Causes of pain under the left shoulder blade with osteochondrosis. Stages and diagnosis of the disease. Methods of traditional and surgical treatment.
The content of the article:- Symptoms and stages of osteochondrosis
- The main causes of pain under the left shoulder blade
- Diagnostic methods
- Methods for treating osteochondrosis
- Medicines
- Physiotherapy
- Surgical intervention
Osteochondrosis under the left shoulder blade is a disease caused by degeneration of cartilage tissue in the joints and intervertebral discs. The cause of the pathology is poor nutrition and a sedentary lifestyle. The treatment is long-term and lasts for several months.
Symptoms and stages of osteochondrosis under the left scapula
If osteochondrosis causes pain under the left shoulder blade, the disease affects the cervical or thoracic spine. The sensations may vary in intensity and duration. The pain radiates to the arm, back, shoulder, sometimes reaching the lower back.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis under the left shoulder blade are complemented by numbness, a feeling of a “stake” in the spine in the morning. Sharp pain under the shoulder blade occurs during movement, when the patient tries to stretch the muscles. Sometimes the sensations become aching, pulling, as with heart disease, accompanied by difficulty breathing, tingling in the chest.
The result of the pathology is restriction of movement, loss of elasticity in the spine, changes in posture (a person often takes a comfortable position in which pain is felt to a lesser extent), increased fatigue.
Along with subscapular pain, other signs of the disease are present:
- muscle spasms;
- “floaters” or spots before the eyes;
- dizziness;
- decreased muscle tone.
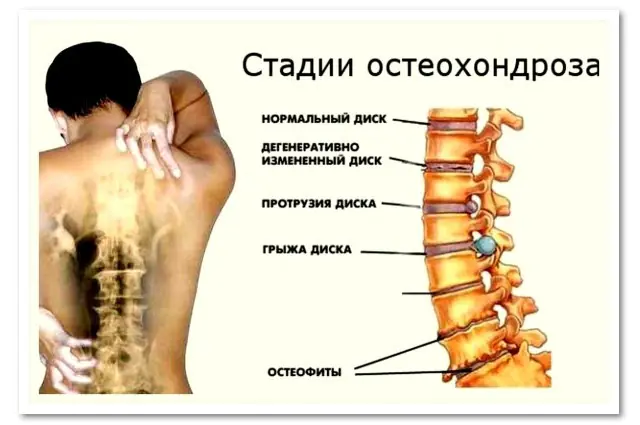
The disease goes through 4 stages in its development:
- Stage 1. Due to dehydration of the nucleus pulposus, the height of the intervertebral disc decreases and a crack appears in the fibrous ring. The pain is almost not expressed or occurs with prolonged static position or active load.
- Stage 2. The muscles of the spine sag, the distance between the vertebrae decreases. The vertebrae become mobile, which threatens their displacement. At this stage, pain is felt with movement and increased stress.
- Stage 3. Disc protrusion occurs, pain under the shoulder blade becomes stronger, and can occur even in a calm state. When you try to raise your arm, turn your neck or body, you feel tingling, numbness, and stiffness.
- Stage 4. The vertebrae become hypermobile, and osteophytes—bone formations—form between them. They can pinch nerves and lead to microtrauma of the vertebrae.
Severe pain in the left subscapular area occurs at stages 3-4. Sometimes they become unbearable and urgent medical attention is required.
The main causes of pain under the left shoulder blade
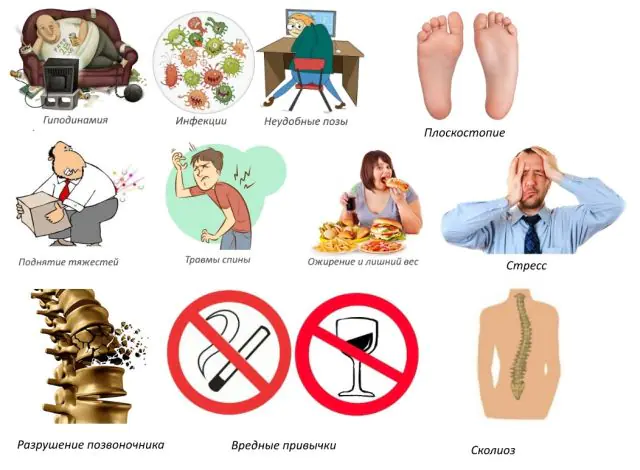

Osteochondrosis in the cervical or thoracic region occurs due to uneven load on different parts of the spine. The main reasons: incorrect posture while sitting, sleeping on a high pillow or soft feather bed, poor quality shoes, habit of carrying a load in one hand.
Additional factors worth noting include:
- lack of sufficient physical activity or overexertion;
- nervous exhaustion;
- metabolic disease;
- gastrointestinal diseases leading to poor absorption of nutrients;
- age-related changes in cartilage tissue;
- scoliosis;
- working in a hazardous enterprise;
- injuries;
- hormonal changes.
Under the influence of these reasons, depletion of cartilage tissue slowly develops. In the first stages, a person does not notice any changes, but later the pain syndrome manifests itself more and more strongly.
Methods for diagnosing osteochondrosis
If the etiology of pain is unknown, contact your physician. When a diagnosis is made, treatment for osteochondrosis under the left scapula is prescribed by a traumatologist or neurosurgeon, depending on the severity of the disease and the necessary therapeutic measures.
If the cause of pain is pinched nerves, consultation with a neurologist is necessary. If there are concomitant pathologies, a visit to an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist is recommended.
With osteochondrosis under the left shoulder blade, symptoms and treatment are closely interrelated. The doctor asks the patient about the sensations, their nature, time and duration.
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental studies are required:
- X-ray of the thoracic and cervical spine to determine the etiology of pain under the left shoulder blade;
- neurological examinations;
- myelography (injection of a contrast agent into the spinal canal to obtain images);
- CT, MRI.
Based on the results of the examination, the cause of pain and treatment methods are determined.
Methods for treating osteochondrosis - pain under the left shoulder blade
How to treat osteochondrosis under the left shoulder blade depends on the degree of its development and the severity of pain. You should not count on a quick recovery: the therapeutic course lasts 1-3 months. Subsequently, maintenance activities are recommended throughout the year.
Medicines
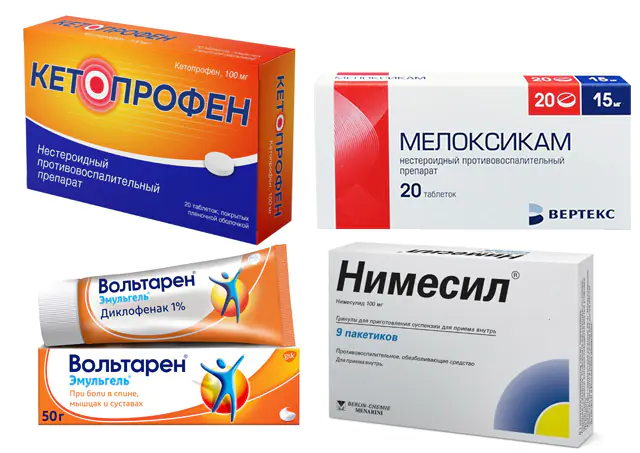
In the photo, drugs for pain under the left shoulder blade with osteochondrosis
Taking medications is recommended in the initial stages to eliminate pain and strengthen cartilage tissue. Anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamin complexes are also prescribed.
Standard therapy includes:
- Anti-inflammatory, analgesic medications for oral administration or in the form of injections, in the form of ointments: Ketoprofen, Meloxicam, Voltaren, Nimesil (price - 50-100 rubles or 20-40 hryvnia).
- Vasodilators for dilating blood vessels and improving blood circulation: Trental, Berlition (price - 700 rubles or 300 hryvnia).
- Relaxants for muscle relaxation: Mydocalm, Baclofen (price - 500 rubles or 200 hryvnia).
- Chondroprotectors for the restoration of bone and cartilage tissue: Structum, Artra, Teraflex (price - 350 rubles or 180 hryvnia).
- Sedatives to relieve tension: Cymbalta, Donormil (price - 1500 rubles or 600 hryvnia).
- Vitamins for tissue nutrition: Milgamma, Neuromultivit (price - 250 rubles or 100 hryvnia).
Medications are recommended in the early stages, when it is possible to strengthen the spine without surgery.
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis
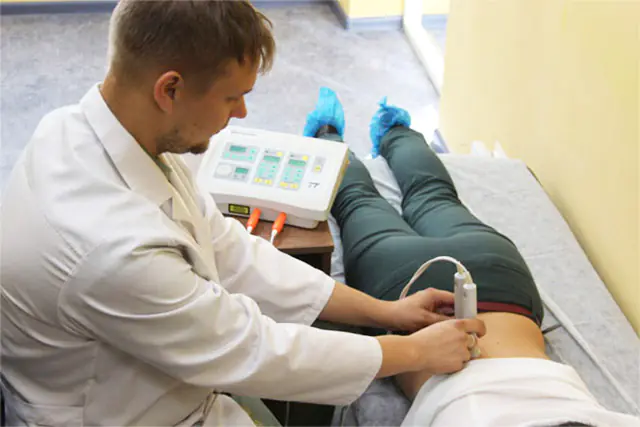
Physiotherapy is used for osteochondrosis alone or in combination with medication. In the acute phase, massage and exercise therapy are recommended.
During the recovery period, the following procedures are suitable:
- Ultraviolet irradiation: promotes the production of vitamin D and better absorption of calcium, reduces pain, inflammation, inhibits microbes;
- Ultrasound therapy: ultrasound exposure is combined with the administration of painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications;
- Detensor therapy: stretching the spine under the patient’s own weight;
- Shock wave therapy for pain under the left shoulder blade: exposure to the affected area with an acoustic wave to relieve pain and inflammation, improve microcirculation;
- Magnetotherapy: the action of the magnet is aimed at relieving swelling and spasms;
- Electrotherapy: low-frequency impulses reduce pain and stimulate tissue nutrition;
- Treatment of osteochondrosis with mineral waters and mud: baths and showers stimulate the penetration of minerals into the deep layers of the dermis and activate nerve receptors;
- Laser therapy: neon laser with helium activates biological processes and relieves inflammation in the roots.
To treat osteochondrosis, these methods are often combined.
To strengthen the muscles around the spine and shoulder blades, the patient is recommended to wear orthopedic corsets. They support posture, take on part of the load, and have a warming effect.
Surgical intervention for osteochondrosis
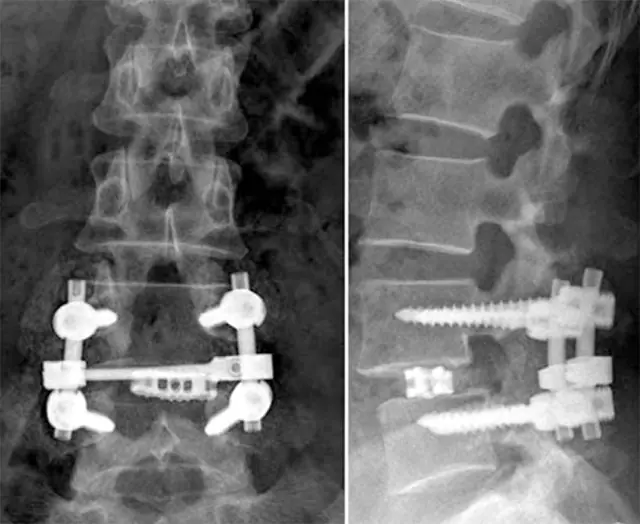
Surgery is resorted to when traditional treatment is powerless. To remove a hernia that has arisen as a complication of osteochondrosis, microsurgical discectomy is used.
The essence of the operation is that access to the formation is provided through a skin incision and bone structures of the spine. Without damaging the fibrous ring and nerves, the surgeon removes the hernia. Manipulations are controlled using a microscope. The rehabilitation period is up to 6 weeks.
To enhance the fusion of healthy intervertebral discs in the place where the hernia was removed, the doctor may install a cage - an artificial insert for stabilization.
For cervical osteochondrosis, a Shants collar is worn for immobilization. In case of severe pain and weakened muscles, it takes on part of the load. However, the device cannot be worn for a long time. You need to train your muscle corset to restore your posture.
Video about the causes of pain under the shoulder blade and 5 tips on how to remove this pain (Dr. Dlin’s clinic):
Pain under the left shoulder blade as a result of osteochondrosis requires careful medical examination and careful treatment. The disease is dangerous due to rupture of the fibrous ring, the formation of a hernia, poor posture and other serious problems.



