Causes of oophoritis in women and characteristic symptoms. How dangerous is the disease? Proper diet, treatment and prevention of ovarian inflammation.
The content of the article:- What is ovarian inflammation
- Causes
- Symptoms of oophoritis
- Diagnostic methods
- Treatment options
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
- Nutrition
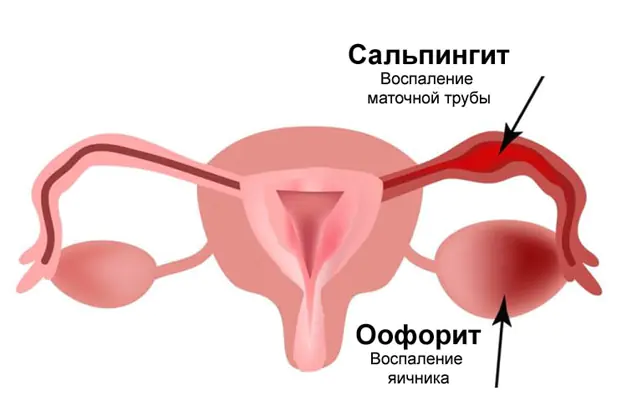
Oophoritis is an inflammatory infectious process that affects a woman’s ovaries. The disease negatively affects hormonal levels, disrupting the natural rhythm of menstruation, and in its advanced form can lead to infertility. The disease rarely occurs in a single form; more often a general disease of the uterine appendages occurs - adnexitis.
What is ovarian inflammation?
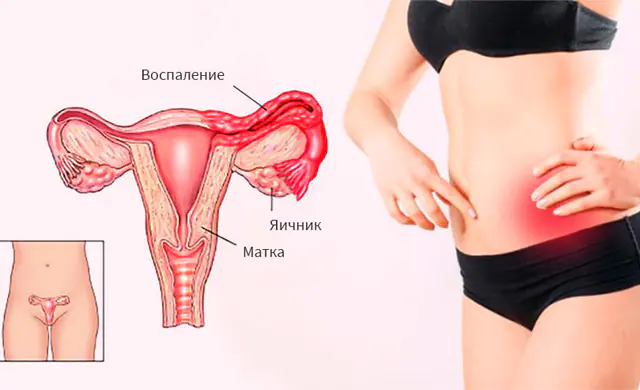
Oophoritis is a female inflammatory disease caused by infection in the ovaries. It occurs in acute and chronic forms and can affect either one of the ovaries or both at once. In general, the disease can be successfully treated with antibiotics, but it is important not to neglect it in order to prevent infertility.
Main types of ovarian inflammation:
- Left-sided oophoritis. It has a high temperature and is resistant to antipyretic drugs. The location of the pain is on the left side of the abdomen. Painful sensations accompany the process of urination. Characteristic discharge mixed with pus.
- Right-sided oophoritis. The symptoms of this type of inflammation are similar to those of appendicitis, so there is a danger of misdiagnosis. If treatment is not provided on time, the disease may spread to other pelvic organs.
- Bilateral oophoritis. With it, inflammation occurs on both ovaries. Characterized by intense pain and a specific discharge with an odor.
The disease will definitely affect the course of pregnancy, since the ovaries have a direct impact on the woman’s hormonal levels and the formation of eggs. Why is oophoritis dangerous during this period:
- Miscarriage. Inflammation seriously destabilizes hormonal levels, which can lead to miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. With the disease, there is always a risk of the formation of adnexal adhesions, which can lead to an ectopic pregnancy.
- Infection of a child. The infection can spread from the affected area to the embryo or to the baby during birth.
- Infertility. Destructiveness of the ovaries can negatively affect the production of eggs and lead to infertility in a woman.
In general, the prognosis for ovarian inflammation is positive, and surgery is started only as a last resort. It is important not to delay your visit to the doctor to prevent negative consequences.
The main causes of oophoritis

The cause of inflammation of the ovaries is often an infectious disease. Damaging factors may include:
- Tuberculosis. Koch's bacillus, which causes this disease, can spread to the woman's reproductive organs, and against this background, one- or two-sided oophoritis develops. According to statistics, 32% of women are susceptible to developing the disease due to tuberculosis. In this case, tuberculous tubercles and tumors appear on the ovaries.
- Sexual infections. Direct entry of harmful bacteria into a woman’s reproductive organs causes inflammation of both ovaries at once.
- Pathogenic microorganisms. Any other infectious diseases in the body caused by streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa can also cause oophoritis.
A woman’s ovaries have a dense protective capsule that prevents various types of infections. However, there are diseases whose course can destroy this capsule:
- Female reproductive system diseases. Diseases of the area close to the reproductive organs, such as colpitis or endometritis, can cause harmful bacteria to enter the ovaries.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease. These include peritonitis, cystitis, inflammation, peritoneal cancer, ascites and others.
- Ovarian tumors. The direct appearance of tumors on the ovaries will destroy the protective layer and allow the entry of pathogenic bacteria.
In addition to the direct culprits of the disease, the following factors can create a favorable environment for ovarian inflammation in women:
- Complicated childbirth. During problematic childbirth, the likelihood of infection entering the woman’s reproductive organs increases, and the immune system at this time is unable to fully fight bacteria.
- Surgical and other interventions. Abortions, genital surgeries, IUD insertion and other procedures also increase the risk of infection.
- Promiscuous sex life. Constantly changing partners during unprotected sexual intercourse increases the chance of various harmful infections entering the body that can cause inflammation of the ovaries.
- Weak immunity. Reduced immunity weakly resists various diseases, including infectious ones, and it becomes easier for bacteria to penetrate, including into a woman’s reproductive organs. Immunity can be affected by the presence of various diseases, poor diet, bad habits, hypothermia, and more.
- Other diseases. Diabetes mellitus, obesity, and chronic diseases have a negative impact on the general state of the immune system, which can lead to ovarian infection. This risk is highest with hormonal imbalances in the body.
- Stress. Finding the body under constant stress can also affect physical immunity, which becomes unable to fully fight infections.
- Incorrect use of drugs. Excessive use of antibiotics results in the body’s inability to fully resist harmful microorganisms.
- Poor personal hygiene. Insufficient self-care, excessive douching and other procedures can disrupt the vaginal microflora, making it more susceptible to various types of infections.
Symptoms of the development of oophoritis
Signs of ovarian inflammation manifest themselves differently depending on the stage of the disease, the nature of the inflammation and its location. In general, the following symptoms of oophoritis are distinguished:
- Pain. With inflammation, a woman begins to experience aching or cramping pain in the lower abdomen. It is also common to experience pain during sexual intercourse.
- Discharge. When the disease occurs, purulent discharge with a specific shade and smell occurs.
- Menstruation disorders. It may be observed as an increase in discharge during menstruation or its complete disappearance. The menstrual cycle gets confused and may become more frequent or less frequent. Menstrual pain increases.
- General weakness. Excessive fatigue, weakness, malaise, and pain in the relics appear.
- Disorders. Discomfort from the disease can provoke nervous disorders, decreased libido, and affect the quality of sleep.
Signs of oophoritis depending on the stages of the disease:
- Acute. The acute type of the disease is characterized by cutting pain during urination, cramping pain, and the appearance of serous discharge. The temperature becomes very high, sleep disturbances appear, including insomnia. When palpated, you can notice an increase in the woman’s appendages.
- Subacute. This stage is uncommon and is caused by tuberculosis or mycotic infections. It is intermediate between acute and chronic forms of the disease. Symptoms of the acute phase are observed, but less pronounced.
- Chronic. Oophoritis is observed for a long time, and its symptoms are extremely weakened, and the woman may mistakenly think about recovery. This is especially dangerous because untreated chronic inflammation can lead to infertility.
If the listed signs appear, it is important not to postpone a visit to the doctor in order to prevent the chronic course of the disease, which is fraught with serious consequences.
Methods for diagnosing oophoritis
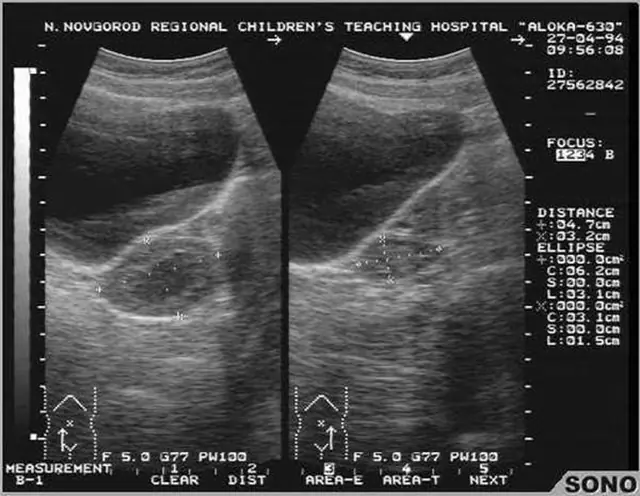
For a reliable diagnosis, diagnostics are performed. Methods for determining the disease include:
- Examination by a gynecologist. The doctor checks for the presence of compactions and enlargements characteristic of oophoritis. When palpated, painful sensations appear.
- Ultrasound. In this way, the size and smoothness of the surface of the glands, their structure, and the presence of inflammation of the fallopian tubes are checked.
- Laparoscopy. Surgery in the uterine area helps to most accurately diagnose oophoritis and conduct more detailed tests.
- Analyzes. The following tests are carried out: general, microscopy, vaginal discharge, immunological blood test, to identify antigens and microorganisms leading to infectious diseases. In some cases, a tuberculin test is used.
With a positive diagnosis of oophoritis, the doctor advises the patient how to treat inflammation of the ovaries.
Methods for treating oophoritis
To treat the disease, treatment with antibiotics and drugs that relieve inflammation is used. Sometimes surgery may be performed.
Medicines for ovarian inflammation
The treatment of ovarian inflammation uses a comprehensive approach that includes different types of medications.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics. To combat pathogenic bacteria in oophoritis, antibiotics are used: Tetracycline (26-133 rubles in Russia, 16-20 hryvnia in Ukraine), Augmentin (123-404 rubles, 127-128 UAH), Levofloxacin (55-743 rubles, 52 - 90 UAH). Antibiotics for inflammation of the ovaries are taken according to the dosage prescribed by the doctor. Suppositories for ovarian inflammation are especially effective: Clindamycin (386-613 rubles in Russia, 57-61 hryvnia in Ukraine). They should be administered once a day.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Among this category of drugs, Meloxicam (37-430 rubles in Russia, 44-64 UAH in Ukraine), Xefocam (218-760 rubles, 66-77 UAH), Celebrex (152-1392 rubles, 333 UAH) are most often prescribed. -400 UAH).
- Antimicrobials. In addition to antibiotics, antimicrobial drugs are used for inflammation of the ovaries. These are Tinidazole (92-132 rubles in Russia, 45-57 hryvnia in Ukraine) and Metronidazole (15-140 rubles, 16-43 UAH).
- Enzyme preparations. The doctor prescribes Creon (275-1408 rubles, 107-124 UAH), Ermital (148-986 rubles, 94-126 UAH), Pancreatin (34-73 rubles, 12-42 UAH).
- Painkillers. To relieve pain during oophoritis, drugs such as Ibuprofen (30-169 rubles in Russia, 17-40 hryvnia in Ukraine) and Diclofenac (19-137 rubles, 10-29 UAH) are used.
- Immunostimulants. Interferon (RUB 82-125 in Russia) and its analog Laferobion (RUB 67-112 in Ukraine), Dekaris (RUB 61-81, UAH 75-82) and Lykopid (RUB 270-1690, RUB 240-285 UAH).
When a period of remission occurs, the doctor prescribes therapy to increase immunity and restore the functions of the reproductive and endocrine systems.
Important! Surgery is performed only if serious complications arise during the course of the disease. For example, various purulent-inflammatory diseases or adhesions of the appendages. The operation is aimed at preventing the patient from becoming infertile.Folk remedies for the treatment of oophoritis

Traditional methods can also be used in the treatment of ovarian inflammation. Before treating oophoritis in this way, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Effective folk remedies for ovarian inflammation:
- Chamomile and linden. You need to take a glass of chamomile and linden, add 2 glasses of water and boil for 25 minutes. Then leave for half an hour. Strain the resulting broth and use it as a microenema for 2 weeks.
- Oak and linden. You will need 2 tablespoons of crushed oak bark and 1 spoon of linden flowers. You need to add 1.5 liters of water to them. The mixture should be placed in a water bath for half an hour. Douche with the decoction twice a day.
- Kalanchoe juice. You need to take the leaves of the plant, wash them and grind them into a paste. Next, use gauze to squeeze out the juice. Take 1 teaspoon 1 time per day, freshly squeezed. You can also use tampons with Kalanchoe juice. To do this, first dilute it with boiled water.
Nutrition for oophoritis
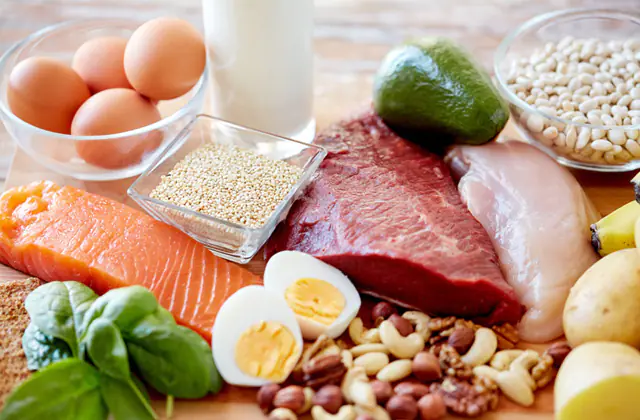

To strengthen the immune system during treatment of ovarian inflammation and for some time after, it is recommended to diversify your diet with the following products:
- Chicken eggs. The lecithin contained in them will help regulate hormonal levels and saturate the body with vitamins.
- Fatty fish. This product contains healthy Omega-3 fats, which help reduce inflammation and normalize hormonal levels.
- Olive oil. The vitamin E contained in it will also have a positive effect on a woman’s hormonal cycle.
- Dairy products. They contain large amounts of protein and calcium, as well as B vitamins, which help strengthen the immune system.
To avoid inflammation of the ovaries, it is important to follow some rules of prevention: active lifestyle, proper nutrition, personal hygiene, use of contraceptives, regular examination by a gynecologist.
What is ovarian inflammation - watch the video:



