Folliculitis is a pustular infectious disease. This pathological process is provoked by bacterial, viral or fungal agents. It occurs on the outside of the head in the hair follicle, sometimes it can penetrate much deeper. The disease is more typical for males, in rare cases it occurs in children and women. If it gets inside the scalp, the disease becomes chronic. What is folliculitis of the scalp, treatment of this disease, diagnosis, symptoms and prevention is the topic of this article.
What kind of disease is this?
Folliculitis is a purulent-inflammatory disease that manifests itself in the hair follicle. The disease is complex formations in the form of medium-sized red-pink blisters turn into an abscess with yellow-green liquid after a few days. When contacting them, a person experiences painful sensations. The pain on the surface of the head is cutting and continuous.
Folliculitis of the scalp is typical for southern countries with a hot and humid climate, which contributes to the development of infections. Also, similar inflammatory processes occur in people living in unsanitary conditions.
Development of the disease
The follicle affected by the disease has the shape of a ball containing pus. This formation affects not only the bulb, but also the nearby sebaceous glands. Folliculitis of the scalp occurs in several stages:
This skin disease is characterized by both superficial and internal lesions. According to statistics, internal inflammation is most often diagnosed.
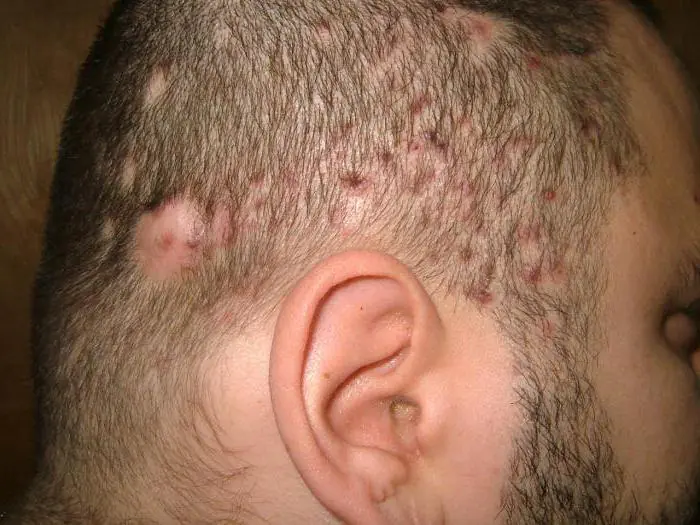
What contributes to the development of the disease?
The cause of the development of a disease such as folliculitis of the scalp, the photo of which you see above, can be, for example:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, scalp contamination.
- Incorrectly or untimely applied tight sealed bandage, which is used for wounds on the head.
- Climate conditions (high ambient temperature).
- Use of various drugs.
- Injury to the scalp.
- Use of tight synthetic quality hats.
- Diseases (diabetes mellitus, liver dysfunction) and malnutrition.
The likelihood of infection entering the follicle increases in the presence of itchy dermatoses, minor microtraumas or damage to the scalp.

Types of disease
Any bacteria or fungus can provoke the development of the disease. Folliculitis of the scalp has various forms, each of which has its own symptoms and treatment:
- Staphylococcal.
- Hoffmann's folliculitis.
- Decalcifying.
- Candida.
- Herpetic.
- Syphilitic.
- Parasitic.
Staphylococcal folliculitis. The causative agent is a bacterium that manifests itself externally and internally. This disease can occur in men when shaving their heads bald, as small scratches allow the entry of pathogenic bacteria and fungi. If the disease becomes internal, a boil may form.
Hoffmann's folliculitis of the scalp. The course of this type of disease is quite rare. Its symptoms are practically unknown. It is believed that the inflammatory process in some cases becomes chronic this is Hoffmann’s folliculitis of the scalp. The reasons are associated with occlusion of the pilosebaceous follicles. A long course of the disease can affect not only the hair follicle, but also parts of the skin around it. This form of the disease has a fairly large affected area. In the affected areas, hair growth stops completely. The neglected process leads to irreversible consequences, since the hair in these places falls out, and its further growth is impossible. Abscesses formed on the skin take a very long time to heal, leaving behind deep scars.
Decalcifying. It is chronic and can develop due to fungi and infections. This type of folliculitis develops mainly in dark areas of the hair.
Candida. A form of folliculitis caused by fungi. It appears as large bubbles in the center of the hair follicle. This disease occurs in patients who are constantly lying down on their back.
Herpetic. The cause of this form of the disease is the herpes virus. First, bubbles form, and then they burst and dry, forming a crust. This type is quite common in the nasolabial triangle in men.
Syphilitic. This is secondary syphilis. It appears as a red rash, it often has the shape of an oval or circle, and hair does not grow in these places.
Parasitic. Caused by a parasitic mite. The affected areas have roughness and roughness of the skin.
Symptoms of the disease
Folliculitis manifests itself in the form of pustules of medium size. These pimples are shaped like a cone. There is almost always a reddish outline around the bubble, which indicates an inflammatory process. In most cases, a person does not experience any pain or itching. The disease progresses within 2-5 days. After this, the blisters burst, the wound dries out, and at this stage itching and peeling are possible.
With internal folliculitis, dense subcutaneous pimples form and can cause pain. Such nodes also have a rim of inflammation, but it is less noticeable. If you press on the formation, it bursts, releasing pus and an unpleasant odor. After this, the wound heals, forming a crust, but the most unpleasant and painful period for a person is the process of maturation of the subcutaneous nodes.
Disease in children
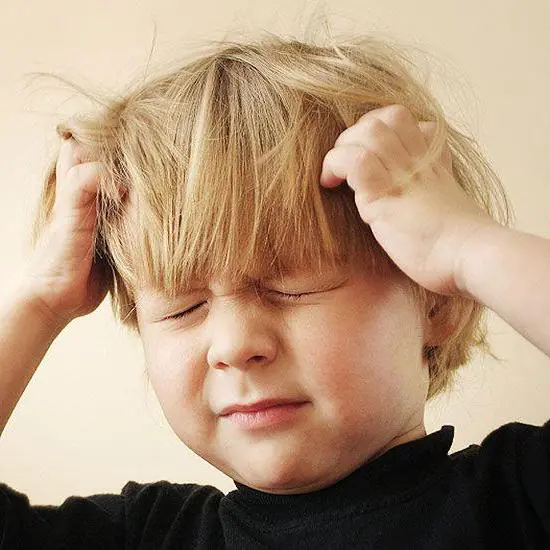

This disease is quite dangerous for children in infancy. The development of the disease is usually provoked by bacteria trapped under the skin. The disease manifests itself in the form of blisters filled with white or red liquid.
If parents notice such symptoms in their children, they should immediately consult a doctor. To a greater extent, this disease is treated with traditional methods, such as tea tree oil. Apply this solution to the affected areas several times a day.
Diagnostics
There is an opinion that such a disease is not dangerous - this is a misconception. It is very important to consult a specialist at the slightest sign he will diagnose folliculitis of the scalp, determine the causes and treatment in accordance with the stage of the disease. Timely medical therapy will help eliminate the disease faster.

If folliculitis appears, it is important to determine its causative agent, as well as possible diseases that can provoke its complication. A dermatologist examines the patient, performs dermatoscopy, and samples the discharge from the pimple for examination. This analysis makes it possible to determine the nature of the disease and its causative agent this method will help to select the correct treatment and therapy.
How to get rid of this disease?
Therapeutic therapy will be much more effective if the patient begins to fight the disease at the initial stages of the inflammatory process. Although today medications are widely used against such a severe form of the disease as deep folliculitis of the scalp. There is the following treatment algorithm:
- The resulting pimples and the surface of the scalp must be treated with antiseptic preparations (salicylic or camphor alcohol (2% solution), brilliant green, Fukortsin).

- A large cluster of deep pimples is opened by a specialist, followed by treatment with an antiseptic solution.
- In order for healing to proceed faster, special ointments are used that are used to treat the affected areas of the skin several times a day (for example, ichthyol ointment).
- If the disease is severe, the specialist will prescribe a special course of antibiotics based on a study of the fluid in the blisters.
- In some cases, medications are used to boost immunity.
To prevent scars from remaining on the skin, the doctor prescribes physical therapy, but only after the disease has subsided.
Folliculitis of the scalp: treatment with folk remedies
A large number of people treat this disease at home. The following effective recipes exist:
- Chamomile decoction.
- A mixture of herbs.
- Woodruff fragrant.
- Dandelion infusion.
- Burdock infusion.
How to prepare such decoctions?
Traditional medicine can offer a huge list of remedies to get rid of folliculitis of the scalp. Such medicines can be very easily prepared at home.
To prepare a chamomile-based decoction, you need to take a tablespoon of the plant’s flowers and pour one liter of boiling water. Then let it brew. The resulting solution is wiped over the affected areas of the skin.
For the herbal decoction you need: rose hips and viburnum berries, approximately 150-250 g each, add 150 g of nettle and 25-50 g of walnut bark. Pour everything with water and mix, put on fire and boil for 7-9 minutes. This decoction should sit, then it is added to cottage cheese or honey, mixed and masks are made. This method is quite effective in the treatment of folliculitis. The procedure is performed 2-3 times a day for 10-15 minutes.
For treatment, woodruff pulp prepared from leaves is used procedures are performed in the form of applying bandages, several times a day.
Dandelion decoction is taken orally, 2-3 glasses per day. In order to prepare it, you need to take the leaves and roots of the plant, chop it and pour boiling water over it. This is an excellent way to treat internal folliculitis.
Burdock infusion is taken 3-4 times a day. To prepare, grind the root of the plant, pour one liter of boiling water over it and let it settle. After this, strain and cool.
Traditional medicine today is a fairly common method of treating a huge number of diseases.
How to prevent the recurrence of the disease?
Prevention is important in the treatment of a disease such as folliculitis of the scalp. Timely measures will help prevent the development of the disease. The main rule is to maintain personal hygiene of the scalp and hair.

When even small wounds appear on the skin, they must be treated with antiseptic or disinfectants. Men should pay great attention to this procedure after shaving their heads.
Conclusion
A disease such as folliculitis of the scalp must be treated its consequences can have a bad outcome, and if it is accompanied by some other illness, this can seriously complicate the situation. That is why it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor at the slightest symptoms. A specialist dermatologist will conduct a full range of examinations, perform a blood test, as well as the fluid contained in the blisters. Such data will help you easily determine the symptoms and type of disease and select the necessary drugs for treatment.
Abscessing (undermining) Hoffmann's folliculitis refers to a number of dermatological diseases of a purulent nature. It affects skin that is rich in hair follicles. The provoking factor in the formation of the disease is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin and those areas of the body that are covered with hair. It is characterized by slow development and the possibility of becoming chronic. Folliculitis is most often diagnosed in representatives of the stronger half of humanity aged 17 to 40 years. To prevent relapses, timely treatment is recommended.
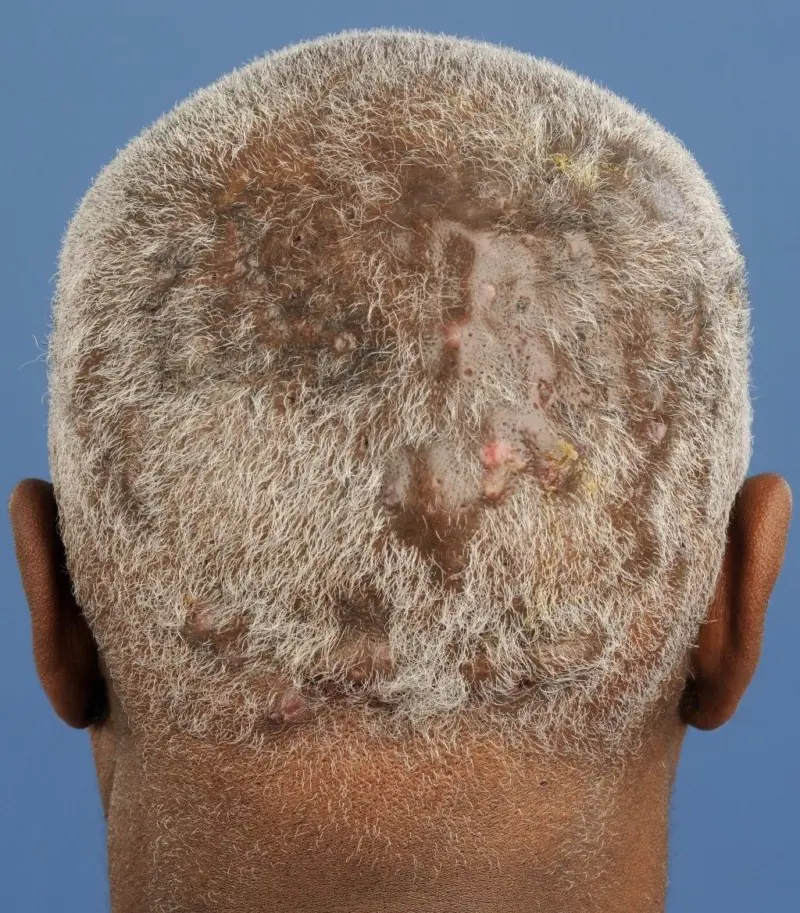
Causes
Hoffmann's folliculitis is most often caused by:
- staphylococci
- streptococci
- Staphylococcus aureus.
Various factors can provoke its appearance they are divided into endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous includes:
- undergoing a long course of antibiotic therapy
- carbohydrate imbalance
- cancer diseases
- immunodeficiency
- diabetes
- hormonal imbalance
- liver diseases
- carrying out chemotherapy
- anemia
- long-term use of glucocorticoids
- decreased protective function of the skin
- infectious processes.
Exogenous provoking factors are:
- exposure to cold or hot air over a long period of time
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules
- violation of the integrity of the skin in the form of abrasions, cracks, burns and animal scratches
- skin contamination at work
- wearing tight clothing made from synthetic fabrics
- incorrect or untimely application of occlusive dressings
- non-compliance with skin care rules after laser hair removal and other cosmetic procedures.
There are also factors that indirectly contribute to the formation of the disease, these include:
- periodontal disease
- gingivitis
- caries
- chronic tonsillitis
- chronic pharyngitis
- obesity.
These conditions deplete the immune system, resulting in the skin losing its ability to resist skin infections.
As the disease progresses, the pathological process spreads to adjacent areas of the skin, and abscess formation of the deep layers of the epidermis and hair follicles is observed. Abscesses and fistulas form and merge with each other. The disease can be transmitted at the genetic level.
Clinical picture
As already noted, Hoffmann folliculitis affects men 20-35 years old the favorite areas of localization are areas of the body with developed hair.
At the initial stages of the development of the disease, itching and burning appear. There are several affected areas, they become hyperemic. In rare cases, undermining folliculitis occupies most of the head, while healthy areas look like narrow stripes. As the disease progresses, the formation of oblong or hemispherical nodes is observed they are surrounded by areas of hair loss.
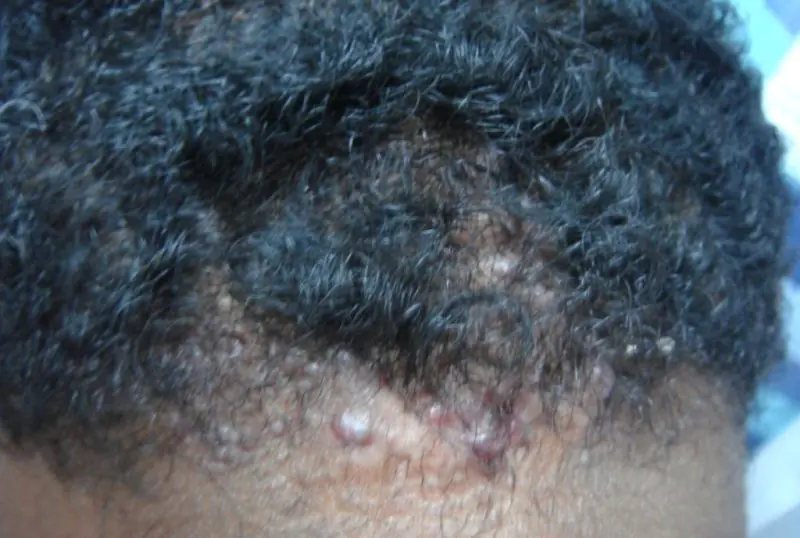
If left untreated, the nodes turn into fistulas, the size of which reaches 1-2 centimeters when they are palpated, pus is released, sometimes mixed with blood. In complicated cases, ulcers form at the site of nodes and fistulas, the surrounding skin becomes thinner, and alopecia (areas where hair is completely absent) spreads 1-2 centimeters around.
The general condition of the patient also changes, an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes and an increase in body temperature are observed.
In the absence of adequate therapy, abscess folliculitis may persist for several weeks, after which the ulcers heal, forming scars in their place. Alopecia persists and is accompanied by the formation of new nodes and abscesses. The disease is prone to relapse and may be present for several years.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hoffmann's folliculitis responds well to treatment, the main thing is to start it on time. If pathological symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible, namely a dermatologist or infectious disease specialist. After a thorough examination of the patient, he will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen.
Diagnostic methods
First of all, the doctor collects the patient’s complaints and anamnestic data, specifying the time of onset of pathological symptoms, the presence of chronic diseases and similar problems in relatives. After this, a dermatoscopy (examination of the patient) is performed. Inflamed follicles are examined under multiple magnification, this allows you to determine the depth of the inflammatory process.
- Bacteriological culture of discharge from pustules. The study makes it possible to establish the type of pathogen, and in the future also determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
- PCR diagnostics. It is carried out to exclude the presence of diseases such as syphilis and gonorrhea.
- Test for the presence of fungal flora. To do this, scraping is carried out from the affected area and examined under a microscope.
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
It is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis deep folliculitis must be differentiated:
- with a superficial form of the disease (ostiofolliculitis)
- with streptococcal impetigo
- furunculosis
- nodular cystic acne
- drug toxicoderma.
If necessary, the patient is referred for examination to an immunologist and allergist.
Treatment
First of all, it is necessary to direct all efforts to strengthen the body’s immune defense. You need to monitor your diet your diet should include as many vitamins, vegetables and fruits as possible, as well as protein-rich foods. The consumption of sweets, baked goods, seasonings, spicy and salty foods should be kept to a minimum.
An important point is compliance with the drinking regime. During an exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water, because pathogenic microorganisms leave the body cavity with liquid.
Of the medications, the following drugs are considered justified:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics, preference is given to penicillins of semi-synthetic origin: Unazine, Augmentin, Clavulin, Amoxiclav, Claventin. Cephalesporin derivatives - Cephobid, Claforan, Kefzol, Cefuroxime - can also be used. If such antibiotic therapy is impossible for certain reasons, then sulfonamides are used: Septrin, Groseptol, Bactrim and Biseptol.
- Immunostimulants, such as Immunoglobulin, Bacteriophage, Antifagin.
- Vitamins and restoratives vitamins E, A, C, and group B are considered the drugs of choice.
For topical use use:
- antibacterial ointments
- Ichthyol
- Fulevil
- Levosin
- Levomekol.
After opening abscesses and fistulas, clean them using antiseptic solutions, such as:
- Nitrofuran
- Iodoform
- Potassium permanganate
- Hydrogen peroxide.
The course of treatment ranges from 7 to 12 days to consolidate the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to repeat it after 10 days.
In advanced and complicated cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
A high level of effectiveness is observed when combining drug treatment of acute folliculitis with physiotherapeutic methods. The use of ultraviolet rays is considered the most effective, because ultraviolet rays penetrate into the thickness of tissues, providing an anti-inflammatory and restorative effect. Good results are also observed when using:
- carbon dioxide laser
- low-intensity UHF therapy
- magnetic therapy
- dry heat.
Forecast
With timely therapy, the prognosis is favorable foci of inflammation can be completely eliminated within 2 weeks. Patients who self-medicate most often encounter complications such as:
- furunculosis
- carbunculosis
- abscess
- dermatophytosis
- lymphadenitis.
Damage to the deeper layers of the skin leads to the formation of scars and dark spots. In severe cases, complications can threaten the patient's life.
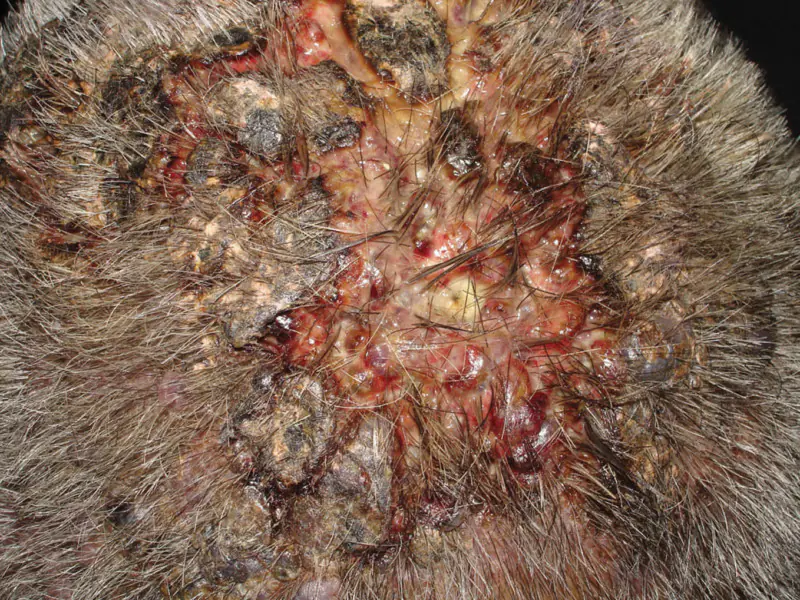
Remember that pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the development of folliculitis can be transmitted through contact, so for the sake of the health of your family, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Preventive actions
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. To avoid skin problems, it is recommended:
- Carry out personal hygiene manipulations in areas with active hair growth with caution.
- Regularly undergo medical examination if you have a history of diabetes.
- Men should shave, and women should depilate only with the use of special products with disinfectant properties.
- Treat damaged or abraded skin with antiseptic solutions.
- Conduct timely treatment of diseases that can provoke the development of Hoffmann folliculitis.
- Carefully ensure that chemical solutions and compounds do not come into contact with your skin.
- If even minor pathological symptoms appear that resemble disruptive folliculitis, seek help from a doctor.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Enrich the body with vitamins A and E.
- Avoid excessively greasy hair.
To summarize, I would like to focus on the fact that Hoffmann’s folliculitis is a rather dangerous disease that requires timely treatment. Remember this, be attentive to your body, and it will thank you with good health.
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis (abscessing) is a rare dermatological disease with a purulent nature. The disease affects the hair follicles and scalp, but can also appear on other hairy parts of the body. Today, the main cause of Hoffmann's folliculitis is considered to be bacterial infection of the skin near the hairline. The disease mainly affects men aged 17-40 years. Racial predisposition to Hoffmann's folliculitis has also been proven - the disease is less common in European men than in African Americans. Undermining folliculitis most often develops slowly. It is characterized by a sluggish, chronic and long-term course, which sometimes takes several years. Only correct and timely treatment can speed up the recovery process and prevent relapse.
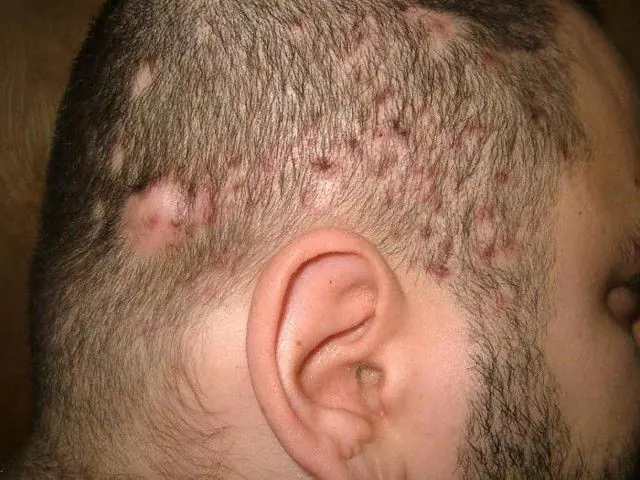
Causes of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
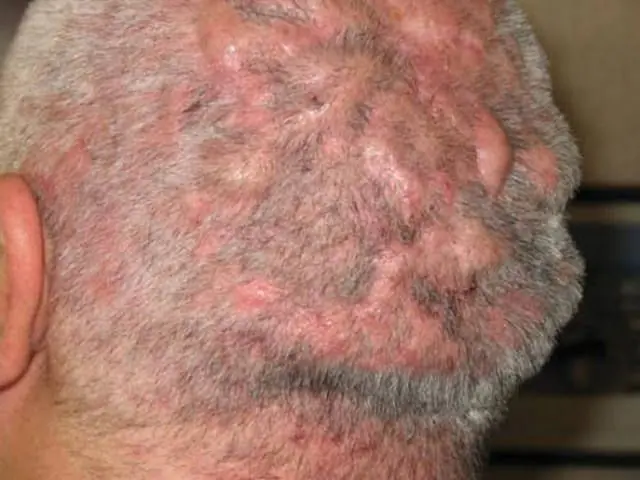
The photo shows an advanced form of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Since E. Hoffman's study of abscess folliculitis, pathogenic staphylococcal flora was considered the only cause of the disease. It has now become clear that the disease develops not only due to infection by microorganisms, but also due to the physiological characteristics of the skin. Bacteria colonize around the hair roots, which provokes the development of the disease.
In almost all patients, the secretion of the sebaceous glands changes, and after a while they become clogged. Similar symptoms of Hoffmann folliculitis indicate many other dermatological diseases (acne, comedones). However, for the development of perifolliculitis, an additional pathological reaction of the skin to the components of the breakdown of clogged sebaceous glands, in particular keratin, is necessary. Studies have shown that in patients with this pathology, granulomatous inflammation is formed due to the breakdown products of keratin. This aggravates infection with staphylococcal flora. Similar processes and disturbances of microcirculation in the dermis lead to the occurrence of Hoffmann's folliculitis.
In addition, Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis can be hereditary and occur due to other factors:
- Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Diabetes.
- Hypothermia.
- Oncological diseases.
- Disturbance of the hormonal system.
- Chemotherapy.
- Liver diseases.
- Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Symptoms of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
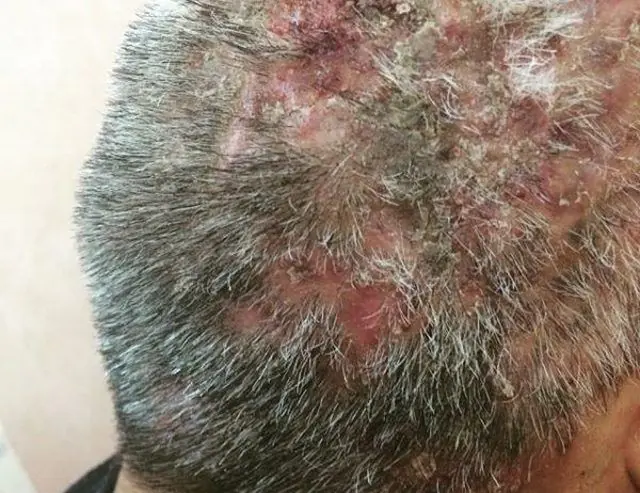
With abscess folliculitis, the hair follicles become inflamed. At the initial stages of the disease, a burning sensation, itching appears and small seals measuring 0.5 cm are formed. With the progression of undermining folliculitis, the seals soften and increase to 2 cm, oblong or hemispherical nodes are formed, which are surrounded by places of hair loss. There may be several affected areas, they become hyperemic. The general condition of the patient also changes: regional lymph nodes enlarge and body temperature rises. When complicated, Hoffmann's folliculitis often causes the formation of fistulas in the lesions. After the pus comes out, a wound forms, which heals, but a scar forms in its place. The disease is prone to relapses, can last several years and is always accompanied by:
- redness of the skin over the formation
- hair loss
- discharge of pus with blood when pressing on the affected areas
- abscess formation.
Diagnosis of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
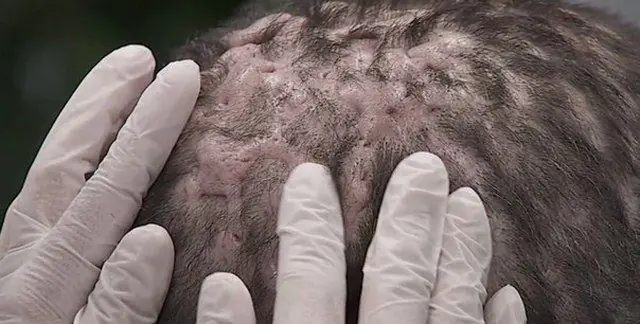
The photo shows a medical examination of the head of a patient with Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's folliculitis is treated by a dermatologist and an infectious disease specialist. Specialists examine the patient and carry out a number of activities as part of the study:
- Dermatological examination.
- Histological study of affected tissues.
- Microbiological examination of abscess discharge.
- The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined in order to select the optimal treatment.
- A general blood test is prescribed to determine the nonspecific features of purulent inflammation.
- The presence of similar problems in relatives and chronic diseases is clarified.
Treatment of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
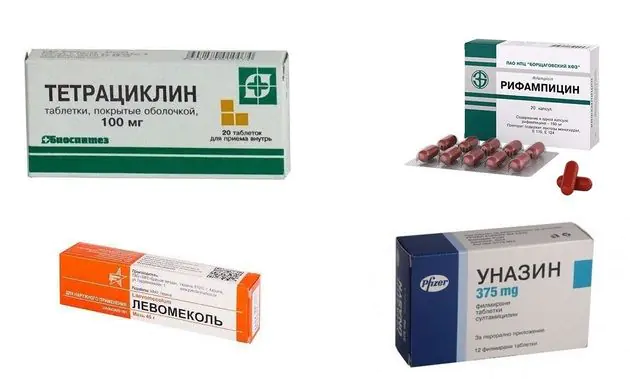
To treat Hoffmann's folliculitis, drug therapy is prescribed: antibacterial drugs internally (Clindamycin, Tetracycline, Rifampicin) and externally (Clindamycin). For local use use: Levosin, Levomekol, Ichthyol, Fulevil, antibacterial ointments.
According to some doctors, the effect of antibacterial drugs is short-term it is more effective to simultaneously combine antibiotics with injections of corticosteroids in the affected areas. Of the antibiotics, broad-spectrum penicillin drugs of semi-synthetic origin are considered justified: Augmentin, Clavulin, Unazin, Amoxiclav, Claventin. Sometimes the cephalosporin series is used: Kefzol, Cefobid, Cefuroxime, Claforan. If antibiotic therapy is not possible, then sulfonamides are prescribed: Biseptol, Septrin, Groseptol, Bactrim.
High effectiveness is observed when drug treatment is combined with physiotherapeutic methods. UV therapy is effective because ultraviolet rays penetrate the tissue, providing a general strengthening and anti-inflammatory effect. Good results are observed when using: magnetic therapy, low-intensity UHF therapy, dry heat and carbon dioxide laser.
In case of complications and in advanced cases of Hoffmann's folliculitis, surgical intervention is resorted to. Surgical treatment is carried out against the background of antibacterial therapy with resection of the affected tissues of the head and subsequent reconstruction of the skin.
In addition to the above therapy It is necessary to strengthen the body’s immune system and monitor the diet. The menu should contain vitamins, vegetables, fruits and protein-rich foods. It is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets, baked goods, spicy and salty foods. It is important to maintain a drinking regime, because pathogenic microorganisms leave the body with liquid. During an exacerbation, it is recommended to drink 2 liters of water.
Prognosis and prevention of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
With proper treatment, the prognosis for abscessing undermining folliculitis is favorable. However, treatment is long and relapses are possible, since the disease is mainly caused by certain physiological characteristics of the skin. After the ulcers heal, noticeable scars remain, which are an aesthetic defect. This can be corrected with plastic surgery. Conservative and cosmetic treatment does not restore hair growth. For prevention purposes, you should avoid getting your hair dirty and maintain personal hygiene.
Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
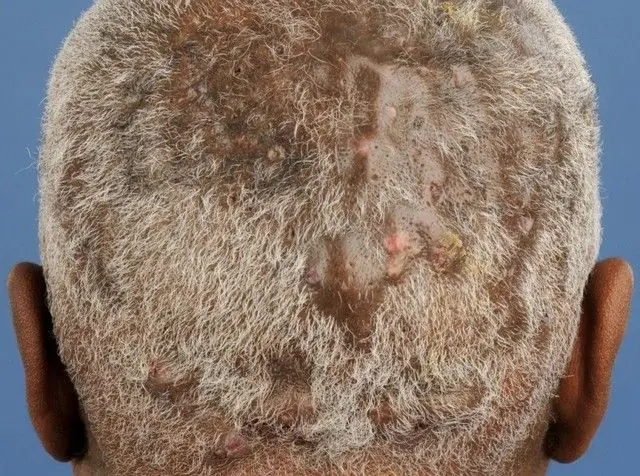
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is not life-threatening. The disease must be treated because it causes aesthetic discomfort and sometimes pain to the patient. If you neglect the disease and do not adhere to hygiene standards, folliculitis will spread to other parts of the skin with hair. Abscess folliculitis can lead to the following complications:
- Scarring of the affected skin.
- Carbuncles.
- Boils.
- Abscesses.
In advanced and severe cases, the patient’s life is at risk, since with reduced immunity, pneumonia, meningitis and other disorders develop.

City Dermatovenerologic Dispensary of St. Petersburg



