In the human body there are cells responsible for skin color. They are called melanocytes. A mole (nevus) is an accumulation of such cells in one area. These formations come in various colors, shapes and topography. They appear both at birth and throughout life. Most often, moles do not cause any discomfort or health problems. However, recently, nevi of an oncological nature appear quite often. Even congenital benign formations can degenerate into cancer. There are quite a few reasons for this. A mole or nevus should be monitored periodically. When it changes color or shape, you should urgently consult a doctor. If there is such a formation on the body, then it cannot be injured. When taking a bath, it is better not to use a washcloth where moles grow. Often people are unhappy with the presence of such a cosmetic defect and try in every possible way to get rid of it. It is completely unacceptable to engage in such procedures at home. If the mole really looks bad, it is better to visit a medical facility. There, experienced doctors will help solve the problem without harm.
Types of moles
Main types of moles:
- Pigmented - can be light or black, small or very large. The main difference from the rest of the skin is the color.
- Vascular (hemangiomas) are pink or red formations with a bluish tint. They lighten when you press on the surface.
- Warty - raised, lumpy. Most often burgundy or pink. Sometimes they are flesh-colored.
Regardless of the group, they can all be benign or vice versa.
There are many nevi, each of which has its own medical name:
- blue moles;
- Sutton moles;
- complex moles;
- intradermal moles;
- giant pigmented moles;
- dysplastic nevi.
Sometimes it happens that hair grows from a mole. This is not some kind of alarming symptom. The most important thing is not to pull them out, so as not to injure the formation itself.
Reasons for the degeneration of a nevus into cancer
Often, most moles do not pose any danger. This requires a certain push. The most common causes of mole degeneration:
- Hormonal imbalance - during hormonal changes, skin cells change. It is necessary to carefully monitor nevi during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. If a mole begins to grow, you should definitely consult a doctor.
- Excessive sun exposure is a major factor in the development of skin cancer. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation promotes cell degeneration. It is very important, while in the sun, to minimize the likelihood of developing burns; they greatly weaken the skin’s immunity and cause irreversible changes in it. Particular care must be taken to hide from the sun the places where moles grow.
- Trauma - Many people take moles on their body lightly. Few people know that injury to such a benign formation can quickly degenerate into cancer. Places where moles grow should not be rubbed with a washcloth. They should not be squeezed out or pulled with thread. If the mole still bothers you greatly, it is better to consult a doctor.
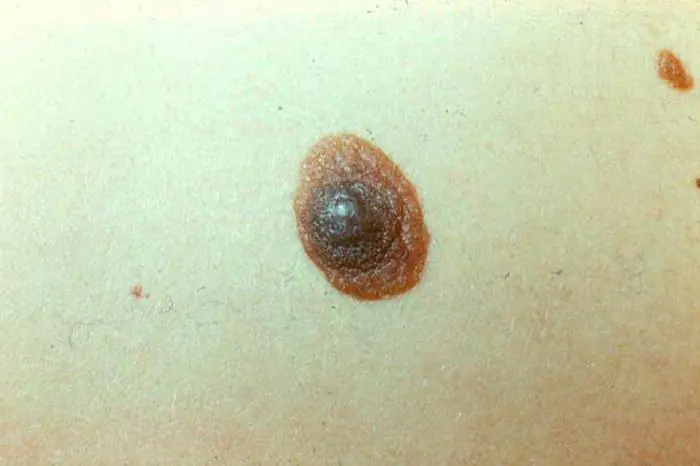
Dangerous moles
Why moles grow and how safe they are is of concern to many. You need to be very careful about them. Any changes in appearance should alert you. Periodically, congenital moles, under the influence of certain factors, can turn into cancer. The main thing here is not to miss the first symptoms. In the early stages, these diseases are easily treatable. The number of recovered people is almost 100%. In later stages, the prognosis is less optimistic and the disease can be fatal. You need to go to the hospital if a mole is growing very quickly. The doctor will tell you what to do in this case.
Symptoms of mole degeneration:
- changes in size, color;
- inflammation around the mole;
- its elevation above the surface of the skin;
- change in structure, varnish mole;
- discomfort associated with itching;
- formation of nodules, hardening;
- blurring of contours.
As for new moles, you should treat them even more carefully. Any new skin lesions larger than 0.5 centimeters require medical supervision. You should also go to the hospital immediately if a mole is growing rapidly. Not many people know which doctor to go to. Oncologists treat these diseases.
Safe moles
Most moles on the human body do not pose a health threat. Small congenital formations that are not compacted and have clear edges are completely harmless. They can degenerate into oncology only when exposed to certain factors. There is a certain type of benign nevi that can increase in size. Why moles grow is interesting to many. These types include hemangioma. This is a benign tumor caused by the accumulation of a large number of cells in the blood vessels. If the formation quickly increases in size, it is removed surgically. In most cases, treatment is carried out with hormonal drugs.

What moles need to be treated and how?
All suspicious formations on the skin require close medical supervision. Self-medication or removal at home is strictly prohibited. If the mole is benign and is a cosmetic defect, it is simply removed surgically. Laser therapy is also popular in this matter. With malignant tumors everything is more complicated. To begin with, many studies are carried out to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the stage. Then treatment is carried out. In the early stages, removal of the mole and further observation is sufficient. Advanced diseases are extremely difficult to treat. General chemical and radiation therapy is used. The prognosis may be unfavorable.
Complications after mole removal
In order to avoid complications after surgery to remove a mole, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions:
- treat the wound daily with an antiseptic solution;
- apply antibiotic ointment;
- Do not remove the crust from the surface of the wound yourself;
- Do not apply various cosmetics to the skin for 7-10 days.
As a rule, complete healing of the wound occurs after 3 weeks.
If a malignant mole has been removed, the patient must carefully monitor his body for a long time for new formations. If a relapse occurs, the patient is sent to oncology to continue treatment.
After removing ordinary moles and following all the doctor’s instructions, the risk of complications during this operation is minimal. If the size of the formation was large, scars and scars may remain, which can then be removed with a laser.
What not to do with moles
Any formations on the skin should be monitored. If the nevus does not manifest itself in any way for a long time, there is no need to worry. You should visit a doctor if new, suspicious moles appear. If existing ones begin to change, this also requires urgent medical consultation. When hair grows from a mole, under no circumstances should you pull it out or shave it off. This leads to injury, which can trigger the process of degeneration of the formation into oncology. To prevent a mole from causing problems, you must adhere to some simple rules:
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun;
- do not use a washcloth in places where moles accumulate;
- do not pull out hairs from them;
- Moles cannot be squeezed out or combed.
If the mole is injured, you should consult a doctor.

Moles in children
When moles grow on children's bodies, it causes a lot of worry for parents. The largest number of nevi in babies appear from birth to one year. Almost every child has small flat moles on the body. Require more attention:
- nevi more than 0.5 centimeters in diameter;
- elevated above the surface;
- with fuzzy edges;
- fast growing;
- changing color;
- itchy and inflamed.
If suspicious moles are identified, you should visit an oncologist.

Folk signs about moles
Since ancient times, there has been a belief that a large number of moles portends a happy life for a person. By the place where moles grow, you can determine the nature:
- on the forehead - wisdom;
- on the cheeks and under the eyes - kindness and tenderness;
- on the cheekbones - courage, determination;
- on the scalp - a philosophical mindset;
- on the temple on the right - subtle intuition;
- on the ears - boasting;
- in language - such people are overly talkative;
- on the neck - high intelligence;
- on the shoulders - a karmic sign of strong people who do not recognize authorities;
- on the stomach - hysteria;
- on the eyelids - sensuality;
- above the upper lip - deceit;
- on the nose - a sense of humor, frivolity;
- on the foot - vital energy;
- On the shins - ease of instep;
- on your knees - impatience;
- on the palms - a hermit lifestyle;
- on the elbows - inability;
- on the back - demandingness towards oneself and others.
Many people are not interested in the meaning of moles on the body, and in vain, because these formations on the skin can be very dangerous for the body. There are many types of such formations, they differ in shape, size, color. Some people have a huge number of them, others only a few, but everyone has at least one. Read why these formations appear on the skin, how to understand which of them are dangerous, and learn about effective removal methods.
What are moles
Every person should know the nature of formations, which in scientific language are usually called nevi. Moles are a concentration of melanocyte cells. Melanin, the pigment that determines color, is concentrated in them. They come in different shades of brown, black, red, yellow and even purple. According to their shape, they are classified as flat, convex, hanging, lumpy, or with a stem.
Moles are of a similar nature to birthmarks. The difference is that the former can appear, change and even disappear throughout life (the most active period is from six months to 25 years), while the latter are given to a person from birth. They can be located on any part of the skin: both the face and the body. There are cases of their occurrence on mucous membranes.
Why moles appear
You have already read that pigmented formations can appear and disappear at any age, but what does this depend on? Factors that provoke the appearance of moles on the body:
- Heredity. Often in children, nevi appear in the same areas as in their parents, and sometimes in even greater numbers.
- Sun rays. Melanin under their influence is produced several times more intensely. Staying in the sun for a long time is dangerous not only because new ones can form, but also because old ones can transform into a tumor, even malignant.
- Viruses, injuries, radiation, x-ray exposure. Under the influence of each of these factors, melanocytes can group and come to the surface of the skin.
- Hormonal changes. Any surge in hormones (especially in women) can trigger the appearance or disappearance.
- Cluster of blood vessels. Nevi occur due to the accumulation of small processes of blood vessels.
- Dysfunctions of internal organs and systems. More often they lead to the appearance of vascular nevi. They can develop due to dermatological diseases, dysfunction of the large intestine, pancreatic dysfunction, and imbalance of lipid metabolism.
Reasons for the appearance of moles on the body in women
The occurrence of nevi is directly related to hormonal surges, of which there are plenty in the female body. The reasons for the appearance of moles on the body in women can be changes in the body associated with pregnancy (nevi often form on the skin of the abdomen, legs), menopause, and puberty. Sometimes, although rarely, they occur before or during menstruation.
How moles appear
Skin cells become more and more melanin pigment and transform into melanocytes. This occurs under the influence of one of the causes of nevi listed above (sun exposure, hormones, etc.). The accumulation of melanocytes is the reason why moles appear on the body. Whatever the nature of the nevus, the mechanism of its development always looks like this.
Types of moles
Formations can look very different, but according to a number of characteristics they are usually combined into several groups. The following types of moles are distinguished according to the nature of their occurrence:
- Angiomas. Formed due to pathological transformation of blood vessels. They can be flat or convex, pink, red, purple. They will never become malignant.
- Hemangiomas. A type of angioma. They appear shortly after birth in a child, gradually turn red and slightly swell, and have clear boundaries. Most often localized on the neck and face.
- Vascular malformation. There are two types of defect. The first is called port-wine stains and affects the torso, face, and arms. At first they are pale pink, but then they become scarlet or crimson, and with any dilation of the blood vessels they acquire brightness. The second type of malformation is a stork bite. Deformation of blood vessels in a child due to excessive pressure from the mother’s pelvic bones. These are asymmetrical reddish spots that last up to a year.
- Lentigo. Flat, different shades of brown. Small, reminiscent of freckles, but slightly darker in color.
- Mongolian spots. Clusters of large bluish or brown nevi in the lumbar and sacrum areas, completely flat.
- Blue. Dense round small nodules. They can take on all shades of blue. Most often appear on the buttocks, face, and limbs.
- Coffee stains. Flat, light shade, different sizes.
- White. Appear due to the production of a reduced number of melanocytes.
- Sutton's nevi. Flat, the skin around which is not pigmented.
You read about the origins of moles. They also differ in the depth of the skin layer in which they are formed:
- Epidermal. In the top layer of skin, flat. They most often form in the groin, feet and palms. The shade can range from pale beige to coffee brown.
- Intradermal. Convex. They can be smooth or rough, often dark. If hair grows from the intradermal, then this is a sign that it is safe.
- Borderline. Flat, any shape, smooth. There is never any hair on them.
Classification by appearance:
- Flat. Dry and smooth, they do not pose a health hazard. The most common type for humans.
- Warty. Very dark and wart-like. Their condition must be constantly monitored.
- Convex. Dark, can be either smooth or rough, covered with coarse or vellus hair.
- small – up to 1.5 cm in diameter;
- medium – up to 10 cm;
- large – more than 10 cm;
- gigantic - cover significant areas of the body or face.
Dangerous moles
Some nevi, under the influence of one reason or another, can develop into cancerous tumors. As a rule, this occurs due to injury to the formation or prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays. Dangerous moles are considered to be those that appear in adulthood, rapidly change their appearance and exceed a centimeter in diameter. A person should monitor such suspicious formations very carefully and regularly see a dermatologist.
People at increased risk of their occurrence include:
- fair-skinned, red-haired, with many freckles and age spots;
- have already removed malignant tumors;
- over 50 years of age;
- who have many dark ones;
- quickly “burn” in the sun;
- whose relatives had skin cancer.
What dangerous moles look like
Several types of formations are considered these:
- Nodal. A spot with a surface of uniform color, even black.
- Blue. A dense, smooth knot without hair, rising above the surface of the skin.
- Halo nevus. A colored formation on the skin surrounded by a colorless ring.
- Skin pigmentation. Slightly convex, pale, sometimes covered with hairs.
- Gigantic. Any formation of enormous size is dangerous.
- Nevus Ota. Dark brown or gray-blue formation, very large.
- Dubreuil's melanosis. Precancerous formation with uneven contours.
If dangerous moles look as described above, then there is a high risk of their degeneration into melanoma, a type of skin cancer. It is worth noting that such a tumor is highly treatable if detected in time. You should immediately contact a dermatologist if the following symptoms appear:
- deformations;
- discharge of blood or fluid;
- symmetry violations;
- burning;
- changes in surface texture;
- pain;
- hair loss;
- itching;
- the appearance of ulcers or cracks;
- seals;
- inflammation;
- color changes, appearance of inclusions.
How to identify a malignant mole
You need to periodically examine your body in order to promptly consult a doctor if there are suspicious signals. To identify a malignant mole, use the basic ACORD rule:
- "A - asymmetry." If it is no longer the same shape, it may be reborn.
- "K - contour." Uneven, fuzzy, blurry edges are a warning sign.
- “O—shade.” Any changes in color, the appearance of dots, inclusions, stripes and specks may indicate a malignant formation.
- "R - size." If it suddenly begins to grow, consult a doctor immediately. The maximum acceptable diameter for the norm is 6 mm.
- "D - dynamics." If crusts, cracks appear on the formation, or blood or any substance begins to come out of it, then you need to visit a specialist. Suspect nevi that become too soft, become covered with nodules, become painful, or are surrounded by inflamed red skin. A sudden increase in altitude is dangerous.
How to remove moles on the body
Dangerous and suspicious formations are removed for medical reasons. A person can also remove moles on the body at his own request if they cause him aesthetic or practical discomfort (they cling to clothes, are constantly touched by nails). There are several ways to get rid of nevi: laser beam, surgery, radio waves, liquid nitrogen. Each of them needs to be discussed in more detail.
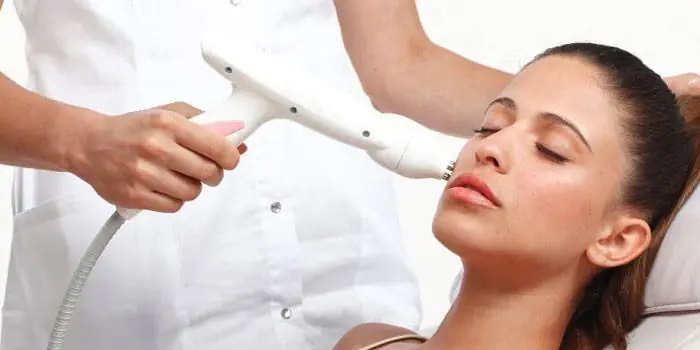
Laser removal
A very gentle and effective method of destroying formations with a directed beam. Laser mole removal can be performed using two techniques:
- Layer-by-layer evaporation. The beam gradually removes layers from the surface to the deep.
- Excision with a laser knife. The material after such an operation can be sent for histological examination.
- the method is absolutely safe;
- the risk of complications is minimized;
- there is no blood, because laser radiation immediately “seals the vessels;
- there are practically no contraindications;
- As a rule, one session is enough;
- painless (local anesthesia is performed);
- no recovery time after surgery is required;
- non-contact technology ensures complete sterility;
- the procedure is carried out very quickly.
- infection may occur;
- The wound takes a long time to heal, leaving a scar.
- diabetes;
- sun allergy;
- infections in the body;
- heat;
- oncological diseases;
- epilepsy;
- any skin inflammation;
- pregnancy.
Surgical method
A very affordable method, the only one suitable when there is no possibility of alternative procedures. The surgical method is reliable and is often used for formations with suspected malignancy. The formation and a small area of skin adjacent to it are excised with an ordinary scalpel under general or local anesthesia. The material can be immediately sent for histological examination.
- whatever the size of the formation, it will be removed in one go;
- low price;
- relapses almost never occur;
- complete absence of contraindications;
- the method is safe.
- A scar remains, although modern techniques for applying cosmetic sutures make it possible to make it as thin, even and invisible as possible. In addition, the use of modern anti-scar ointments will help reduce it to nothing.
- The wound takes a long time to heal. It needs to be processed regularly and carefully.
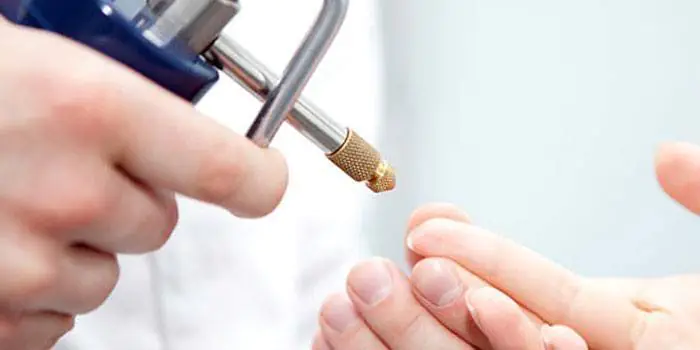
Cryodestruction
This is the name for the process of destroying formations with liquid nitrogen. To put it simply, the mole is frozen and its cells die from the cold. Cryodestruction is performed without anesthesia at all or with local anesthesia. This procedure will be most effective for flat formations on the body that do not go into the deeper layers of the skin. Nitrogen is applied by lubricating the surgical site with a cotton swab or using a special applicator.
- inflammatory, infectious processes;
- pregnancy;
- malignancy of formation;
- convulsions;
- epilepsy.
- removal is painless;
- the risk of complications is very small;
- cryodestruction is carried out quickly;
- the operation is inexpensive.
- the formation may not disappear completely, because nitrogen does not act on the deep layers of the skin;
- very high risk of scars;
- there is a possibility of damaging healthy tissue and causing a burn;
- for large sizes, several cryodestruction sessions may be required;
- recovery takes a very long time and during this period the use of cosmetics and exposure to the sun is prohibited.
There are from several to several dozen moles on the body of an adult. Nevi differ in shape (hanging, flat or convex), size, and susceptibility to external irritating factors. They also differ in color: from light red to black shades. With age, their number on the body increases. Initially, they are safe and do not bother people. However, under the influence of various conditions, birthmarks can change. Every person who observes this phenomenon will ask what to do if a mole grows and what actions to take.
Why does a mole start to grow?
A mole is growing; what this means can be answered by a dermatologist or oncologist after a thorough examination. However, a rapidly growing nevus does not always indicate that the development of a malignant tumor or melanoma has begun. This is a dangerous disease characterized by the rapid proliferation of metastases. There are other factors that cause a mole to grow. Reasons for growth:
- Treatment with hormonal drugs. Women taking hormonal medications can provoke the growth of formations that are located on the face, neck or head. If there are many nevi on a woman’s face, they can grow under the influence of hormonal agents.
- Pressing and scratching. Formations can be located in areas that are constantly exposed to mechanical stress (back, palms, stomach, legs, shoulders). Nevus on the feet can be injured by tight shoes. If your back starts to itch, you can accidentally tear the nevus when scratching. A woman can rip off a mole on her shoulder with a bag strap. The formation on the legs can be shaved off during depilation.
- Hereditary factor. A child is born without formations on the body, but with age they can appear in the same quantity and in the places where they are located on the parents.
- Action of ultraviolet light. If the formation begins to grow, exposure to direct sunlight may contribute to this. In summer, you should spend less time under the sun, use protective equipment, and also limit your visits to the solarium.
- Regular injury. A man can damage a nevus on his face while shaving. Poor location requires their removal to avoid the risk of degeneration into cancer.
- Impaired thyroid function. It is responsible for the production of hormones, and a failure in its work leads to the growth of the nevus.
- Hormonal disorders. The height and width of the growth may change during a period of hormonal imbalance. This happens during pregnancy, during puberty in adolescents, at the onset of menopause, as well as with frequent stress, termination of pregnancy, and menstruation.
Are growing moles dangerous?
If a mole grows, this does not mean that cancer is developing. The growth of a nevus depends on many factors. However, it is not recommended to ignore modifications. It is necessary to visit a doctor who will conduct an examination and prescribe an examination, as a result of which he can determine why moles are growing. Attention should be paid to those formations that are located in open areas of the body that are constantly exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
If a mole has increased to 0.7 centimeters in diameter, and has suddenly become darker and painful, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. He will conduct an examination with a dermatoscope, and based on the examination, he will tell you when a mole is growing, what it means, and what actions need to be taken. The reason for visiting a dermatologist is the transformation of the surface of the nevus. From rough it can become smooth and shiny.
Particular attention should be paid to signs of degeneration of the formation into a malignant tumor. If you seek help in a timely manner, you can recognize the disease at an early stage, when it can be treated. In such a situation, the issue of removing the nevus is raised.
Symptoms of growth transformation:
- the surface of the nevus is covered with cracks;
- the nevus is covered with small black or white dots;
- hairs from the mole began to fall off;
- the nevus has changed its color: a sharp lightening or darkening of the growth indicates that a pathological process has begun;
- itching appeared;
- clearly defined boundaries of education disappeared;
- a burning sensation appeared in the area of the spot;
- the surface of the growth peels off;
- due to the inflammatory process, redness appears around the birthmark;
- discharge of blood or clear fluid;
- pain when pressing or touching clothing, shoes, etc.;
- On palpation, a compaction is felt inside the spot.
What to do if a mole grows
Often there is no sharp increase in education, so it is difficult for a person to follow such a change. This is especially true for those nevi that are located in places inaccessible to the eye. If symptoms other than an increase in size appear, you should contact a dermatologist or oncodermatologist. The doctor will visually assess the condition of the nevus, then use a manual or digital dermatoscope to analyze the structure of the formation. If a digital dermatoscope is used, the program will capture an image of the spot, which the doctor can carefully examine and make a diagnosis with further recommendations.
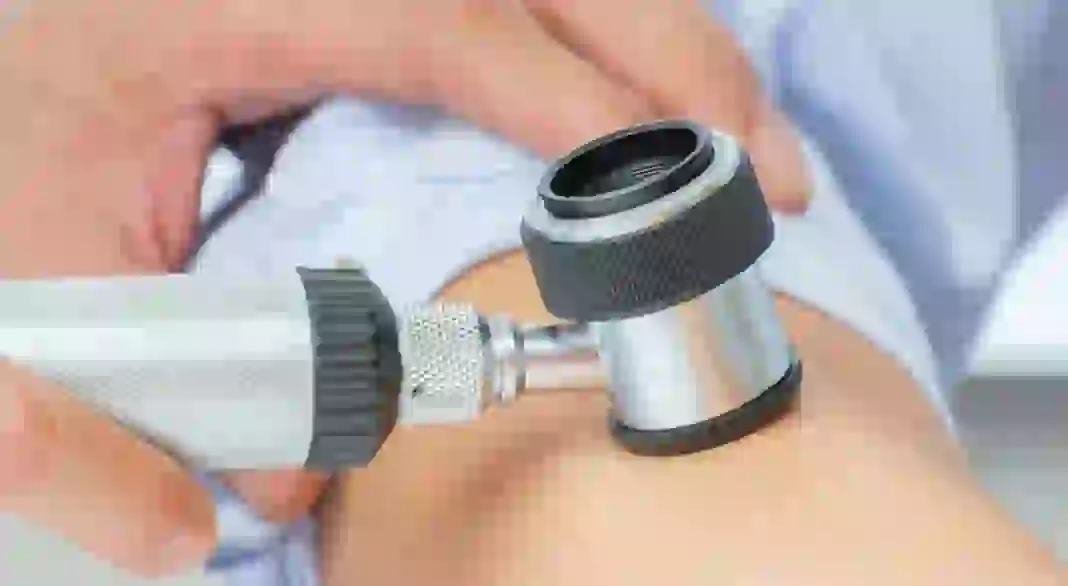
In the absence of dangerous symptoms, in addition to an increase in the size of the growth, it is necessary to monitor how it develops. Under the influence of prolonged exposure to the sun, during pregnancy, or taking hormonal medications, the mole may enlarge, but at this stage its transformation will end. The condition is the absence of irritating factors that cause melanin activation.
At the slightest change, it is recommended to visit a doctor. Self-treatment, let alone removal, is fraught with life-threatening consequences. The wounded growth can become infected.
Do growing moles need to be removed?
After passing the examination, the doctor may prescribe removal of the nevus. Another reason why a person seeks surgical removal is aesthetic discomfort. If a large mole is on the face, it will ruin a person's appearance. Doctors recommend removing moles that are located in places that are constantly subject to mechanical damage. With constant trauma to the growth, the process of degeneration into a malignant formation may begin.
Modern medicine offers several methods that can quickly, painlessly and without consequences for the body remove a birthmark. Removal methods:
- Electrocoagulation. Current is used for the operation. The procedure causes minor pain, so an anesthetic is administered before the excision.
- Surgical removal. Using a scalpel, the doctor is able to remove not only a small nevus, but also a nevus that has grown to a large size. It is not recommended to choose this method of removal if the mole is localized on a visible area of the body, since a scar remains at the site of excision.
- Cryodestruction. The growth is frozen using liquid nitrogen. After freezing it disappears. This method is not popular, as there is a high risk of re-formation of a mole in this place. This is explained by the fact that there is no possibility of controlling the depth of freezing, and the layer of the stain located deep in the dermis may not be removed.
- Laser surgery. The beam that comes from the laser removes the stain along with all tissues. Therefore, it is not possible to send the lesion for histological examination. The most popular method, despite the higher cost, since it leaves no scars and no bleeding during the excision process.
- Removal by radio waves. Using high-frequency waves, the doctor removes the birthmark. The advantage of the method is the absence of scars after surgery; the procedure and wound healing period do not take much time. Removal of small growths is indicated.
After removal, the doctor must explain how to care for the wound, taking into account the specifics of the formation. After two days, a crust forms at the removal site. Make sure that it is not damaged. After five to seven days, it will disappear spontaneously. If you tear it off, bleeding may open, which will be difficult to stop, and also cause infection.
It is recommended that the wound should not be exposed to direct sunlight and that visiting the solarium should be limited. Lubricate the wound with a solution of potassium permanganate for a week. Carry out the procedure three times a day. You can use hydrogen peroxide. Until the wound heals, it is not recommended to swim in the pool or apply cosmetics to it.
Several reasons for concern
If a person observes any changes in his mole, this is a reason to consult a doctor. It is not recommended to use traditional methods of treatment or removal. This can cause the development of melanoma, which is life-threatening. If a mole begins to itch, hurt, peel or bleed, there is no need to scratch it out or lubricate it with medications. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will conduct an examination that will not take much time and is painless. Timely detection of developing cancer cells can save a person from dangerous consequences.



