Moles, or in other words nevi, are pigmented growths on the skin that appear throughout life, as well as at birth. Every person on earth has such skin defects, to a greater or lesser extent. By the age of 10, their growth may slow down, but much depends on heredity and individual perception of solar ultraviolet radiation. All moles can be different in size, shape, color and, of course, location.
According to statistics, moles can most often be found on the skin of the face, due to the fact that the face is exposed to the sun more than other places on the body. But from a medical point of view, a nevus can form anywhere in a person. It happened when moles were found in the mouth or on the mucous membranes, as well as on intimate places, the anus and vagina. Women most often have moles in the mouth; a similar trend has not been observed in men.
To size nevi can be divided into certain groups:
- Giant - nevi that can cover any anatomical surface, for example, a person’s chest or face;
- Large – nevi measuring at least 10 centimeters;
- Medium – moles no larger than 10 centimeters in size;
- Small – birthmarks up to 15 millimeters in size;
- In addition to classification by size, nevi are epidermal, borderline and intradermal.
Let's take a closer look
Now in more detail for each type:
- epidermal – moles that are formed by the concentration of melonocyte cells in the upper spheres of the skin;
- border – moles that are located between the dermis and epidermis;
- intradermal – are located deep under the skin, which can be dangerous in case of diseases associated with moles and skin.
According to other parameters, such as color, location on the body, shape of the nevus, they can be divided into separate groups:
- Vascular or hemangiomas are moles of different shades: blue, pinkish or red. Consist of involuting endothelial cells;
- Non-vascular - unusual plaques with a keratinized surface, which have different shapes and colors;
- Setton's nevus is a benign formation that is surrounded by a ring of skin without pigment;
- Blue are dense birthmarks, which may be slightly higher than the skin level, have a smooth surface of blue or dark blue color;
- Dysplastic - spots with a diameter of no more than 12 millimeters with unclear boundaries of a brown-red or brown color.
Currently, medicine, together with dermato-oncology, believes that moles can be melanoma-dangerous (such spots can become cancerous in the future) and melanoma-non-dangerous.
The question of why and where moles come from has tormented people for decades. What could be causing this and is it possible to stop moles from growing back? There are no answers to such questions, but they may not always be unambiguous.
Based on why moles appeared, they can be acquired or congenital. Congenital ones arise as a result of disturbances in the transport of melanoblasts from the neuroectodermal tube to the epithelial tissues of the embryo. It is the accumulation of such melanoblasts that contributes to the formation of moles in the baby. Their number will depend on how many melanoblasts have accumulated.
Over the course of a person’s entire life, the number of birthmarks on the surface of a person’s body may change. There are a number of the most common causes of moles on the human body:
- Endocrine cause. During pregnancy and puberty, the body undergoes a restructuring in the endocrine system, which can lead to the appearance of moles;
- Inflammation of the epidermis. Such inflammation can lead to the development of any skin infections, which in turn leads to the appearance of moles in the future;
- Long lasting tan. It's no secret that prolonged exposure to the sun can not only get skin cancer, but also increase the number of moles throughout the body. It is solar ultraviolet, or in other words, solar radiation that affects the body’s skin so that moles increase in size. They can become larger in area and in height above the skin level. Therefore, those people who notice that their moles have begun to increase due to prolonged exposure to the sun should consult a doctor and try to cover up the growing spots more.
Over the course of a lifetime, nevi can change their appearance on the human body; they can change their appearance, color, and size. Moreover, such changes can be natural or pathological. Natural ones are caused by specific changes that have occurred in the human body, but pathological ones indicate that the person most likely has cancer.
The natural reasons for the growth of nevi are completely consistent with those why they appear on the human body. Most often, moles naturally increase in size under the sun's rays, followed by dermatological diseases, and not thirdly, hormonal imbalances.
The pathological growth of moles is due to the fact that oncological changes have begun to occur in the body, that is, the nevi have become malignant and not benign. But in order to accurately determine the diagnosis, you should contact an experienced oncologist or dermatologist.
This is the only way to accurately determine benign or malignant nevi.
Dangerous consequences of a mole injury
Such operations to remove birthmarks should be entrusted to experienced doctors who know how everything needs to be carried out and what consequences may arise. In 96% of cases, when a nevus ruptures on its own, this leads to the development of inflammation, sepsis, melanoma and other extremely unpleasant complications.
In case of unintentional injury to the skin where there is a mole, you should stop the bleeding, if any, with cotton wool, and rinse with hydrogen peroxide, and then consult a doctor for help. If the stain has been completely torn off, then it must be preserved and taken to a specialist in a hospital, where special tests will be carried out to determine the presence of cancer cells.
There are reasons that will help determine whether a mole is malignant:
- after receiving an injury, feelings of pain or scabies arise at the site where the mole was;
- inflammation of the skin around the mole;
- hair began to fall out in the damaged area;
- small nodules began to appear around the mole;
- the spot increases in size;
- the skin changes its shade at the site where the mole is removed.
What can be classified as dangerous moles?
According to the risk of developing a malignant tumor, moles are divided into melanoma-hazardous And melanoma-free.
TO melanoma-hazardous include moles that can transform into cancerous formations under radiation or chemical influence:
- blue moles;
- extremely large pigment spots;
- nevi of Ota;
- Dubreuil's precancerous melanoma.
Distinctive signs of dangerous nevi:
- the mole has an asymmetrical shape;
- the nevus is blurred, the edges are not smooth;
- The mole began to increase greatly in size.
If such situations occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
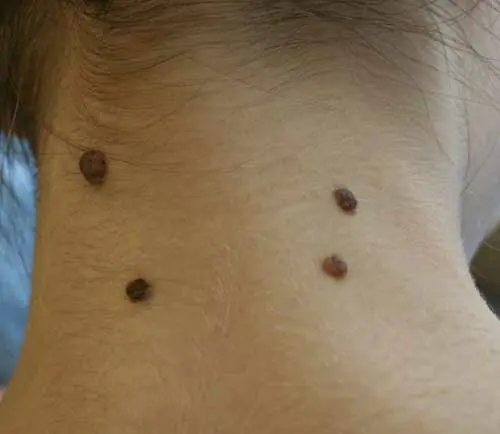
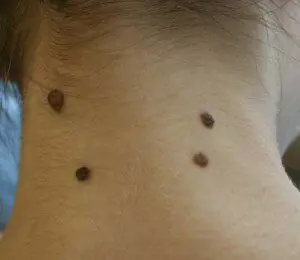
Moles (nevi) are acquired during life or congenital benign pigmented neoplasms on the skin. Similar skin defects occur in every person over 10 years of age. However, moles can vary in size, shape and color.
According to statistics, age spots are most often found on the skin of the face. However, it has been proven that there is not a single place on the human body where a nevus could not form. There are frequent cases of detection of moles in the oral cavity, on the mucous membranes, in the anus and in the vagina. At the same time, birthmarks on the mucous epithelium are found much more often in women than in men.
Types of moles
Depending on their size, nevi are usually divided into:
- giant (covering the entire anatomical area, for example, the chest or face);
- large (from 10 cm);
- medium (up to 10 cm);
- small (up to 15 mm).
In addition, birthmarks are divided into epidermal, intradermal and borderline. Epidermal moles are a concentration of melanocyte cells in the upper layers of the skin, border moles are at the border of the dermis and epidermis, and intradermal moles are in the deep layers of the skin.



