Many women, after visiting a doctor, hear a diagnosis of hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the cervix. But not every patient understands what it is and what causes the development of the disease. Another name for the disease is leukoplakia. The disease occurs in women of different ages and consists of severe thickening and keratinization of the uterine epithelium. The disease is diagnosed during examination in a gynecological chair.
Related articles:
-
Follicular hyperkeratosis - causes -
Hyperkeratosis of the feet - causes and treatment -
We successfully treat hyperkeratosis at home -
Treating plantar warts at home -
Effective methods for treating seborrheic dermatitis on the face
Types of uterine hyperkeratosis
Normally, the uterine mucosa has a shiny and smooth pink surface. As the pathology develops, its surface swells and acquires a bright red tint. After the inflammatory process becomes chronic, the body begins to build up epithelium in the affected areas, trying to protect the tissue.
Hyperkeratosis in medical practice is divided into the following types:
Simple look. Here, small areas of the epithelium are affected; the pathology does not pose a great danger to the patient’s health. Proliferative hyperkeratosis. It is a severe form, often causing malignant formations.In most cases, pathology is diagnosed in older women, especially during menopause. In young girls, leukoplakia is much less common.
Hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the vagina is often diagnosed during an examination of the patient on a gynecological chair using a mirror.
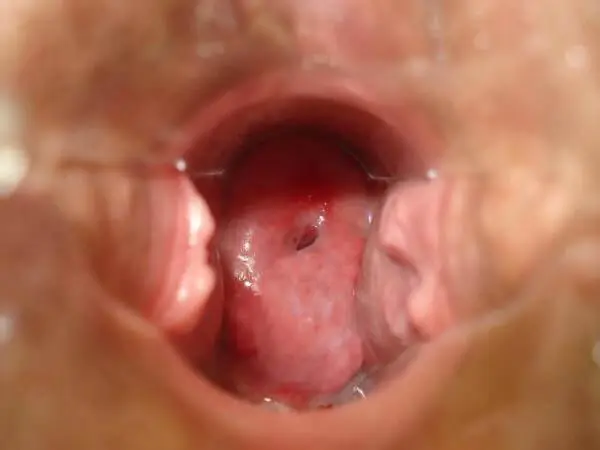
Important! The pathology may be asymptomatic. Preventative examinations with a doctor will help to exclude the disease and begin timely treatment if it is detected.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many factors that can lead to the appearance of hyperkeratosis in women. The most common reasons include:
- Cervical cancer.
- Presence of papilloma virus. Hyperkeratosis is often diagnosed with indirect signs of HPV. This indicates the influence of the human papillomavirus on the uterine mucosa.
- Hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the vulva can also develop against the background of some sexually transmitted diseases. This could be chlamydia, gonorrhea.
- Epithelium with signs of hyperkeratosis can be diagnosed in women after injury. Most often this happens during childbirth, abortion, and less often during gynecological examinations.
Internal factors can also provoke changes in the epithelial layer. These include:
- Hyperkeratosis of the intermediate layer of the uterus can appear against the background of diseases of the endocrine system. These could be pathologies of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus.
- Also, the disease often develops due to the presence of an inflammatory process in the female organs.
- Often the pathology is diagnosed against the background of stress and chronic fatigue.
- During artificial termination of pregnancy in the form of abortion, the uterine epithelium is injured, which often causes its hardening.
- Another reason may be incorrect insertion of the uterine device.
The combination of one or more causes cannot guarantee the occurrence of the disease in a woman, but they significantly increase the risk of developing pathology.
Diagnostics
Often visiting a doctor with cervical hyperkeratosis, a woman hears a result such as a cytogram corresponding to hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium. This indicates the presence of the disease and the appearance of one or more white spots on the epithelium of the cervix, indicating layering of the epithelium.
Also, against the background of the disease, the presence of a benign tumor (dermatofibroma) is often detected. In such cases, patients are interested in the question of what dermatofibroma with hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium means. When diagnosing the disease, the identification of benign formations is not uncommon.
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using the following methods:
- examination of the patient;
- taking anamnesis;
- ultrasound appointment;
- analysis of the patient’s microflora;
- study of hormone levels in the blood;
- biopsy of samples of the epithelium of the affected areas.
As a result of the research, single accumulations of scales or multiple formations are detected on the surface of the mucous membrane of the cervix. After making a diagnosis and identifying the provoking causes, it is necessary to begin treatment. In such cases, the pathology will have a positive prognosis.
Important! Timely detection of the disease and proper treatment will help avoid complications of the pathology in the future.
Treatment
Often patients, faced with cervical hyperkeratosis, wonder how the pathology is treated. With mild hyperkeratosis, patients are prescribed medications that help restore the natural functions of the epithelium. These may be medications from the following groups:
- probiotics;
- vitamins A and C;
- folic acid.
For more serious forms of the disease, treatment may involve the use of a method such as chemical coagulation. In simple terms, this is cauterization of the affected tissue. This method is used for mild to moderate damage to the epithelium.
In severe forms, surgical intervention is indicated. These could be the following methods:
- Electroconization involves the removal of affected areas of the epithelium using a special surgical loop through which a current is passed.
- Cryotherapy - cold is used to get rid of the problem.
- Laser treatment is a method based on the use of laser equipment.
- Ultrasound - irradiation.
- Knife conization – involves the removal of damaged uterine tissue.
- Complete amputation.
Important! Drug treatment is selected by the attending physician based on the examination of the patient and the characteristics of the course of the pathology. Indications for surgery may include severe forms of the disease and precancerous conditions.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment with folk remedies for hyperkeratosis can be used in the form of auxiliary methods of therapy. Popular recipes include the following:
Douching
When the epithelium of the cervix is damaged, various decoctions against the background of medicinal herbs work well. It can be chamomile, calendula, yarrow, celandine. Brew the herb at the rate of one tablespoon per 500 ml. water. Douching is carried out with a warm decoction.
Use of oils
Vegetable oils have a beneficial effect on human mucous membranes. For these purposes, sea buckthorn, olive, and sunflower oil are used. Treatment is carried out using tampons soaked in oil.

Treatment with suppositories
Candles are used based on cocoa butter. To do this, the product in an amount of 150 g is placed in a water bath. After purchasing the oil in liquid form, add a few drops of tea tree oil, 10 drops of calendula tincture, 5 drops of vitamin A (can be bought at the pharmacy). Afterwards, the resulting mixture is poured into specially prepared foil molds to make candles. Candles are placed daily at night. The course is 10 days.
Important! Using folk remedies, you must carefully monitor the condition of your body. With this type of therapy, an allergy to one or another component of the drug often occurs.
Timely diagnosis of pathology and its proper treatment will help to avoid complications and preserve women’s health for many years.
Medicine has been familiar with this disease since 1887. The Greeks called it “white plaque”, translated as leukoplakia. This pathological process determines excessive keratinization of the epithelial layers, which disrupts the formation of keratinocytes. Today this disease is called – hyperkeratosis of the cervix.
The transitional part between the vagina and the body of the uterus is the cervix. It is a hollow cylinder 3–4 cm long and is divided into the vaginal part and the supravaginal part. The vaginal part of the cervix can be felt with your hand and seen with a vaginal speculum.
The visible part of it is lined with multilayered squamous epithelium, which in turn consists of superficial, intermediate, parabasal and basal layers. If keratinization occurs in the superficial layer, cervical hyperkeratosis appears, which looks like a white spot and is called leukoplakia. Treatment of cervical hyperkeratosis depends on the degree of epithelial damage.
Hyperkeratosis - pathology of the cervix
The squamous epithelium in childbearing age is saturated with glycogen and well differentiated. For beneficial bacteria, glycogen creates favorable conditions and helps maintain an acidic environment in the vagina. With age, hormone levels decrease, acidity decreases, squamous epithelial cells shorten, and atrophy begins.
Tissue hypertrophy and proliferation impairs cell maturation and reproduction. There are certain factors that contribute to the development of this disease.
Important! Cervical hyperkeratosis is a pathological condition that belongs to precancerous diseases, turning into a malignant form of the course.
Reasons for the development of hyperkeratosis
There are certain factors that can contribute to the appearance of this disease:
- Endogenous – processes within the body.
- Exogenous - the result of external influence.
Endogenous factors include:
- decreased immunity;
- disruption of hormonal levels in the body;
- hereditary predisposition.
Exogenous factors are:
- lack of hygiene;
- long-term use of oral and vaginal contraception;
- the onset of sexual intercourse in adolescence;
- venereal diseases;
- promiscuity;
- cervical injuries during childbirth;
- surgical interventions on the cervix.
There may be a combination of reasons that lead to hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the cervix.
The mechanism of formation of this pathology is not fully understood. In order to diagnose this disease in a timely manner, it is necessary to promptly inform the doctor about any problems that have arisen.
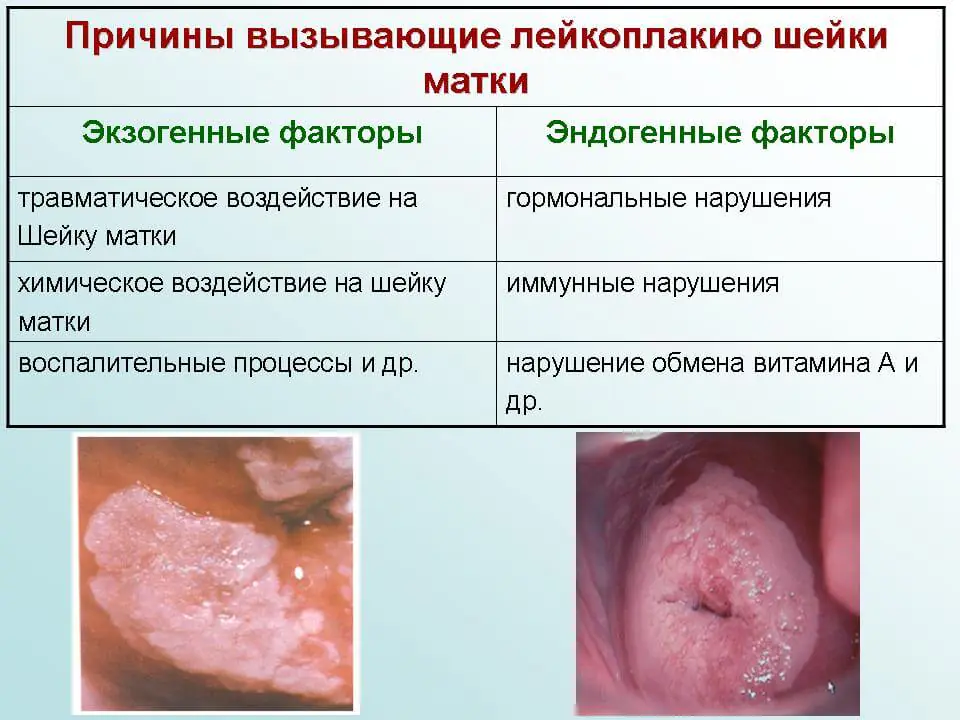
Main reasons
Symptoms of the disease
The disease is asymptomatic. The onset of the disease can be easily missed if you do not undergo an annual preventive examination by a gynecologist. Considering that there are no specific complaints, the symptoms of cervical hyperkeratosis, which are expressed by a certain discomfort, attract attention.
First signs
In some cases, a woman experiences the following manifestations of the disease:
- increased amount of leucorrhoea;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- spotting after intimate intercourse.
The keratinization of squamous epithelium may be dystrophic in nature, or may be the beginning of a malignant process.
According to the degree of keratinization, stratified squamous epithelium is divided into the following types:
Minor keratosis
Dyskeratosis is a pathological keratinization that appears in individual cells of stratified squamous epithelium as a result of impaired maturation. Human papillomavirus is the cause of dyskeratosis. Under its influence, degenerative changes appear in the epithelium.
Focal keratosis
If the keratinized epithelium occupies an entire layer, this is parakeratosis. It develops due to certain reasons:
- past inflammatory processes;
- long-term use of contraceptives;
- cervical injuries during abortion, IUD insertion.
Extreme degree of keratosis
The highest degree of keratinization is called hyperkeratosis..
In this case, epithelial cells divide at high speed. The keratinized epithelium is layered on top of each other and forms a thick layer. The division process may become uncontrollable. There is a risk of degeneration of benign cells into a malignant neoplasm.
Attention! If leukoplakia is suspected, a biopsy of the affected area is necessarily taken for histological examination.
Hyperkeratosis during pregnancy: consequences and complications
When registering for pregnancy, a woman is recommended to have a colposcopy for diagnostic purposes. When identifying hyperkeratosis, the following factors are taken into account:
- degree of leukoplakia;
- gestational age;
- test results.
The examination package includes:
- cytological examination of a smear from the cervical canal;
- bacterial culture of vaginal discharge;
- virological examination of the blood of a pregnant woman;
- cervical biopsy (if necessary);
- colposcopy.
The approach to each pregnant woman should be individual. Keratosis of the cervix is not an indication for termination of pregnancy. The question of its completion arises only when the malignant course of the process is confirmed. In advanced pregnancy, cervical cancer is treated only after childbirth.
Treatment of hyperkeratosis during pregnancy is mainly local and aimed at strengthening the body.
Local treatments include:
- anti-inflammatory suppositories (synthomycin, sea buckthorn, methyluracil);
- antifungal suppositories (“Terzhinan”, “Mikozhinaks”, “Pimafucin”);
- restoratives (“Revitaxa”, “Mumiyo”);
- probiotics to restore flora in the vagina (Vaginorm, Vagisan, Vagilak);
During pregnancy, immunity in the female body decreases. To restore it, you need vitamins and good nutrition.
The preferred vitamin complexes, in which the amount of necessary vitamins is balanced, are “Elevit”, “Pregnavit”.
Vitamins of group “E”, “C”, “A”, “B” should be included in the diet. They are found in the following products:
- rich in vitamin B - apricots, nuts, potatoes, green peas, beans;
- there is a lot of vitamin E in fish, liver, nuts, beef;
- carrots, eggs, fish, liver, cilantro, cheese, milk are sources of vitamin A;
- Vitamin C is found in lemons, kiwi, black currants, cabbage, lettuce and spinach.
The pregnancy period is long and stressful. Family members must provide a comfortable state for a woman who will bring a little joy to the house. To create conditions it is desirable:
- organize evening walks;
- take on homework;
- monitor proper nutrition;
- surround with care and love.
There is nothing complicated about this, just pleasant troubles.
If a pregnant woman has hyperkeratosis of stratified squamous epithelium in the early stages, with proper treatment, there will be no consequences. A woman can continue her family more than once.
A complication is the degeneration of squamous epithelial cells, from benign to malignant. Pregnancy provokes the division process, it becomes chaotic and uncontrollable.
Hyperkeratosis is not an indication for termination of pregnancy
Diagnosis of squamous epithelium
Hyperkeratosis of the squamous epithelium of the cervix is an insidious disease. Diagnosis of this disease presents certain difficulties.
Don't forget! The disease has no characteristic symptoms. Only a doctor can identify this pathology.
The doctor is responsible for the woman’s life, which depends on proper examination and treatment. During the reception:
- Collection of anamnesis of the disease.
- External inspection.
- Vaginal speculum examination.
- Prescription of additional examination methods.
A correctly collected anamnesis is half the diagnosis. Noteworthy:
- number of births and injuries during them;
- quantity and quality of abortions;
- duration of taking contraceptives (hormonal, IUD, vaginal);
- gynecological inflammatory processes;
- past infectious diseases (venereal, viral, bacterial);
- state of the immune system (frequency and duration of diseases);
- presence of surgical interventions;
- genetic predisposition.
During external examination, the following matters:
- skin color;
- body type;
- the presence of external damage (postoperative scars, rash on the body, papillomas);
The most informative is a vaginal examination in the speculum. It is easier to suspect hyperkeratosis in this way. Please pay attention to the presence of:
- damage to the neck;
- uniform coloring of the cervical epithelium;
- fabric uniformity.
For a final diagnosis, additional research methods will be needed:
- smear microscopy;
- examination for viral infection;
- cytological analysis of scrapings from the cervical canal and vagina;
- biopsy of a suspicious area on the cervix;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
The examination complex gives a complete picture of the disease. The extent of the lesion can be confirmed by biopsy and colposcopy.
A cervical biopsy is performed after pre-treatment with antiseptic agents. A piece of tissue is “bitten off” by a conchotome and sent to the histology laboratory. A thorough examination of the material reveals the presence or absence of malignant cells in the MPE and the depth of damage to the organ.
A biopsy is performed immediately after the end of menstruation. By this time, the cervix is most suitable for examination and the woman cannot be pregnant.
The method is quite informative, but takes time. A quick and no less effective is colposcopy - examination of the cervix using a microscope.
Colposcopy is performed after pre-treatment of the cervix with 3% Lugol's solution (Schiller test). The size of the affected tissue has a wide range. Using a colposcope, hyperkeratosis should appear as a fine-grained surface with clear edges, without blood vessels. And in the case of malignant degeneration, atypical cells are visible. Interpretation of colposcopy results is necessary for correct diagnosis.
After the correct diagnosis is made, treatment for cervical hyperkeratosis is prescribed.
Treatment methods
The strategy for its treatment depends on the form of keratosis. First, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, background diseases are removed. In some cases this is enough.
Medicines
Any conservative treatment includes:
- local treatment (douching, suppositories, ointment tampons, vaginal tablets);
- immunostimulating drugs;
- vitamin therapy.
Ointments for tampons:
Traditional treatment of cervical hyperkeratosis
Chemicals help well, but they are not suitable for everyone. Recently, many medications cause an allergic reaction. In this case, a traditional method of treatment comes to the rescue.
To increase immunity, you can use sprouted wheat grains and milk thistle seeds. Tinctures, decoctions, and herbal extracts such as ginseng, calendula, and eucalyptus are used.
For vaginal tampons, it is better to use rosehip, sea buckthorn, and cocoa oil.
Of the ready-made herbal preparations, pharmacies offer “Immunal” and “Immunorm”.
Let's remember! Hyperkeratosis is a precancerous condition. There is no time for experiments. Traditional medicine does not replace consultation with a specialist.
If keratosis is not treated, the disease can persist for a long period, but when at least one atypical cell appears, the development of malignant degeneration accelerates.
Surgical treatment
The most effective form of treatment remains surgery:
- cryotherapy;
- laser valorization;
- radio wave destruction;
- coagulation with chemicals;
- diathermocoagulation.
Minimally invasive types of destruction are performed on an outpatient basis. A follow-up examination is carried out every month. During this period, it is recommended to maintain sexual rest and maintain hygiene.
In case of deep invasion of the pathological process, suspicion of malignancy of the disease, the presence of scars on the neck, the following is carried out:
The treatment was successful, but follow-up continues. Every 6 months a woman is required to visit a doctor. At the appointment, the doctor takes a smear from the patient for bacteriological, cytological, virological studies, and performs a colposcopy.
If the indicators remain satisfactory within two years, the patient is removed from dispensary observation and transferred to normal mode. The prognosis after treatment of hyperkeratosis MPE is usually favorable.
Prevention
Considering the causes of the disease, in order to prevent the development of this pathology it is necessary:
- avoid casual sex;
- use barrier contraception (condoms);
- correct the menstrual cycle in time;
- visit a gynecologist in a timely manner;
- eat well;
- maintain hygiene;
- exercise.
Conclusion - hyperkeratosis of the MPE of the cervix is not oncology. With the right behavior and regular examination, one stressful situation in life can be avoided.
Galina Savina Reading time: 7 min 5,944 Views
The cervix looks like a cylinder, measurements showed that its length is 3 - 4 cm, and its diameter is 2 - 2.5 cm. A normal and healthy appearance of the cervix looks like a smooth pink surface of the mucous membrane and is located 12 cm from the vestibule of the vagina, the thickness of the walls vagina 3-4 mm. The internal genital organs change depending on the menstrual cycle and the woman’s age, but it often happens that the cause of the changes is disease. Cervical hyperkeratosis or leukoplakia is a pathological process that manifests itself in keratinization of tissue. Women after 35–40 years of age are susceptible to hyperkeratosis.
Classification of the disease
Hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium of the cervix
This is keratinization of epithelial cells. White film, clear boundaries, which cannot be removed mechanically. With hyperkeratosis of the MPE (stratified squamous epithelium) of the cervix, all layers are affected: the basal, parabasal, intermediate, and superficial layers. Both part of the mucosa and the entire epithelial layer of the cervix are susceptible to tissue destruction.
Focal hyperkeratosis
This is a serious deficiency of female hormones. It looks like clearly defined white spots with a matte sheen on the cervix. This condition is also called pseudo-erosion.
Parakeratosis of the cervix
One of the pathological processes is parakeratosis. This is a change in the mucous layer, a violation of keratinization of the lining of the organ. It is much less common than hyperkeratosis of squamous epithelium. It occurs as a result of injury to the internal genital organs of a woman during rough sex, as well as during medical procedures: installation of a spiral, cleaning, abortion. With parakeratosis, a tissue cell ceases to produce keratohyalin, which is responsible for the elasticity of the epithelial layer, so the mucous membrane is more susceptible to damage and injury.
Dyskeratosis
It differs from other species in that the cells divide chaotically at a high speed, the neoplasms grow and become similar in appearance to cauliflower, which grows on the epithelial layer. Since exfoliation of keratinized cells does not occur, scale by scale they form layers - the size of the neoplasms becomes impressive. Dyskeratosis is dangerous because uncontrolled growth of tumor cells can occur in a short period of time. Human papillomavirus (HPV) and HIV infections are important; they increase the risk of cells degenerating from benign to malignant.
Danger
The disease poses a threat to the health and life of women. If focal keratosis is not detected during the procedure, the consequence is cervical atrophy. The estrogen hormone is reduced, the epithelium is suppressed, the tissue is smoothed out. Atrophic vaginitis is a common phenomenon. Postmenopause is one of the reasons. Often occurs against the background of cancer pathologies. The most recognizable symptoms are intermittent bleeding, as well as vaginal dryness, and a constant urge to urinate.
Cervical atrophy causes infertility and cervicitis, which is characterized by purulent discharge, pain during intercourse and urination. The uterine pharynx and vagina have an inflammatory process that is often neglected. If a couple wants to have a child, then first it is necessary to cure cervicitis, otherwise the child may be born with developmental disabilities.
But the most dangerous is dyskeratosis. Over a short period of time, uncontrolled growth of tumor cells can occur. Human papillomavirus (HPV) and HIV infections are important; they increase the risk of cells degenerating from benign to malignant.
Signs of cervical hyperkeratosis and diagnosis
The anomaly as a whole occurs without any symptoms, almost without manifesting itself. The woman’s condition is satisfactory, so keratosis is diagnosed during a visit to the doctor for a routine medical examination. But still, some signs of leukoplakia exist. If an infectious disease of the reproductive system provokes hyperkeratosis, then the following may occur:
- vaginal itching, burning;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- discomfort and pain during or after sexual intercourse.
During the examination, the female doctor discovers damage to the cervical mucosa in the form of white plaques. A whitish coating is localized in the vaginal part, in the vulva area. Gynecology identifies several forms of this disease:
- flat or simple;
- verrucous or verrucous.
If flat leukoplakia is not treated promptly, the pathology degenerates into a warty form and looks like a lumpy lesion of the white mucosa.
Diagnosis
To determine the type of leukoplakia, a number of examinations are carried out. A biopsy, ultrasound, smear for oncocytology and smear examination for histology will most fully reflect the clinical picture. Elements of hyperkeratosis are atypical cells that can develop progressively and turn into cancer. The treatment strategy directly depends on the identified form.
Causes of the disease
Statistical tables show that the popularity of vaginal keratosis among women is growing.
Factors of pathological mutations are:
- severe and chronic forms of sexually transmitted diseases;
- long-term course of candidiasis in the vagina;
- contraceptives;
- a large number of abortions or births;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- promiscuity;.
- erosion;
- inflammatory diseases, for example, colpitis or vaginitis;
- weak immunity;
- viral diseases.
Treatment
Therapy for keratosis is prescribed individually and depends on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane, localization, and cytology results.
Medication method
Taking medications restores the epithelium and these drugs include:
- pre- and probiotics;
- hormones;
- immunostimulating;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- macro- and microelements, vitamins;
- antibacterial agents;
- antiviral drugs.
Surgical method
But in most cases, the problem is solved by surgical intervention:
- diathermocoagulation – thermal cauterization with electric current;
- chemical coagulation - cauterization with acids: “solkovagin” and “vagotil”;
- electroconization – removal using an electric loop;
- laser therapy – the therapeutic use of laser light;
- radio wave therapy is the most highly effective and minimally painful method, in which removal occurs using an electrode with high-frequency waves;
- knife conization - removal of fragments with a scalpel;
- cryodestruction – exposure of the lesion to extremely low temperatures;
- amputation - an organ is removed.
To avoid scars, young women undergo:
- radiosurgical treatment;
- laser vaporization;
- cryo destruction.
It is very important to eat right during treatment. The rate of vitamin A intake is one of the important conditions: pork and beef liver, cheese, cottage cheese, cream, egg yolk, cod or halibut fish oil, also medical. Beta-keratin is found in carrots, pumpkin, apricots, greens and black currants, and the body independently synthesizes retinol from it. It is necessary to remove hot, spicy, salty foods from the diet. To strengthen the immune system, vitamins contained in vegetables and fruits are necessary. Additionally, sexual rest, abstinence from alcohol and smoking, proper rest, and proper hygienic care are prescribed for 4–8 weeks.
Pregnancy and vaginal hyperkeratosis
A mild degree of leukoplakia does not affect the ability to get pregnant. If the disease has reached a severe stage, then the decision on treatment is made by the doctor individually after examination.
In the case of leukoplakia discovered during pregnancy, there is no need to panic. First of all, you need to take the recommended tests: blood, a smear, a section of the cervix for histology, circicometry, and the abdominal cavity is examined using an ultrasound machine. Keratosis of the cervix is not a reason to terminate a pregnancy. An indication for abortion may be rapidly progressing cancer, and even in this case the week of pregnancy plays a role. Basically, experts insist on continuing the pregnancy. The fetus is regularly monitored for the disease.
Drug treatment is selected depending on the trimester; if therapy is unsuccessful, then surgery occurs after childbirth. If the focus of whitish spots is small, then they can disappear without any drugs or medical procedures, on their own.
Women often get scared when they hear a diagnosis, so they immediately want to read information on the Internet about who had it and how they managed to overcome the disease. A forum where the female sex often finds communication can persistently advise folk remedies.
Hyperkeratosis is no joke. The disease is very serious. To avoid leukoplakia, you need to treat even minor diseases in time, do not expose the internal genital organs to injury (coils, abortions), maintain proper hygiene and do not forget to check with a gynecologist every six months.



