- Causes of folliculitis in children
- Symptoms of folliculitis in children
- Which doctor should I contact for folliculitis in children?
- Diagnosis of folliculitis in a child
- Complications of folliculitis in a child
- Treatment of folliculitis in children
- Prevention of folliculitis in children
Folliculitis in a child is a bacterial infection that manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle, which is accompanied by a purulent process. A blister appears on the affected area, inside of which there is often a yellow or white liquid, sometimes with bloody spots. In childhood, the symptoms are very pronounced, the inflammation is severe and causes discomfort to the child, and after healing, scars and pigmentation remain on the body. If the disease is stopped in time, the recovery process will go faster: the hairline will quickly recover and there will be no marks on the skin. In the article we will learn the main symptoms, causes and treatment options for folliculitis in children.
Causes of folliculitis in children
In the photo are staphylococci that cause folliculitis in children
According to etiology, folliculitis in children is divided into:
- Bacterial (staphylococcus).
- Viral (herpetic type).
- Fungal (fungi of the genus Candida, dermatophytes).
- Parasitic (mites).
According to statistics, every tenth child is susceptible to this disease. Children with weakened immune systems, itchy dermatitis and lack of proper hygiene are at risk. In this case, a weakened immune system can cause a relapse of the disease. A harbinger of folliculitis can be ostiofolliculitis and seborrhea of the head. Like many infectious diseases, folliculitis is contagious and can be transmitted through household contact. The following reasons for the development of folliculitis in children are identified:
- Frequent microtraumas of the skin (cuts, scratches, abrasions).
- Swimming in poor quality water.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Climatic conditions (heat and high humidity).
- Increased sweating.
- Taking medications (glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressants).
- Tight synthetic clothing.
- Presence of diseases (diabetes mellitus, anemia, liver problems).
Symptoms of folliculitis in children
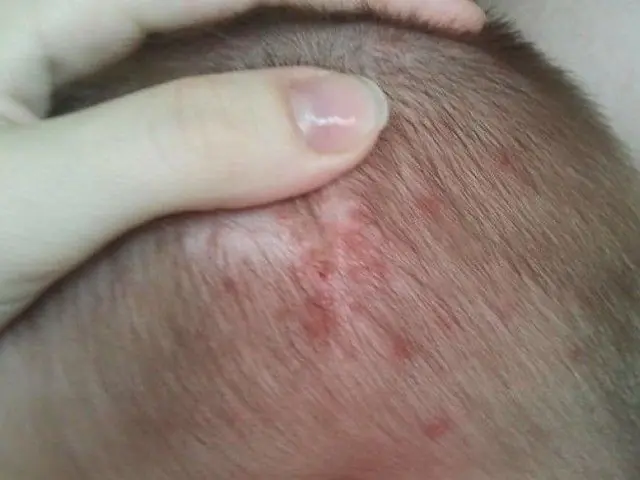
In the photo there is folliculitis on a child’s face
Children's folliculitis is manifested by the formation of reddish nodules on the skin with a diameter of about 1 cm. Sometimes the lymph nodes near the affected area become inflamed. The formations are painful, so the baby may have trouble sleeping. Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- itching;
- blisters with pus;
- restlessness.
With bacterial folliculitis, the formation is localized in the hair growth area. The blisters fill with yellow, white or bloody contents. Symptoms of fungal folliculitis are a flat area surrounded by a border. White plaques form in compacted areas. In children, the buttocks, groin and external genitalia are most often affected. The temperature often rises and the general condition worsens.
Which doctor should I contact for folliculitis in children?
When the first skin lesions appear, the child should be shown to a dermatologist so that he can make a diagnosis and rule out the presence of underlying diseases and hidden infections. The specialist will examine the baby, study symptoms and complaints, analyze the medical history and prescribe additional tests.
Diagnosis of folliculitis in a child
Diagnosis of childhood folliculitis is as follows:
- Determination of the depth of follicle damage.
- Determining the cause that caused the inflammation of the pathogen.
- Identification of concomitant diseases that affect the development of the inflammation process.
- Exclusion of etiology (infantile syphilis or gonorrhea).
- Determining the mental state of the child, since folliculitis often appears against the background of stress and strong emotional experiences.
To clarify the diagnosis of folliculitis in a child, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- Take a blood test to determine your glucose level and rule out diabetes.
- Perform dermatoscopy to determine the depth of the lesion.
- Conduct a biopsy of the child's skin to determine the pathogen.
- Conduct an RPR test and PCR reaction to exclude specific diseases.
- Examine for the presence of mushrooms.
- Make a bacteriological culture of the contents of the pustules.
- If a child is suspected of having staphylococcal folliculitis, culture the child on nutrient media.
Carrying out an informative study (microscopy of purulent discharge) will determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics, which is important for effective treatment. It will not be superfluous to analyze the presence of parasites in the body.
- Read about Hoffmann's folliculitis
Complications of folliculitis in a child
If you do not start treatment in a timely manner and do not eliminate the factors that provoked the occurrence of folliculitis, the disease will become chronic, inflammation of the lymph nodes and blood vessels will begin, and boils will appear. If folliculitis affects a newborn, then in the future the child will face a skin disease, and inflammatory processes in the lungs, kidneys and lining of the brain are also possible.
Treatment of folliculitis in children
The main condition for treating the disease is good hygiene and elimination of the factors that provoked the disease. After diagnosing and studying the test results, the dermatologist prescribes medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and diet.
Drug treatment prescribed depending on the type of folliculitis. For the candidiasis type, they are treated with antifungal medications, for the staphylococcal type - with antibiotics, for herpes - with acyclovir. For external treatment of blisters, iodine, brilliant green, camphor alcohol, salicylic alcohol, erythromycin and syntomycin ointments are used.
If there is an immunodeficiency, then it is brought back to normal using Vitaferon or Immunal. In difficult cases, the doctor opens the papules under sterile conditions and removes the pus. The empty cavity is treated with antiseptic solutions. To relieve the acute inflammatory process, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out: laser therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, dermabrasion.
Diet for folliculitis implies an increase in protein intake and a decrease in fats, fast carbohydrates, sugary drinks and sweets. It is important that the child eats a lot of fresh fruits and vegetables rich in fiber and vitamins. In winter, the child needs to ensure that the body receives vitamins and minerals. For this purpose, vitamin and mineral complexes are often taken.
When treating folliculitis in children, do not wash the affected area (especially with hot water), crush ulcers, or use wet compresses. To reduce inflammation, change your laundry regularly and iron it after washing.- Read about the treatment of folliculitis with folk remedies
Prevention of folliculitis in children
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, you need to take proper care of your child:
- Observe hygiene rules.
- Trim your nails on time.
- Do not use other people's hygiene products (washcloths, towels).
- Treat scratches, skin microtraumas and insect bites with an antiseptic.
- Ensure the correct microclimate in the apartment: ventilate the room so as not to provoke excessive sweating in the baby.
- Monitor your diet.