
What is a mole? This is a type of congenital or acquired benign tumor that forms on the surface of the skin.
A mole can be located on any part of the body, has several color options, and most often does not cause discomfort.
A mole as a phenomenon is familiar to every person. In 90% of cases, moles on the body are absolutely safe and do not cause harm to human health. In some cases, with certain changes in the body, a mole may degenerate from a benign tumor to a malignant one.
There is a kind of “risk group”, which includes those groups of people who should be attentive to all changes in the skin and monitor the condition of especially large moles. The risk group is:
- People with very fair and thin skin;
- Persons characterized by an abundance of freckles and various birthmarks;
- People with a large number of moles on the body, regardless of their size and location;
- Pregnant women;
- Persons who have particularly large birthmarks, moles, age spots, regardless of location on the body.
You should not worry about the presence of moles or age spots: if they do not cause discomfort and do not show signs of degeneration, there is no reason to worry.
When moles cause concern
Moles and birthmarks for the most part do not cause concern - the formations on the skin, regardless of size, are painless and not sensitive, and do not contain blood vessels or nerves.
There are two main reasons for the degeneration of moles to begin:
Negative effects of ultraviolet rays
Prolonged exposure to the sun, lack of skin protection and systematic sunburn can provoke the degeneration of one or more large moles.
Mechanical damage to a mole
A cut on the surface of a mole, accidental removal of part of it, or any other violation of the integrity of the body of the mole most often leads to unpleasant consequences - inflammation or degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
A healthy mole has a light brown color, smooth edges and a round shape. The surface of the mole is uniform, without bumps or compactions. The body of the mole is soft, painless, thickness does not exceed 1 mm or is completely flat.
Most often, if there is an infection or damage, the mole begins to bleed, hurt, and there is itching and burning around the mole. In this case, you should consult a doctor immediately. Also, each of the following symptoms is a reason to visit a cosmetologist:
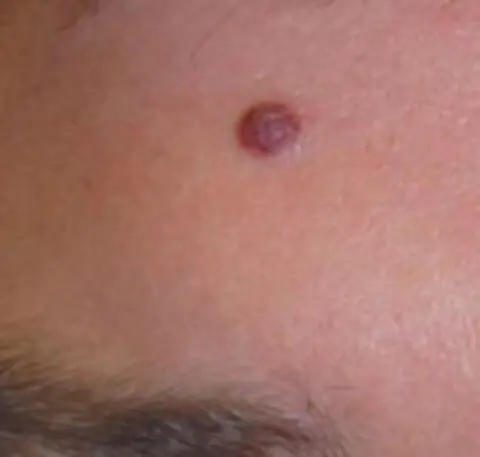
- Changing shape - any changes in the shape of a mole indicate a pathological process. For example, stretching the body of a mole to one side, the formation of polygons, pointed neoplasms;
- Breaking the edge - a change in shape most often leads to disruption of the edge of the mole: blurred contour, wavy, bumpy, etc.;
- Color change - Regardless of the original color of the mole, a change in shade is a cause for concern. Most often, moles begin to darken or acquire an unnatural shade - green, blue, red;
- Change of structure - the appearance of roughness, compactions, bumps and tubercles on the body of the mole;
- Increase in size - if a mole begins to increase in size, you must urgently seek medical help;
- Discomfort - pain, itching, burning or redness around the body of the mole, discharge and bleeding.
If you notice at least one of the symptoms, you should seek medical help. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can avoid not only undesirable consequences, but also the removal of a mole.
Ways to remove moles
If the patient's current condition, as well as the appearance of the mole, require surgical intervention, the mole is removed. There are several ways:
Laser
A quick and painless way to remove a mole. The laser allows you to “dissolve” cells without pain, blood loss, and also has an antibacterial effect. With proper care, traces of laser use disappear in 3-10 days, depending on the depth and area of exposure.
The procedure takes only a few minutes and requires only local anesthesia. The laser destroys the mole completely, regardless of its size and location.
Cryodestruction
Removing moles with liquid nitrogen. It is also an effective method, however, it is not used for removing moles on the face and areas with thin skin. The healing period is from 7 to 14 days. The procedure is painless, and with proper care, inflammation does not occur. During healing, it is best to limit exposure to sunlight, cold and moisture.
Electrocoagulation
This method involves “burning out” the body of the mole from the skin using an electric current. Electrocoagulation is a painless and harmless procedure. It is not used when removing moles from the face and areas with thin skin.
Surgical excision
In essence, it is a simple surgical operation involving cutting out part of the skin. It is used only in the most extreme cases, when the size and depth of the mole do not allow using another method of removal.
It's rare to see a person without small dark marks on their body. Is it worth paying attention to these points? Only a doctor will distinguish between dangerous and normal moles - malignant melanoma or harmless nevus - and give recommendations on what to do with them. Is it worth worrying about the appearance of new formations, when immediate contact with specialists is required, what are the signs of cancer development - the answers to these questions remain to be found out. No one is immune from disaster, and early diagnosis will protect you from severe consequences.
What is a mole
The first tiny spots may appear in children in infancy. A mole is a small formation on the skin - a nevus - that is considered benign and harmless. The basis for their appearance is melanocyte cells that accumulate the natural pigment melanin. Depending on its quantity, a difference in color is observed. Available colors:
The shape of the tumors depends on the location and concentration of melanin. They may have a stalk or be located under the skin, be flat and convex. The most common type is round, but there are exceptions. The development of neoplasms is provoked by ultraviolet radiation - natural from the sun, in a solarium. Hereditary factors cannot be excluded. A common cause of growth is hormonal imbalance, characteristic of periods:
- puberty;
- pregnancy;
- menopause.
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin– congenital, newly acquired;
- structure– pigment, vascular;
- place of education – in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin – flat – even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats – dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
Safe moles
Those who have dark spots on their skin should be wary of their changes. In time, detected signs of degeneration into melanoma contribute to the timely removal of the formation and preservation of health. Safe moles are different:
- the presence of a stalk – it cannot be formed by malignant cells that grow randomly;
- long-term condition without changes.
Spots that appear shortly after birth are not considered dangerous. It is important that they are small in size. Good – non-dangerous – signs of neoplasms include:
- flesh tone;
- unchanged pattern of the skin of the nevus and adjacent tissues;
- soft consistency;
- hair on the surface of the neoplasm - growing from the skin, indicates the absence of pathologies;
- diameter no more than 5 mm;
- symmetry;
- nevus in the form of a spot.
Which moles are dangerous?
Why do people with nevi on their bodies need to monitor their changes? There is always a threat of degeneration of non-dangerous tumors into a cancerous tumor. What moles are dangerous to health? Key signs you need to know:
- change in shades towards the dark side, the appearance of multi-color;
- rapid increase in size - exceeds two millimeters per year;
- occurrence of cracks;
- the formation of asymmetry due to uneven growth;
- lack of elasticity;
- the appearance of itching, burning;
- presence of discomfort.
The appearance of dangerous moles requires an immediate visit to a specialist to clarify the nature of the changes and the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Pathological transformations provoke:
- injury to the nevus due to negligence;
- self-removal;
- abuse of exposure to the sun, use of a solarium;
- location of the formation in places of frequent contact with clothing - on the neck, head, genitals, legs;
- placement in the hair, on the face, palms - where there is a high probability of injury;
- previously removed melanoma.
Why are moles dangerous?
Not a single person is protected from the sudden proliferation of cells of a harmless mole. Melanoma is an extremely serious disease. Changes not detected at the initial stage can result in death. The provoking factor is unsuccessful independent removal of tumors. Moles are dangerous because of their ability to:
- transform into an atypical – precancerous form;
- grow to large sizes;
- turn into cancerous;
- with minor external changes, metastases actively spread throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic channels.
How quickly does melanoma develop from a mole?
The transformation of a nevus into a cancerous formation can occur in different ways. The process depends on the stage of the disease and the type of tumor. Instant metastases are dangerous. Begins:
- growth of cancer (oncological) cells in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- their entry into the blood and lymph;
- penetration into the lungs, liver, kidneys;
- growth in these organs;
- complete damage to the body;
- death.
The growth phases of pigment cells are observed, along which melanoma develops from a mole. There are varieties:
- horizontal– damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs, lasting up to 10 years, but metastases do not appear;
- vertical– accompanied by the spread of cancer cells throughout the organs, can last two years, has an unfavorable prognosis;
- nodal – especially dangerous – characterized by deep spread within two months.
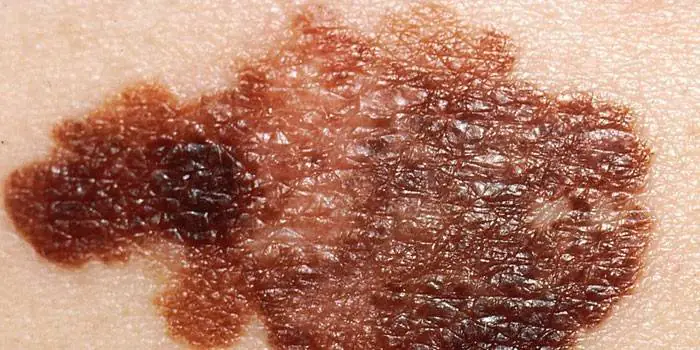
The first signs of melanoma
The patient can be assisted only when suspicious changes begin to be identified. The diagnosis, research, and referral for surgical treatment save a person’s life. The first signs of melanoma:
- increase in the height of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of discharge;
- redness;
- burning, itching;
- swelling of tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- the appearance of a crust;
- thickening;
- hair loss;
- expansion of pigmentation around the lesion.
With the further development of dangerous melanoma, the following are observed:
- significant change in size;
- the appearance of pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- surface ulceration;
- formation of new foci;
- bleeding from places of pigmentation;
- liquid separation;
- skin thickening;
- the appearance of an earthy tint;
- signs of metastases are chronic cough, weight loss, cramps, headaches.
How to distinguish a mole from melanoma
To recognize which moles are dangerous and which are not dangerous, you need to know what they look like. A person with nevi, in order to avoid dire consequences, must constantly monitor the appearance of new formations and changes that occur. You can distinguish a mole from melanoma by its signs. Non-dangerous neoplasm:
- symmetrical;
- with smooth edges;
- uniform in color;
- with dimensions not exceeding 6 millimeters.
Features of dangerous melanoma that require seeking help from dermatologists:
- growth in a short time;
- pronounced asymmetry of shape;
- heterogeneity in color - the presence of inclusions of several shades;
- lack of clear boundaries - the contour line is blurred, jagged, and looks like a coastline on a geographical map;
- increased diameter over six millimeters;
- variability of any parameters - color, size, shape.
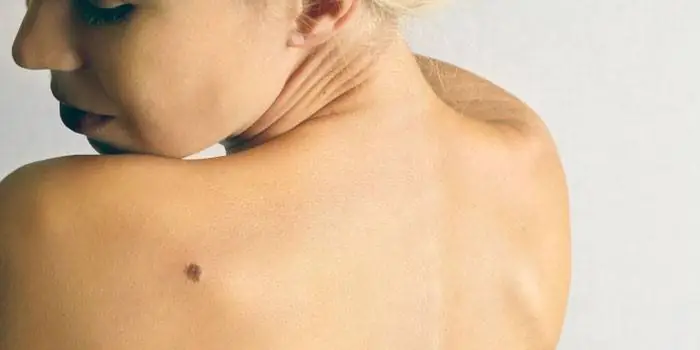
What dangerous moles look like
What do nevi that are subject to pathological changes look like? Only a doctor can correctly distinguish between non-dangerous tumors. Dangerous formations look like this:
- blue– compactions under the skin with clear boundaries, with dimensions no more than 10 mm;
- nodal– round, flat in shape, color – brown, black;
- cutaneous– often pale, convex;
- halo nevus – pigment surrounded by a light or white rim;
- spitz- looks like a dome-shaped tumor of pink shades, with the possible presence of a hole through which blood and liquid leak;
- connecting- connect individual entities into a whole.
Mole with jagged edges
One of the signs of a non-hazardous formation turning into a dangerous one is a change in contours. It often has blurred edges and scalloped borders. There are non-dangerous types of nevi - dysplastic. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis. A mole with uneven edges can be dangerous if there are additional signs of melanoma:
- accelerated changes in size;
- the presence of clearly defined asymmetry;
- the appearance of highly indented boundaries.
Rough mole
Such a neoplasm is harmless if its diameter is no more than 5 mm and remains constant in size. Often its appearance signals a lack of vitamins and nutritional disorders. Doctors advise coming for a consultation if it is discovered that:
- the smooth nevus turned into a rough one;
- bothered by burning, itching, tingling;
- irregularities and compactions appeared in the middle;
- areas with different shades formed;
- diameter has increased significantly.
A dangerous rough mole requires immediate examination if:
- the appearance of bleeding;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- rapid change in size;
- formation of asymmetry;
- formation of purulent discharge;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when touched;
- the emergence of an irregular shape, blurred boundaries, along the edges of the neoplasm.
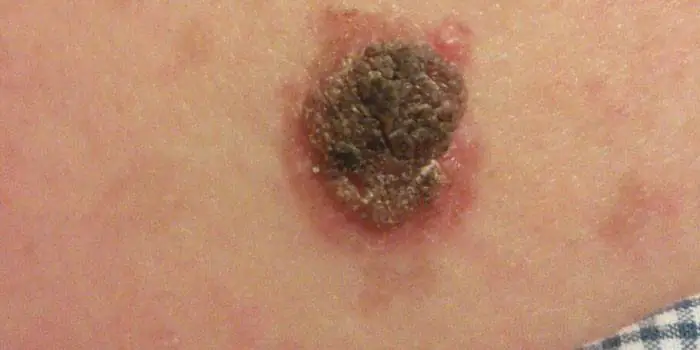
Large moles
Large formations on the skin are pigment spots. When they remain unchanged and do not cause inconvenience, this is not a dangerous phenomenon. It is important to constantly monitor their appearance, color, and size. To eliminate worries, you need to consult a dermatologist. During the visit, the specialist will conduct a diagnosis and give a forecast of the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm. Large moles become dangerous if they:
- injured;
- thickened;
- started to itch;
- were unsuccessfully removed independently;
- changed in size, shape;
- are bleeding.
What moles can be removed
Often nevi cause trouble for women when they are in a visible place - the face, neck. Even if they do not bother you, using removal will be the right decision - the appearance will improve significantly. After the procedure, the doctor must necessarily send the tissue for histological analysis to decide whether the mole is malignant or not. If the neoplasm is not dangerous, does not bother you, and does not change in size, surgery is not required. What moles cannot be removed? Experts believe:
- there are no contraindications;
- It is important to choose the right excision technique.
You should be careful about skin growths; it is unacceptable to remove them yourself. Only the doctor will determine whether a nevus is dangerous or not and decide what to do with it. You can delete it if:
- injured from clothing - on the neck, in the groin area, under the armpits;
- cause pain when touched;
- are located under the hair on the head and can be damaged when combing or cutting;
- change color, shape, outline;
- significantly increase in size;
- characterized by the presence of burning, itching;
- accompanied by inflammation and bleeding.
Moles in medical terminology they are called nevi.
They can be found on the body of any person in the form of small round dots, small spherical formations that rise above the surface of the body, and large pigmented areas of the skin.
What it is?
Moles consist of specialized cells of the epidermis - melanocytes, responsible for the production of melanin in the body (a pigment that colors the skin in various shades of brown). Under the influence of external or internal factors, an excess amount of them accumulates in certain places of the skin - this is why moles appear on the body of an adult, child or elderly person.

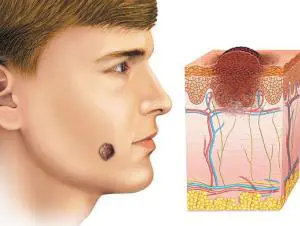
In some people, nevi remain unchanged on the skin all their lives, in others they disappear, in others they grow or change their shape and color. The latter become dangerous and can degenerate into malignant formations.
- Common moles have a rounded symmetrical shape, depending on the concentration of melanin in them, nevi are colored beige, brown or black.
- Meet and red dots on the body as moles, for the most part this phenomenon is associated with impaired skin pigmentation due to hepatic or endocrine pathology, as well as natural age-related changes (i.e. as a result of aging).
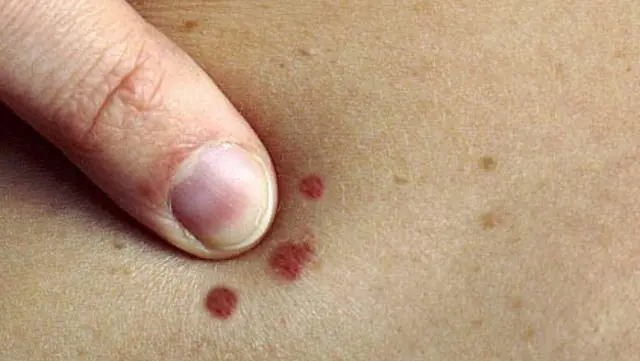
The difference between these spots and moles is that they usually appear in groups on a limited area of the skin. When metabolic processes are restored, the red spots disappear.
In adults, the appearance of nevi is associated with hormonal crises due to illness, menopause or nervous exhaustion. The appearance of moles in them can be observed constantly or appear spontaneously, in response to a certain stimulus. In childhood, science has noted the wavy growth of nevi.
Periods when moles appear in children:
- 6 months - six months, at this moment the child’s endocrine system adapts to external conditions;
- 5-7 years, the stage of active growth of the skeletal system and skeletal muscles, requiring rapid metabolic reactions;
- 12-16 years, puberty with significant changes in the functions of the whole organism.
Why do they appear?
Nevi are essentially benign skin formations.
Some people get scared when they see many moles on their body. What does this mean for a specialist? Only that the patient’s body is prone to accumulation (accumulation) of melanin in the surface layers of the epidermis.
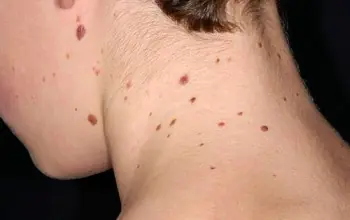
The reasons for the appearance of numerous or single nevi are varied.:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation, one of the most common factors in the formation of moles due to increased melanin levels during tanning;
- traumatic damage to the epidermis, systematic violations of the integrity of the skin contribute to the appearance of pathological changes in it;
- exposure to radiation, which rapidly changes normal skin cells;
- consumption of harmful products (GMOs, fast food, alcohol) and smoking, these habits negatively affect metabolic processes in the body.
- endocrine disorders and diseases, any changes in hormonal levels can cause the appearance of skin pathologies, pigmentation, moles;
- hereditary predisposition, the presence of various nevi in the family.
Classification and photo
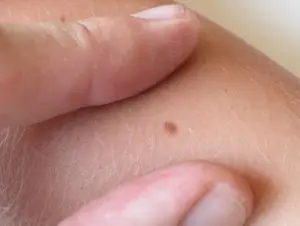
1. A flat nevus or birthmark is a pigmented island of skin with clearly defined boundaries. It can take the form of lentigo - multiple brown or brownish formations in the upper layers of the epidermis.
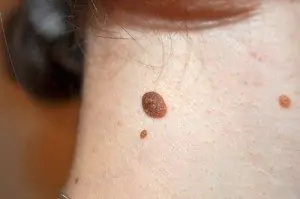
2. Convex nevus or mole. It has a diameter of up to a centimeter, a smooth or lumpy surface and rises above the level of the skin. Its color varies from beige to black, and a hair is usually located in the center of such a formation.
3. Blue nevus or blue mole. It looks like a smooth hemisphere, slightly raised above the skin, sometimes reaching a size of 2 cm. The color of this benign formation ranges from blue to dark blue.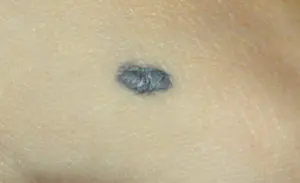
4. Giant nevus. It is a large spot on the body, gray, bright beige (sometimes brick), black or brown.
Dangerous and non-dangerous moles
Ordinary nevi do not cause any discomfort to their carriers; sometimes they even disappear without a trace. Their shape is stable, size and color remain unchanged.
But benign moles are sometimes removed to prevent their degeneration if they are of rather large size (pedunculated) and are located in areas of the body where a person constantly injures them (during vigorous activity or parts of clothing).

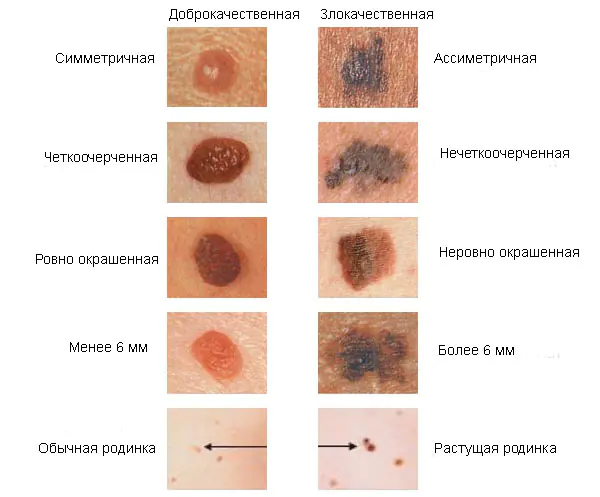
Remember dangerous moles in the photo and be vigilant!
If nevi degenerate into cancerous moles, this is dangerous, since such neoplasms quickly metastasize to other organs.
Therefore, it is very important to see signs of malignancy in time.:
1. The shape of the mole changes, it loses its symmetry and begins to grow in one direction.
2. The edges of the nevus become uneven (“cut up”, “torn”).
3. The color of the mole is uneven and contains yellow, red or black inclusions.
4. The nevus grows or “shrinks”, its size changes quickly.
5. The texture of the mole becomes different, smooth becomes rough, bumpy becomes flat, etc.
6. Loss of hair growing from the nevus.
7. Itching, peeling and burning in the mole area.
There are several reasons why a nevus itches:
– pathological cells multiply;
– there are active processes of death of healthy tissues;
– the area around the formation becomes inflamed and swollen.
8. The appearance of microcracks and ulcerations.
9. Bleeding and soreness of the mole.
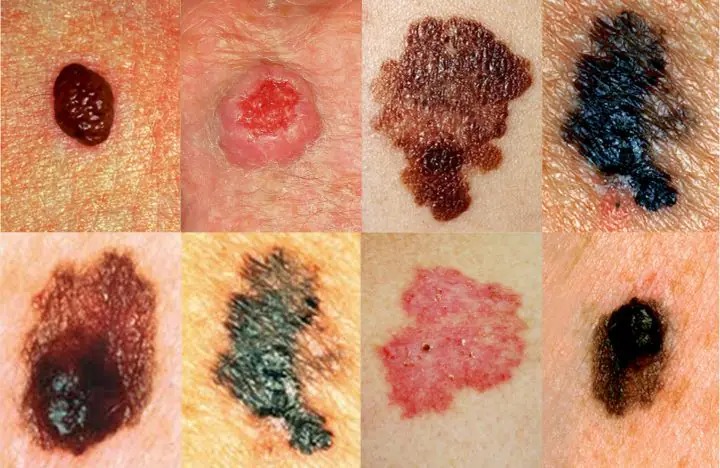
Cancerous moles (melanomas): photo
What happens if you rip off a mole?
You cannot remove a nevus yourself.
Firstly, it is dangerous, and secondly, it is simply ineffective. If the mole is located close to blood vessels, prolonged bleeding may develop. Often such self-medication leads to re-formation of the nevus, its growth or malignancy.
Therefore, it is difficult to predict what will happen if a mole is torn off. It may have no consequences, or it may cause serious complications for the health and life of patients.
Doctors warn that any trauma to the nevus is extremely undesirable, but pedunculated moles or small convex formations can be accidentally removed with nails or hard items of clothing.
What to do if you rip off a mole:
- cauterize the wound with an alcohol solution;
- stop the bleeding by applying a gauze bandage;
- come to see a specialist.
In cases of partial removal of a mole, do not touch the remaining formation, do not cut it off or tear it off.
Sometimes such pigmentation appears before the disappearance of a mole (as a sign of depigmentation), and in other cases it may signal its degeneration.
White spots around the mole appear as a characteristic sign of Setton's nevus. This formation is considered harmless in terms of degeneration into a more malignant form, however, melonomas (aggressive cancerous formations) can also have such a white rim, so the appearance of white spots is a reason to contact a medical specialist.
Diagnostics
Dermatologists and oncologists are involved in determining the type of nevus.
Using a dermatoscope, the doctor examines the formation and determines its nature (benign or malignant). Sometimes a histological examination (scraping method) is required.
Biopsy (tissue sampling) for nevi is not used due to their trauma during this procedure. And as you know, it’s better not to touch moles again!
Removal
Many people want to get rid of birthmarks and nevi not only in cases of malignancy (pathological change), but also to correct a cosmetic defect.
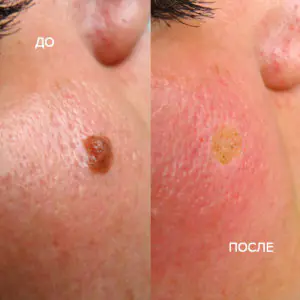
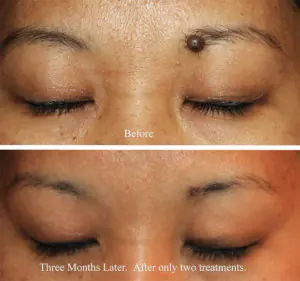
However, removal is carried out at the oncology center for people with malignant tumors and with a high probability of degeneration of nevi.
Often the indication for surgery is the localization of moles on the body: on the scalp, on the neck, on the chin, in the area of the shoulder blades.
Methods for removing nevi (with information on how much it costs to remove them):
- surgical, using local anesthesia and a scalpel (in municipal surgical hospitals, according to indications - free of charge, in medical centers from 300-500 rubles)
- cryofreezing with liquid nitrogen (1000-1500 rubles);
- electrocoagulation - cauterization with electric current (600-1300 rubles);
- photodynamic - ultraviolet irradiation (1000-1200 rubles);
- laser - removal of moles with a beam (800-2000 rubles);
- radio wave, destruction of nevi by shock radio wave (RUB 700-1400)
The choice of method for removing moles is made by the doctor; prices for these procedures depend on the size and type of nevus.
Prevention of malignancy
Preventive methods for reducing the risk of malignancy of moles include:
- limited sunbathing, cancellation of visits to the solarium;
- minimizing skin trauma;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle (healthy eating and avoiding bad habits).



