The only effective method to get rid of a mole is to remove it. This is done for aesthetic reasons and medical reasons. Surgery is required if the growth is constantly traumatized, if its size, contours or color change. What happens after a mole is removed and how to care for it to avoid complications?
Popular methods and care
Currently, there are several methods for eliminating moles; the choice is usually made by a specialist. The doctor takes into account many factors - localization, likelihood of malignancy, area of skin damage.
Laser
The most precise impact is achieved when using a laser. This method is currently the most optimal. Experts highlight a number of positive aspects of this manipulation:
- local anesthesia makes the procedure virtually painless, even a child can easily endure it;
- duration is only 5-10 minutes;
- narrowly targeted beam exposure and the ability to control the depth of action prevent damage to surrounding tissues;
- soft and layer-by-layer removal of the nevus occurs;
- no bleeding;
- There are almost never any traces left after manipulation;
- minimum rehabilitation period (no more than 1-2 weeks).
Despite the positive aspects of laser destruction, it also has some disadvantages:
- inability to conduct histology of a mole after removal;
- not all hospitals have the most modern equipment;
- For normal healing, it is necessary to exclude ultraviolet irradiation and thermal procedures for some time.
The application area is treated with any antiseptics that do not contain alcohol, otherwise a burn to the young skin may occur, after which a scar will form.
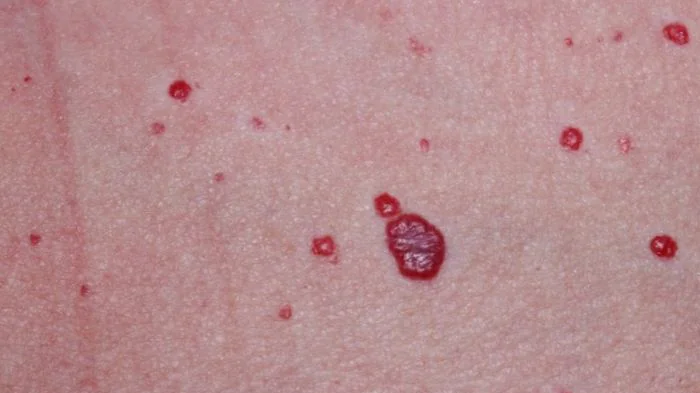
If everything is done correctly, the resulting crust falls off, and a red spot may remain in its place for some time. But then it disappears. Therefore, laser removal is used mainly to eliminate formations on open parts of the body.
If a scar forms at the site of removal, you can get rid of it by using a special patch with a silicone base. Contractubex or Dermatix ointment is also suitable. You can apply Panthenol or similar products to speed up regeneration.
Cryodestruction
This method uses liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which is minus 180 degrees Celsius. In this case, the tissue completely dies, a crust forms on top, under which the dermis is gradually restored. The procedure is not practiced in the facial area. Complete healing may take about a month.
Cryodestruction allows you to remove even a fairly large formation. During the session, the application site is completely disinfected due to the low temperature. The removal process itself proceeds quickly, leaving no traces in the form of a scar or scar. In addition, the patient does not experience pain.
The negative aspects of this method include:
- inability to conduct histological examination;
- getting burned;
- the need for a repeat procedure.
The doctor's lack of experience in such manipulations often leads to damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
On the first day, it is recommended to use hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate to treat a cold burn. For sensitive skin, antihistamine or antipruritic ointment (Fenistil, Nezulin) will help relieve itching. You should not scratch, as this easily damages the crust and the unformed tissue underneath it. For some time after the manipulation, a red spot may persist, gradually acquiring the color of normal skin.
Radio wave therapy
The radio wave method allows you to treat any problem area and at the same time preserve the tissue for research. The healthy part of the dermis is not disturbed, and no scars are left.
The method is especially suitable for cutting out tubercles that protrude greatly above the surface. The disadvantage of this technique is the impossibility of removing large formations. The risk of repeating the process, when the mole may appear again, is practically eliminated.
After radio wave removal, you should not wet the resulting crust and expose your body to the sun’s rays.. Only disinfection should be carried out: rinse with antiseptics in the first hours, lubricate with antibacterial ointments. The doctor may prescribe Chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate, Levomycetin, Pantoderm. You cannot use cosmetics.
Electrocoagulation
This procedure eliminates various formations using high current. In this case, tissue coagulation occurs, a crust appears, which then falls off. Manipulation is performed on any area of the skin. One session is enough. After this, no wound surface is formed, no bleeding is observed, since the vessels coagulate along with the mole.
After the crust is separated, a scar in this place can remain only in exceptional cases. Most often, a small spot appears, slightly lighter than normal skin, which will go away over time. If electrocoagulation or radioknife is used, the removed tissue is preserved. It can be examined for the presence of atypical cells.
The procedure is prescribed if it is necessary to eliminate warts, papillomas, hemangiomas, keratomas (in old age), and complicated acne. It is successfully used in the treatment of atheroma, spider veins, and formations after the introduction of molluscum contagiosum. Electrocoagulation is effective for removing a mixed type of nevus when cancerous degeneration is suspected. A positive aspect of the method is the ability to control the depth of exposure.
Do not wet the crust at the surgical site or expose it to insolation.. Then she needs to be protected from traumatization. Additional care in the form of applying local antibiotics and antiseptics is required only in case of infection.
Using a scalpel
The oldest method is to cut out the spot or nevus using conventional surgery. It is time-tested, its price is affordable for everyone. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia and lasts approximately an hour. After excision, a wound is formed that requires treatment. When a wart or mole is located deeply, a hole is formed. If a large nevus is removed, then for normal healing the doctor applies a suture, which is removed after a week.
- high probability of scarring;
- bleeding during and after surgery;
- the patient needs rehabilitation.
- no need to look for a clinic with expensive equipment;
- the operation can be performed by a surgeon without additional skills and long-term experience;
- It is possible to excise formations of any depth and area of the lesion.
It is also important that the operation allows you to preserve the tissue intact in order to ensure the absence of oncological pathology based on the results of histological examination. It is very important to properly care for the excision site after this.
Healing takes a long time - from 2 to 4 weeks. At this time, you should treat the surface in the same way as a regular wound:
- rinse with an antiseptic;
- carry out hygiene of the skin around the wound;
- apply a bandage for the first few days to prevent infection;
- if the wound is subject to frequent friction, you will need to wear a bandage for a long time.
It is also important to avoid injury and exposure to sunlight during the entire healing period.
Possible consequences
Most often, nevus removal proceeds safely, but in some cases negative consequences of manipulation may occur:
- the appearance of inflammation and infection;
- swelling or new formation (high probability of developing a tumor);
- swelling and hyperemia;
- bleeding;
- soreness and discomfort;
- keloid scar;
- compaction;
- area of hypo- or hyperpigmentation;
- increase in local or general temperature.
In some cases, a new one may appear at the site of the removed spot. This phenomenon occurs when the manipulation is carried out incorrectly, when some of the mutated cells remain in the tissue.
Relapse requires an even more thorough examination and is eliminated exclusively by repeated removal with mandatory histological examination. This is especially important if there is a sore that itches or bleeds.
Normal recovery after surgery
If the intervention is performed by an experienced specialist, then the wound healing process proceeds normally. All you need is time and proper care.
- In the first week, a crust forms. The most important thing is not to touch her. In the first few hours, the wound may bleed a little, especially if it was removed using a scalpel. Avoid getting it wet or accidentally damaging it. In some cases, it is recommended to rinse with a light solution of potassium permanganate and apply an antibacterial ointment prescribed by a doctor.
- Second week - the crust on a small growth often falls off. In larger formations, it may still persist, and the skin underneath may itch. The exposed layer of thin epidermis requires protection from sunlight, and visiting a solarium is prohibited at this time.
- By the third week, the operation site should no longer hurt or bleed, even when affecting a large area. The redness goes away. If the laser method was used, then everything should be fine by this time. The application site is no different from normal skin.
- The fourth week is considered the last. At this moment, the patient forgets that he was once bothered by a nevus or birthmark. And the wound heals completely.
Violations after removal
If the damaged area in the area of the removed lesion becomes inflamed and pus begins to ooze, the associated infection is treated with antibiotics. Sometimes Tetracycline ointment is combined with oral broad-spectrum agents. If the wound begins to spontaneously become wet and a light liquid is released, then the area can be smeared with Zinc ointment, which dries and destroys pathogenic microflora. You should use any product only after consulting a doctor.
A hypertrophic scar may remain if the patient independently tears off the crust or exposes the removal site to constant friction or pressure. In this case, the wound will take quite a long time to heal and may turn into a scar. To eliminate a keloid scar after mole removal, a laser is often used.
A hypertrophic scar may appear as a depression in the skin with crater-like edges. This pathology can be eliminated with the help of physiotherapy or cosmetic surgery.
The hypopigmented area after nevus removal may resolve over time and is not usually a cause for concern. In this case, it is recommended to avoid sunlight.
Hyperpigmentation, or recurrent nevus, can occur after any method of removing a mole or spot. It resembles melanoma, has ragged, uneven outlines, and is dark in color. Differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of histological data. To eliminate this phenomenon, repeated removal is carried out.
The desire to get rid of moles is due to both aesthetic discomfort and potential danger. Bleeding from a mole, inflammation, increase in size - all this can lead to transformation into a malignant tumor. To get rid of the tumor, many people opt for laser removal.
Benefits of laser removal
Having decided to undergo laser removal of tumors, their owners ask questions about the safety of the method. What are the advantages over other methods?
- painlessness;
- efficiency;
- non-invasiveness (no exposure to surgical instruments - needles, scalpels, etc.);
- sterility;
- fast healing;
- minimum contraindications;
- no scars after surgery.
Modern technologies make it possible to control the process with millimeter precision, quickly getting rid of the tumor. The laser ensures rapid tissue regeneration and does not cause bleeding, reducing the chances of infection.
The procedure is becoming more popular than other methods. The cost of the operation will depend on the choice of medical institution. It is preferable to carry out the procedure in a clinic rather than with cosmetologists.
Indications for removal
You should consult a doctor if:
- the mole grows in size;
- pigmentation goes beyond its limits;
- dryness and flaking;
- hair does not grow on the surface;
- the mole itches;
- the surface is wet or bleeding.
Even if the mole does not have similar symptoms, consulting a doctor will not be superfluous. The specialist will determine the degree of danger of the neoplasm.
Contraindications
Despite the safety of the procedure, it has a number of contraindications:
- skin diseases;
- diabetes;
- suspicion of malignancy of the neoplasm;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- allergy to ultraviolet rays.
The doctor must conduct a mandatory consultation and examination before surgery. Laser removal of a mole in the presence of skin diseases can lead to a number of side effects.
Removing moles on the face
The presence of formations on the face sometimes causes both aesthetic and physical discomfort. Located on the face, it is often injured, bleeds and causes pain. The presence of a large or uneven mole on the face sometimes makes you feel complex about your appearance.
Removing a mole from the skin of the face is the same as from other parts of the body. The neoplasm is examined, the patient undergoes consultation with doctors. Removal, depending on the size of the mole, takes from a few seconds to 5 minutes. In cases where the neoplasm is large, it will require removal in layers. Several days should pass between procedures.
The operation does not leave bruises or bruises, only a wound that will cover itself with a protective crust.
Removing red moles
Removal of angiomas is also possible using the laser method. Red vascular neoplasms cause inconvenience when large in size. The nature of their appearance and malignancy are also determined by doctors during the examination. If necessary, the patient is tested for the absence of diseases that may be contraindications for removal.
The removal and healing process is no different from removing a regular mole.
Photos before and after removal
Before surgery, many people are concerned about how the site will look after removal. Below are photos before and after surgery:
Despite the apparent pain of the procedure, it is performed under anesthesia. The healing process depends on following the recommendations of the attending physician and one’s own responsibility. The after photos are presented after the healing time has passed (from four months to a year).
Video of mole removal
Complete and detailed mole removal process.
Healing process
Immediately after the operation, a scar remains at the site of the mole. The doctor thoroughly disinfects it and gives recommendations for care. During the day after the procedure, a protective crust forms at the site of the mole. Under no circumstances should you get rid of it - it will promote healthy and rapid healing.
For several days after the crust has formed, it may be damp; the doctor will prescribe disinfectants to treat the affected area. The surrounding skin may begin to itch - this indicates the healing process.
Healing time directly depends on wound care, and it is strictly individual. With fast regenerating ability, the process will take two to three weeks, with slow regenerating ability, the process can drag on for months. To speed up the process, special care is required for the affected area.
How to treat a wound after removal
If a bleeding wound opens after removal, tell your doctor. After laser removal, a dry crust of skin should form; disinfectants should be prescribed by a doctor. When the crust falls off on its own, pink skin forms in its place. This will indicate healthy skin healing.
It is not recommended to use cosmetics or other skin products during healing. It is also strictly prohibited to visit swimming pools, baths and saunas. The healing site should not be disturbed with bandages, tissues, sponges or washcloths. As soon as the crust falls off, the skin should carefully protect from ultraviolet rays - use protective creams with a filter of at least 60.
Consequences
If the operation is performed correctly and all doctor’s recommendations are followed, the healing process will accelerate. If a mole is not completely removed, serious skin problems can occur; this risk can be reduced by choosing an experienced specialist. The clinic must be equipped with modern technologies and have a good reputation.
If you do not follow the recommendations within three days after surgery, the skin may become inflamed. The process of treatment and healing of the wound in this case can take a long time. In addition, if you subject the skin to mechanical stress or try to get rid of the crust, a scar may remain.
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light on an already healed wound, during the first four months, can lead to skin pigmentation. There is a risk of a new growth appearing in place of the old one.
If all conditions are met, the complete healing process will take four to six months.
Complications after removal
Complications depend on the size of the removed mole and the complexity of the operation. A large wound takes longer to heal, has a greater chance of developing inflammation, and the scar from it takes a long time to heal. When small moles are removed, the chances of complications are reduced.
If the removal took place in several stages, and healing does not occur for a long time after the first operation, the doctor may suggest removing the remainder in other ways.
Complications can arise from incomplete removal of a mole or laser treatment of too deep layers of skin. Incomplete removal leads to the reappearance of the mole. Interference with its functioning, which led to incomplete removal, can lead to the development of a tumor. The new one is removed after the results of the first procedure have completely healed.
Sometimes complications in the form of inflammation or bleeding can occur in women experiencing hormonal problems. Before the operation, a qualified doctor prescribes all types of tests associated with the procedure.
If not properly cared for, pus will form at the scar site. You should not self-medicate; it is better to consult your doctor. A difficult healing process increases the chances of developing a non-healing scar on the skin.
Scars and scars after removal
After four months, a white, sunken surface or raised scar remains on the skin. If the healing process is favorable, the doctor may suggest products that help skin regeneration. If recommendations are not followed or rehabilitation is difficult, the scar may not heal for a long time.
If there are no neoplasm cells and the wound has completely healed, it is possible to visit a cosmetologist. Consult a doctor; laser scar correction can be performed to heal the scar. It takes at least a year for the scar to correct after surgery.
During the rehabilitation process after laser removal of a mole, it is important to follow all the recommendations of the attending physician, not expose the skin to ultraviolet radiation, and undergo regular examinations - this will help speed up the regeneration process.
Medical expert article
Very often, moles on the body cause discomfort, for example, when wearing clothes or jewelry. And aesthetically, such formations are not always appropriate. A few decades ago, mole removal was carried out only surgically - using a scalpel. Nowadays, you can remove an unwanted nevus in a variety of ways, after consulting with a doctor.
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]
Is mole removal dangerous?
In many cases, the very existence of a mole can be more dangerous than its removal. Despite the fact that birthmarks are benign formations, under certain conditions they can degenerate into melanoma - a cancerous tumor.
However, this does not mean that it is necessary to remove absolutely all nevi on the body. It is advisable to get rid of only potentially dangerous formations:
- exposed to constant injury from clothing or accessories;
- periodically disturbing for other reasons.
Don't worry that the surgery will cause new birthmarks to appear - it won't. Moreover, some stains may be so unfavorable that they must be removed.
It can be dangerous to get rid of moles yourself at home, using traditional methods, as well as using the services of a non-specialist - a person who does not have the appropriate education and skills.
What indications are considered sufficient for mole removal?
- Noticeable growth of a birthmark in a relatively short period.
- Change in spot color (both lightening and darkening).
- Development of the inflammatory process (redness, swelling).
- The appearance of blood, ulcers and other elements on the surface of the birthmark.
- Asymmetry of the spot.
- The appearance of peeling, crusts, blisters.
- Change in nevus consistency (hardening, softening).
- The size of the mole is too large.
- Location in areas of friction with clothing or other traumatic areas.
Any of the listed symptoms is considered a direct indication for mandatory elimination of the tumor.
Is special preparation required for the removal procedure?
If the birthmark is removed for aesthetic reasons, then special preparation may not be required. The doctor will examine the formation, assess its condition and depth, and then choose the most optimal method of removal.
If the removal of a nevus is carried out on suspicion of a malignant formation, then preparation may include taking certain tests and conducting research.
What tests need to be done to remove a mole? It depends on the individual patient. In most cases, the following types of diagnostics may be needed:
- general blood analysis;
- coagulogram (study of the blood coagulation system);
- blood test for tumor markers.
If necessary, if local anesthesia is planned, a drug reaction test may be performed to avoid allergies to anesthetic drugs. Most often, doctors use lidocaine-based products for this.
What kind of doctor removes moles?
Mole removal can be performed by a general surgeon in any hospital or clinic, as well as by specialized specialists:
It is much safer to carry out the procedure in medical institutions, where all the necessary equipment is available that supports most of the most common methods of getting rid of moles. In such medical centers, the doctor will be able to carry out the necessary diagnostics and select the most appropriate type of treatment for a particular patient.
It is strongly not recommended to remove tumors in dubious salons, or to trust your health to incompetent persons without the appropriate education and experience - this can be dangerous.
Mole removal methods: which one to choose?
There are many known ways to remove a mole. Each of these methods has its own indications, positive and negative sides. You can get rid of a birthmark using a scalpel, laser or “electronic knife”. Typically, the choice of method is made together with the doctor who will perform the procedure.
- Laser mole removal is a quick and effective way to get rid of unwanted skin lesions. One session is enough for this. In this case, healthy skin is not affected, so there are no scars left after removal, and the risk of bleeding is reduced to zero. A few months after the laser procedure, only a barely noticeable spot remains.
- Removing moles with nitrogen (cryodestruction method) is not a very popular method, which sometimes does not allow the tumor to be removed in one procedure, since it is not possible to accurately determine the depth of tissue damage by nitrogen. In addition, sometimes after the removal procedure there is a thermal burn, after which a trace of scar tissue may remain. Removal of moles by cryodestruction has a long recovery period for the skin, however, the low price of this method is often the main criterion for choosing patients.
- Surgical removal of a mole is the only method that allows a patient to be qualitatively relieved of deep-lying and large-sized formations on the skin. Most often, mole removal with a scalpel is carried out on areas of the skin hidden under clothing, since a scar usually remains after the operation. The size of the scar depends on the initial size of the birthmark and the extent to which the surgeon has captured nearby healthy tissue. The huge advantages of this method are its relatively low cost, guaranteed quality of removal, and the ability to send the resulting tissue elements for histological examination.
- Radio wave removal of moles is also called the radiosurgical method - this is a non-contact procedure for treating tissue and removing moles using a radio knife, that is, removal using radio waves. A radioknife is a special electrode, at the end of which energy is generated that heats and evaporates tissue. Radio wave removal of moles is considered a gentle method that does not leave behind scars and scars, and healing occurs quickly and without complications.
- Removing a mole by electrocoagulation is a thermal effect on the desired area of skin using high-frequency current. The essence of the method is to apply current and heat a special platinum loop to 200°C. With this loop, the doctor performs the procedure using “cutting” and “coagulation” waves. Removing moles with electric current allows you to “cut off” unnecessary tissue, exposing a small wound. This wound heals by primary intention and leaves virtually no scar.
Technique: how is a mole removed?
Important: removal of a birthmark should only be carried out by a specialist with relevant experience. Getting rid of nevi on your own can have serious consequences.
Any of the selected procedures is performed under local anesthesia - using an injection of an anesthetic or a special external anesthetic gel.
Removal of moles on the face is most often performed with a laser. This method allows you to eliminate the tumor without further scar formation. The procedure itself lasts only a few minutes, so, if desired, the doctor can simultaneously remove several formations at once. Within five minutes after the session, the patient can go home.
Removal of hanging moles is usually carried out using electrocoagulation. The entire session lasts no longer than 15-20 minutes, which depends on the diameter and number of birthmarks to be removed. Before the procedure, the doctor administers anesthesia by applying a special anesthetic gel or by injection. Next, by heating the tungsten electrode with an electric discharge, the hanging formation is “cut off” at once. Healthy tissues located in close proximity are cauterized, which prevents bleeding from the wound. The material obtained after removal can be sent for histology, and the wound itself usually heals within one week. Convex moles can be removed in a similar way if they are small and not particularly deep.
Removal of large moles is carried out only surgically. This operation is performed under local anesthesia, and all removed tissue elements are sent for histology (to exclude or confirm a cancerous tumor). The entire area around the formation is treated with an antiseptic. During the operation, the doctor partially cuts off healthy tissue to prevent regrowth of the birthmark. After this, suture material is applied, which is removed after about one week. The operated patient can immediately go home, but he will have to visit the doctor several more times for dressings and suture removal.
Removal of moles with histological examination is a mandatory procedure for a surgeon if a malignant tumor is suspected. Only such a study will help detect even the initial stage of tissue degeneration, cancerous and precancerous processes. In order to send tissue for research, it must be as intact as possible. Therefore, histology is possible only when tumors are removed surgically or using electrocoagulation.
Removing moles in children is done using the same methods as in adults. The choice of procedure is determined depending on the patient’s age and his individual sensitivity threshold, as well as on some psychological aspects of upbringing. Often, especially when working with young children, doctors prefer to use less traumatic methods - gluing plasters, applying keratolytic preparations, etc. The effectiveness of such procedures is noticeably lower, and the birthmark, having disappeared, may appear again. However, the choice of removal technique remains with the doctor who will directly deal with a particular child. They try to remove tumors when the child reaches adolescence. However, if they cause certain inconvenience to the baby, or if the moles behave unnaturally, they are removed at any period of the little patient’s life.