- Causes
- What do papillomas on the tonsils look like in children?
- Diagnostic features
- Complications
- Methods for treating tonsil papillomas
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
- Removal of papillomas on the tonsil in a child
Papilloma on the tonsil in a child is a fairly common pathology, which is diagnosed in 40% of cases where growths are detected on this organ. It looks like an epithelial growth with a granular surface and uneven edges. The cause of this neoplasm is exclusively human papillomavirus.
Causes of papillomas on the tonsils in a child
The only factor that causes the formation of papillomas on the tonsils is the activity of HPV. This virus affects both adults and children and is very common throughout the world. About 60-90% of the population is infected with it.
There are a large number of strains of this pathogen. Depending on the type of virus, it can affect different organs. Strains 6 and 11 are responsible for the appearance of papillomas on the tonsil in a child. These types are considered non-oncogenic, which means they rarely lead to malignancy of tumors.
Infection of a child most often occurs through contact at home or in public places. In more rare cases, children receive HPV from their mother during childbirth or through the umbilical cord during embryonic development.
Once on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and tonsils, the pathogen penetrates into the deep layers of the epithelium and begins destructive activities. In particular, papillomavirus damages DNA and leads to pathologies during cell division. The latter begin to divide too actively, and characteristic unhealthy growths appear on the mucous membrane.
For a long time, the virus may not manifest itself or provoke the appearance of tonsil papillomas in a child. Only favorable factors can “awaken” HPV.
These include:
- Chronic, severe infectious diseases, especially those associated with the ENT system;
- Problems with the immune system, its weakening;
- Chronic fatigue, severe stress or nervous tension;
- Regular “passive smoking” with smoking parents;
- Poor, unbalanced nutrition;
- Frequent hypothermia.
- Read also why papillomas appear in a child’s throat
What do papillomas on the tonsils look like in children?
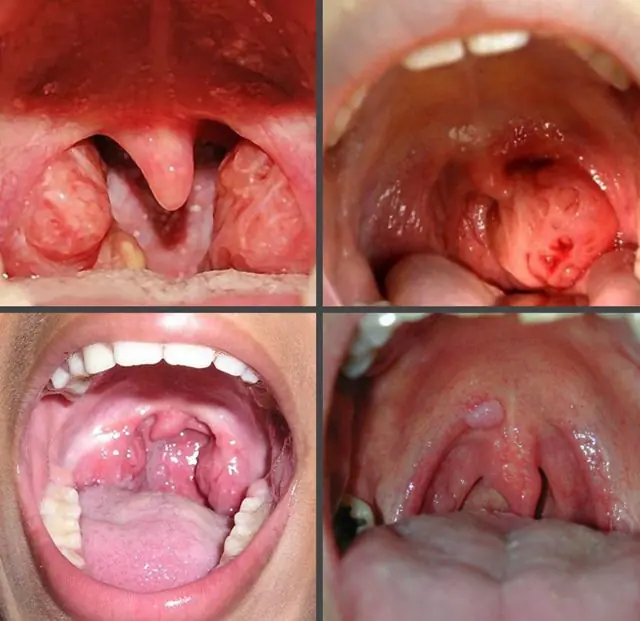
Photos of papillomas on the tonsil in children
In most cases, tonsil papilloma in a child does not cause any discomfort or discomfort. This is especially true for growths at the initial stage, when they are single and small in size.
In the future, as the tumors grow, they can cause some inconvenience. In particular, there is a feeling of a foreign object in the throat, sore and sore throat for no obvious reason, discomfort when swallowing or chewing food.
If the papilloma on the child's tonsil continues to grow uncontrollably, additional symptoms may appear. Sometimes the voice changes, it becomes more dull and hoarse. The speech of children with this pathology becomes slurred and awkward. There may also be difficulty breathing. This leads to oxygen starvation of the brain. Difficulties with swallowing provoke refusal of food and digestive disorders.Often papillomas on the tonsils in a child cause a chronic cough, which leads to throat irritation and cardiovascular pathologies.
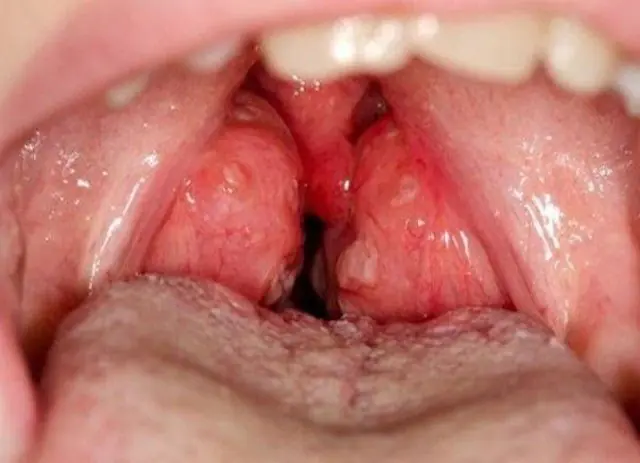
If you conduct an independent visual examination of the baby’s tonsils, you can detect small single or multiple growths on the epithelium. They protrude upward above the mucosa, have a soft, fine-grained structure, and are sometimes rough with uneven edges. Their shade is slightly different from healthy areas of the mucous membrane. The color can range from light pink to red.
Tonsil papillomas in children, more often than in adults, acquire a creeping character, that is, they quickly grow and cover large areas of the organ, affecting neighboring areas of the mouth or throat.
Papillomas whose size exceeds 15-20 mm begin to cause noticeable discomfort.
- Read also what papillomas look like in a child’s mouth
Features of diagnosing papillomas on the tonsil in a child

It is necessary to diagnose papillomatosis in a child using several methods simultaneously. This allows not only to identify growths, but also to determine their size, prevalence and the degree of viral load on the baby’s body.
The most popular diagnostic methods for suspected tonsil papillomas in a child:
- Visual examination of the throat and tonsils using a laryngoscope;
- Microlaryngoscopy (a microlaryngoscope is used);
- X-ray and CT scan of the tonsils and arches;
- Blood test and PCR diagnostics to determine the type of virus and the extent of damage to the body.
If the doctor suspects the spread of papillomas in a child from the tonsils to the vocal cords, laryngostroboscopy and electroglottography may be performed to examine the vocal mechanism.
Only after a complete examination is an accurate diagnosis made and special treatment for papillomatosis can be prescribed.
Complications of papillomas on the tonsil in a child

It should be remembered that any pathological inflammatory processes occurring in the throat and tonsils are dangerous, primarily from the point of view of deterioration of respiratory function.
Single papillomas on the tonsil in a child cannot lead to dangerous consequences. However, they tend to grow and cover large areas of the mucosa. Obstructive growths can lead to swelling of the tonsils and larynx and impair respiratory function.
There are three degrees of stenosis when tonsils are affected by papillomas in a child:
- Compensatory. Children develop hoarseness and noise when breathing.
- Decompensatory. The baby complains of a lack of oxygen when breathing.
- Asphyxia. The child suffocates, may lose consciousness, and heart function deteriorates sharply.
If you do not start timely treatment, then death is quite possible.
Methods for treating papillomas on the tonsil in a child
To avoid the growth of papillomas on the tonsils in children, they are advised to remove growths using various surgical methods. However, such treatment is quite traumatic; in addition, it does not protect against relapses of papillomatosis. Therefore, an integrated approach using immunostimulating and antiviral therapy is recommended.
Medicines for tonsil papillomas in children
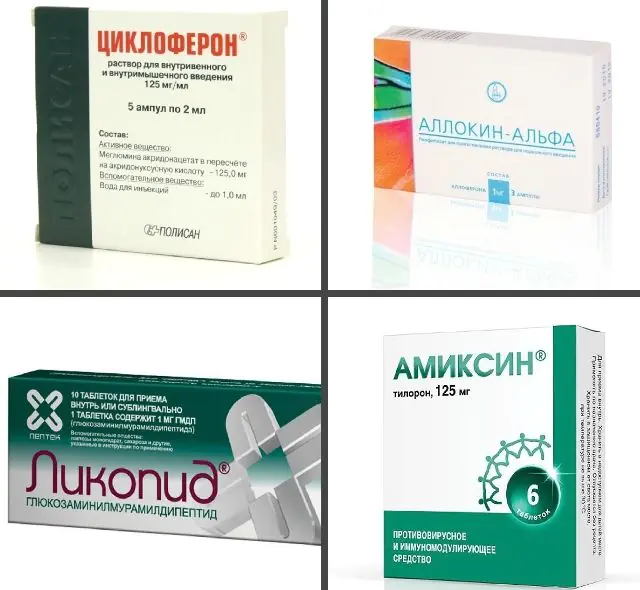
In the photo there are medications for papillomas on the tonsil in a child
The groups of drugs used to treat papillomas on the tonsil in a child are antiviral and immunomodulators. Let's look at the most popular products for children:
- Immunomodulators. They help strengthen the child’s immune system and stimulate the body to protect itself from infections. They can be in tablet form, injectable form or in the form of sprays for the tonsils. The following products showed good results: Amiksin (about 600-700 rubles), IRS-19 (from 500 rubles) and their analogues - Lykopid (about 400 rubles) and Derinat (from 350 rubles).
- Antiviral. To treat papillomas on the tonsil in a child, medications in the form of tablets or rectal suppositories can be used. In some cases, anti-HPV injections may be prescribed. Drugs in this group suppress the papillomavirus and block its activity. Thus, the viral load on the child’s body is reduced. The following products are popular: Panavir (about 1500-2000 rubles) and Viferon (from 350 rubles) and their analogues Cycloferon (from 200 rubles) and Allokin-Alpha (about 3500-4000 rubles).
In rare cases, chemical cauterizing agents may be prescribed, which act directly on tonsil papillomas in a child. These can be various acids and alkalis. However, such manipulations are quite unsafe, as they can cause burns and swelling of the mucous membrane. In addition, it is quite difficult to control the depth of penetration of an aggressive substance deep into the tissue. Such procedures can only be performed by a doctor. And if possible, it is better to abandon such chemical exposure in favor of more gentle methods of destruction of tumors.
Folk remedies against papillomas on the tonsil in a child

Herbal and natural medicines are good as adjuvant therapy, as well as during the recovery phase after surgery.
It is recommended to gargle or irrigate the tonsils for papillomas in a child with the following decoctions:
- Calendula. It has a disinfecting effect, is a natural antiseptic, and enhances the regeneration process of damaged epithelium.
- Daisies. A decoction based on this plant relieves inflammation and swelling, inhibits the activity of microbes in the oral cavity and on the tonsils.
- Eucalyptus. Reduces pain in the tonsils after surgical removal of papillomas, relieves swelling.
- Sage. Kills many pathogenic bacteria and fungi, eliminates the inflammatory process.
- oak bark. Enhances blood clotting, relieves inflammation, kills pathogenic microflora.
These decoctions are prepared in clean water in the proportion of 1 tablespoon of dry plant material per glass of water. Bring the mixture to a boil and leave to infuse. After the product has cooled, strain and gargle with warm broth. It is recommended to repeat the procedure for treating tonsil papillomas in a child at least 4-5 times a day.
You can also give him immunostimulating infusions and decoctions based on the leaves of black currant, mint, chamomile, coltsfoot, St. John's wort, and echinacea.
Before starting to use any traditional medicine recipes, you should consult your doctor.- See also, immunomodulatory treatment of papillomas in the mouth with folk remedies
Removal of papillomas on the tonsil in a child
Usually doctors insist on physical removal of papillomas on the child’s tonsils. This is a surer way to get rid of discomfort and avoid the possible dangerous consequences of the growth of growths.
There are several methods of radical treatment of papillomas, let’s consider them:
- Classic surgery. This method involves the use of a scalpel, loop or scissors and local anesthesia. Objectively, it is considered an outdated method and is used in extreme cases in the absence of newer and more technologically advanced equipment for removing papillomas on the tonsils of a child. May cause bleeding and inflammation. The cost of surgical treatment of papillomas in children is 750-1600 rubles in Russia and 270-500 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Laser destruction. A more preferable treatment method, since the laser has a cauterizing ability and prevents bleeding from developing after the elimination of the growth. Also, the use of a laser beam reduces the risk of wound infection. The price of the procedure is 1500-2400 rubles in Russia and 350-700 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Radiosurgical removal. In this case, a radio knife or a special loop is used. This procedure is minimally invasive, which means there is virtually no threat of blood loss and the development of inflammatory processes. The rehabilitation period is quite short. The cost of radiosurgical removal of papillomas on a child’s tonsils is 2400-3400 rubles in Russia and 550-1200 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Electrocoagulation. To remove tumors on the tonsils and arches, an electric current of a special frequency is used. This method is rarely used to treat children, as it is considered painful and can lead to swelling. The price of electrocoagulation of papillomas on the tonsils is 1200-2300 rubles in Russia and 250-600 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Watch a video about papillomas in children:
Photos of papillomas on a child’s tonsil are easy to find on the Internet. Here you can find various recommendations for the treatment of this disease. However, only a pediatrician can prescribe therapy after a complete examination of the baby. Do not self-medicate to prevent serious complications of papillomatosis.
- Related article: Which doctor should I contact for oral papillomas?



