- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
Among skin dermatological diseases, staphylococcal folliculitis is quite common. This is an acute inflammatory pustular lesion of the pilosebaceous follicle, which occurs when pathogenic staphylococci penetrate. Men are more likely to suffer from the disease due to regular razor use. However, the disease also affects women, localizing in the area where hair removal is performed (bikini, legs, armpits). Staphylococcal infection also occurs in newborns. It causes acute pyoderma and in the future can cause the development of eczema, so carriers of staphylococcus pose a particular danger to young children.
Causes of staphylococcal folliculitis
In the photo, Staphylococcus aureus is the most dangerous causative agent of staphylococcal folliculitis
The causative agents of this type of folliculitis are staphylococci. The most dangerous of them is golden. Infection usually occurs by airborne droplets or contact. However, in the etiology of the pathology there are factors that increase the chance of getting sick - non-compliance with hygiene and nutritional rules. Also, pathogenic purulent pustules appear on the skin when the normal functioning of the body is disrupted, caused by the following reasons:
- The presence in the diet of a large amount of quickly digestible carbohydrates. A large amount of sweets creates a good “nutrient medium” for staphylococcus.
- Deficiency or absence of certain vitamins, proteins and minerals in the diet.
- Frequent stress, insomnia, chronic fatigue.
- Reduced immunity.
- Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract - constipation, dysbiosis, pancreatic dysfunction, chronic colitis and enterocolitis.
- The use of certain medications (for example, Iodomarin) without prior examination of thyroid hormones.
- Chronic inflammation and dental diseases.
- The presence of staphylococcus in the oral and nasal cavities, which is detected by bacterial culture.
- Hormonal disorders of the ovaries, adrenal glands, and thyroid glands.
- Abrasions, scratches and other violations of the integrity of the skin.
It is worth noting that a high level of immune defense of the body does not lead to contamination of the skin with staphylococcus. If you strengthen your immune system and monitor the condition of your skin, then there will be no problems with the epidermis.
- Learn about all types of folliculitis
Symptoms of staphylococcal folliculitis
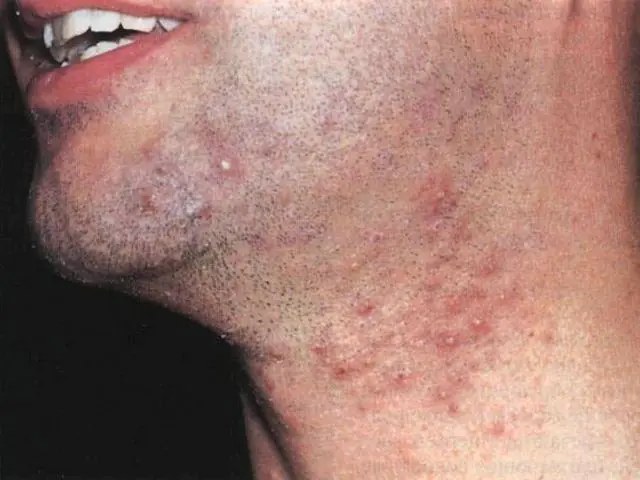
The photo shows an area of skin affected by staphylococcal folliculitis
Regardless of the lesion, staphylococcal dermatitis can be superficial and deep, their symptoms are similar. Pyoderma in adults is characterized by frequent exacerbation, chronic course and drug resistance. In children, the disease occurs with an increase in body temperature. Symptoms of staphylococcal folliculitis differ depending on the location of the lesion:
- Face. The favorite places for pustules to appear on the face are the nose, forehead, cheekbones and chin in men due to infection during shaving.
- Hair part of the head. A small abscess with a red rim forms near the hair follicle. Read in detail about the symptoms of folliculitis decalvans on the head.
- Neck. The follicle occurs on the neck because the skin there is thin and delicate. The rash is very painful in this area.
- Women's legs. Symptoms occur if hair removal was performed before going outside.
- External genitalia and buttocks. Infection of these parts is typical for newborns, especially if there is no prevention of dermatological disease.
When the skin is affected by staphylococcal folliculitis, a superficial inflammatory process begins around the hair: pustules are small (like poppy seeds) or large and dense. After a couple of days, the pustule dries out and a yellow, cone-shaped crust forms. Soon it is rejected, leaving no scars. Pustules can be single or multiple.
If the infection has penetrated deep into the hair follicle, then a deep small abscess of a hemispherical or conical shape develops in the center with a pierced hair. Or the rash may become larger, firmer to the touch, and surrounded by a pinkish-red color. When folliculitis dries, a crust forms, which, after rejection, leaves a pigment spot for a short time.
Diagnosis of staphylococcal folliculitis
To diagnose and speed up the treatment process, you need to be examined and pass a list of tests:
- Microscopic seeding of the purulent contents of the follicles. Sometimes staphylococcal skin diseases are aggravated due to demodicosis.
- Determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Examine the blood (culture of the nutrient medium) to exclude the allergic etiology of the disease.
- For patients over 20 years of age, it is important to have their blood sugar levels checked. Because sometimes staphylococcal folliculitis is the first sign of impaired glucose tolerance.
- Conduct an intestinal diagnosis, since follicles are often caused by worms in the body.
- Do an ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas to determine the level of performance of the liver and intestines. If abnormalities are detected, you should undergo a course of treatment.
Treatment of staphylococcal folliculitis
Pictured are drugs for the treatment of staphylococcal folliculitis
To clear the skin of staphylococcal folliculitis and avoid remission, you need to carry out comprehensive treatment. To do this, all methods are used: antibiotics, ultraviolet lamps, medicinal herbs, cleansing enemas for the large intestine.
Antibiotics are selected based on the results of bacterial cultures. Most often, Amoxiclav and staphylococcal bacteriophage are prescribed for 10 days. For local use, wounds are treated with a solution of Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, salicylic alcohol or alcohol tincture of propolis. After eliminating the purulent contents, apply an antibiotic ointment - Methyluracil or Solcoseryl ointment - to speed up the process of tissue regeneration and avoid scar formation. When the symptoms of the disease subside, you can use hormonal drugs on small areas of the affected skin. Children are prescribed ointments with salicylic acid to dry out purulent formations. They reduce symptoms, dry out and protect the skin from scarring.
In folk medicine, herbs that need to be washed daily provide invaluable assistance in the fight against folliculitis - a decoction of chamomile, celandine, oak bark.
- Read about treating folliculitis at home using traditional methods.
It is important to follow a diet: Eliminate sweets from your diet and introduce plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. The latter should make up half of the daily diet. Eat more plant fiber, which ensures regular bowel movements and prevents the absorption of toxins into the blood. In the morning after waking up and in the evening before going to bed, drink a glass of clean water, since a large volume of liquid makes the skin elastic, which allows it to fight pathogens.
It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene and thoroughly disinfect items used for skin care. You need to get rid of expired and open lotions and creams, and start using new products after completing a course of antibiotics.