Human skin is the largest organ, which, like a litmus test, reflects what is happening inside the body. Any rash is the first sign of disease or infection, so do not hesitate if a rash appears on your body. If you have skin rashes, you should see a dermatologist, and if the rash appears in the genital area, you should see a gynecologist or urologist.
rash, rash
Types of rash and causes of its appearance
A rash is a visual change in the structure and color of the skin; it is characterized by redness, itching, peeling and even pain. The halo of the rash, despite its external integrity, consists of individual elements, which include:
- ulcers (defects on the surface of the epidermis caused by slowing down the regenerative processes in the upper layers of the skin);
- erosion (superficial epithelial defect without scar formation)
- papule (dense nodule located above the surface of the skin);
- vesicle (a fluid-filled capsule located in the upper layers of the epidermis);
- pustule (a cavity formation on the surface of the skin filled with pus);
- blister (an element on the surface of the skin caused by inflammation and swelling of the papillary dermis);
- nodes (dense, painless nodules on the skin);
- hemorrhages (subcutaneous hemorrhages caused by high permeability of the vascular walls);
- petechiae (pinpoint subcutaneous hemorrhages caused by capillary injury);
- ulcers (deeply located formations filled with pus).
Depending on the location of the skin rash, the source of the problem can be determined. In particular:
- Allergic reactions cause a rash on the hands and face;
- Infections are characterized by rashes on the torso (abdomen, back);
- STIs are localized on the genitals, inner thighs and skin around the anus;
- Stress weakens the immune system, so the rash is localized throughout the body (but, unlike allergies or rashes due to infections, the reaction to allergens and immunoglobulin will be negative)%;
- Problems of the gastrointestinal tract are expressed in the form of serious skin abnormalities (with ulcerative colitis - erythema nodosum (inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue and blood vessels in the form of nodes), with problems with the pancreas - atopic dermatitis, intestinal infections provoke pyoderma - ulcers on the skin);
- Rashes due to problems with blood or blood vessels appear on the abdomen and then spread throughout the body. It is characterized by the absence of itching.
What type of rash is typical for allergies?
Allergy skin rashes are not caused by an immune reaction of the blood to allergic elements. This is due to haptens - simple chemical compounds that are not immunogenic. But they tend to bind to the carrier protein. Attaching to a macromolecule, the newly formed complex synthesizes immunoglobulins. The body perceives it as foreign, causing an increase in the level of leukocytes. As a result, the skin becomes covered with red spots of different sizes and different locations.
An allergic rash is characterized by the following characteristics:
- It does not always cause itching and fever;
- Accompanied by swelling of the face, eyelids, runny nose;
- The area of the rash corresponds to the places where the skin comes into contact with the allergen (if you are allergic to jewelry - on the wrist or fingers, to deodorant - in the armpits, to cosmetics - on the eyelids or around the mouth);
- A blood test shows an increase in the number of eosinophils;
- The biochemical blood test remains unchanged.
The most common form of allergy rash is hives. In appearance, it resembles pink spots that appear on the skin after contact with nettles. Hives are a reaction to pollen, cosmetics, and dust. Often localized on the bends of the elbows, knees and wrists. Accompanied by severe itching and peeling of the skin.
Depending on the allergen, the rash has the following types:
- Allergy to food. It is an erythematous rash in the form of rough spots rising above the surface of the epidermis. A characteristic feature of food allergies is severe itching.
- Cold allergy. Occurs when exposed areas of skin come into contact with cold (air, water). Although cold does not directly provoke an allergic reaction, it is a trigger for an allergic reaction to improper functioning of the thyroid gland, spleen, etc. Cold allergies are accompanied by lacrimation, nasal discharge, as well as the appearance of whitish and pink, scratch-like spots on the skin, which disappear on their own after some time. If a person has ever had an allergy to cold, he needs to see a doctor to find out the true cause of the malfunction of the body.
- Allergy (atopic dermatitis) to dust/animal hair. It is often diagnosed in children. It manifests itself in the form of an itchy rash, accompanied by increased dryness of the skin. In some cases there are weeping ulcers. The simplest test to identify atopic dermatitis: take an ordinary school ruler and press on the area of the rash for 20 seconds. If a white streak remains on the skin after a few minutes, it is atopic dermatitis. If the skin has regained its previous shade, this is a rash of a different nature.
- Allergy to alcohol. Alcohol has a vasodilating effect. Accordingly, more substances, including toxic ones, are absorbed into the blood. The more components in an alcoholic drink, the stronger the allergy to it. The most “dangerous” drink is absinthe, which contains wormwood, anise, fennel, coriander, and lemon balm. The skin becomes covered with red spots, as if from burns. In chronic alcoholics who drink cheap wine every day, a red, weather-beaten face is a consequence of constant alcohol intoxication of the body. If such a reaction occurs in an ordinary person, he needs to find out the source of the allergy and consult a doctor. The biggest danger is Quincke's edema, when the lungs swell and a person dies within a few minutes.
There are 4 types of allergic rashes: food, contact, respiratory and respiratory. The biggest allergy sufferers are children. It should be remembered that not all products consumed by adults are suitable for children.
A child’s rash should not be ignored. The most dangerous is the rash caused by meningococcal infection. Outwardly, it resembles a food allergy, but at the same time the body temperature rises. It’s better to be on the safe side, and if your baby has any rash, you should consult a doctor.
Infectious rash: characteristic features and difference from allergic rashes
The distinctive features of an allergic rash are vesicles (capsules with liquid inside), papules (grain-like compactions) and pustules (bubbles with pus). An infectious rash has these symptoms.
Various infections and viruses entering the body damage, first of all, the mucous membrane, as well as the skin. Unlike an allergic rash, an infectious rash is always accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Also characteristic signs of infection:
- body intoxication, vomiting, headache
- fast fatiguability
- phasing, spread of the rash to other parts of the body with each new day
- enlarged lymph nodes
- rashes look like papules, vesicles and pustules
- the skin dries out and flakes off.
The infection rash is not itchy, but touching it is painful. The causes of rashes are the following diseases:
- Herpes: depending on the type of virus, the skin of the face (lips) or the genitals (head of the penis, labia) are affected. The rash looks like blisters, which gradually open up and ulcers form in their place. Upon completion, a crust will form that should not be touched;
- Scabies: The causative agent is a microscopic mite that leaves tiny tunnels under the skin. Unbearable itching occurs;
- Chickenpox: The rash resembles a mosquito bite, filled with serous fluid. Vesicles spread throughout the body, including the scalp. The soles and palms remain intact;
- Scarlet fever: the rash looks like roseola - pinpoint pink spots of various shapes. After a few days, the rash fades and turns brownish. After the temperature normalizes, the skin peels and flakes. A characteristic feature is redness of the tongue and enlargement of the papillae;
- Measles: the rash looks like papules, which are localized on the inside of the cheeks and gums. The rash spreads from the neck down the back, lastly moving to the limbs. The mucous membrane of the eyes becomes inflamed;
- Rubella: the skin becomes covered with red spots, localized in the thighs and buttocks, and malaise is observed;
- Infectious mononucleosis: lymph nodes enlarge, adenoids swell. The rash is observed throughout the body, including on the roof of the mouth;
- Meningococcal infection: This is an extremely dangerous infection that can lead to the death or disability of a child. It is by the appearance of the rash that you can notice the symptoms of the disease on the first day of infection. A rash with meningococcal infection is a consequence of exposure to toxins caused by the activity of meningococcus, which increase vascular permeability. The rash is hemorrhagic in nature, that is, it looks like small hemorrhages. Mainly localized on the buttocks and limbs.
There is an effective test to distinguish meningococcal rash from other rashes. You need to take a glass, turn it over, press on the area of the rash and twist it a little until the skin around it turns white. If the skin turns pale at the site of the rash, then it is not a meningococcal infection. If the rash remains the same color, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Rash caused by diseases of the blood and blood vessels
A rash due to diseases of the blood or blood vessels is caused by damage to the walls of the capillaries, as a result of which petechiae - small bright red dots - appear on the surface of the skin. Unlike ordinary hemorrhages, a rash due to blood diseases does not change color when pressed. Other signs indicate the disease:
- joint pain (knees, ankles);
- black stools, diarrhea, sharp pain in the abdomen as if poisoned;
- the rash covers the entire body.
Diseases that cause hemorrhagic rash include:
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof's disease) is a blood disease in which small arteries and capillaries are blocked by blood clots. Mainly found in children, especially newborns. The disease has autoimmune causes of unknown etymology. Those. Your own immune cells perceive platelets as a foreign body and attack them. The rash is painless, occurs as a reaction to the administration of any medication, and is localized at the injection site.
Hemoblastosis. This is a malignant tumor that occurs very often in childhood. The rash has several types:
- hemispheres of red-brown color, covered with a crust;
- blisters with serous fluid inside;
- rashes similar to bruises, both large in size and in the form of bloody dots that appear without any reason.
In all cases, the rash causes severe itching. Blood tests for hemoblastosis show a significant increase in the number of leukocytes due to decreased immunity. Hemoglobin drops, lymph nodes enlarge. Platelet counts drop and the child gets tired quickly. The main cause of rash in diseases of the blood or blood vessels is a decrease in the number of platelets and a disruption in the synthesis of proteins involved in blood clot formation. This rash also occurs when taking medications that thin the blood (Aspirin, Warfarin, Heparin).
Diabetic angiopathy. This is a violation of the vascular capacity of the lower extremities, provoked by type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to the disease, the walls of blood vessels become thinner and become fragile. This causes skin dystrophy. Ulcers and erosions appear on the skin.
Rash caused by digestive problems
The condition of the skin largely depends on the functioning of the internal organs. Using a map of rashes on the face, you can determine which organs have problems.
- pimples on the forehead indicate problems with the intestines;
- a rash along the hairline indicates problems with the gallbladder;
- pimples on the bridge of the nose - liver problems;
- ulcers on the temples - problems with the spleen;
- rashes above the lip - disruption of intestinal function;
- pimples on the nose - heart disease or endocrine disorders;
- rash on the chin - gynecological problems.
Rashes due to liver diseases
In the early stages of liver disease, they practically do not manifest themselves at all. The earliest symptom is specific skin rashes. They are caused by an increase in the amount of bile acid in the blood, which causes general intoxication of the body. The skin takes on a yellowish tint.
With cholestasis (blockage of the bile ducts), the rash is localized on the feet and palms, looking like marks from a burn. With cirrhosis, liver cells die and the whole body becomes covered with spots. Parasitic liver diseases cause rashes resembling hives. They are localized in the lumbar region and abdomen.
Also characteristic is a combination of rash and spider veins, which cause severe itching, which intensifies at night. Taking antihistamines (allergy medications) does not provide relief. Increased bilirubin gives the skin a yellowish tint.
Rashes due to intestinal diseases
If the contents of the intestines are poorly removed from the body, then some of the toxins will begin to penetrate into the blood. The body begins to get rid of poisons itself through the excretory system. Because of this, the condition of the skin worsens, and it becomes characteristic of:
- increased fat content
- dull complexion
- acne, not only on the face, but also on the back, stomach, chest
- noticeable “black dots” similar to volcanic craters
- skin becomes dry and dehydrated
- After acne heals, scars remain.
After the New Year holidays, many people note a deterioration in their skin condition and notice minor rashes that go away on their own. They are associated with contamination of the body with toxins caused by eating large amounts of heavy food.
Rash due to diseases of the pancreas
The pancreas regulates secretory functions, so disruption of the organ affects the condition of the skin. When pancreatitis worsens, hemorrhoidal (bruise-like) rashes are localized around the navel, and the skin itself acquires a marbled tint. Hives are located throughout the body in stripes, and red “drops” on the skin are also noticeable - vascular aneurysms. The more red protruding dots on the body, the more intense the disease.
Nervous rash
Stress and nervous tension often cause skin rashes. Under the influence of a stressful situation, the immune system is suppressed. The body spends its resources to maintain the normal state of internal organs. For this reason, previously hidden diseases worsen. Also, weakened immunity provokes urticaria - a small rash similar to the reaction of the epidermis to the touch of nettles. This pathology is otherwise called nervous eczema. It, unlike a normal allergic reaction, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe itching that is not relieved by antihistamines
- pulse quickens, hand tremors are felt
- restless sleep, night sweats
- panic attacks, feelings of anxiety and danger
- swelling of the face and limbs.
Typically, nervous eczema occurs after a traumatic situation or severe stress. Treating skin rashes with creams or medications does not help. Improvement comes only after the life situation normalizes. Itchy urticaria due to nervousness can be soothed by baths with sea salt, which also have a good effect on the nervous system.
Skin rashes due to gynecological problems
The condition of a woman’s reproductive organs is closely dependent on her hormonal levels. Many diseases (uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, endometriosis) are caused by hormonal imbalance, in particular, the ratio of androgens (male sex hormones) and female sex hormones, which is primarily signaled by a specific rash on the skin. Androgens, particularly testosterone and DHT (dihydrotestosterone), are produced in women by the adrenal glands and testicles. The cells lining the sebaceous glands of the skin have androgen receptors. When the amount of hormones increases, the receptors react and the skin secretes more sebum, creating a nutritional base for bacteria. Moreover, DHT begins to be produced by the adrenal glands even before the onset of puberty, so in adolescents, especially girls, rashes have been observed since the age of 10-12.
When a woman has polycystic ovary syndrome, the amount of female hormones estrogen and progesterone decreases and the level of androgens increases sharply. Along with menstrual irregularities, a woman develops severe “teenage” acne on her face and chest. Darkening of the skin is noticeable in the groin, armpits and around the neck. The woman also notes increased hairiness on her legs, arms, and above her lip. All this is due to hormonal imbalance.
An increase in the level of female hormones also affects the condition of the skin. In addition to acne on the face and body, excess estrogen makes the skin dull and dull. She seems to be losing her tone. There is also a decrease in blood sugar levels and an increase in platelet counts.
The increase in progesterone also does not go away without leaving a trace. The skin has progesterone receptors, which respond to the growth of the hormone by increasing the production of sebum until the appearance of oily seborrhea. The scalp becomes covered with crusts, pink spots appear on the face and body, the skin on which flakes and flakes off. In adolescents, the face becomes covered with bumps, which, when pressed, release a liquid sebaceous secretion.
Babies also experience hormonal rashes, which can be very frightening for a new mother. This is the so-called neonatal cephalic pustulosis. It arises because the baby begins to live separately from the mother’s body, and for him this is a serious hormonal shock. The secretion of the sebaceous glands increases, the ducts become clogged, which creates favorable conditions for the activity of microbes.
Also, the newborn’s body gets rid of the hormones that its mother supplied it with during pregnancy. In addition to skin rashes, girls have swollen breasts and vaginal discharge. In boys, the scrotum and penis swell. All these symptoms go away on their own after a few days. The mother needs to make sure that the baby does not sweat and that bacteria do not multiply on the skin.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter
The skin is the largest human organ and it is not surprising that in the process of diseases occurring inside the body, side effects in the form of various kinds of rashes appear on the skin. Any symptom requires careful consideration; in this article about skin rashes in adults, we analyze the causes with photos, help you identify the culprit of the rashes, and also consider diseases, the early symptoms of which are often skin manifestations.
Since skin rashes are the first sign of many diseases, this signal cannot be ignored; any suspicious rash that suddenly appears should be examined by a qualified doctor (dermatologist, allergist or therapist), since the disease in a weakened form can manifest itself as skin changes, without additional symptoms.
A rash may indicate:
- Immune system problems.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Allergic reactions.
- Problems with the nervous system caused by stress.
So what is a skin rash?
It is generally accepted that a rash is caused by changes in the skin and (or) mucous membranes. Changes may include primarily changes in color, texture of the skin surface, peeling, itching in the red area and pain.
The rash can be localized in completely different places on the body, for different types of rash there are typical places of appearance, for example, rashes associated with allergic reactions most often manifest themselves on the hands and face, while manifestations on the surface of the body are more often associated with infectious diseases.
Remember, scratching the rash is unacceptable in any case, this will lead to even greater skin irritation and the possible formation of ulcers.
Types of rash
Primary - occur in areas of healthy skin or mucous membranes due to pathological processes in the body.
Secondary – arise at the site of the primary ones for certain reasons (for example, lack of treatment)
By far the most favorable from the point of view of diagnostic possibilities and subsequent successful therapy are primary protrusions. All protrusions differ in external characteristics such as size, shape, content, degree of color, grouping, etc.
Let's look at the main types of performances
Spot – Manifested by changes in skin tone or redness. It occurs in diseases such as syphilitic roseola, vitiligo, dermatitis, and birthmarks and freckles are also included in this type of manifestation.
| Spot on the skin |
Bubble – Located in the thickness of the skin, filled inside with hemorrhagic fluid, measuring from 2 to 6 mm, usually occurs with eczema, herpes, allergic dermatitis.
| Blisters on the skin |
Blister – Swollen redness with smooth edges, can be of regular or irregular shape, common causes of appearance: urticaria, insect bites, toxicoderma, usually does not require special treatment.
| Blister on the skin |
Pustule - a formation filled with pus in the layers of the epidermis, divided by type into superficial and deep. Accompanying diseases such as acne, impetigo, furunculosis, ulcerative pyoderma.
| Pustule on the skin |
Bubble – a bubble greatly enlarged in size, can reach a size of 100 mm.
| Blister on the skin |
Nodule – can be found in all layers of the skin, externally it looks like a change in the surface of the epidermis with redness and a difference in density from the surrounding tissues, usually ranging in size from 1 to 10 mm. Typical manifestations of the nodule are caused by: psoriasis, several types of lichen, eczema, papillomas, various warts.
| Nodule on the skin |
Allergy rash
The cause of constant skin itching and visible rashes on the skin is often an allergy; this is a fairly common occurrence in our time, about 70 percent of people are in one way or another susceptible to or have experienced allergic reactions.
What is an allergy? This is an aggravated reaction of the human immune system to an allergen that has entered the body, while in the process of getting rid of the presence of the allergen, a person’s blood vessels dilate, histamine is produced in large quantities, and redness, inflammation, swelling, and skin itching are almost always added to the above symptoms.
Attention! In the event of an acute allergic reaction with the formation of edema, the patient should immediately call an ambulance!
Allergic dermatitis also often manifests itself - when exposed to an allergen, a rash area forms at the point of contact, for example, when reacting to clothing - rashes in the waist, back and those places on the body where clothing fits most tightly to the skin, or when reacting to perfume or deodorant – in the area of greatest contact with the substance (often under the arms)
| Allergic dermatitis |
In a mild form of an allergic reaction, the symptoms resemble those of a cold: runny nose, possibly increased saliva and watery eyes. If you experience symptoms such as dizziness, tachycardia, convulsions and nausea, this may indicate a severe allergic reaction in which there is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Allergies can be caused by:
- Pet hair
- Plant pollen in summer or autumn
- Medications
- Food products (chocolate, milk, citrus fruits, etc.)
- Various nutritional supplements
- Substances contained in perfumes or household chemicals
- Substances that make up wardrobe items (fabric, metals, dyes)
Rash due to infectious diseases
Rashes in infectious diseases are often characterized by stages of appearance, first it appears in one place, then in another, also for each infection there are typical places for rashes, a specific shape and size, it is important to remember all the details and, when interviewing, report all this information to the doctor.
Below we look at rashes associated with various infectious diseases:
Rubella – in the initial stage of the disease, a small rash appears on the face and neck, then within 2 to 6 hours the rash spreads throughout the body. Usually appears as round or oval redness ranging from 2 to 10 mm in size. Remains on the skin for up to 72 hours, then disappears without visible traces. If you find yourself with a similar rash, you need to consult and examine a doctor, since similar rashes are symptoms of many infectious diseases. We also recall that rubella poses a particular danger to pregnant women, since if the mother is ill, the infection can harm the fetus.
Measles – measles disease usually manifests itself with catarrhal manifestations. The rash appears after 2-7 days. The primary places of protrusion are on the skin of the nose and behind the ears, then within 24 hours it spreads to the skin of the chest, face, then the arms and neck also become covered with rashes. After 72 hours, the rash also covers the legs; the rash is most often intense and confluent. After the active phase of the disease, the rash changes color and forms something like pigment spots.
Chicken pox – with the onset of the disease it manifests itself as red spots, then bubbles with a red ring and liquid inside appear, similar in appearance to dewdrops. After two days, the outer surface of the bubble collapses and becomes less elastic. Subsequently, the blisters become coarser, crust over and disappear within seven days without leaving any visible traces.
Scarlet fever — Rashes with scarlet fever appear 24 hours after infection, the areas of active manifestations are the back, groin, elbow and knee bends, and armpit skin. Then inflammation appears on the skin, sometimes there is a slight blue discoloration at the sites of roseola formation. The face with scarlet fever is usually not affected by a rash.
| Chicken pox | Scarlet fever |
Let's look at the reasons with photos:
Rashes caused by infection:
Herpes – a scattering of small transparent bubbles of regular shape forms on the surface of the skin of the face and lips, then within 72 hours the bubbles become cloudy, dry out with the formation of darkish or gray-yellow crusts.
| Herpes on the face |
Warts – the skin of the extremities is usually affected; they look like dense, rough, irregularly shaped formations of a grayish color.
| Warts on the hand |
Syphilis – the appearance of rashes generally always accompanies secondary syphilis; the rash is almost always varied in the visual signs of the elements and their number on the patient’s skin. Typically, a syphilis rash is not accompanied by any additional sensations or unpleasant effects, and after disappearance there are no traces left on the skin. Secondary syphilis is accompanied by spotty rashes, which are characterized by a symmetrical arrangement, brightness and abundance. After 60 days, the rash usually goes away, after some time the rash appears again, not as abundant, more dull in color, localized in places of skin trauma, between the buttock muscles, in the groin, on the shoulders and on the chest.
| Secondary syphilis |
Candidiasis – (yeast diaper rash) the usual places of manifestation are in the area of folds of the skin, folds of the abdomen, most often affects overweight people, the first stage of the disease is accompanied by small blisters and pustules, which, when bursting, transform into wet erosions of a reddish-brownish color, showing a tendency to merge . Cracks and accumulations of whitish, mushy tissue form on the surface of the patient's skin.
| Candidiasis |
Scabies - as a rule, it is usually manifested by the formation of blisters, vesicles or papules at the site of penetration of the parasite into the skin, so-called scabies burrows are also noticeable on the skin, they look like a whitish bulging line with a bulge at the tip, the disease is characterized by severe itching, intensifying at night . Most common on the arms and legs, these tend to be the feet, wrists and hands.
| Scabies |
Pityriasis versicolor – a disease caused by a fungus, characterized by low contagiousness and associated with excessive sweating. The development of the disease begins in the area of the hair follicle, where yellow dots appear, after the dot they increase in size and turn into yellowish-brownish spots with visible borders, ranging in size from 10 mm or more, the skin in the affected areas is covered with pityriasis-like scales.
| Pityriasis versicolor |
Pityriasis rosea – at the beginning of the disease, a red-pinkish spot appears on the skin of the chest and/or back with peeling in the central part, after which a spot-like rash of usually symmetrical shape forms on other parts of the body.
| Pityriasis rosea |
Shingles – manifests itself in the initial period as a group of blisters up to 50 mm, localized on one side of the chest, abdomen, head or shoulder; when they appear on the affected area, sensitivity worsens, accompanied by pain; after the blisters disappear, areas of hyperpigmentation and/or scars remain on the skin.
| Shingles |
Lichen planus - usually the rash appears in the form of clusters of nodules and forms lines, rings or arcs on the skin with equidistant elements. Common sites of injury: torso, inner surface of extremities, genitals. The disease causes itching.
| Lichen planus |
Molluscum contagiosum – shiny bubbles with smooth walls, translucent with a typical inclusion of pinkish, reddish or yellow colors in the center, with sizes from 2 to 10 mm. Upon palpation, white mushy contents are released.
| Molluscum contagiosum |
Rubrophytia – a disease of a fungal nature, in one hundred percent of cases a person’s feet are affected, at the initial stage it is keratinization and peeling of the skin between the 3rd and 4th toes; during the course of the disease, manifestations in the form of erosion and blisters are possible; if the disease develops, the entire surface of the foot is affected.
| Rubrophytia |
Ostiofolliculitis – pustules up to 3 mm containing whitish-gray pus inside with a pink border around the circumference, frequent places of manifestation are the face, scalp, places where the surface of the extremities is folded, within a week the pustules dry out with the formation of a yellowish crust, after the crust comes off, signs of peeling remain and age spots.
| Ostiofolliculitis |
Athlete's inguinal – skin lesions are usually in the area of folds in the groin (locations may vary). In the initial stage of the disease, spots of a reddish hue of regular shape and with an unchanged surface appear. As the disease progresses, the heel usually merges and forms a lesion on the skin with scalloped borders. The main area of the lesion is covered with crusts, erosions and scales.
| Athlete's inguinal |
Rash of non-infectious nature:
Hives – blisters of large and medium sizes that suddenly appear and sometimes merge with each other. There is a pinkish border at the edges; the central part of the blister has a dull appearance.
| Hives |
Acne – can appear all over the body, but more often occur on the face, usually during puberty, and are divided into comedones (clogged pores), papules, pustules, and cysts. With illiterate treatment and an advanced form, scars may appear on the skin after treating acne on the skin.
| Acne |
Lupus erythematosus – manifests itself primarily in open areas of the body: the upper body, face, head, neck; skin changes are often noticeable on the cheeks and bridge of the nose, shaped like a butterfly with wings.
| Lupus erythematosus |
Vitiligo – white spots of various shapes and sizes become noticeable on the skin; the spots may merge into one.
| Vitiligo |
Solar keratosis – formed as a result of excessive exposure to sunlight on unprotected skin, looks first as redness then as a keratinized dry crust, affects mainly older people; if not treated in time, carcinoma (skin cancer) can develop
| Solar keratosis |
Psoriasis – characterized by the appearance of a large number of bright pink papules covered with scales; as the disease progresses, the number of papules increases, they merge into large plaques, most often the rash at the initial stage appears in the area of the bends of the elbows and legs, as well as on the head.

Skin rashes appear as a sudden appearance on the skin in any area of the body. The rash is characterized by changes in the skin, redness or blanching, and itching. A symptom can form as a local reaction to external provoking factors or manifest itself as a sign of the development of a pathological process. There are quite a lot of diseases that manifest themselves in the form of skin rashes, therefore the etiology of the symptom is varied.
Etiology
Skin rashes in adults and children can be formed under the influence of the following factors:
- infections;
- allergy;
- disease of the blood and blood vessels.
The most common cause of symptoms is considered to be infectious infection. Doctors include such diseases as measles, rubella, chickenpox, scarlet fever, herpes, etc. These diseases manifest themselves in a characteristic rash, which is accompanied by high fever, loss of appetite, chills, pain in the head, throat and abdomen, runny nose, cough and stool disorder.
Allergic skin rashes are also often diagnosed by doctors. This form of symptom development can be recognized by the absence of signs of infectious infection, as well as contact with the allergen. Very often, parents can notice a similar reaction on the child’s body. Provoking factors include food, animals, chemicals, and drugs.
If blood circulation is impaired and vascular disease, the patient may experience a rash for the following reasons:
- decreased number or impaired functionality of platelets;
- impaired vascular permeability.
Sometimes a symptom develops in non-infectious diseases, these include:
Skin rashes form due to liver disease. If the organ's functioning is disrupted, the patient's skin tone changes and a rash appears.
Characteristic red rashes can be from insect bites, acne, psoriasis, fungal diseases and scabies. Also, redness on the skin can be caused by prickly heat.
Classification
Clinicians have determined that the types of rashes can include the following manifestations:
- spots – there are red, brown, white macules;
- blisters - appear as a dense and rough formation on the skin;
- papules - an element that looks like nodules in the thickness of the skin;
- blisters - they can be large or small, formed in the skin cavity with a clear liquid;
- erosions and ulcers – when formed, the integrity of the skin is compromised;
- crusts - appear on the site of former blisters, pustules, ulcers.
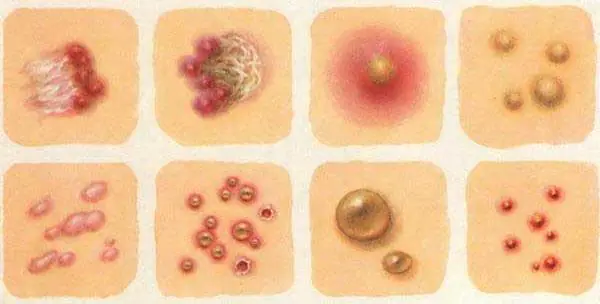
All of the listed types of rashes on the body are divided into primary and secondary. The first type includes nodules, blisters, ulcers, and blisters. And the second group of types of rash consists of the appearance of peeling, erosion, abrasions, and crusts.
Symptoms
If skin rashes in children and adults develop against the background of deteriorating liver function, then characteristic symptoms may indicate this:
- yellow tint of the skin;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- foul odor;
- heavy sweating;
- pain in the liver area;
- itchy rashes on the body;
- sudden weight loss;
- broken stool;
- brown tongue;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- the appearance of cracks in the tongue;
- elevated temperature;
- venous pattern on the abdomen.
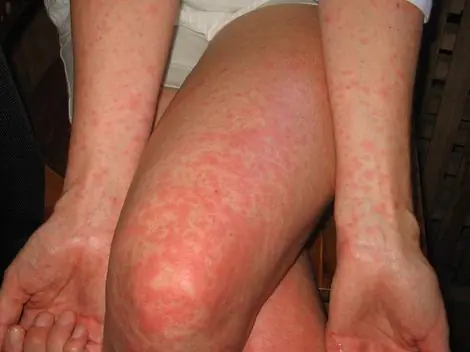
If the cause is an infectious disease, then a person’s skin rashes can begin on the skin of the hands, move to the face, legs, and gradually affect the whole body. With rubella, the patient is first overcome by a rash on the face and spreads throughout the skin. The first foci of inflammation are localized in places where the surface of the limbs is most often bent, near the joints, on the back and buttocks. All rashes can be of different shades - pink, red, pale, brown.
Infectious pathologies often manifest themselves not only in rashes, but also in other signs. The disease can be established in more detail using the following clinical picture:
- elevated temperature;
- malaise;
- weakness;
- painful attacks;
- certain areas on the patient’s body become inflamed, for example, eyes, tonsils, etc.;
- may be photophobia;
- rapid heartbeat;
- drowsiness;
- itching;
- burning.
Rashes on the skin in the form of red spots are characteristic of the development of such infectious diseases as chickenpox, rubella, measles, scarlet fever.
Diagnostics
If any manifestations of the above symptoms are detected, the patient should urgently seek the help of a doctor. You can consult an allergist or infectious disease specialist about skin rashes. After an initial physical examination and minimal testing, the doctor will refer the patient to another specialist if the cause of the illness is not inflammation, allergy or infection.
Treatment
Treatment of allergic skin rashes is prescribed by a doctor only after diagnosis has been made. Therapy is based on eliminating the etiological factor, so the drugs must be selected accordingly.
If a person develops a rash from mechanical damage or prickly heat, then there is nothing wrong with such a manifestation. At home, you can anoint the inflamed area with cream or oil to slightly relieve swelling and itching. Over time, the symptom will disappear. You can also eliminate the symptoms of the disease at home with the following advice from doctors:
- wear things made of natural cotton to avoid irritation;
- wash the body with baby soap or shower gel;
- Eliminate from life all things that can cause skin rashes.
If the patient’s symptoms are more pronounced, have characteristic indicators, and cause discomfort to the patient, then a consultation with a dermatologist is necessary.
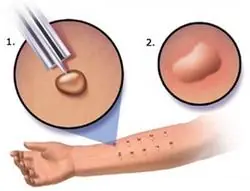
If the disease is caused by an allergy, then it is important for the doctor to identify this allergen using a test and then prescribe treatment. The patient must move away from this item or remove the product from the diet. This symptom can also be cured with antihistamine ointments and tablets.
In case of food allergies, doctors always prescribe the enterosorbent Enterosgel in a course to remove allergens. The drug is a gel soaked in water. It gently envelops the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, collects allergens from them and removes them from the body. An important advantage of Enterosgel is that allergens are firmly bound to the gel and are not released in the lower intestines. Enterosgel, like a porous sponge, absorbs mainly harmful substances without interacting with beneficial microflora and microelements, so it can be taken for more than 2 weeks.
If an external sign, namely a rash, has developed from a virus, and the symptoms of the disease are supplemented by fever, then the patient can be given antipyretic medications. When the disease becomes more complicated, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed.
Quite often, skin rashes due to diabetes, liver disease, infectious diseases or allergies are not very easily recognized by doctors, since the symptom often manifests itself in the same indicators - itching, redness, swelling. In this regard, doctors first prescribe therapy to the patient, which is aimed at getting rid of the signs, and not the causes of the disease.
Effective treatment uses comprehensive measures to eliminate the clinical picture, within which the patient must comply with the following methods:
- daily regime;
- take medications;
- diet;
- psychotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, the patient must adhere to special rules. If a person knows that he is allergic to certain things, then it is advisable to immediately distance himself from them and eliminate all allergens from his life. To prevent rashes from fungi and infections, doctors advise following these measures:
- take care of personal hygiene - wash the body, wipe dry, trim nails and keep the ears clean;
- do not share personal belongings with strangers and do not use other people’s towels, toothbrushes, do not change clothes and slippers;
- wash clothes regularly;
- clean the room from dust.
To reduce the risk of heat rash or damage, you need to use special creams, dress according to the season and be careful when traveling to the forests and mountains.



