different. Let us now dwell in more detail on what can cause the skin to turn darker at such an early age:
- Most often, a birthmark is found on the body of a child who was born prematurely. Doctors still cannot explain the nature of this phenomenon. But in most cases, pregnant women are warned that a premature baby may have a birthmark on the body or back of the head.
- Sometimes the meaning of a birthmark in a baby is associated with severe fright or other emotional distress of the mother during pregnancy. Therefore, women who are carrying a child under their hearts are advised to remain calm throughout the entire 9 months.
- Over the years, obstetricians have noticed a trend that birthmarks appear much more often in girls than in boys. They can appear even at the age of 2-3 years. The true reason for this phenomenon also remains a mystery. But some scientists associate this with natural hormonal levels.
- Babies who have very fair skin, which is inherited from their parents, are most susceptible to the appearance of birthmarks. Moreover, they may already be on the body at birth or appear after a short period of time.
- In some cases, the appearance of birthmarks in a child may cause a predisposition to certain skin diseases. Most often these are oncological diseases. If one of the parents suffered from cancer, this can be passed on to the baby. But the disease itself may not manifest itself in any way throughout your life; a birthmark will simply appear on some part of the face or body.
Types of birthmarks
All birthmarks in newborns are divided into 3 main types.
These are hemangiomas, pigmented nevi and vascular defects. Each variety has its own characteristics. Let's look at all these types of spots in babies.
Vascular defects and hemangiomas
Vascular defects are considered the safest. They are caused by ruptured capillaries in the skin, which can result in burgundy, red or purple spots appearing on the body. Such defects go away quite quickly. Most often found in children who had a difficult birth.
Hemangiomas, in turn, are divided into several types.
- The first type is warty birthmarks.
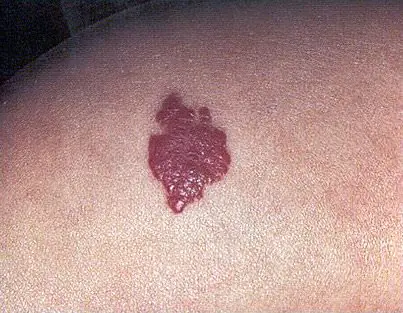
The photo clearly shows that the defect protrudes noticeably above the skin and has a somewhat keratinized surface. The color of such hemangiomas can be dark gray or brown. Such formations require surgical removal. Even minor damage to them can have serious health consequences in the future. - Medial hemangiomas are most often located on the back of the head, in the forehead or nose of the child. They have a soft pink color and are small in size. Most often, such birthmarks disappear after the first year of life and do not cause any harm to health.
- Some children may have Mongolian hemangiomas, which are located in the thighs or on the legs. They are often the result of a difficult birth process. Outwardly, they look very similar to large bruises. Usually they disappear without a trace after 1.5-2 years.
Types of nevi
There are also many types of nevi that can occur in both newborns and adults. Let's consider several main types of such age spots, which in most cases are observed in newborn babies.
- The most worrying thing for parents is fire nevi in children. They are also called port-wine stains. Usually these are large spots, which are most often located on the face or back of the head.
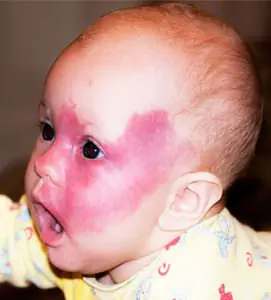
They are flat, but have a dark red color, which is clearly visible in the photo. Such nevi do not go away on their own, causing many complexes in adulthood. Moreover, these birthmarks require constant close attention from doctors, since in some cases they can degenerate into malignant neoplasms. - Hairy and halonevus are widespread. Hair nevi resemble large moles that become covered with hair over time. Sometimes parents notice that such a spot appears on the baby’s leg or arm over time. It does not go away on its own, but it usually does not pose a health hazard. Halonevus resemble oval or round moles. Their peculiarity is that the skin around them is very light. But the halonevus themselves are brown in color. If you do not touch them, then they also do not pose a danger.
- Sometimes a blue nevus is located on the child’s hands or face, an example of which can be seen in the photo.
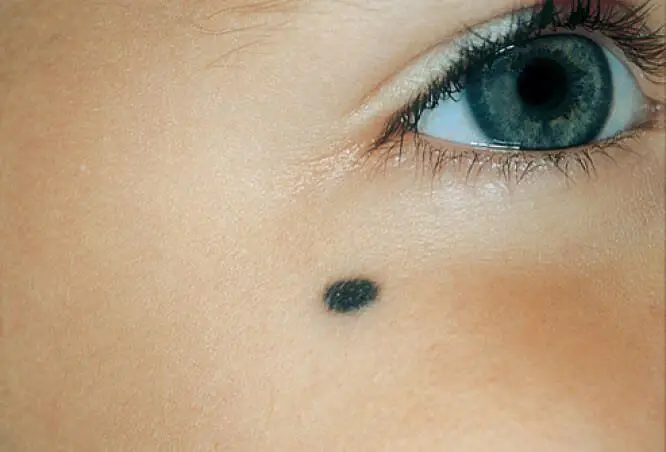
Such a nevus instills fear in parents, as it has a non-standard color. Sometimes it is black. Birthmarks of this nature can sometimes go away on their own, sometimes they can remain for life. It is best to examine them immediately after birth to completely eliminate the risk to the baby’s health.
What is important to remember
If a baby is born with a birthmark, you need to take action. You should immediately consult a specialist. Under no circumstances should you fight such tumors on your own! Some actions can cause great harm to the baby's health.
You should not cover moles with adhesive tape. This will lead to a greenhouse effect, which may cause tumor formation in the future. You should also try not to damage birthmarks mechanically so that their integrity is not compromised.
If we are talking about birthmarks, the surface of which is covered with hair, then there is no need to remove these hairs with tweezers or a razor. Damaging the bulb can cause the mole to increase in size or cause new ones to appear around it.
So, birthmarks in newborns are not yet a reason for severe panic. If you do not take rash actions and consult with specialists in a timely manner, you will not have to worry about the child’s health. Indeed, in most cases, birthmarks in newborns are not a pathology and soon disappear without a trace.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
We will be very grateful if you rate it and share it on social networks



