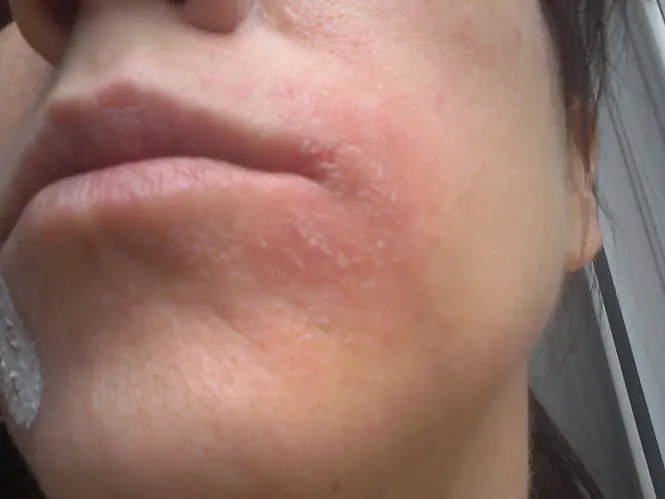
Skin dermatoses are quite common. They often make themselves known by the appearance of spots on the face - pink, bright red, flaky, itchy. Irritations on the skin of the face can be either permanent or temporary. They tend to either disappear on their own or progress into more complex skin formations that cause pain and provoke the development of complexes in sick people.
Symptoms of facial spotting
A person faces the problem of red spots on the face throughout his life:
- in infancy (manifestations of diathesis and eczema);
- in adolescence (acne, acne, seborrhea, allergies);
- aged 20 to 30 years (hormonal imbalance, vitamin deficiencies);
- in old age (endocrine changes).
What can red spots on the face indicate?
The appearance of red spots with signs of peeling is due to:
- or age-related changes;
- or pathological processes;
- or the development of infectious diseases;
- or by provoking a hereditary factor.
Flaky redness on the face may indicate problems such as:
- fungal, bacterial or viral infection of the skin;
- the presence of parasites (helminthic infestations) in the body;
- infection of the facial skin with a subcutaneous mite - demodex;
- hypertension;
- diseases of internal organs (gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, gall bladder);
- venereal diseases (AIDS, syphilis);
- HIV infection;
- contact dermatitis, manifested by the use of cosmetics, medications, exposure to cold, ultraviolet radiation;
- hormonal changes;
- metabolic disease;
- decreased immunity.
Almost any malfunction in the human body is reflected on the face in the form of redness in certain areas of the face. In this case, the eyes, nose, lips, and ears may suffer.
Signs of red spots on the face
Experts diagnose dermatoses of various etiologies based on certain symptoms:
- When an allergic reaction occurs in the facial area, redness of a vague form is observed, easily flaking, the skin gradually becomes crusted, which tightens it, the inflamed areas itch. Allergic spots are most often localized in the nose area, on the chin, and cover the cheeks.
- Lichen spots can affect the forehead, cheeks, and eyelids. They are pink or red neoplasms with a clear round or oval border. The skin inside the circle has a lighter appearance and is taut. Depending on the type of shingles infection, the spots may become scaly and develop into blisters, plaques, or papules.
- Eczema makes itself felt by very itchy red spots, the skin on the face cracks, and rough scaly areas form in place of the spots. Gradually, the scales peel off, but the skin is not completely cleansed, but suffers from a lack of moisture. It is very difficult to resist scratching, so deep scratches form in areas of inflammation.
- Flaky spots on the face, which appear as a result of minor nervous shocks and experiences, are often short-lived. A few scales quickly peel off, the itching is mild, and the skin defect disappears within a month.
- Red spots on the eyelids may indicate the development of conjunctivitis; they do not spread over the entire face, but are localized specifically in the eye area. Redness indicates inflammation of the eyelid outside and inside, and severe redness is also observed in the eye sac.
- Psoriatic red scaly spots on the face have a raised, round shape; at the initial stage of the disease they have a pinpoint arrangement and are localized on the forehead, cheeks, eyelids, lips and chin. If left untreated, red scaly dots form a single inflammatory carpet, covered with a rough crust.
- With lupus erythematosus, red spots of a round shape, having clear boundaries in the form of a ring of a brighter shade compared to the center, are localized in the cheeks and nose, forming a pronounced butterfly.
Possible consequences of the appearance of red spots
Irritation and inflammation of the skin of the face can be accompanied by symptoms indicating the development of complex diseases rather than a cosmetic problem. You should always compare the appearance of red spots with signs of deterioration in health, such as:
- joint pain;
- dizziness;
- increased body temperature;
- changes in blood pressure;
- intestinal colitis;
- pain and tingling in the heart;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- nausea and vomiting;
- physical weakness.
Regardless of the extent of facial redness or the type of red spots, consultation is required:
- dermatologist;
- neurologist;
- immunologist;
- endocrinologist;
- allergist;
- gastroenterologist.
How to treat spots on the face?
Treatment of red spots on the face requires an integrated approach to studying the problem. Since the reasons for their appearance are external, internal, and hereditary factors, the specialist needs to have a detailed picture of the patient’s health status.
Diagnostics
Treatment for red, scaly spots on the face begins with confirming the diagnosis.
To determine the root causes of such skin manifestations, the patient is prescribed the following tests:
- immunogram;
- allergen reaction tests;
- detailed blood test;
- scraping from inflamed areas;
- biopsy;
- ultrasound examination of internal organs;
- gastroscopy.
Medicinal practice
Based on the research results, the patient may be prescribed medications taken orally:
- sedatives (Valerian, Motherwort tincture, Glycine, Novo-passit);
- antiallergic drugs (antihistamines “Cetrin”, “Diazolin”, “Claritin”, “Dezal”);
- vitamins E and A;
- preparations containing zinc and calcium;
- enterosorbents (“Lactofiltrum”);
- antifungal drugs (“Fluconazole”, “Mycomax”, “Futsis”);
- antiviral drugs (“Acyclovir”, “Gerpevir”);
- antibiotics;
- corticosteroids (“Prednisolone”, “Dexamethasone”, “Triamcinolone”);
- immunostimulants (“Chlorbutin”, “Cyclophosphamide”, “Myelosan”).
Particular attention is paid to the use of medicinal creams, ointments and gels:
- against allergies (“Gistan”, “Traumel”, “Elidel”);
- glucocorticosteroids (Advantan, Hydrocortisone, Locoid, Oxycord, Akriderm);
- herbal remedies containing extracts of celandine, chamomile, calendula, sage, birch leaves and buds;
- preparations containing zinc (“Zinerit”);
- tar soap, tar ointment;
- antifungal agents (Nizoral, Triderm);
- products containing sulfur;
- antiseptics (salicylic acid, naphthalan ointment, ichthyol ointment, “Tsindol” suspension);
- antiviral drugs (“Acyclovir”);
- keratolytics (“Cygnoderm”).
- antibiotics (“Celestoderm”).
People's recommendations
Along with drug treatment, masks made from components such as:
- alcohol tincture on birch buds;
- decoctions of celandine, yarrow, chamomile;
- parsley and cucumber juice;
- cabbage leaves;
- cereals;
- egg yolk;
- seaweed;
- sour cream and honey;
- raw potatoes;
- cottage cheese with lemon juice.
Masks and facial wipes help moisturize the skin, relieve itching, inhibit inflammatory processes, exfoliate skin particles, and cleanse the skin.
Preventing spots on the face
Red spots on the face may indicate chronic disease. In order to increase the period between relapses of symptoms, a number of preventive measures should be performed along with treatment:
- give up bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking);
- promptly treat concomitant diseases;
- limit contact with allergens that cause an inflammatory reaction of the facial skin;
- reduce the intake of medications that provoke an allergic reaction;
- adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Healthy lifestyle
Skin health is affected by people's lifestyle. If you have problematic dermatoses, you should lead an active lifestyle:
- exercise;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- pay attention to psychological relaxation of the body;
- to harden;
- sleep at least eight hours a day.
Proper skin care
In order to reduce inflammatory processes, you should:
- use daily high-quality hypoallergenic cosmetics for facial skin care, nourishing and moisturizing creams and lotions;
- protect the skin with special creams before going out into the cold and wind;
- refuse facial peeling and scrubs;
- use herbal medicines;
- make nourishing anti-inflammatory masks.
Diet
Facial skin is a reflection of what a person eats. Lack of vitamins, moisture, minerals, excess carbohydrates, fats and preservatives lead to sagging, redness, and aging. For dermatoses of various etiologies, experts recommend following a diet that excludes everything harmful from the patient’s diet:
Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits that are not included in the list of allergens. Food should be boiled or steamed.
Changing the pace of life and making the recommended adjustments will allow you to forget about the problem of red, flaky spots on your face for a long time.
Facial diseases can be caused by external and internal causes. It is important to understand that there may be several factors that provoke the appearance of skin diseases. The exact causes of the problem can only be determined by a dermatologist, who must know the full picture of your health. In particular, exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases is often accompanied by skin rashes and changes in complexion.
Causes of skin diseases