- Kinds
- Classification
- Causes
- Drug treatment
Chronic folliculitis is a disease caused by staphylococci. These microorganisms are present on the skin of most people, but only 10% have the pathogenic strains (bacteria) caused by this disease. Moreover, after folliculitis, the incidence of pathogenic staphylococcal infections increases to 90%, which contributes to the chronic course of the disease.
Types of folliculitis
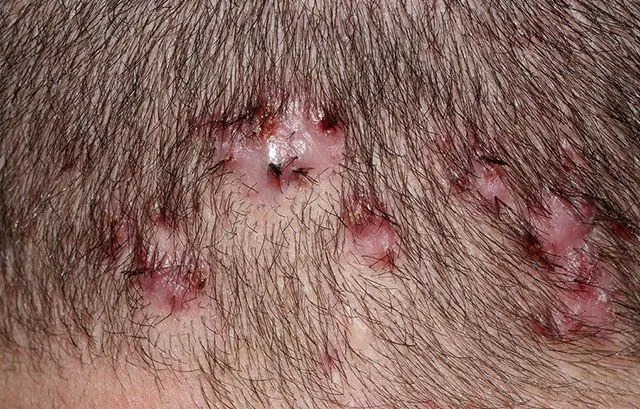
In the photo, Hoffmann's abscessed folliculitis
The course of folliculitis can be acute (symptoms are very pronounced, the affected area quickly increases) and chronic (accompanies a person throughout his life, followed by remission and periods of exacerbation). Based on symptoms and type of manifestation, there are 6 types:
- Professional - Affects the palms and outer forearms of people who work with chemicals.
- Depilatory - is provoked by constant friction of clothing against the skin in hot weather with high humidity, which inflames the follicles, mainly on the lower extremities.
- Impetigo Bockhart - appears when the skin gets wet (staying in water for a long time and applying compresses).
- Eosinophilic - not fully studied, but scientists believe that the cause of the formation of papules is eosinophils (special cells of the immune system) that accumulate under the skin. Often affects patients with HIV infection.
- Decalvating - chronic form. Affects the scalp, groin and armpits. In place of the papules, scars form on which hair does not grow. The exact causes of the disease are not fully understood.
- Hoffmann's abscess folliculitis — a chronic dermatological disease is diagnosed in men 18–40 years old on the scalp. Develops due to blockage of hair follicles. Hair falls out in the affected areas and scars form in their place.
Classification of chronic folliculitis
Chronic folliculitis is accompanied by the emergence of new inflammatory processes. Pustules of different stages: just emerging, purulent, drying out and scarring. They are characterized by a fusion of lesions affecting a large surface of the skin. Random lesions alone are rare. A red border forms around the affected follicles. The free ends of shaved hair grow into the skin and often the inflammation is complicated by a staphylococcal infection. New lesions are at different stages of development:
- Permeated in the middle with hair.
- Contain thick yellow or green pus.
- Accompanied by skin itching.
- Painful.
Causes of chronic folliculitis
The main form of chronic folliculitis is sycosis. Chronic relapsing course is mainly caused by staphylococci and dermatophyte fungi. When diagnosing, smears are taken for culture from the mucous membrane of the nose and anus to establish Staphylococcus aureus. In men, pustules are localized on the face in the area of the beard and mustache, in women - on the pubic part and legs. Provoking factors - skin damage (during shaving or hair removal) in combination with endogenous causes:
- Decreased immunity.
- The presence of foci of chronic infection (caries, tonsillitis).
- Changes in sensitivity to staphylococcal antigens.
- Hypofunction of the gonads.
- Find out how folliculitis is diagnosed
Drug treatment of chronic folliculitis
Pustules on the skin are treated with antiseptic solutions (salicylic alcohol, boric acid, potassium permanganate) and local agents in the form of ointments with an antibacterial effect (Lincomycin, Erythromycin, Dalacin-T, Epiderm, Zinerit). In case of a chronic process, combination drugs are prescribed that contain antibiotics and hormones: Dermozolon, Oxycort. For internal use, antibacterial drugs are prescribed (Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Cephalosporin). If necessary, estrogens, gestagens, immunostimulants, vitamins A, C, E are prescribed. Physiotherapy (ultraviolet and laser radiation, electrophoresis) is prescribed when the inflammatory process improves and subsides, so that there is no scarring.
Treatment can be supplemented with home folk remedies. Take an infusion of burdock roots internally. Rub homeopathic medicines into the skin several times a day, for example, Traumeel S ointment. Supplement the treatment with herbal medicine by rubbing the affected areas:
- Fresh plantain juice.
- Infusions of elecampane, St. John's wort and calendula.
- Decoction of willow bark.
- Infusion of birch leaves.
If folliculitis is not treated, the infection will spread deeper into the skin and boils, abscesses, carbuncles will form, and a fungal infection will also develop - dermatophytosis. If microorganisms enter the blood, such diseases can threaten the patient’s life. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly begin treatment of chronic folliculitis and take preventive measures:
- Eliminate provoking factors of folliculitis.
- Maintain proper nutrition.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Use antiseptic soap.
- Treat your skin regularly with benzoyl peroxide.
- Increase and strengthen immunity.
Video about sycosis of the beard and mustache:
- Related article: home recipes for treating folliculitis