Oddly enough, most often a blush on the face appears as a result of vivid emotional experiences, both negative and positive. An awkward situation or stress often causes a person to start blushing and cannot do anything about it. However, such a reaction does not last long. But what to do when the blush on your face is constantly present?
Blush as a sign of health

Many international clinical studies confirm the fact that a slight blush on the cheeks indicates good health. Scientists start from the fact that the inner layers of our skin (dermis) are enriched with a large number of blood vessels that supply tissues with oxygen and nutrients, and also take away waste products of metabolism. For people in optimal psychological and physical condition, it is quite normal to periodically blush and have a slight flush on the face.
At the same time, the detection of excessive redness of the face of a local or widespread nature may indicate serious health problems.
Blush and sinusitis
As clinical practice shows, constantly red cheeks may indicate an inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses, in particular in the maxillary sinus. But it should be noted that, in addition to this symptom, there must be a number of signs that indicate the development of sinusitis:
- Breathing through the nose is difficult, or may even be absent.
- If there is an acute course or an exacerbation of the chronic form, discharge from the nasal passages will be observed. The nature of the discharge is very different: from mucous or mucopurulent to purely purulent. Their greatest number is observed in the morning after waking up.
- The patient feels “pressure and heaviness” in the front of the face. Soreness may spread to the temple.
- Reduced olfactory function.
- Exacerbations are usually accompanied by a rise in temperature.
The exact reason why the blush persists on the cheeks can only be determined by a qualified and experienced medical specialist.
Blush and tuberculosis
If you notice the appearance of an unhealthy blush on your face, which does not go away for quite a long time, these may be the first signs of a tuberculosis process in the organs of the respiratory system. However, there is no need to panic right away. It is enough to consult a doctor and undergo a full clinical examination to rule out serious pathology. Let us highlight some of the main clinical symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis:
Other causes of flushed cheeks
In addition to inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and tuberculosis in the organs of the respiratory system, blush on the cheeks can be observed with the following diseases or pathological conditions:
- Rosacea (rosacea).
- Allergic reaction.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
A persistent, unhealthy blush on the cheeks is a sign that always indicates some kind of disease.
Provoking factors
Quite a few factors can lead to local redness on the face. Let's list the most common ones:
- Stressful situations that provoke a surge of strong emotions.
- Sudden change in temperature.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Prolonged exposure to the sun or visiting a solarium.
- Poor quality cosmetics.
- Use of aggressive skin care products.
In children, blush on the cheeks is often a manifestation of diathesis.
How to treat?

Independent attempts to get rid of an unhealthy blush on the face often do not bring success. Nevertheless, in the first stages, especially if you know the probable cause of the skin reaction (for example, prolonged exposure to the sun or freezing), you can try protective medications in the form of creams, ointments, lotions, etc.
The most advisable thing is to visit a dermatologist to exclude or confirm skin pathology. If a skin disease is detected, a qualified specialist will prescribe appropriate treatment for you. If you do not have skin problems, but the unhealthy blush on your face does not go away, we recommend that you consult a therapist for a full medical examination. We strongly advise against using any traditional medicine recipes.
Self-treatment, as a rule, does not lead to anything good. Entrust your health to professionals who have sufficient experience and qualifications in their field of activity.
The problem of red, bright cheeks on the face in adults and children may be associated with manifestations of allergies on the skin, but this is not the only reason that medical practice diagnoses. Inflammations and rashes often cause discomfort and can be symptoms of diseases. The reason for this phenomenon needs to be clarified and measures taken. A bright blush on the cheeks is not always a sign of health.
What are red cheeks
A slight blush has always been considered a sign of health or a characteristic of modest people. From a physiological point of view, the cause of red cheeks is a rush of blood to this part of the face. The skin contains a large number of capillaries that provide thermoregulation processes. What causes the increase in body temperature, flushing of the face and redness is not always immediately clear. The reasons need to be looked for in order to adjust the treatment.
Causes
There are many main reasons why cheeks are red. This:
- fluctuations in the emotional state (a person does not control these reactions, their manifestation is associated with the work of the autonomic nervous system, its sympathetic department);
- hormonal changes in the body (adolescence, menopause);
- taking medications (especially hormonal ones);
- alcohol consumption;
- in rare cases - liver or stomach diseases;
- allergic reactions;
- hypersensitivity and skin diseases.
Flushing, which externally manifests itself as red cheeks, causes stretching of the capillary walls and their thinning. As a result, blood stagnates in small blood vessels and produces harmful substances. Frequent redness of the cheeks leads to serious consequences - the development of rosacea. It is easy to identify it at home, but for treatment you need to see a doctor.
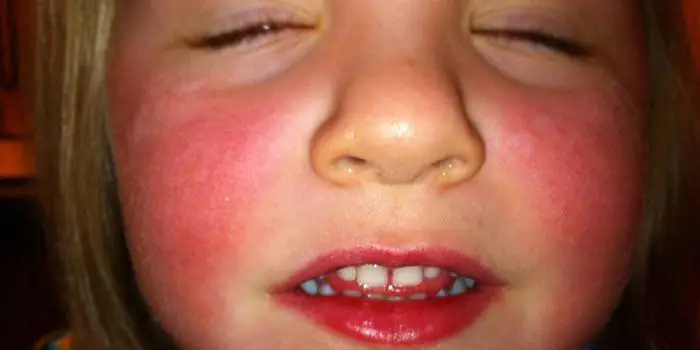
The child has
The baby's rosy cheeks delight parents and are perceived as an indicator of health; the pale skin of young children is more worrying. If your child’s cheeks suddenly turn red or this phenomenon occurs frequently, it may be associated with illness or the presence of a disease. Don’t worry right away if your child’s skin turns red due to certain factors:
- after playing in the cold, walking in the cool season (the blush lasts about half an hour after returning indoors);
- psychological reaction of the child (anger, shyness) - the redness will disappear when the child calms down;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- in children 1-2 years old, redness is observed after eating (especially in those who can eat on their own, the remains of some dishes cause irritation on the baby’s delicate skin).
There are reasons that should definitely alert attentive parents:
- red spots on the cheeks when the skin of the nose and the skin around the mouth turns red and burns when teething;
- redness of the entire face and chin - indicates dryness and high temperature in the room;
- red spots on a child’s cheeks, peeling, itching – appear due to diathesis and allergies;
- redness of a point nature, followed by the appearance of tubercles - may be an indicator of the presence of parasites in the child;
- red hot cheeks with pallor of the tip of the nose and lips, lethargy, poor appetite, cough, fever - sure signs of pneumonia;
- Red cheeks during night sleep are evidence of heart disease.
A ruddy complexion has long been considered an indicator of good health. But is it only the blush on the cheeks that can signal this? Why does he appear?
How's normal?
The facial area is rich in blood vessels of different diameters. Usually small vessels are not clearly visible, and therefore the skin color is pale or slightly pinkish.
The reason for the appearance of blush on the cheeks and redness of other areas of the face can be exposure to the cold. Blushing occurs at elevated temperatures, in a stuffy room. Drinking red wine or hot pepper will also add redness to our cheeks.
Could blush be a sign of pathology? It turns out yes. Let's briefly look at some of them.
Increased body temperature. Of course, not every infection is accompanied by fever, but, for example, for widespread colds, this symptom is not uncommon. Do you see the blush on your cheeks? Measure your body temperature - perhaps the cause is a feverish state. In this case, there are often other manifestations: general weakness, deterioration or lack of appetite, body aches, cough, runny nose, as well as other symptoms characteristic of a particular disease.
Read the material on the topic: What is ARVI?
Scarlet fever. A relatively rare infectious pathology today. The group A streptococci that cause it secrete a special toxin that leads to diffuse redness of the skin with a pinkish-red tint. With scarlet fever, fever, skin rashes, and a crimson-red color of the tongue are noted.
Remember that elevated body temperature can indicate not only infectious diseases: it also occurs in diseases that are not in any way related to infections.
Another cause of facial redness is overheating.
An unhealthy blush may indicate allergies.
Rosacea. With this disease, the vascular network grows, the skin on the face thickens. In addition to redness, nodules and pustules appear on it, itching is noted, and the secretion of sebum increases. One form of this disease is rhinophyma, when the skin on the nose thickens significantly.
The skin of the face turns red and with various dermatitis, acne.
Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. Develops with excessive release of glucocorticoids (a type of hormone) - for example, a neoplasm of the adrenal gland, a lipid cell tumor of the ovary; prolonged administration of drugs containing glucocorticoids (in this case, drug-induced Itsenko-Cushing syndrome occurs).
Manifestations of pathology include obesity; rounding the contours of the face; red-violet “stretch marks” on the skin of the abdomen and thighs; increased blood pressure and a number of others.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). It develops when cells and tissues are attacked by their own antibodies and immune complexes. The manifestations are varied. In addition to the “butterfly” flush of the cheeks, joint pain, fever, malaise, damage to the oral mucosa, and often widespread or local hair loss are noted. An increase in various groups of lymph nodes is often observed (especially in children and young people); in 10% of patients, an enlargement of the spleen is detected.
Damage to the cardiovascular, bronchopulmonary, nervous, digestive systems, kidneys, and hematopoiesis is also possible. In addition, women can have early and late miscarriages. During pregnancy, the disease may worsen.
Mitral stenosis. One of the heart defects. The cause is rheumatic fever. The basis of this disease is a narrowing of the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
High blood pressure. In addition to an objective increase in blood pressure and other symptoms, one of the signs may be redness of the skin of the face.
Diabetes. This disease affects a large portion of the population around the world. Symptoms include: increased thirst, increased frequency of urination and the release of large amounts of urine, general weakness, and fatigue. Sometimes there is an increase in appetite. Possible weight loss, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision. Wounds heal worse, and there is a predisposition to bacterial and fungal infections. Redness of the cheeks is also common.
Read the material on the topic: How to determine diabetes?
Hypothyroidism. A syndrome that develops when there is a lack of thyroid hormones in the body, or a decrease in their biological effect at the tissue level.
Manifestations of hypothyroidism are usually nonspecific. Some of them: increased body weight (even obesity), brittle hair, snoring at night, a feeling of chilliness, swelling under the eyes in the morning, decreased heart rate, constipation, deterioration of memory or attention, depression, depression. In women, the menstrual cycle may additionally be disrupted.
In laboratory tests - an increase in cholesterol levels, a decrease in hemoglobin levels.
Menopause. Due to hormonal changes, among other things, so-called hot flashes may occur, with warming and redness of the skin (especially the face, head and neck).
Polycythemia vera. Chronic pathology of the blood system, which is based on an increase in the total mass of red blood cells. In addition to facial redness, there are symptoms such as general weakness, headache, dizziness, blurred vision, fatigue and shortness of breath. Itching is often observed, especially after a hot bath; enlarged liver, in > 75% of patients - spleen.
Theoretically, facial redness can also occur with increased formation of red blood cells of a different origin.
Erythrophobia (blushing syndrome, erythrophobia, stress flushing of the face). A type of neurosis characterized by a pathological fear of blushing in the presence of people. This fear itself can cause the skin to become red. It is based on dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Carcinoid syndrome. It develops when there is a carcinoid in the body - a tumor from a certain type of cell of the neuroendocrine system. There is a rush of blood to the face and neck caused by emotional stress or ingestion of food, hot or alcoholic drinks. Complaints of abdominal cramps and diarrhea are common. There may be a deficiency of vitamins and proteins, and anemia due to deterioration of absorption processes in the small intestine. Damage to the heart valves and the appearance of murmurs are possible; weakened sexual desire and erectile dysfunction.
Can cause facial redness taking certain medications.
What to do?
We have listed some of the possible reasons for this manifestation. To find out what kind of disease a blush on the cheeks and other areas of the face may be a sign of, you must definitely seek medical help. If the situation is not an emergency, you can first consult a general practitioner or therapist. Depending on what diagnosis is made or suspected, consultation with related specialists may be necessary.
Since pathologies relate to different organs and systems, the range of prescribed studies may also be different.
Text: Enver Aliyev



