Burns are the most common household injuries that every person encounters repeatedly. But it is impossible to treat them as something not worth attention. Even a seemingly minor burn can have serious consequences if left untreated.
Degrees and types of burns
Before treating a burn with any other means, you need to find out its degree and take into account the type.
All burns are divided into thermal (resulting from exposure to a hot substance - water, steam, oil, sunlight, etc.), chemical (tissues are damaged by caustic chemicals - alkali, acid, etc.) and electrical (formed under the influence of electric current).
If you receive chemical or electrical burns, it is not advisable to self-medicate, except to provide first aid. But you can eliminate the consequences of thermal burns yourself. But here it all depends on the degree. There are four of them:
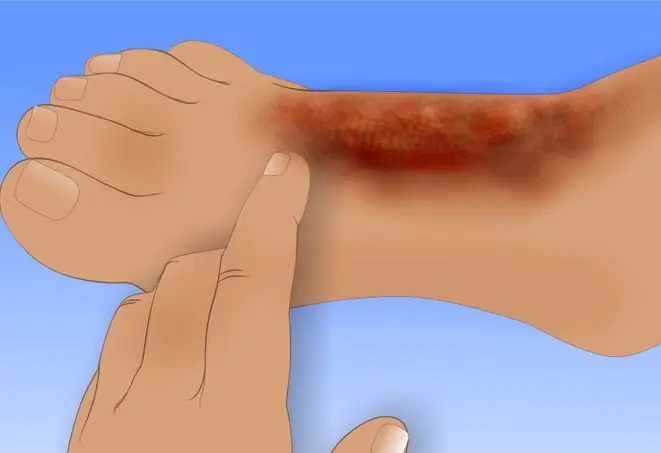
- The first is manifested by redness of the skin, a burning or tingling sensation and slight swelling.
- The second degree is manifested by severe redness of the skin and blisters.
- A third-degree burn is accompanied by severe pain, from which the victim can go into shock and even lose consciousness. Burns to large areas of the body can be fatal.
- The fourth degree is manifested by charring of the skin. Muscles and even bones are destroyed. Often the victim does not feel pain due to damage to the nerve endings.
If there is a third or fourth degree burn, even on a small area of skin, the first thing to do is to immediately take the victim to the hospital. But with the first and second degrees, it is quite possible to do without the participation of doctors.
First aid for first and second degree burns
Before treating a burn, you need to cool the affected area. This will reduce the pain. It is good to place the wound under running water for 10-20 minutes.
Next, at the first stage, you can treat the wound with some kind of antibacterial agent or healing cream. If the skin at the burn site is contaminated, it should be wiped with an alcohol solution (40%) before treatment.
In case of a second degree burn, the damage is treated with antiseptic agents based on furatsilin, rivanol, etc. Anti-inflammatory and film-forming aerosols are used. You can also apply a bandage soaked in a solution of novocaine, or take painkillers orally.
What not to do
For first and second degree burns, there are taboos, the violation of which is fraught with complications. So, what should you never do?
- Apply ice to the burned area of skin.
- Apply oil or rich creams to the wound. Although they relieve pain in the first minutes, they retain heat and slow down the healing process.
- Lubricate the wound with sour cream, kefir and other dairy products (unless we are talking about a sunburn).
- Use cauterizing agents such as brilliant green or iodine.
- Bandage the wound.
- In case of second degree burns, it is forbidden to rip off the blisters.
How to treat a burn? List of medications
Furacilin ointment has proven itself well as a primary treatment for burns (especially for children). “Plastubol” and “Iodvinisol” have film-forming properties. Aerosols “Olazol” and “Lioxazide” have high medicinal properties. Ointments “Bepanten”, “Rescuer”, “Levomekol” are also suitable.
The best answer to the question of how to treat a burn with boiling water is the Panthenol aerosol. In this case, it is simply irreplaceable. If you don’t have any of the listed remedies at hand, you can use traditional methods of treating burns, which will be discussed below.
Folk remedies for thermal burns
The centuries-old “burn practice” has not passed without a trace for humanity. People have come up with a lot of options for how to treat a burn at home, without resorting to traditional medicine.
Here are the most popular and accessible:
- Toothpaste (preferably with propolis or mint). Applying it to the burned area relieves pain and prevents blisters.
- Potatoes or carrots - grated raw, they are applied to the wound and fixed with gauze.
- Cabbage. The cabbage leaf is cooled and applied to the affected area before heating. Then take another cooled sheet.
- Soda. One tablespoon per glass of water. Gauze is moistened with the solution and applied to the burn site.
- Green or black tea. Cooled fresh tea leaves are poured over the wound.
- Egg white. You can simply apply it to the wound, or you can mix it with sauerkraut (finely chopped) and apply it.
- Onion. Finely chopped vegetables are fried in a large amount of sunflower oil until brown. Then the mass is cooled and filtered. Onion oil is applied to the burned areas.
- Dill. The juice squeezed out of it is diluted with water in a ratio of one to two and applied to the burn in the form of lotions.
- Calendula. The tincture of this flower is mixed with Vaseline in a ratio of one to two. The resulting ointment treats burns well.
Many people are interested in the question of whether it is possible to treat a burn with urine. There is no clear answer to this. Some say that urine in this case is a panacea, while others categorically deny it, claiming that urine contains toxins that can cause inflammation of the affected area.
Treatment of burns with hydrogen peroxide
Another pressing question: “Can a burn be treated with peroxide?” This product, unlike special ointments, is in almost every first aid kit. It is used to stop bleeding and treat wounds. A solution of hydrogen peroxide (three percent) does not cause burning of the skin or other pain, but acts quickly. And it's inexpensive. But what about burns?
If the damage is of the first or second degree and does not occupy a large area, then it is quite possible to treat the burn with peroxide.
To do this, soak a napkin or bandage with the product and apply a compress to the wound. Hold for a few minutes. Repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day for three days. The product quickly relieves swelling and pain.
But peroxide cannot replace other drugs. After treating the wound with a solution, it is recommended to apply ointments like Levomekol to the burn.
Thermal oil burns
Injuries caused by hot oil, which housewives often encounter, deserve special attention. Treatment for such thermal burns is somewhat different from those caused by steam, hot water, metal, etc.
If hot oil gets on your skin, the first thing you need to do is place the injured area under cold water for about ten minutes. Remove the oil from the skin using cotton wool and take a closer look at the burn. If everything turns out to be redness or small blisters, you can try to deal with the problem yourself.
What else can you use to treat a burn?
- In this case, dark household soap has proven itself to be excellent.
- It is good to apply soda, chalk or starch to the sore spot. They relieve swelling.
- Honey compresses relieve pain and heal wounds.
- If pustules appear (which often happens with oil burns), you can use antimicrobial ointments. For example, Fuzimet.
Specifics of sunburn treatment
The faster first aid for a sunburn is provided, the “less blood” this situation will cost the victim. And it consists in eliminating the influence of sunlight and moisturizing the affected areas of the skin. True, a cold shower is not recommended - it is better to cover the burned areas with a wet cloth of natural origin.
This must be done before treating the sunburn with any nourishing product. For example, a solution of aloe and vitamin E. By the way, this vitamin can also be taken orally - it promotes tissue restoration.
Among the folk remedies, the most popular for the treatment of sunburn are traditional yogurt with sour cream, which is applied to the burned areas, potato juice, chamomile and oak infusions, as well as regular black tea.
Chemical burns
As noted above, if you receive chemical burns, you cannot self-medicate. After all, they are characterized not only by skin injuries, but also by the entry of harmful substances into the body. Therefore, medical supervision is necessary.
But if the degree of burn is not higher than second, then first aid measures can and should be taken. The action algorithm is as follows:
- Rinse the wound with running water for 20 minutes.
- Treat the burn with a neutralizing solution. If the injury was caused by acid, a soap solution will help; if the alkali is boric, citric or acetic acid (two percent solution).
- It is good to treat the areas around the wound with ammonia (0.5% solution).
- After removing dead pieces of epithelium, apply a compress with Vishnevsky ointment or syntomycin emulsion.
And be sure to see a doctor, whose help, by the way, will be needed for any degree and for any type of burns, if the wound does not heal for a long time, rots, hurts, has an elevated body temperature, etc. It is important to always remember that such a seemingly trivial injury, like a burn, can cause serious complications, including death.
Degrees of burns
There are four degrees:
First, the skin at the site of the lesion turns red,
Second - a blister appears,
Third, the deeper layers of the skin also die,
Fourth - the affected area is charred.
The degree of damage is influenced by the volume of affected tissue, as well as how deep into the body the damaging factor has passed. Lesion area in the medical environment is measured as a percentage of the total skin area. With severe degrees of damage, the body at the site of the burn becomes insensitive, and veins may stand out. Often the actual depth of thermal impact can be revealed only five to seven days after the incident. This is due to the fact that new tissues suffering from lack of nutrition are added to already destroyed tissues. If more than 10–15% of the body surface is affected, the patient develops a burn disease. The severity of its course depends on whether the respiratory organs are affected, as well as the general condition of the patient and his age. If more than 15% of the body area is affected, burn shock develops.
What can't you do?
1. Before transferring a patient or transporting him, you should definitely check whether, in addition to burns, there are also fractures, and whether the respiratory organs are affected.
2. Treat the affected surface with any improvised or folk remedies, this may aggravate the condition.
3. Without anesthesia and sterile bandages, try to clean the wound.
4. Apply bandages if you do not know how to do this in a particular case. Since an incorrectly applied bandage provokes increased swelling.
5. Use a tourniquet unless there is an emergency indication. The burn disease intensifies, there is a possibility of tissue death and subsequent amputation.
6. If there are several victims, you should first pay attention to those who are unconscious or in a state of shock, since their condition is worse than those who can call for help.
7. Do not puncture the resulting bubbles.
8. Do not remove clothing stuck to wounds.
First aid for thermal injury
1. Eliminate the heat source (fire, hot liquid, steam).
2. Remove the tissue from the affected area; in case of first or second degree damage, you need to pour cool water on the affected area for 5 - 10 minutes. If charring of the tissue or an open wound is observed (third and fourth degree), a clean, damp cloth is applied.
3. Give 500 ml of water with half a teaspoon of salt and a quarter teaspoon of soda to drink.
4. Give 0.05 g. diphenhydramine (can be given as an injection) and 1 – 2 g. aspirin.
5. Remove all things that can be removed from the affected part of the body, including jewelry, watches, belts; if clothing is stuck to the wound, it must be carefully trimmed around it.
6. Call an ambulance.
You should definitely call an ambulance if:
a child or an old man was injured,
the area of the affected surface is more than five palms of the victim himself,
there are open wounds,
the groin is affected,
head is affected
respiratory organs, mouth and nose,
two arms or two legs are affected (or one arm and one leg).
Bepanten is a Swiss drug based on provitamin B5, which helps restore damaged tissue cells and accelerate the process of skin regeneration after a burn, injury, etc.
Due to the dihydrochloride contained in chlorhexidine, the ointment has a strong antiseptic effect and prevents the development of infection in areas of skin damage. The drug is completely safe, so it can be used to treat burns even in the youngest children. Main contraindication: intolerance to the components of the product, side effects from the use of Bepanten ointment have not been identified.
Argosulfan is an antimicrobial drug that contains a substance active against various types of bacteria - sulfathiazole and silver ions, which help slow down the process of bacterial cell division.
The ointment is not prescribed for some hereditary diseases, intolerance to its components, pregnancy, lactation, and for the treatment of children under 2 months. Side effects from its use include: urticaria, itching, burning in the area of application, leukopenia.
Panthenol is a regenerating agent based on pantothenic acid derivatives, a tissue regeneration stimulator, available in the form of ointment, cream, spray, emulsion, and injection solution. The main active ingredient is dexpanthenol.
Levomekol is one of the drugs prescribed for 2-3 degree burns that helps accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues. Active components of the ointment: methyluracil (accelerates the division of healthy cells, has a slight anti-inflammatory effect), chloramphenicol (an antibiotic active against various types of bacteria).
Levomekol is contraindicated in the presence of hypersensitivity to its components; treatment during pregnancy is carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Side effects of the drug include allergic skin rashes. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the burn and the presence of complications.
Proper and timely treatment of the wound will not only help avoid various complications, but will also increase the speed of wound healing.
- Treat the wound only with clean hands.
- Before treatment, it is necessary to remove foreign bodies from the wound, then rinse with clean water (preferably boiled and running), do not use soap. If there are no foreign bodies in the wound, then immediately begin treatment.
- If the wound is bleeding heavily, then you first need to stop the bleeding; cold can help you with this; it will constrict the blood vessels, which will reduce the flow of blood to the damaged area.
- If the insides are visible from the wound, do not touch them, apply a bandage and consult a doctor.
- After washing the wound, treat it with an antiseptic (for example, chlorhesidine). Remember that iodine and brilliant green are used only to treat the edges of the wound; these products should not be poured into the wound itself.
- After you have treated the wound, it should be protected from dirt and germs. To do this, you will need a plaster, a bandage, and, if possible, a sterile napkin for treating wounds. If the wound is not large, then simply cover it with a band-aid so that the tissue layer is on the wound itself. If the wound is large, then you should apply a napkin moistened with an antiseptic to the wound, and then bandage it, or secure it with a plaster.
- You should not just wrap the wound with a bandage - it will be difficult to change it, as it will stick to the wound.
- The bandage should cover both the wound and some of the skin around it.
- The bandage must be changed daily, but carefully so as not to disturb the damaged tissue.
- If you do not have special means to treat the wound, you can cover it with a clean handkerchief.
- If the wound is deep, you need to see a doctor to avoid disastrous consequences. The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests, possibly x-rays, and treatment.
- Abrasions and minor scratches should not be bandaged. They heal better and faster outdoors.
- If the napkin sticks to the wound, drop hydrogen peroxide on it and carefully separate it from the wound.
Everyone knows that hydrogen peroxide has a disfiguring effect, but it does not last very long. How to treat a wound with peroxide? A three percent peroxide solution is suitable for treating wounds; moisten a cotton swab or disk with this solution and treat the edges of the wound several times, then apply the moistened sterile napkin to the wound and bandage it.
How to treat an open wound
If the wound is bleeding and cold does not help, then apply a pressure bandage. Do not touch the wound with your hands; remove all foreign bodies, for this you can use treated tweezers, then treat the edges of the wound with an antiseptic. The wound dressing should not be very tight or thick.
How to treat a purulent wound
Treating such a wound simply with an antiseptic will not give the desired effect, since all the bacteria are contained in festering tissues. After the usual treatment of such a wound, you should apply Vishnevsky ointment (or its analogues) to a napkin and bandage it.
When answering the question of how to treat a wound, you should understand that if the wound is serious, then after the initial treatment, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Zelenka. The use of brilliant green is prohibited if there is a heavily bleeding wound or damage to the mucous membrane. Only the edges of the wound.
Iodine 5% solution. The iodine solution should not be mixed with ammonia or ichthyol (ichthyol ointment); it should not be used to treat wounds on mucous surfaces. Only the edges of the wound.
Hydrogen peroxide 3% solution. A hydrogen peroxide solution is useful for soaking dried bandages. Hydrogen peroxide is very sensitive to storage in light: its antibacterial properties are inactivated within 24 hours, especially if the container with it has been left open.
Chlorhexidine digluconate. Available in the form of a solution. It has a fairly wide spectrum of action: it affects not only bacteria, but also viruses, protozoa and fungi. It is used for the initial treatment of wounds after it has been cleaned with hydrogen peroxide, and for the treatment of purulent wounds. To do this, you do not need to use a large amount of it; a few milliliters are enough, which are drawn into a syringe from which the wound is watered.
Potassium permanganate. A weak solution of this powder in saline solution (it should be barely pink) is used to wash wounds (both on the skin and mucous membranes) as both a primary treatment and those that have become suppurated, especially in cases where there is a danger of anaerobic microorganisms entering the wound . Before washing wounds, you need to prepare a fresh solution each time.
A burn is an injury that leads to disruption of tissue integrity. They are distinguished by the type of traumatic factor and the depth of damage.
According to the type of damaging factor, the following are known: thermal, chemical, electrical, wave types of damage. According to the degree of penetration of the burn, 4 stages are known. In the second and higher stages of the burn, blisters appear on the dermis, which burst after a while. After this, lesions remain on the skin that are susceptible to getting wet.
Description
A person faces various types of trauma throughout his life, starting from childhood. Before treating a lesion, you need to know everything about this type of injury. The damage is a violation of tissue trophism, which can be localized in various parts of the body. Weeping damage can cover different areas and depths of penetration. In this case, various structures from the dermis and blood vessels to bones and internal organs can be affected. Non-healing weeping lesions occur when the skin humidity is high. The mechanism of occurrence of such burns is similar to the way of formation of ordinary injuries.
There are several phases in it:
- inflammatory process;
- regeneration;
- scarring.
Restoration and healing of weeping type wounds should be carried out according to the scheme. It is necessary to constantly bandage the open wound, use restorative and disinfecting medications.
Treatment of weeping wounds after burns
A weeping burn must be treated carefully. In order to reduce the risk of adverse events, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the injured areas. Carefully remove dust, dirt and pus. A disinfectant medication is applied to damaged tissue. For this manipulation, antibacterial agents such as betadine are used. Hydrogen peroxide has a good effect. If this solution is not available, then soapy water can be used. The skin around the injury site is lubricated with alcohol solutions of brilliant green or iodine. This is done to dry the edges of the damage and prevent infection. The next step is to protect the wound from pathogenic flora. To do this, apply a bandage. If the burn penetrates deeply, you must take painkillers. In some cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
How to treat each stage?
Wet-type injuries have the following periods: the stage of inflammation, recovery and scarring.
So how to treat weeping wounds after a burn? During the inflammatory process, antiseptics are applied to the wound. You can use any available one. After this manipulation, it is necessary to apply a bandage made of sterile material, which will prevent the entry of moisture.
The fluid that flows from the affected area helps restore the wound and speeds up the healing process. During this period, it is necessary to change the dressing as often as possible. If excess moisture is released, then healing is carried out using the open method. For areas of the body where fluid production is highest, hygroscopic dressings are used.
During dressing it is necessary to treat with special means. Antibacterial drugs or alcohol-based products can only be used after being prescribed by a specialist.
If there is severe pain, then it is necessary to take analgesics. This can be in tablet form, injection solutions or special aerosols that are most convenient to apply.
During the purulent-necrotic period, agents with antibacterial activity are applied under the bandage. But you cannot use ordinary ointments with antibiotics for this; they do not cope with cleansing the wound. It is better to give preference to water-based ointments, such as Levosin or Levomekol.
At the second stage, when the inflammation process has already passed, and the lesion is clean and the tissues have been restored, special burn patches are applied to the site of injury. It is impregnated with medicinal preparations, which, upon contact with the skin under the influence of heat, transform into a gel structure and have a therapeutic effect.
In the third period, Solcoseryl is applied under the gauze. This helps speed up the recovery process and scar formation.
As part of complex therapy, vitamin and mineral complexes must be prescribed. Essential substances such as vitamin A, C and E help produce collagen and start the healing process.
How to treat a weeping wound after a burn
It is better to entrust the choice of drug to a doctor. The following are the most effective drugs.
Solcoseryl is one of the most effective medications for healing the skin. It is most often prescribed by doctors for burns. The formula of the medication includes active components that nourish the skin, help deliver oxygen to cells and regenerate cells. Solcoseryl is available in the form of a gel or ointment. For weeping wounds, it is better to use a gel consistency.
Lioxazine is a high-tech medicine that provides pain relief after injury. It is able to accelerate regeneration processes and prevent the penetration of microorganisms into the wound.
Combination drugs
Amprovisol is a medicine in the form of an aerosol. It is very convenient to use for burns, since there is no need to contact the affected area. This remedy helps relieve inflammation in burns, disinfect and anesthetize the wound. Also ensures quick recovery.
Olazol is a local drug with a healing effect. Available in aerosol form. Contains sea buckthorn fruit oil. Due to the antimicrobial, analgesic effect, the process of epithelial restoration is significantly accelerated.
Traditional methods
If the burn gets wet, what should you do at home? You can use folk recipes. The most effective are the following:
Potato
The young root vegetable is peeled, grated on a coarse grater, and squeezed using gauze. This juice is moistened with a clean dressing material and applied to the wound. The dressing is changed 4 times a day.
Onion
The onion must be grated on a fine grater, then the mixture is applied to a bandage and applied to the damaged area. With the help of an onion, the injury site is disinfected, the severity of pain is reduced and swelling is neutralized.
Aloe juice
You can squeeze the juice from the leaves of the plant or tear off the skin. The fabric is blotted with liquid and applied to the injury site. When using a whole sheet, it is attached to the wound for several hours.
Sea buckthorn
Sea buckthorn oil is an excellent remedy, but it must be sterilized before using it to treat a burn. I apply wipes moistened with this product to the wound. It is better to perform this manipulation once a day.
To treat the wound, prepare a decoction or infusion of water. Take a dry plant and fill it with water, leaving it for several days. Moisten the bandage with this solution.
You can carry out these activities yourself only if the injury is not life-threatening. Before using various remedies, it is important to consult a doctor. The best way to prevent injury is to follow safety precautions and follow all safety precautions.