- Concept and clinical symptoms
- Drug therapy
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Prevention
Itching with folliculitis is an unpleasant sensation that appears on the skin due to the development of folliculitis and is accompanied by a strong desire to scratch the itchy area. This feeling can be so strong that it is difficult for a person to control himself and he tears his skin until it bleeds.
Constantly scratching blisters and ulcers during folliculitis can lead to complications of the disease and slow down recovery.
Concept and clinical symptoms of folliculitis
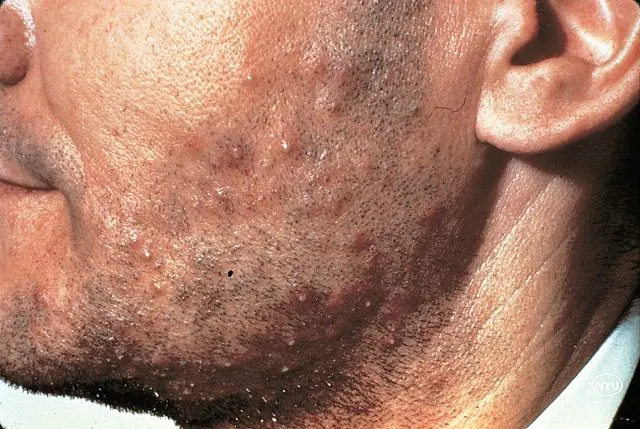
In the photo there is folliculitis on a man’s face
Folliculitis is a skin infectious disease. The mechanism of its development is the formation of papules at the mouth of the follicle with hair permeated in the center. After some time, a crust forms at the site of formation. The disease is localized on parts of the body with an abundance of vellus hair, most often occurring on the scalp, back, extensor surfaces of the legs and arms.
At the initial stage, the skin in the area of the inflamed follicles turns red, moderate pain and severe itching appear, and pustules form around the hair. Then the surface of the skin acquires a yellowish color and a cone-shaped or spherical shape, which is associated with the accumulation of pus. After opening the pustule, the pus comes out and the skin area turns red. Follicles can be single or reach a huge number.
The inflammatory process develops quite rapidly. If proper treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease will progress and become more severe. In this case, the hair follicles located deep in the skin are affected, and the disease can become chronic. Sometimes the lymph nodes enlarge, abscesses, boils, carbuncles, and furunculosis form. In isolated cases, severe complications may occur against the background of folliculitis - meningitis, nephritis and pneumonia.
- See also symptoms of folliculitis decalvans
What to do if folliculitis itches - drug therapy
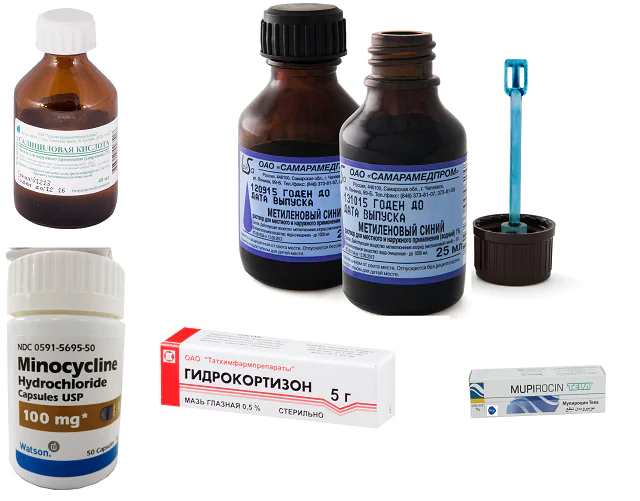
As soon as you feel itching, don’t flatter yourself that it will go away soon. The very next day you can wake up with sores on your skin. The first step towards recovery is to find out what causes scabies. To do this, it is better to consult a dermatologist. The doctor will conduct diagnostics, prescribe tests, establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
If a dermatologist discovers folliculitis in the initial form of the disease, then simple but effective measures are taken: the pustules are treated with 2% camphor or salicylic alcohol, a 2% solution of brilliant green, fucorcin or a solution of methylene blue. Ointment with hydrocortisone 1% will suppress the itching, relieve irritation and relieve pain. Apply it to the affected area, rubbing in with clean fingers or an applicator 2-5 times a day.
When folliculitis reaches deep forms and a lot of pus accumulates, the pustules are opened and treated with one of the above solutions. Also, 1-2 times a day, compresses with ichthyol are applied to the affected areas and treated with ointments (Mupirocin, Inflarax, Oflocain).
Chronic folliculitis is treated with antibiotics (Cefalexin, Cefadroxil, Dicloxacillin, Methicillin, Minocycline) for at least 10 days, since there is a risk of relapse of the inflammatory process. Strong medications from the sulfonamide group are also required to be included in the treatment. For this form of the disease, immunostimulating therapy is indicated: Vitaferon, Timalin, Immunal. Non-drug therapy includes irradiation with ultraviolet rays every other day for a total course of 6–10 times.
If folliculitis develops against the background of other diseases, then additional therapy is prescribed to treat the original source. The likelihood of developing folliculitis is higher in people with existing skin diseases: scabies, eczema, atopic dermatitis, Dühring's dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis. Persons with diabetes mellitus, HIV, and syphilis are prone to developing folliculitis.
Let's consider the treatment of special cases of folliculitis:
- Staphylococcal folliculitis treated with Muporcin ointment and internal administration of Cephalexin, Dicloxacillin, Erythromycin or Methicillin.
- Pseudomonas form treated with Ciprofloxacin.
- Folliculitis caused by gram-negative bacteria, treated topically with benzoyl peroxide.
- Fungal infection treated with internal medications (Terbinafine, Fluconazole, Intraconazole) and local therapy (Bifonazole, Nizoral, Clotrimazole).
- Herpetic folliculitis treated with Acyclovir.
Read more about drug treatment of herpetic folliculitis.
Treatment of itching with folliculitis with folk remedies
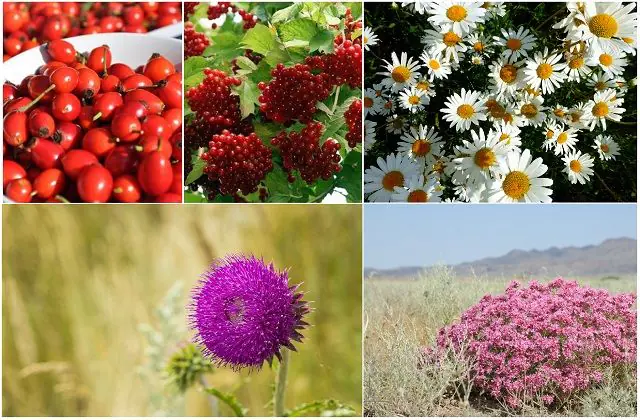

In the treatment of folliculitis, a large role is given to folk remedies that have proven themselves well. However, they should only be used in combination with medications. To alleviate the patient’s condition, relieve inflammation and itching, the following compresses and mixtures are used:
- Mixture for compresses from viburnum and rose hips. 200 g of viburnum and rose hips, 100 g of dried nettle, 10 g of walnut shells, pour 2 tbsp. water and boil for 10 minutes. The mixture is infused for 24 hours, filtered and mixed with 50 g of cottage cheese and 50 g of bee honey.
- A mixture of cottage cheese with a strong viburnum decoction is stirred until it becomes a puree consistency and applied to the affected area 3 times a day for 20 minutes.
- Thorns are used for compresses, baths and soothing dressings. 50 g of root is boiled for half an hour in 0.5 liters of water. The broth is infused for one hour and filtered.
- Wash your face with a strong chamomile decoction and wipe the sore spots 3 times a day.
- Locally they use prickly tartar (also called thistle). A fresh paste is made from the leaves of the plant, which is applied to the affected area.
- A powder is made from the dried flowers of the tenacious bedstraw and sprinkled on the sore spot under a medicinal bandage.
- Locally, under a medicinal bandage, a freshly prepared pulp from the leaves of the fragrant woodruff is applied to the site of the abscess. The dressing is changed 2 times a day.
- To prevent staphylococcal folliculitis, after shaving, apply a moistened hot towel to your face for a minute.
Read also about the treatment of bacterial folliculitis using traditional methods.
Prevention of folliculitis - how to prevent the disease

- Practice good personal hygiene: change bed linens, use clean towels and wear clean clothes.
- Bath and wash your face with antibacterial soap twice a day. Dry your body with a clean towel.
- Do not use harsh soaps or harsh scrubs for washing and bathing. This will increase irritation and itching.
- Do not shave the affected area. Constant shaving worsens the condition. If shaving is necessary, do it carefully with an electric razor, not a razor with blades. Shave according to the length, not against the hair.
- Do not touch the affected area with your hands to avoid transferring bacteria.
- Do not wear tight or tight clothing. Friction from tight clothing develops folliculitis, transmits infection and causes itching.
- Clothing that covers the affected area with folliculitis should not be wet or damp. This will increase irritation.
- Discard any oils, lotions, creams, or other cosmetics you may have used.
- Do not swim in open water, pools or visit saunas.
Read also about the prevention of oil folliculitis.



