According to popular beliefs, moles are special marks that carry information about the fate, character, hidden potential and natural abilities of a certain person. And if there are many such signs, then the person marked by them should be incredibly happy in life.
Causes of moles
The appearance of moles on the body is explained by several reasons: heredity, weak immunity and the result of direct exposure to sunlight, to which the head is most exposed. If nevi (the medical name for moles) are well known to their owner, do not bother them, do not grow or change color and shape, there is no need to worry too much.
According to their structure, moles are divided into:
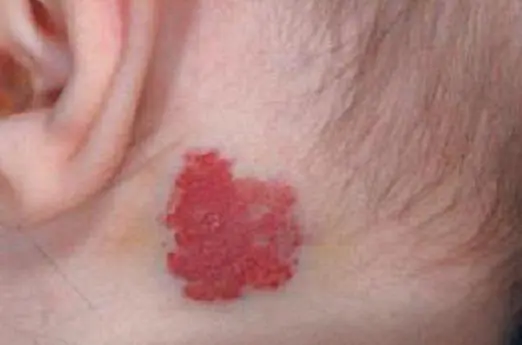
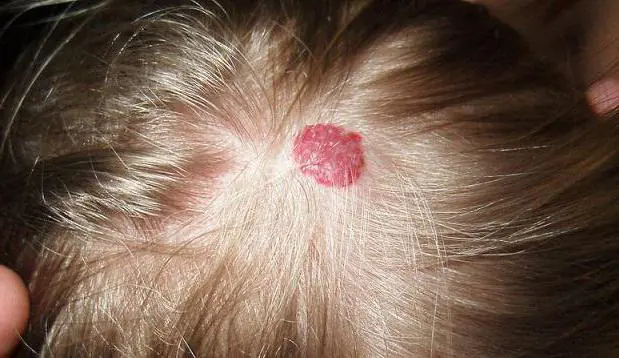
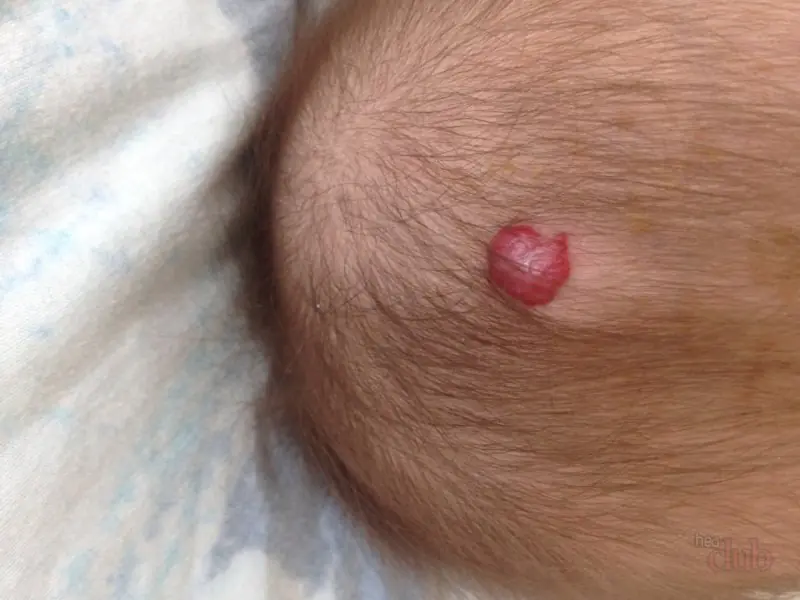
- Vascular. (Looks like a red mole on the head, formed with the participation of blood vessels that form nodules as they grow).
- Non-vascular. (They are the result of an accumulation of melanocytes (pigment cells), the number of which determines the color of the nevus; the more there are, the darker the mole).
Shapes of moles
A mole on the head in the hair also varies in shape and can be flat or convex. The flat formation is located in the upper layer of the skin and looks like a spot. Usually it does not require special attention, since it does not cause concern to a person. A convex nevus rises above the surface of the epidermis, sometimes has some resemblance to warts and is always at risk of injury. If for some reason a mole on the head is damaged, you should immediately stop the bleeding using a tampon soaked in hydrogen peroxide. Apply dry gauze folded several times to the affected area, press it to the wound and hold it there for 5-10 minutes. Then be sure to contact a medical facility for help. The partially torn mole will be professionally removed by specialists and immediately sent for analysis. If the nevus is completely torn off, the latter must be wrapped in gauze moistened with saline solution and also submitted for histological examination, which makes it possible to determine the type of neoplasm and make the correct diagnosis. Such analysis is an indispensable basis for recognizing cancer diseases.
How to care for a mole on your head
Moles on the head (photo) are not only a cosmetic defect; This is a fairly serious problem that requires close attention and careful handling.

Caring for a mole of this type should be very careful and careful. You should not use peelings and scrubs in the place of its formation, in particular on the head. The mole may be located under the hair, so you need to comb it carefully, try to knead the area and not touch the skin in this area with the comb. You need to make sure that the nevus is not put under pressure by a headgear or glasses. It is imperative to monitor the size, shape and color of the mole on the head and consult a doctor in case of any pathologies.
No self-medication!
A large convex mole on the head or under the hair most often needs to be removed, especially if it creates a clear aesthetic defect. It is highly not recommended to take independent measures to remove a mole (tying with red thread, using celandine, etc.). Even if good friends gave valuable advice, and they helped someone, you should not touch the mole! You should not cover large nevi with a band-aid, as this will create a greenhouse effect - comfortable conditions for the degeneration of a harmless mole into a dangerous melanoma. The very first step in caring for or removing a tumor should be to contact a dermatologist.
Signs of degeneration of a mole on the head
Any mole on the head under the hair, when exposed to certain internal and external factors, is at risk of becoming a malignant formation. Therefore, sometimes its removal, especially in the scalp, is the best option to avoid a much greater danger. There are 5 signs by which you can determine the degeneration of a mole and start sounding the alarm:
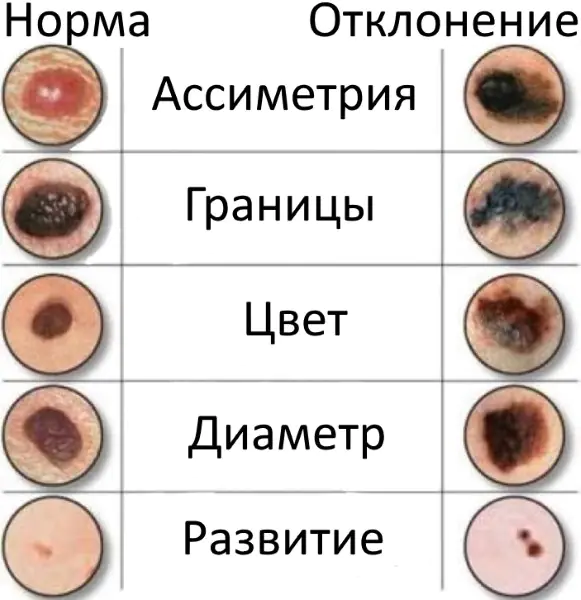
- Asymmetry. Using an imaginary axis, you need to divide the mole into two parts; a bad nevus will have halves of different sizes. In clinics, for accurate diagnosis, they use a special drug that evaluates the mole using a 12-axis method.
- Color. A mole located on the head has changed color: it has turned black or red, and the skin around it has turned white.
- The edges. Changes and irregularities are observed along the contour.
- Dimensions. Large moles (more than 6 mm) are most likely to degenerate. Although there have been cases of transformation into melanoma of a 1-mm nevus.
- Dynamics. The manifestation of various external changes - peeling, crusts, cracks, bleeding, up to the sudden disappearance of the mole.
When to see a dermatologist
If you detect at least one of the 5 signs, as well as pain in the mole or its damage, you should immediately consult a doctor. The specialist will tell you the sequence of further actions: either removal of the tumor, or further monitoring of it and careful care.
The transformation of a mole into melanoma can be confirmed by clinical diagnosis at the first stage and epiluminescent computer dermatoscopy at the second. Under no circumstances should you do a biopsy of the tumor - an examination that involves removing a piece of material. The diagnosis of melanoma can be refuted or confirmed only after a histological analysis.
Hair on a mole: how to get rid of it
You cannot remove hair from moles; it is recommended to simply cut them off. By the way, vegetation on a nevus is a good sign, indicating a high degree of cell maturity and a minimum chance of degeneration into melanoma.
Why do you need to get rid of a mole?
Nevi located on the head, especially in the scalp, most often need to be removed. Reasons confirming the correctness of this decision:
- high probability of damage;
- regular exposure to cosmetics (shampoo, soap, skin care products);
- incomplete protection from ultraviolet rays (moles on the head receive them many times more than on other parts of the body);
- aesthetic unattractiveness.
Should I delete or not?
You should definitely listen to your own intuition and feelings. Maybe a mole located on the head does not interfere at all, and the person is accustomed to its presence. Then extreme caution should be exercised in relation to such a problem area. In any case, you will need competent consultation with a specialist who is able to assess the potential danger of pigment formation and suggest what measures are best to take: regularly monitor or remove.
Ways to remove moles
Surgical method. The mole is cut out along with adjacent tissues. The disadvantage of this method is the scar at the excision site. Advantage: the ability to take material for histological analysis.
Laser. It is low-traumatic, safe, painless, which is why it is most in demand. The laser beam, which has a bactericidal effect, stops bleeding without causing complications. In addition, after the procedure there will be no scars left on the skin: only nevus cells will be removed, without affecting the surrounding tissues.
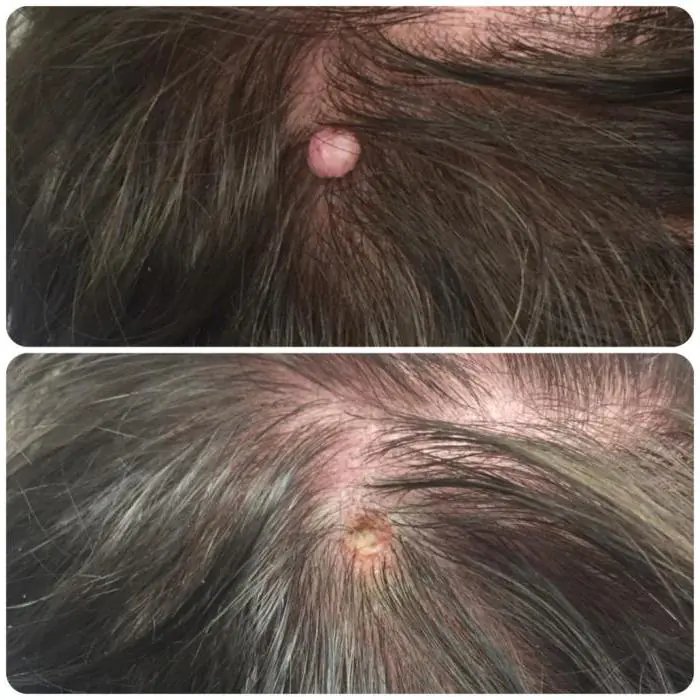
Cryodestruction. The destruction of nevus tissue is carried out by ultra-low temperature liquid nitrogen (down to -196 o C), which is enough to instantly freeze and destroy any organic formation. The procedure takes from 10 seconds to 3 minutes and does not cause any pain.
Electrocoagulation. A method in which the mole is exposed to high-frequency current discharges, playing the role of a kind of scalpel. With the help of delivered discharges, micro-incisions are made step by step, cutting off the mole in small layers. The strong thermal effect generated by the electric field prevents bleeding, thereby minimizing the risk of infection.
Radio wave. A gentle, non-contact technique based on careful tissue cutting and the literal evaporation of pigmented cells using radio waves. The advantage of this method is the absence of physical pressure on the upper skin layers, painlessness, absence of scars and cicatrices, and the possibility of histological analysis.
If the mole is benign, then it is better to choose the least painful method, after which the lesion will quickly heal and will not remind you of the operation with scars or scars. If a tumor is suspected of being malignant, it is better to use a method that allows for histological analysis of tissue.
What does a mole on the head mean?
Each mole carries certain information about a person. Located in the hair, it is a favorable sign and is found in people who are capable of thinking. It most often marks great minds and outstanding researchers. A hidden and invisible mole will indicate a secretive person.
Pigment formation on the crown of the head, a special energy point, is characteristic of people with extraordinary thinking abilities. These individuals can easily achieve success in professional and intellectual fields and are able to lead a detached lifestyle. Often such people have the gift of clairvoyance, but not everyone knows how to properly develop this potential.
A mole on the back of the head is inaccessible to the eye of its owner, whose characteristic signs are isolation and aloofness. Such a person will never flaunt his personal life and will not discuss his own problems with others. It is quite difficult to have a conversation with him.

The temples are considered a very vulnerable area, so a mole in this place will indicate a person’s high sensitivity and vulnerability. True, it is not always possible to guess this: the closer the nevus is located to the hair, the more carefully the person hides her vulnerable nature. A mole located on the right temple will reveal a special person, with developed intuition, who can subtly grasp the mood of his interlocutor and delve into the true reasons for his actions. This allows him to quickly assess any situation and make smart decisions.
A mole on the top of the head portends success and wealth, and the darker it is, the more significant these benefits will be.
A mole on the forehead is a symbol of success
A mole in the upper part of the forehead indicates a courageous and strong-willed person, capable of achieving success in any field. Those around him easily obey his charisma. Such individuals make good politicians. The lower the mole is located in the forehead area, the less strong a person’s character, even weak-willed.
Wherever a mole is located on the head, it can have both positive and not very pleasant meaning for its owner. In any case, such pigment formation requires special care and supervision from a specialist. Otherwise it can become a source of big problems.
A mole (nevus) is a widespread benign pigmented formation consisting of melanocyte cells that produce melanin. Due to the excess amount of pigment, which is concentrated in certain areas of the skin, a birthmark is formed.
It can form in a child at birth or occur after some time. The bulk of moles appear during puberty or during pregnancy due to hormonal changes in the body.
Nevi are localized on any part of the skin and mucous membranes (mainly in women). In 20% of people, neoplasms occur on the head in the hair (on the back of the head, crown) or on the temples.
Moles in hair, what is the danger
Due to this location, a mole on the head (especially hidden in the hair) goes unnoticed for a long time. It is more susceptible to injury than other areas of the body. It can be damaged when wearing an uncomfortable headdress, when combing, cutting, styling and even washing your hair. Regular exposure of the birthmark to hair care products can cause irritation, swelling, and itching.

It is believed that not all moles have the ability to degenerate into a malignant tumor, but only a few under the influence of certain factors.
Causes of moles
The mechanism of the appearance of birthmarks has not been fully studied, but it is known for sure that such formations are formed as a result of excess content of the melanin pigment.
Also, the appearance of moles is the result of uncontrolled cell division, which the immune system cannot cope with on its own.
There are also some additional factors that provoke the appearance of birthmarks:
- excessive sun exposure;
- frequent visits to the solarium;
- hormonal disorders;
- X-ray and radiation exposure;
- genetic predisposition;
- pathological changes in the functioning of internal organs and systems;
- skin aging;
- repeated injury to the epidermis.
Nevi can change throughout life: grow, change color, shape, sometimes disappear completely or appear in a new place. And it is important not to miss the appearance of dangerous signs of their degeneration into a malignant tumor.
What are the types of moles on the head?
Formations can be different in their structure, shape, and size. There are the following types of moles on the head:
- Large - is a congenital skin defect, has a brown color. It grows with a person and can reach significant sizes.
- Convex - a formation of red, brown or burgundy color that occurs in the inner layer of the skin and rises above it. Often the mole is covered with hairs. This type of mole appears in adulthood and there is a significant risk of damage.
- Flat is the most common type of birthmark on the head. It is located at the same level with the skin and does not cause discomfort to the owner of such a mark.
- Blue is very rare, but this does not mean that it is more dangerous than others. This formation is cone-shaped, bluish in color and protrudes slightly above the level of the epidermis.
- Hanging (in the form of a wart) are rarely found on the head. They are easily damaged and therefore require removal.
- A red - vascular mole is formed at birth; as the child grows older, it can disappear on its own.
How to understand that a neoplasm is not malignant
A benign formation must have the correct shape, small size, symmetry, clear contours, even color, uniform structure, and absence of discharge.
Quite often, hair grows from a mole, which is considered normal and should not be a cause for concern.
If the tumor meets these criteria, then everything is in order.
Differential diagnosis of a mole and skin cancer
All people with birthmarks should closely monitor them, especially those who have a family history of cancer. At the first suspicious symptoms, it is recommended to urgently visit a doctor, who, through diagnostic measures, will find out the cause of this transformation and determine the degree of danger to the person.
The appearance of a malignant tumor is the result of uncontrolled cell division.
To make a diagnosis confirming or refuting the nature of the tumor, a large number of techniques are used:
- visual examination of the mole and medical history;
- blood test - helps to identify a tumor marker characteristic of melanoma;
- dermatoscopy – allows, by magnifying the skin tenfold (using a dermatoscope), to examine not only the upper layer of the epidermis, but also the deeper layers of the skin;
- biopsy - to remove the affected tissue to determine the nature of the formation;
- ultrasound examination - allows you to assess the condition of the lymph nodes, measure the thickness of melanoma and determine the extent of its spread;
- computed tomography – helps to identify metastasis in various organs;
- magnetic resonance imaging – allows you to obtain images in transverse and longitudinal sections;
- radiothermometry – for early diagnosis of malignant tumors by measuring the temperature of internal tissues.
The most effective diagnostic method is positron emission tomography. It is carried out using a special radiopharmaceutical, which is introduced into the body and accumulates in the affected cells. When scanned, it appears as luminous spots.
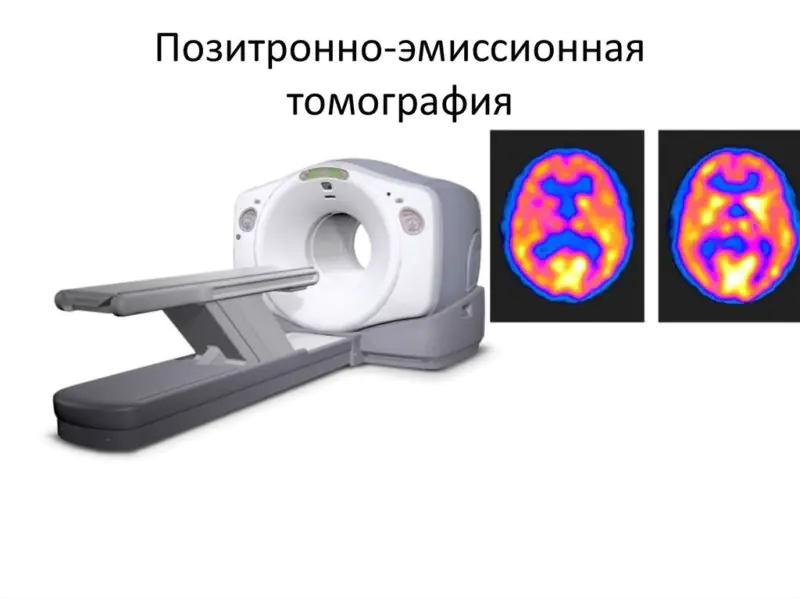
A correct diagnosis allows you to more accurately select the necessary treatment method in each specific case.
When does a tumor need to be removed?
Melanoma is the most dangerous and aggressive malignant tumor, which is formed as a result of the degeneration of melanocyte cells at the site of the mole. It progresses very quickly in the early stages of the disease with multiple metastases (in the lungs, brain, bones).
Once metastasis occurs, the disease is considered incurable and can cause death, so it is very important to closely monitor your moles in order to identify the approaching danger in time.
Signs to pay close attention to:
- a rapid increase in old or new marks begins (size reaches more than 6 mm), while uneven edges of the growth are observed;
- the color of the neoplasm changes (to darker or lighter);
- the presence of individual inclusions, crusts, cracks, and flakes is observed;
- serous fluid is released or bleeding appears;
- there is an increase in lymph nodes;
- a feeling of soreness, burning and itching at the site of formation appears.
People at risk for moles turning into melanoma include:
- with fair skin with a lot of freckles and other growths;
- having increased sensitivity to solar radiation;
- working under the sun;
- sunburned at any age;
- living in hot climates.
If the growth is removed at the initial stage of transformation into a malignant tumor, there is a significant chance of complete recovery.
Ways to combat nevi
The following methods for removing moles on the head are known:
- Laser therapy – removal of a birthmark using a high-precision laser beam. It destroys the cells of formation without leaving any traces.
- Cryodestruction - freezing the nevus using liquid nitrogen. A mole on the head becomes covered with a white crust, which subsequently falls off, leaving behind healthy skin.
- Radio wave therapy - using a radio wave knife, resembles surgical removal, only less traumatic for the head.
- Electrocoagulation is the cauterization of a growth on the head using a high-frequency current, which promotes its peeling and death.
If dangerous symptoms are observed and there is a suspicion that a mole on the head is turning into a malignant formation, immediate surgical intervention is necessary. It is performed by excision of the tumor and adjacent skin with a scalpel. The operation is dangerous due to bleeding and the formation of scars. In some cases, if the formation occupies a large area, skin grafting may be necessary.
Preventing skin cancer
To reduce the risk of melanoma, you must:
- avoid sun exposure to the skin, especially during peak sun activity;
- protect exposed areas of the body (if it is necessary to stay outside for a long time on sunny days);
- use sunscreen;
- exclude visiting the solarium;
- comb and wash hair with care;
- inspect moles daily, in hard-to-reach places, use the help of relatives or friends;
- choose hats that do not cause squeezing and rubbing of moles;
- use non-aggressive hair care products;
- warn the hairdresser about a mole on the head when visiting a beauty salon.
Under no circumstances should you remove the tumor yourself - this will lead to irreversible consequences.
The main protection against an incurable disease is early consultation with a doctor if negative signs appear.
It should be remembered that melanoma can be defeated only with timely treatment.
There is an opinion that moles on the head in the hair are dangerous, although there are also moles whose existence their owner is not even aware of.
Moles or nevi can appear on different parts of the human body. These are neoplasms that stand out on the skin with their color and structure.
It is not uncommon for moles to appear on the head. Such moles can cause a feeling of discomfort and are easily damaged as a result of external influences.
Causes of moles on the head
The factor that causes the appearance of nevi on the head is the increased content of melanin in the upper part of the skin.
This feature can arise as a result of several reasons:
- weakened immune system;
- genetic predisposition;
- strong susceptibility to ultraviolet radiation and sun exposure;
- birth defect;
- skin diseases;
- hormonal imbalance of the body (occurs during the period of teenage changes in the body or pregnancy);
- skin damage.
Such factors that cause the appearance of nevi can occur throughout a person’s life., even in old age, so you should be careful about the occurrence of neoplasms.

To find out which moles on the head in the hair are dangerous, you should visit a dermatologist.
Types of moles that appear on the head in the hair
Nevi can be divided into several different groups depending on different characteristics.
Based on their origin, such neoplasms can be divided into 2 types:
- congenital – arise as a result of disruption of melanocyte division even at the stage of fetal development in utero;
- acquired - appear as a result of external exposure to the skin of an excessive amount of ultraviolet rays.
If we talk about the structure of moles, the following subgroups can be distinguished:
- vascular – arise as a result of the growth and close proximity of several vessels, usually have a reddish or bluish tint;
- non-vascular – appear due to a significant number of melanocytes, have a dark color;
- flat – the most common nevi, they are not damaged as a result of external influences and, as a rule, do not cause any discomfort to the owner;
- convex – rise slightly above the surface of the skin and look like a hemisphere; having similar moles on the head in the hair is dangerous, as they are very easy to injure, so experts usually advise removing them;
- hanging – rarely appear in the head area, they represent a head connected to the skin with a kind of leg; due to the high likelihood of damage, the best option is to remove them.
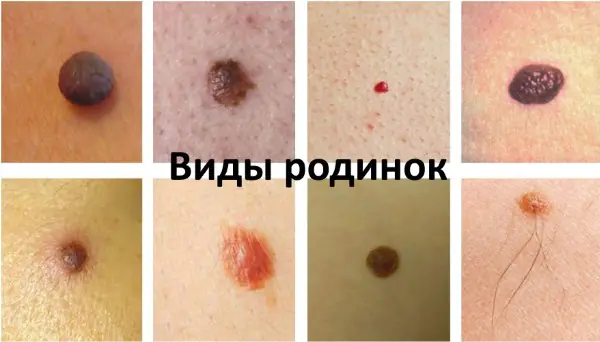
Based on their size, nevi are divided into:
- small – with a diameter of no more than 1.5 cm;
- average – 1.5-10 cm;
- large – with a diameter of more than 10 cm;
- gigantic – occupy more than half of the scalp.
Which moles on the head are safe?
In most cases, moles on the head are benign neoplasms that do not pose any danger to the owner.
The safest in this regard are flat non-vascular nevi, with a diameter not exceeding 0.5 cm. Such moles do not require any special care or special attention.
Any moles on the head in the hair can be dangerous if they begin to cause discomfort to their owner.
Moles in the hair on the head that require specialist consultation
Nevi on the head are not just an external defect, but a phenomenon that requires careful attention and careful handling.
A direct indication for seeking medical advice from a specialist is the presence of large convex, and especially hanging, moles in the hair. Such formations can very easily be injured when combing or washing your hair.
The main problem with such moles is that they can easily degenerate into malignant neoplasms or melanomas., successful treatment of which is possible mainly in the initial stages.

Such neoplasms develop quickly and metastasize to other organs, which can lead to death within a few months.
It is important to know! Often the cause of nevus degeneration is various injuries that provoke negative processes.
That is why moles that rise above the surface of the skin and are large in size require contacting a specialist and making a decision about their removal.
Dangerous resort to traditional methods of removing moles on the head in the hair, this can cause damage and degeneration.
Also, you should not cover such formations with a band-aid, since the greenhouse effect can also provoke unwanted processes.
How to properly care for a mole on your head
Moles in the hair require careful handling.
There are several simple rules that, if followed, can minimize the risk of damage to tumors on the head:
- You should not use cosmetics containing solid substances that can cause mechanical damage to the skin (scrubs, peelings), as well as shampoos and masks that contain strong chemicals;
- Avoid blow-drying this area of the skin;
- Do not scratch or scratch your head with sharp objects, use hairpins and hairpins carefully;
- If the mole is still damaged, it is necessary to treat it with hydrogen peroxide, stop the bleeding, in case of severe damage, seek medical help;
- Carefully monitor the condition of the mole and consult a doctor if any changes occur.
Be careful! Microtrauma to a mole in itself is not dangerous; it is important to prevent infection and inflammation.
Signs of degeneration of a mole
There are 5 main signs of degeneration of a mole, the appearance of which requires urgent medical intervention:
- The emergence of asymmetry – in a normal state, if you mentally divide the mole in half, both parts should be the same;
- Color change – darkening or redness of the nevus is an alarming symptom. Normally, the color of a mole should be uniform and unchanged;
- Jagged edges – benign neoplasms have clear, even boundaries;
- Resizing – if a mole increases in size or becomes convex from flat, then you should immediately contact a specialist;
- The appearance of unpleasant sensations – pain, itching, peeling, bleeding. Under normal circumstances, a nevus should not cause discomfort.
Important to remember! Even the appearance of one of the above signs is a reason to seek medical advice.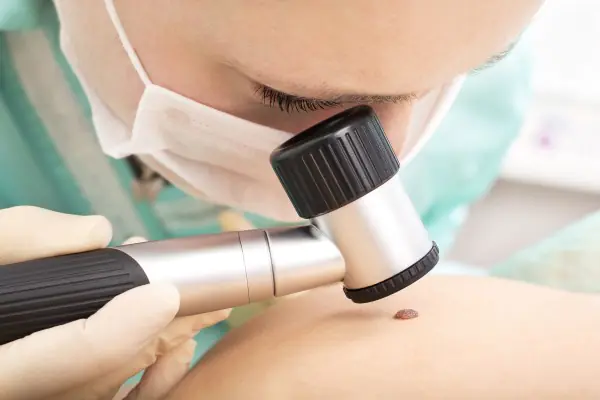
Is it necessary to remove moles on the head in the hair, when is it dangerous?
Very often the question arises: to remove moles or not. The decision should be made only after consultation with a specialist.
There are several indications for removing nevi:
- the emergence of processes of degeneration of a mole into a malignant neoplasm;
- convex or hanging shape of the mole, as it is easy to injure in everyday life;
- finding a mole in a place where it is constantly exposed to mechanical influence;
- a cosmetic defect that causes discomfort to the owner of the mole;
- the appearance of large moles in a child, since children cannot take the necessary precautions.
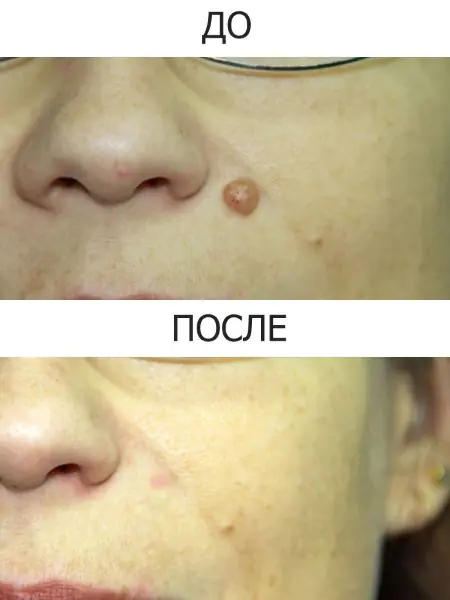
| Methods for removing moles on the head in hair | Peculiarities |
| Surgical | Allows you to send tissue for histological examination and find out whether these formations are dangerous or not. |
| Laser | The most gentle method, leaves no traces. |
| Using liquid nitrogen | It is carried out in several passes and leaves no traces. |
| Electrocoagulation |
Produced using high-frequency current, it can cause discomfort after the procedure. Radio wave A gentle, non-contact method using exposure to radio waves.
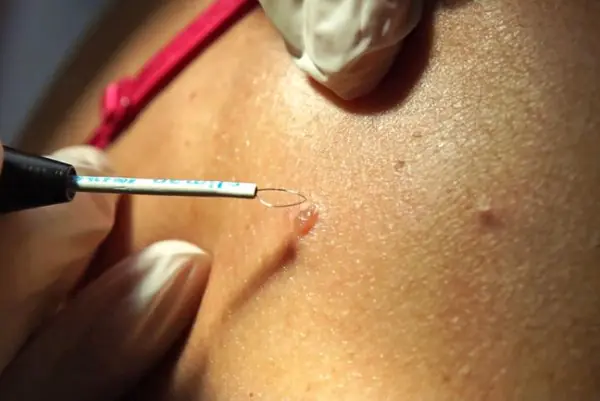
Any new growths on the head require careful and careful treatment.
It is important to follow simple rules to reduce the risk of injury to moles and the development of undesirable consequences. Any change in the nevus or the occurrence of unpleasant sensations is a reason for an immediate visit to the doctor.
This video will tell you about moles on the head, in the hair, on the body, and how dangerous they can be:
In this video you will see and hear which moles can be hazardous to health: