Almost every person has a mole, or non-tumor nevus.
This is an area of skin with a darker pigment color, of various shapes and sizes.
There are formations from light beige, almost invisible on human skin, to dark red and even black.
Most of them are completely safe for children (and adults).
But others are capable of causing fear in their rebirth, and bring trouble.
Moles most often appear between six months and four years. Then the appearance of nevi slows down and the next peak occurs in adolescence, which is due to hormonal changes in the human body. The baby is born, as a rule, with clear skin.
Exceptions also occur and are called birthmarks, which are usually more common in fair-skinned and fair-haired girls. Dark-skinned children are less likely to have moles from birth.
The formation of moles on human skin is a natural process. and is caused by the work of melanocytes, cells that determine skin color, provide tanning and give color to moles and other pigmented formations.
Reasons for appearance
- The most common and natural one is genetic. The number and location of nevi in a child directly depends on the number and location of them in his immediate family. Hence the name of education.
- Internal reasons. Hormonal. The peaks in the formation and disappearance of birthmarks directly depend on the peaks of hormonal changes in the human body, so the first occurs during the period of 2-3 years, the second during adolescence; often during pregnancy, a woman can also notice the appearance or disappearance of nevi. And this process is also natural.
- External reasons. First of all, the activity of melanocytes is influenced by solar activity and the effect of ultraviolet radiation in particular. Under the influence of this particular radiation, a mole can change its size, color, and even degenerate into a deadly disease - melanoma.
- A less common reason (and not yet fully proven) is traumatic. According to this hypothesis, the formation of foci of hyperpigmentation in children can form in the post-traumatic period, after suffering insect bites, skin injuries, as well as viral infections.
Doctor Komarovsky about moles in children
A mole, according to Komarovsky, is a formation in which cancerous (malignant) cells may appear. But it is not a reason to panic. Rather, it should serve as an impetus for obtaining more information about the peculiarities of the functioning of your body (and the child’s body).
A mole is in most cases completely safe; you can live with it (and even if there are many of them) quite comfortably all your life until a ripe old age. Moreover, Evgeniy Olegovich identifies two series of factors that determine the presence of moles in a person and monitoring their safety.
- Genetics or hereditary factor. We cannot influence her in any way. If the baby’s relatives have a scattering of areas of hyperpigmentation on their skin, it is not surprising that the child also has a lot of them.
- The second very important factor is solar Activity. Due to their direct effect on the activity of melanocytes, the sun and ultraviolet radiation in particular are directly related to the number of moles on the skin of both adults and children.
Moreover, ultraviolet light is an aggressive factor that contributes to the degeneration of nevus into a more dangerous form of hyperpigmentation - deadly melanoma.
The third factor that Dr. Komarovsky pays attention to is traumatic damage to moles. Moreover, permanent damage is dangerous. A one-time injury to a nevus, apart from more intense bleeding, cannot cause much concern.Which ones are dangerous?
For a qualitative assessment of the danger of a nevus Komarovsky recommends examining the child twice a year and make a map of the moles of him and his immediate family.
The doctor compiled an easy-to-memorize and quite informative “AKORD” system. What does this mean and how to use it?
Main characteristics of a mole, they also determine the degree of its safety for the body as follows:
- Asymmetry. If you virtually draw a straight line through the center of the mole, both parts should be mutually symmetrical. Otherwise, you should contact a specialist.
- The edges. Moles with even edges, smooth and rounded are safe and do not require contact with a specialist. You should consult a doctor if the edges are jagged or have unclear boundaries.
- Uniformity of color. The color of the nevus itself does not matter much, be it beige, deep brown, wine red or even black. The main thing is that it must be homogeneous.
- Size. A mole size up to 6 mm in diameter is considered safe (for comparison, this is the diameter of an eraser on a standard pencil).
- Growth dynamics. If the mole does not change significantly in size and there is no visible change within a month, it is safe. Anxiety can cause a noticeable increase within one month.
How to care?
Moles are smooth, do not protrude from the surface of the skin and are not subject to constant trauma and do not require special care. When visiting the beach they, like the rest of the skin, should be protected both by sunscreens and by not visiting the beach during peak solar activity (from 12 to 16 noon).
In the case where hair grows from a nevus, this is a cosmetic defect, but it is better to remove it simply by cutting it off, plucking it, or using creams or other methods of depilation.
What is a nevus map?
A mole map is needed to track when new moles appear and how old ones change. It is individual for everyone. It contains information about the location, size, color, symmetry, growth dynamics and edges of moles (that is, all information according to the AKORD system).
Thanks to this map it is possible to detect disturbances in areas of hyperpigmentation in a timely manner and contact a specialist, since although melanoma is often common, its cure with timely treatment reaches 95%.
- Examine the front surface of the body, right and left side with raised arms.
- Examination of the hands, the front and back of the shoulder, forearm and palm.
- Examination of the back of the body and buttocks.
- Examination of the legs, front and back of the thigh, lower leg and feet.
- Examination of the back of the head.
All enter the detected formations into the table indicating the location and characteristics of AKORD. Carry out an inspection twice a year.
How to prevent melanoma?
The best A way to prevent melanoma is the correct attitude towards the sun. And minimizing its negative impact on the child’s skin, including moles.
- Be sure to use a waterproof sunscreen with SPF 30+ or higher.
- Renew the protection every 2 hours (reapply the product to the skin of the body and face), as well as after each bathing.
- Do not specifically look for the sun, and also, if possible, do not sunbathe during the period of peak ultraviolet activity (from 12 to 16 pm).
- Stay in the shade if possible.
- Be especially careful where there is water, sand and snow. Because their reflective properties enhance the negative effects of sunlight on the skin.
- Avoid sunbathing. To give the appearance of tanned skin, use self-tanner. But under no circumstances should we refuse Sanskrins.
- Know your moles.
Thus, although a mole is a group of cells that can degenerate into a malignant form, if treated correctly, treated with care and regularly examined, they are not a cause for panic.
Watch a video on the topic:
Modern science cannot answer the question of where moles come from on children’s bodies. Some children have spots on their bodies from birth, while others develop them over time. But there are also those who are lucky to have clear skin.
Doctors never stop saying that it’s all due to heredity, namely genes passed on from generation to generation. Multiple moles can appear without causing harm, but can also be dangerous if they are cancerous.
What types of nevus occur in the plural?
Nevus has the following forms:
Borderline and complex forms often appear in the plural. Complex nevi often reach 10 millimeters or more. They are characterized by a dense consistency and spherical shape. Often such a nevus is called mixed due to its original color.
The borderline type of nevus is considered to be uniform, pigmented spots with an oval or round shape. Such spots have a clear border and a smooth surface. There is no hair on such nevi.
And they arise from birth. Localization includes the torso, neck, face, and external genitalia. The color range of moles can be different - light brown or dark brown.
Why do many moles appear on a child’s body?
Why does a child have many moles? The process of formation and change in the size of nevi is influenced by such reasons as:
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Baby's mobility.
- Predisposition to the formation of moles.
Using genetics, you can determine the age of a child at which spots will begin to appear on his body. This could be 5 or 10 years of life. Many doctors say that nevi in males appear at a more mature age, while in girls they appear from early childhood. Genetics also influences the multiplicity of moles on the child's body.
The size of moles, as well as their number, depends on the presence in the baby’s body of special cells called melanocytes. They are located in the inner layers of the skin. Moles on a child’s body are common.
Therefore, if there are few of them, there is nothing to worry about. However, if you notice how they begin to enlarge and change their color, this is a reason to think about visiting a specialist.
What is dangerous when children have too many of them?
If parents are worried about spots that have appeared on the baby’s body, they should definitely contact a dermatologist or pediatrician. The doctor will conduct an examination and determine how dangerous it is for the child’s health. Malignant pigment spots at a young age are not a common occurrence. But, it is important to ensure that the moles do not become even larger.
It is also important to take into account the child's reaction for such education. Often nevi appear on the skin due to decreased immune defense. This can also cause changes in the size and color of moles.
Often, inflammatory processes can bother a child when birthmarks degenerate. Taking this information into account, we can say that even barely noticeable nevi can be very dangerous.
But don’t sound the alarm ahead of time. Degeneration of moles is quite rare. Moreover, this does not depend on the number of spots that occur on the baby’s body.
In medicine, there is a special classification of nevi. They can be vascular or regular. The former differ in their structure, since they contain blood vessels.
Their color can take on different shades - from pink to red. Red moles are not dangerous, but in some cases they are removed because such formations do not look aesthetically pleasing.
The second type of moles is considered common. They often have a smooth surface. They take on a light brown or black tint. and their appearance can be observed in the first years of a child’s life. When hair grows in this area, it is considered a good sign. You need to worry about moles that are located on the palms or soles of your feet.
Should I delete it if the quantity starts to bother me?
Many children develop moles at a very young age. This phenomenon is absolutely normal. You can only be wary if many moles appear in 2-3 months. In this case, it is better to visit a dermatologist or oncologist.
The doctor will examine the moles on the baby’s body and tell you about the reason for their multiple appearance. Often, nevi appear as a reaction to tanning and other external factors. In rare cases, they can talk about pathologies associated with the immune system and diseases of the internal organs.
The indication for removal of moles is the threat of degeneration to cancer. The degree of danger is assessed by an oncologist. Doctors say that you should not touch nevi with your hands, as this can lead to their degeneration.
But often they appear in places where a child can catch them with clothes or shoes. Removing nevi is in some cases a simple necessity. But even after a minor operation, a number of complications associated with bleeding and allergies to anesthesia can occur.
Nowadays, the most popular methods of getting rid of moles are:
- surgical.
- Laser cleaning.
- Use of liquid nitrogen.
- Cauterization with electric current.
- Radio wave.
The choice of method is made by the doctor, since it takes into account the properties of moles. Often, tumors similar to cancer are removed with a scalpel in order to completely rid the body of infections. In other cases, cryodestruction and laser cleaning have become extremely popular. Such methods are considered the safest.
The wound at the site of the mole should be treated until complete healing. Using ointments you can speed up this process. To prevent infection from getting into the wound, you need to take into account the following tips:
- You can’t get the crust wet and tear it off.
- It is important to ensure that the wound does not get exposed to the sun. Before your child goes out into the sun, cover it with a plaster.
If a mole has been removed surgically, then its complete healing can be observed after 2 weeks. As for the other methods, they are less painful and the unpleasant sensations will not last more than 7 days.
It is very rare to observe wound inflammation due to infection. In this case, healing may be delayed, and scars may remain after it.
What should I do to prevent the problem from returning again?
A mole is a congenital malformation of the skin or a benign tumor that forms at different stages of life. The following actions can be taken to prevent nevi:
control over exposure to the sun.Your child should not be under the sun at dangerous times, namely from 11.00 to 16.00. if this cannot be avoided, it is important to wear clothes made from natural fabrics to protect the skin and also to avoid overheating. Don't forget about the need for a headdress.
Using sunscreen.Despite the degree of dark skin, children are exposed to the sun much faster than adults. This is why it is worth applying sun protection cream to exposed areas of the body. Wearing loose and comfortable clothes and shoes from natural materials. Nowadays, many modern parents are trying to buy stylish things for their children.But during the summer season and hot days, it is important to consider not only the beauty, but also the safety of certain items of clothing. Often they protect against the harmful effects of the sun and the appearance of moles.
Conclusion
If multiple moles still appear on your baby’s body, be sure to consult a dermatologist for a detailed examination. This way you can rest assured that your child is not in danger.
Most often, children develop normal nevi that do not cause much discomfort. They do not itch or bleed, which means they have no effect. But it is important to check them too, especially if you notice changes in the size of moles and their color.
To record the changes, it is important to undergo examinations by a doctor in order to avoid any unpleasant consequences. This is the only way you can protect your child from problems with nevi in the future.
Small formations that differ in color from the skin are common to most people. These structures have different origins and structures, so it is difficult to name one reason why moles appear. More often than others, benign nevi, papillomas, and hemangiomas occur in humans. The appearance of a neoplasm can occur before the birth of the child, then the baby will be born with a birthmark. As you age, your likelihood of developing moles increases.
What causes moles to appear?
Healthy skin contains a significant number of melanocytes, the function of which is to protect the underlying tissues from ultraviolet radiation. The accumulation of melanin under the influence of sunlight is manifested by a uniform darkening of the skin - tanning. Due to a number of reasons (trauma, burns, hereditary predisposition), melanocytes are able to become activated, and dark spots appear on the body. A type of age spots are ephelides or freckles, characterized by seasonal variability in color.
The bulk of moles are nevi - congenital malformations of the skin. Acquired nevi can appear throughout life; with age, the likelihood of skin tumors increases. Where do moles on the body come from? The main reasons are related to the following conditions:
- excessive sun exposure;
- heredity;
- prolonged mechanical irritation of the skin from clothing parts;
- contact with various chemical agents;
- traumatic skin damage;
- age factor;
- inflammation of the skin of any origin, including allergic;
- hormonal dysfunction.
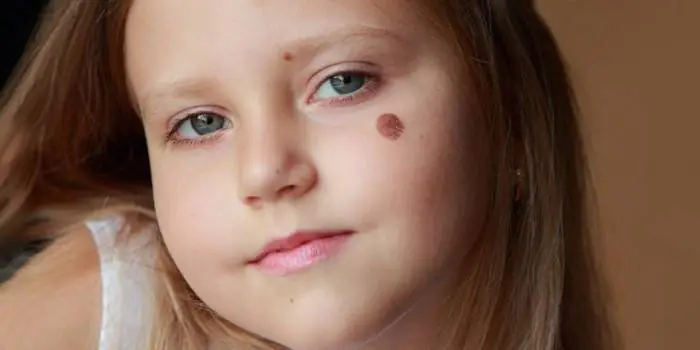
The vast majority of nevi in children are congenital. In newborns, moles are often invisible; they appear over time, gradually acquiring pigmentation. Immediately visible are formations of another, vascular origin - hemangiomas. Pink, red, brown, purple spots fade when lightly pressed, which makes them look different from moles. In children, flat viral warts look like nevi.
Changes in hormonal levels activate the accumulation of pigment in specific melanocyte cells. A pregnant woman's skin may generally darken, and uneven spotting of the face, arms, and lower abdomen often appears. Moles during pregnancy affect only the epidermal layer of the skin, so they are not convex and cannot be detected to the touch. They can disappear on their own over time or become noticeably pale.



