The appearance of moles in children is a common concern for many modern parents. Almost all adults know that some spots on the body can be indicators of a malignant tumor.
And when they appear in inconvenient places, the child can scratch or even tear off the nevus. Parents should be extremely attentive to new formations on the child’s body.
Melanopits and pigment cells are often the source. They are located on every person's body and can occur between different layers of skin. Every body has pigment cells, so the appearance of pigment spots in small numbers is not scary.
Types of moles on children's heads
Moles on a child's body can have different shapes, shades and sizes. The most common types you can find are:
- red spots, also known as stork pinch. They appear after birth and occur due to friction of the skin against the mother's birth canal. They disappear on their own within a year.
- Simple birthmark, which appears at the time of birth or a few months after. Nevus can be of different shapes - borderline, intradermal, complex.
- Crimson (wine) stains on the child’s face they look like overgrown blood vessels. Such pigmentation should be removed, as over time it can become multiple.
- Superficial hematomas, which are divided into congenital and acquired. Their color can be red, and their structure is pliable and smooth. Localization can be observed in the upper layers of the skin.
- Cavernous hemangioma. It occurs in the deep layer of the skin and often takes on a bluish tint. This is a kind of nevus.
The reasons for their occurrence
Nevi are a proliferation of skin cells that look like a growth or thickening. Moles often contain melanin, which gives them a dark color. Melanin is produced by melanocytes as a result of ultraviolet radiation.
The structure of a nevus may contain different cells. It also contains melanotropic hormone produced by the pituitary gland. When a mole forms, uncontrolled cell division occurs.
At some stages of development, it may seem excessive, which leads to the appearance of neoplasms. Unlike skin cancer, nevi grow slowly. Some types of moles are considered congenital, since their growth occurs in parallel with the body. When growth ends, the growth of formations also stops.
Scientists have identified a number of factorsa tumor formed as a result of mutation of melanas, as a result of which nevi appear on the child’s head:
- heredity.
- Developmental defect.
- Ultraviolet radiation.
- Injury.
- Hormonal factor.
- Viruses and infections.
Causes of moles
How can they be dangerous?
Moles that can degenerate into melanoma can be dangerous to a child’s health.
To determine a mole that can degenerate into melanoma, you should pay attention to the following criteria:
- asymmetry. Non-dangerous nevi have a perfectly even shape.
- The edges. Benign tumors have unclear boundaries and sometimes have a jagged shape.
- Color spectrum. Normally, the color should be uniform and not have sharp transitions. The combination of different shades is a reason to panic.
- Diameter. Large moles are more prone to degeneration than those with a diameter of 0.6 cm. A nevus that is too large on the head almost always turns into melanoma.
- Changes. This includes changes that have occurred in growth, shape, color, surface. All this may be a sign of the degeneration of a benign nevus into a tumor.
This characteristic was created by the Academy of Dermatology in America.
When should nevi under hair be removed?
To remove a nevus on a baby’s scalp, the laser method is most often used. But only those tumors that pose a danger due to degeneration into melanoma need to be removed.
Also, a mole should be removed if it bleeds., peels and itches, noticeably increases in size.
Despite the fact that moles in children are not uncommon, the appearance of each of them must be treated with full responsibility. It is important to listen to the advice of doctors and prevent the appearance of moles on the head and other parts of the body.
The study of nevi will allow you to understand which of them are dangerous and which will not harm the small organism.
Caring for neoplasms
If your baby has a small to medium sized spot on his head, you don't have to worry. Such moles do not cause discomfort and do not require special care.
That’s why you shouldn’t forget that you can always show your child to a specialist, namely a dermatologist, who will determine the future fate of the pigment spot on the head.
There are some important recommendations to heed, if your child has a mole on his head:
- You should not use scrubs and shampoos with small exfoliating particles, so as not to injure the nevus area.
- When combing your hair, you should avoid the mole without applying pressure or force in this area of the skin.
- An accessory to protect the head, as well as glasses, should not come into contact with the mole and cause discomfort when worn.
- It is important to measure the size of the mole once a month, and also pay attention to its color.
- You cannot get rid of it yourself, otherwise it can lead to the formation of a tumor, which will lead to negative consequences.
If a danger is detected, the dermatologist will suggest removing the mole on your child's head. The reason for such actions may be not only a malignant tumor, but also cosmetic discomfort. Also, during the research process, he will be able to understand how large the percentage of its degeneration and influence on the baby’s life is.
Is it possible to prevent their occurrence?
Nowadays, there are no special methods that could prevent the appearance of spots on a child’s body. However, parents and children at risk must adhere to the following rules:
- you need to limit your exposure to the sun. Due to the strong influence of ultraviolet radiation, burns form on the body, which can lead to the appearance of a large number of moles. In hot weather, be sure to protect your head with a cap or hat.
- If a suspicious mole occurs, the best solution is to seek help from a specialist. Under no circumstances should you get rid of it yourself.
It is worth noting that it is easier to detect a mole on a boy’s head than a girl’s. This is because they often have short hair. As for girls, you need to be doubly careful here. When you comb your hair or do your hair, do not press the comb too hard on your scalp. This may cause injury to the nevus.
If you or your child does touch a mole, you should immediately contact a specialist to examine the neoplasm.
Conclusion
As you can see, moles on a child’s body, especially on the head, do not pose a threat to life or health if you keep an eye on them. It is very important for parents to monitor neoplasms, since at the slightest changes or if the baby is uncomfortable, it is worth examining the nevus and then removing it.
In this matter, it is important to find an experienced dermatologist who will approach the problem with full responsibility. As for malignant tumors, it would not be a bad idea to contact an oncologist.
It will allow you to examine a new spot on the child’s body in a matter of days in order to select the correct removal method to avoid complications. Here, as in everything else, it is important to be attentive and take into account the new spots that have recently appeared on the baby’s skin.
In ancient times, people believed that birthmarks on a baby were signs of fate and predicted his future. Now scientists are considering more natural reasons for the appearance of such formations. Let's consider what factors influence the appearance of spots, and in what cases do they require removal? Why might a birthmark appear in a newborn?
Types of birthmarks
A child may have a wide variety of birthmarks on his body - smooth or covered with fluff, reddish or brown, convex or flat. The main types of birthmarks in newborns are nevi and angiomas.
What shade can nevi be?
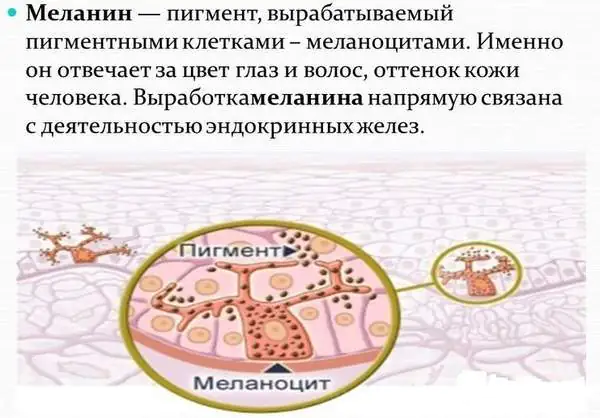
Nevi are among the most common types of skin marks. They usually come in a variety of brownish shades, ranging from dark brown to pale. The basis of nevi are melantocytes. These epidermal cells contain melanin, a pigment that affects skin tone. It is necessary to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. Sometimes these cells are localized in one place, which leads to the appearance of a mole. Dark birthmarks indicate an abundance of melanin, while light ones indicate a lack of it.
A Mongolian spot in a newborn should also not be a cause for concern for parents. It is also a place of concentration of melanin and is a spot, or several spots of different sizes from 1 to 10 cm in diameter, blue, green or even black. The most common location is the baby’s lower back, mainly the tailbone or butt. Mongolian spots are safe, they do not cause any discomfort to the child and go away on their own before adolescence. This type of nevus is named so because of their frequent detection in Mongolian children (90%), Mongolian spots are also often found in Asians, representatives of the Mongoloid and Negroid races.
There are also white formations. These include anemic nevi that arise due to underdeveloped blood vessels.
They need to be distinguished from millet grasses - milia. The latter look like convex dots filled with whitish content. They are a type of skin rash. Anemic nevi are a congenital phenomenon, and they are easy to identify: you need to rub the spot. The surrounding skin will turn red, but the formation will remain white.
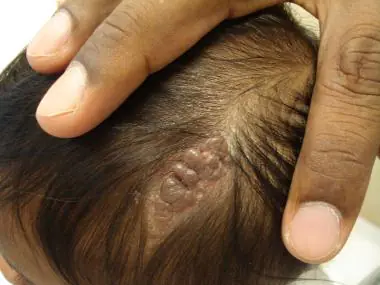
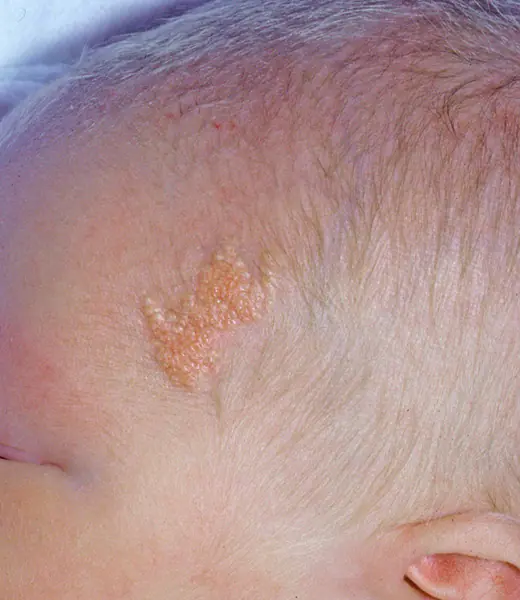
Light brown Jadassohn nevi indicate a congenital defect of the sebaceous glands. They are usually found on the baby's head, under the hairs. This occurs in 3 out of 1000 babies. It is recommended to remove it before adolescence, since in 10-15% of cases, they can subsequently develop into a cancerous tumor.
What if it’s a matter of blood vessels?
Another type of birthmarks is angiomas. They are of vascular nature. Congenital formations of small vessels on the skin are called hemangiomas. If such accumulations form in the lymphatic system, then they are classified as lymphangiomas. Even congenital, they appear externally only by the age of three.
In a newborn, only vascular hemangiomas can be detected. They are distinguished by a whole range of shades of red. Such formations are divided into several subtypes:
Strawberry (strawberry) hemangioma
These formations are convex, similar to red “berries”. They appear immediately after birth, usually on the face. The sizes can be different - from a millimeter to several in width. Strawberry hemangioma can increase in size, which is why it is dangerous, as it can affect the healthy tissues of the child.
Often this type of hemangioma stops growing, gradually brightens, shrinks and disappears completely by the age of 10.
Stellate (spider) angioma
It looks like a star with a bright base and “rays” extending from it. Most often it occurs on the child's neck. Disappears on its own in the first years of life.
Cavernous hemangioma
Loose, purple hemangioma, deeply embedded in the skin. It feels warmer to the touch than the surrounding epidermis. If you press, the baby will cry due to unpleasant sensations. This type of neoplasm requires treatment.
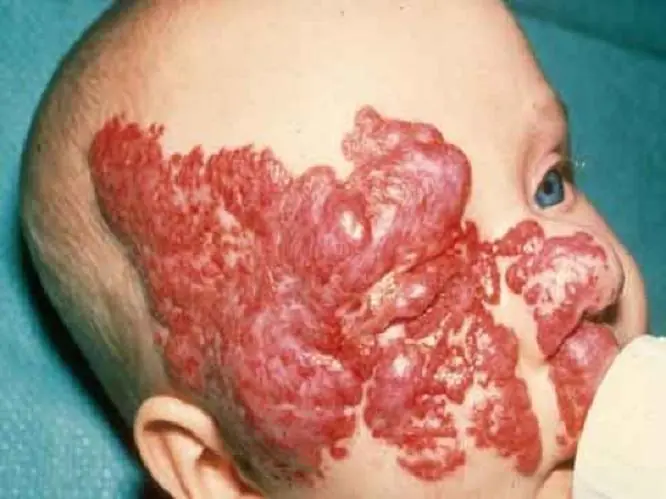
Flaming (fiery) nevus
Looks like a red or purple stain from spilled wine. It can appear anywhere on the baby’s body. Such formations do not go away on their own. If they are not removed, they will remain for life. If the “wine stain” is in a visible place or continues to grow, it is better to take the trouble to correct the defect.
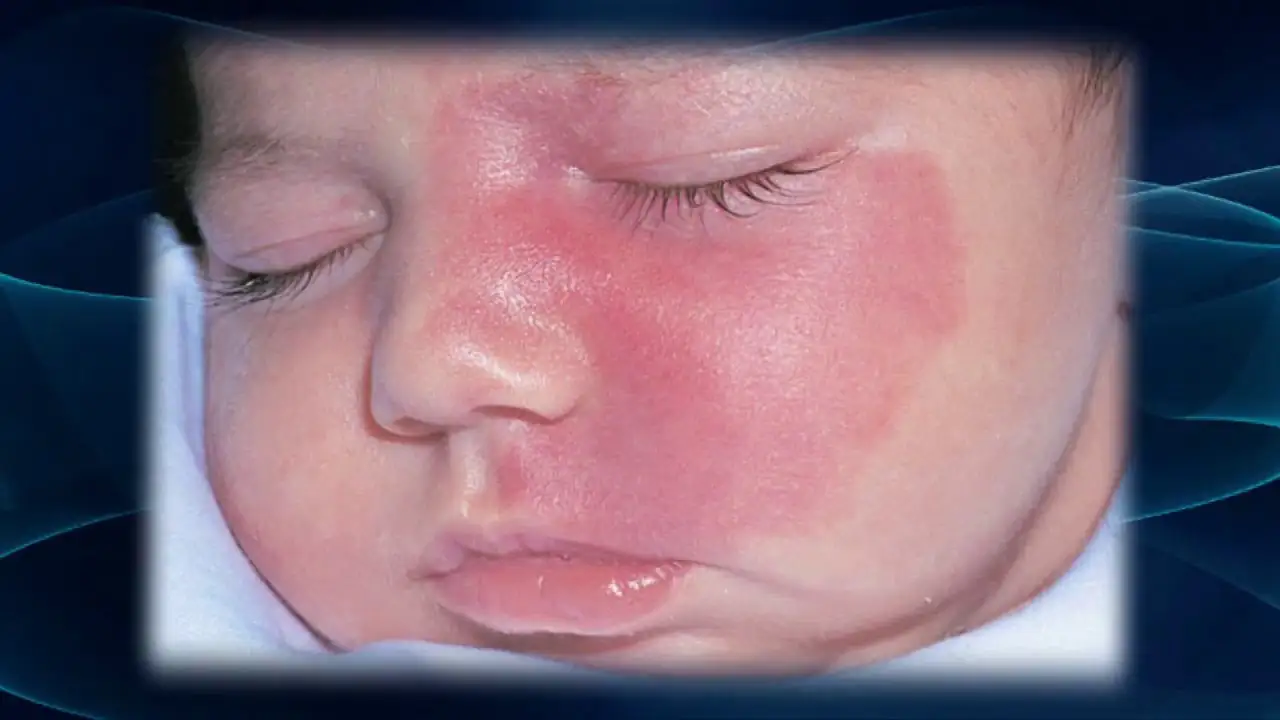
“Stork marks” (capillary hemangioma)
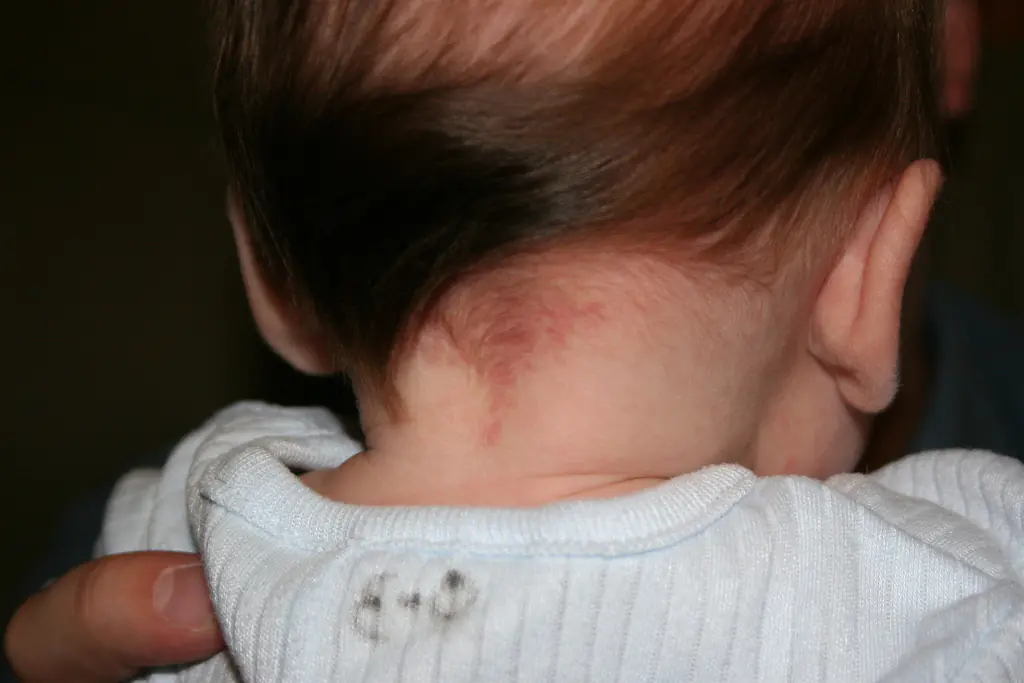
Such marks are also called “stork bites.” And if there is a mark on the baby’s forehead - “an angel’s kiss.” The formation is usually pink or red, but can also be orange, and resembles the mark of a bird's beak, which is how it gets its name. The formation is flat and does not rise above the skin. It is often found on the back of the baby’s head, in the neck area. When stressed, for example, when a baby cries, it acquires a brighter color. By the age of two, “stork marks” in most cases go away on their own.
In addition to the above, there are other types of birthmarks. But they are much less common.
If you notice that a child’s hemangioma is increasing in size, immediately contact a specialist (surgeon). He will be able to assess the danger of the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment or removal of the tumor.
Causes of skin formations

The reasons for a birthmark in a newborn, of course, are not that his mother loved to pet dogs and cats, as the ancients believed. However, scientists cannot say exactly why such marks may appear. Only risk factors for their occurrence have been identified.
Why do birthmarks appear in newborns? This is affected by:
- Hereditary factor;
- Hormonal surges in the expectant mother;
- Exposure to toxic substances on the body of a pregnant woman;
- Bad ecology;
- Climate change;
- Infections of the genitourinary system.
But it happens that a birthmark appears in a newborn even without exposure to risk factors.
Birthmark on a baby: what to do?
Is your baby's birthmark small, smooth, does not grow and does not cause concern to the baby? Everything is fine, nothing to worry about. But you need to take the new growth seriously. Observe the nevus and notice whether the mark grows or hurts. If changes occur, you should visit a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist.
If a newborn has a birthmark on his body, several rules should be followed:
- Keep this area away from direct sunlight.
- Make sure that the baby does not scratch the area with the mark.
- Try to ensure that the nevus is never exposed to caustic substances, such as household chemicals.
In rare cases, marks on the skin can be fatal. Where can it appear? Under the influence of negative factors, a simple mole degenerates into a malignant formation - melanoma. Therefore, if the spot increases in size, you should urgently contact a specialist. If the formation is removed in time, there will be no health consequences.
Should moles be removed from babies?
It is recommended to eliminate formations in infants only if there is a danger to life. In babies, the immune system is not yet very developed, and any intervention can lead to serious consequences.
In what cases do doctors recommend surgery at an early age:
- The birthmark is very large;
- The formation rapidly increases in size;
- There are more than five marks, and they are concentrated in one place;
- The mole is located in a traumatic place (under the armpits, on the belt, on the skin of the eyelid, in the anus);
- Nevus interferes with the normal functioning of organs (on the hand, in the nose, in the eyes).
Particular importance should be given to those cases if a mole transforms - changes color or shape, grows, hairs fall out of it, it begins to bleed or itch.
How to get rid of formations?

The doctor may recommend one of the methods for removing nevi, depending on the size and condition of the formation, as well as the health of the baby:
Use of pharmaceuticals
Special medications are injected into the mole tissue to promote the death of overgrown cells. No anesthesia is required, but is not suitable in case of allergy to the active substances of the drug.
Using a laser
Excision of pathological tissues with a laser beam. It is quick and painless, but the procedure is not always possible for hard-to-reach areas.
Cryotherapy
Exposure of the mole to low temperatures. Suitable for eliminating small nevi.
Surgery
Removal of the formation using surgical instruments. It is used in cases where other methods cannot be used.
Carrying out the intervention under the supervision of a doctor, with preliminary examination of the birthmark tissue, reduces the likelihood of complications to zero. After removal of large formations, scars may remain. If they are located in a visible place, when the baby grows up, you can remove the scar using cosmetic procedures.
If you believe in fate, try telling your baby's destiny using moles. But pay attention only to happy signs:
- A mark on the baby’s cheek means love;
- A spot under the hair means high intelligence;
- Moles on the hands - to talents and good luck;
- Nevi on the back - to a life without worries;
- Mark on the leg - to hard work, calmness, confidence;
- A “sign” on the butt means success with the opposite sex.
As you can see, a mole is not a reason to panic at all. With the right approach, it will not be the cause of illness, but a happy sign that emphasizes the individuality of your son or daughter.
Remember that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis; do not self-medicate without consultation and diagnosis by a qualified doctor.
Scientists have not yet determined how a birthmark appears in a newborn baby. But they know that such formations are not dangerous for the baby and in rare cases require correction. There are different types of nevi. Some disappear on their own, while others need to be constantly monitored. If the mark becomes inflamed or changes, doctors recommend starting treatment as early as possible.
Causes of birthmarks in a newborn
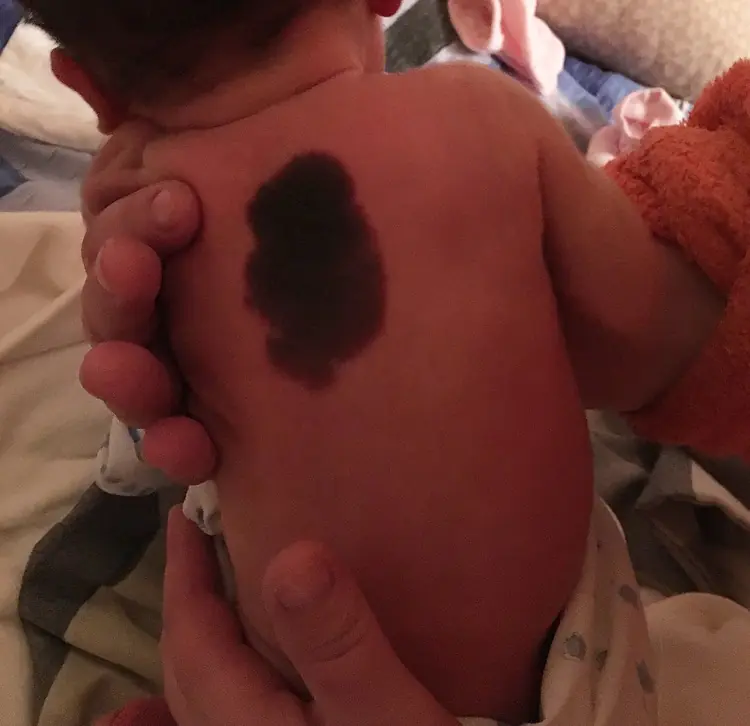
The process of formation of nevi has not yet been fully studied. But scientists were able to determine the range of pathological conditions that provoke the formation of a skin defect. These include:
- Heredity.
- Hormonal surges.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Poisoning by poisons or radiation exposure.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Phototype of the baby's skin (in a child with light skin, marks are formed more often than in infants with dark skin).
- Gender (female babies have moles on their bodies more often than male babies).
- Fetal maturity (children born prematurely are more likely to be born with visible birthmarks).
Types of nevi
The name implies the fact of the transfer of marks by inheritance (by family). Often the same defects are detected in children and their parents. Many babies are born with clear skin. But this does not mean that there is nothing on the covers. It happens that the spots are weakly colored, and at first it is difficult to see them without examining the integument with a magnifying glass.
Distinct birthmarks from birth are detected in only one baby out of a hundred. For the rest, invisible marks darken over time and become visible by the age of five.
In infants, birthmarks of two types can form on the body:
- pigmented moles of brown or blue-black color;
- red spots (angiomas, hemangiomas) of pink, purple-violet, red color.
The color of the marks is determined by the cells involved in the formation of their structure. If the mark is formed from actively dividing melanocytes, the color of the nevi will be brown or black. And the formation of a formation structure from vascular cells gives the mole a red color.
Birthmarks, the structure of which contains pigment cells
There are several types of pigmented formations, which are most often detected in infants. The reasons for the formation of such birthmarks are a high concentration of melanin in a small area of skin.
| Type name | Description |
| Mongolian spot | Appears on the body of infants with Mongoloid genes from birth on the lower back, in the sacrum area. Outwardly it looks like a bruise and disappears completely on its own by the age of five. The health and development of the child is not threatened |
| Dysplastic nevi | These markings are similar to irregularly shaped marks. They have different color intensities and vary in size. There are cases when dysplastic formations are formed from individual point-type elements |
| Moles | They resemble small spots of different colors and sizes and appear on any part of the body |
| Congenital nevus formed from pigment cells | Large markings. Each baby has a different shape of this spot; the color can be light, coffee or blue-black. Hair grows on the surface. This is the main diagnostic sign |
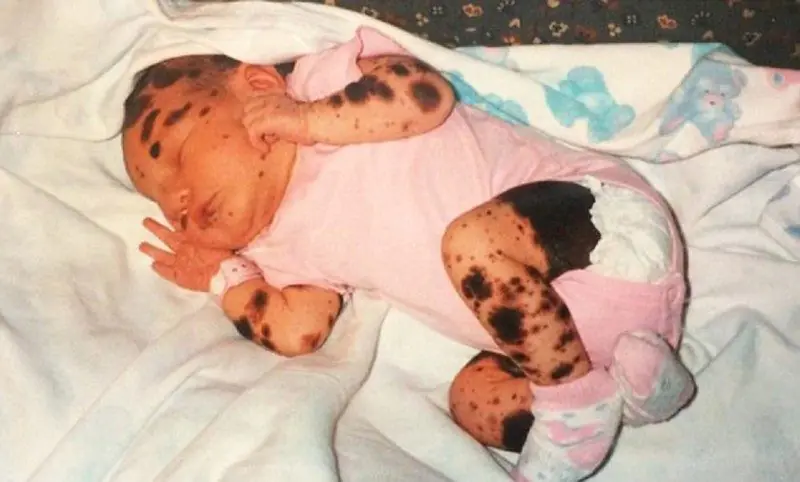
If there are several nevi on the child’s body at once, parents should observe them, control their size and color. If the shape changes, a sharp increase in the size of the formation, or asymmetry appears, you must immediately seek medical help.
You need to start sounding the alarm if the birthmark begins to change color and the skin next to it becomes swollen, red, begins to hurt or itch.
Vascular birthmarks
Hemangiomas appear on the baby’s body from birth; they are clearly visible already in the first weeks of life. The reason for their appearance is the active division of vascular cells, the interweaving of pathologically altered small capillaries. Such formations are constantly growing. By the age of one year, their growth stops, then regression begins: the mark decreases in size and by the age of five it completely disappears on its own without any drug treatment.
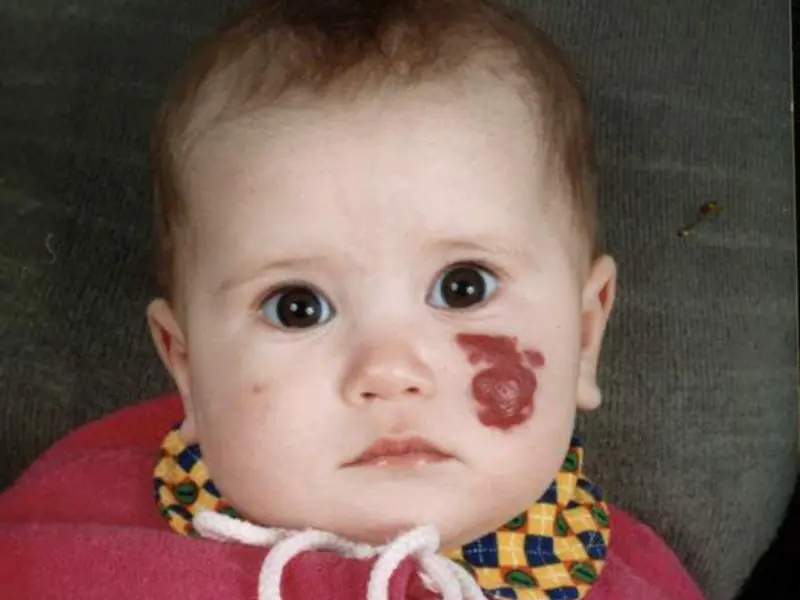
Scientists cannot understand why this happens. There is an assumption that the spot affects the vessels that nourish the skin and subcutaneous tissue. This happens due to a violation of the properties of collagen fibers, which are responsible for the strength of the walls of hollow tubes, and a disruption in the process of cell division that makes up the tissue. Most often, hemangiomas appear in children with low birth weight.
Such spots form under the skin or rise above its surface. They have an unpleasant appearance, so many parents insist on their removal. Pediatricians warn that they do not pose any danger and disappear on their own over time, so there is no need to fear for the health of the children.
Types of hemangioma
There are several types of hemangioma:
| Name | Peculiarities |
| Stork trail | A spot of intense pink color forms on the top of the head, on the back of the head, transitioning to the forehead and bridge of the nose. Its surface may consist of a scattering of small elements |
| Kiss of an angel | The entire surface of the face is covered by one pink-yellow spot. When the baby begins to cry, the intensity of the color intensifies |
| Nevus flamingo | Appears on the head, face, has a bright color, its intensity intensifies over time |
| Strawberry stain | The body of the formation rises above the surface of the skin and is shaped like strawberries. In the first months of life, it actively grows and develops; after the age of three, regression begins. By the time of the first hormonal changes (puberty) it completely disappears. Some children have a scar in its place |
| Cavernous hemangiomas | They can be located on any part of the body; such formations do not have clear boundaries, constantly grow, and quickly increase in size. Their structure consists of several seals located close to each other. If you place one palm on the hemangioma and the other on an area of clean skin, the temperature difference will become noticeable. Where the vascular formation is located, it will be several degrees higher |
| Spider nevus | The shape of the mark is similar to a star, therefore it has the second name “star nevus”. Completely disappears to the surface of the skin by the time of puberty |
Parents of children whose bodies have vascular formations should closely monitor them and try to prevent injury to the surface of the hemangioma. If a red birthmark forms near natural openings (near the ear, eyes, nose) and by the age of two it does not show signs of regression, then it is necessary to seek medical help.
Sizes of nevi and control over them
To facilitate monitoring of birthmarks, a classification of the size of benign formations was created.
- Spots between 5 and 7 mm in diameter are considered small. They do not spoil the appearance and do not pose a threat to the child’s life, so there is no need to remove them.
- Moles measuring from 7 to 12 cm, growing on the back, lower extremities, and forehead, require close monitoring.
- Giant formations have a diameter of more than 14 cm.
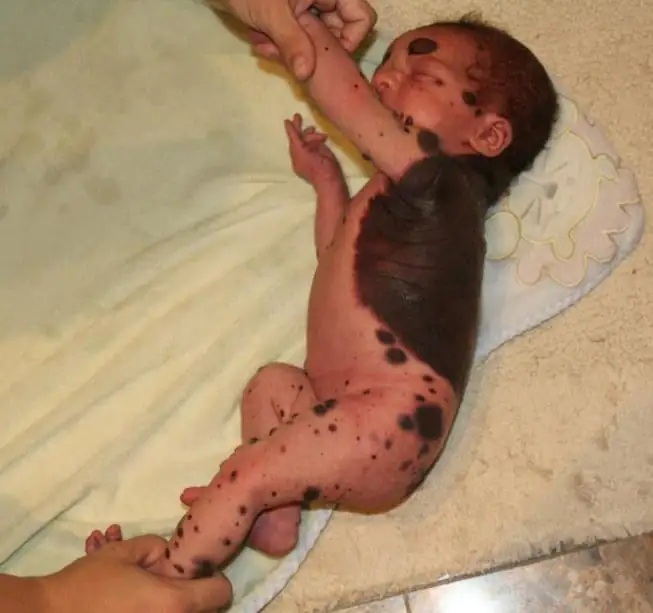
Experts recommend that parents take transparent paper in their hands, apply it to the birthmark, outline the contours of the formation, cut it out with scissors and save it. Such a template can then be periodically applied to the nevus and its new dimensions can be compared with the previous ones. It is useful to take photographs of birthmarks once a month and save them. This will also help track the dynamics of mark formation.
When is it necessary to remove birthmarks?
Radical treatment is used in extremely rare cases, when signs of a pathological change in the birthmark are detected. The following signs indicate its development:
- The surface and shape of the formation change (the birthmark becomes convex, rough folds form).
- The surrounding skin swells and turns red.
- The color becomes lighter or darker.
- The edges become uneven and take on a paneled shape.
The presence of just one sign may indicate the beginning of the transformation of a nevus into a malignant tumor. Therefore, it is important to immediately seek help from a pediatric oncologist when manifestations are detected.
Attention! Skin cancer is an aggressive disease that can metastasize quickly and extensively. Late stages are difficult to treat, but therapy undertaken in the early stages will help save the child’s life.
Methods for removing birthmarks in newborns
Those birthmarks that are localized in places of constant irritation (on the neck, scalp, inside natural folds) are subject to removal.
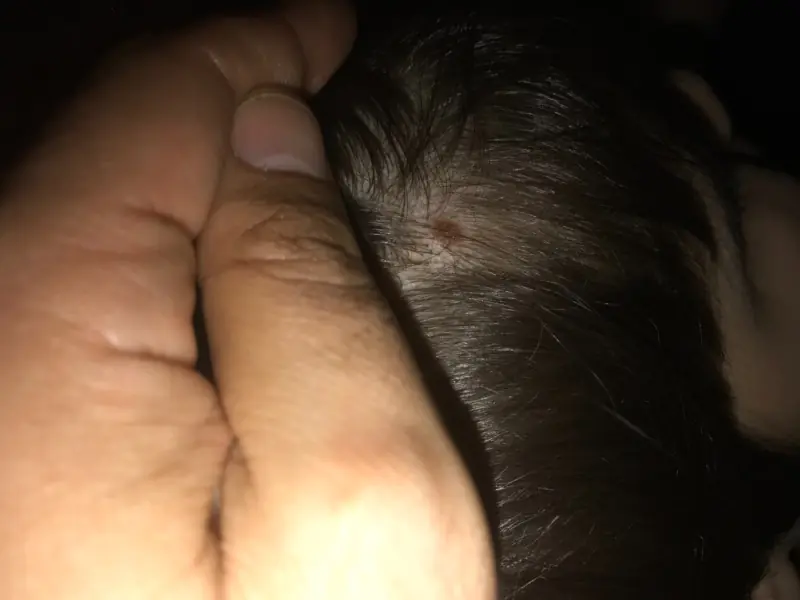
Indications for surgical removal:
- rapid growth of the birthmark;
- the appearance of small bleeding cracks on the surface of the mark;
- statement;
- pain when touching the mark.
To excise the spot, laser therapy, cryodestruction and the use of medications for external use (for older children) can be used.
The choice of remedy depends on various factors: the types of formations, the age of the baby, and the results of a diagnostic study are taken into account. In the absence of suspicion of the presence of malignancy processes, preference is given to laser treatment.
But if there are symptoms of malignancy, the birthmark is removed using the traditional surgical method. Only excision of the tumor with a scalpel will completely remove the formation and obtain biological material suitable for histology.
Prevention of complications
To prevent complications, parents should protect their child’s skin defect from exposure to active sun, injury, and overheating. You should not try to treat yourself with folk remedies, cauterize or lubricate the stain with the juices of medicinal plants. Many of them contain an aggressive formula that can damage the integrity of the formation and provoke its inflammation. It is important to regularly conduct diagnostic examination of the structure of the birthmark. For these purposes, you need to consult a dermatologist.
Birthmarks appear on any part of the body. But many children live with huge nevi on the forehead, lower face, body and limbs without complications. You don't always need to remove them. Any operation or treatment is an additional burden that not every child can easily bear.



