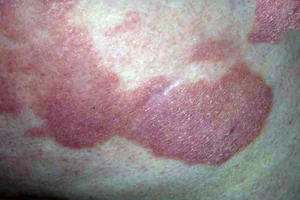
In almost all cases, skin rashes indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the body. If red spots appear on your pubic area, you should consult a doctor. This is due to the fact that rashes in intimate areas often serve as a symptom of various ailments. Less commonly, spots occur for a number of other reasons not associated with diseases. The doctor will conduct diagnostic measures and prescribe treatment based on the research results. The most likely causes of red spots on the pubic area are discussed below (a photo of the rash is presented below).
Ftiriaz
This term refers to a parasitic pathology that belongs to the group of sexually transmitted infections. Another name for the disease is pediculosis pubis.
Typically, lice are spread through close contact with an infected person. The risk group includes the following categories of people:
- Leading a promiscuous lifestyle.
- Adult film actors.
- Homeless.
- Workers of saunas, baths and dry cleaners.
- People who are serving sentences in prison.
- Workers of child care institutions.
- Military personnel who live in barracks.
It is important to know that from the area of primary infection, pubic lice can easily move to the intimate part of the body. As a rule, the pathogen affects the pubis, anus and perineum.
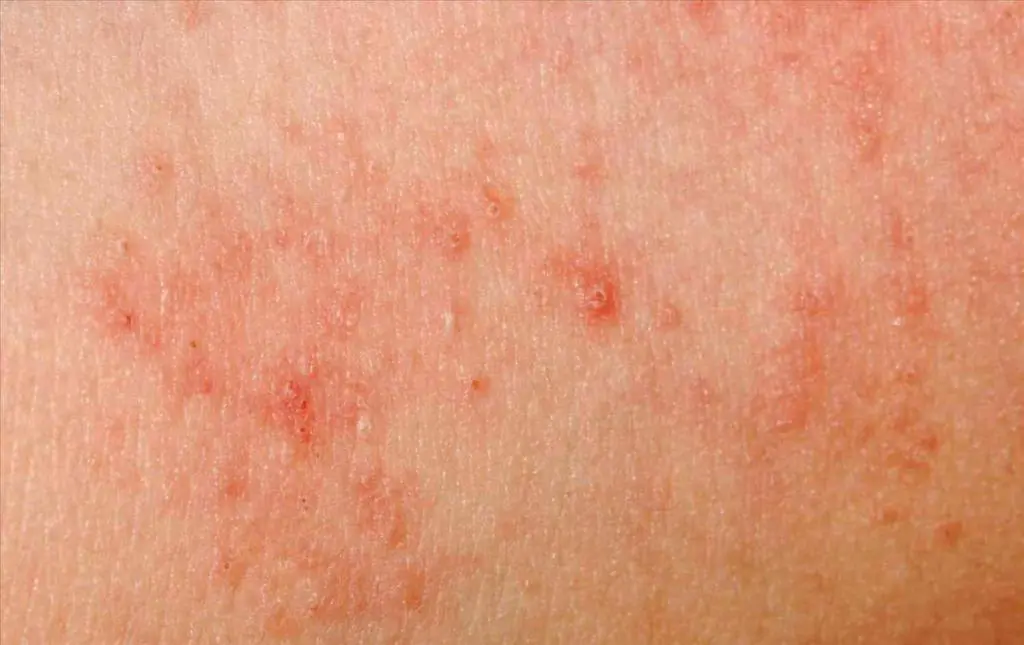
The main symptom of phthiriasis is severe itching. Red spots appear in places where scratching occurs. On the pubic area you can also notice a large number of skin flakes resembling dandruff.
The treatment regimen for lice pubis includes the use of insecticides that destroy lice, preventive measures and treatment of the skin of people who have been in close contact with the patient.
Psoriasis
This term refers to a dermatological disease that significantly worsens a person’s quality of life, especially sexual life.
The disease can develop for the following reasons:
- overstrain (both physical and mental);
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- disruption of the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system.
Genetic predisposition plays an important role.
The disease has specific symptoms. The main symptom is red spots on the pubis, covered with white scales. The boundaries of the rash are clear. In this case, patients are usually not bothered by itching.
With psoriasis in women, red spots on the pubis can be confused with vulvitis. They can also be located on the labia and mucous membrane. In this regard, if rashes appear, you should consult a gynecologist. Only a specialist will be able to carry out differential diagnosis and accurately determine the disease.
In men, spots can be localized not only on the pubis, but also in the folds of the groin and on the penis.
The treatment regimen for psoriasis includes the following points:
- Local application of hormonal ointments and creams.
- Taking antihistamines.
- Physiotherapy.
- A therapeutic diet.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. This means that the disease is not transmitted to a partner through sexual contact.
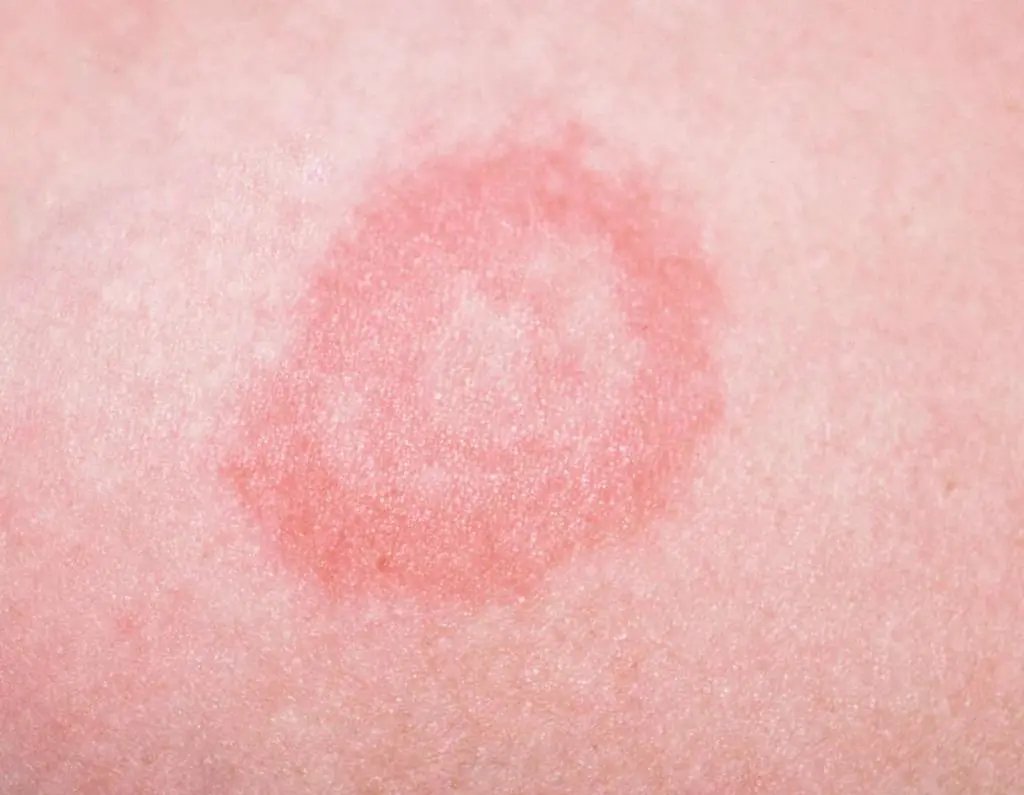
Dermatophytosis
This is a pathology caused by mold fungi. The disease is most often diagnosed in men, women and children; the disease affects very rarely.
The infection is transmitted from animals, infected people and through the soil in which the pathogen lives. In this regard, the risk group includes the following categories of people:
- with a weakened immune system;
- paying insufficient attention to compliance with hygiene rules;
- regularly ride horses;
- agricultural workers;
- frequently using other people's personal items (for example, bath towels).
- Red spots on the pubis. In both men and women, they can be localized in the groin, thighs and buttock folds. The rashes are highly inflamed and symmetrical. The boundaries between them and healthy skin are roller-shaped.
- Pronounced itching and burning.
- Pustules and blisters often form.
To treat the disease, the use and external use of antifungal agents is prescribed. In addition, the skin must be treated with antiseptics. An important step in the treatment of dermatophytosis is regular adherence to hygiene rules.

Scabies
This is a parasitic disease, the causative agent of which can only infect the human body. The scabies mite can move from other parts of the body (from areas of primary infection), gnawing passages in the skin. But at the same time, the genital form of the disease often develops after sexual contact with an infected person.
The first alarming symptoms appear 3 days after infection. Clinical manifestations of the disease:
- Unbearable itching. Its severity increases in the evening and night hours.
- White or gray stripes on the skin are tick burrows.
- Red spots on the pubis, labia, scrotum, glans and foreskin of the penis.
Ignoring the disease leads to the development of complications, which are extremely difficult to get rid of. In this regard, it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor who will select the most effective anti-scabies.

Molluscum contagiosum
This term refers to a pathological condition of a viral nature. Both men, women and children are susceptible to the disease. The pathogen is transmitted not only during intimate intimacy, but also through contact and household contact.
The main sign of the disease is red spots on the pubis, scrotum, labia or penis. The rashes have the shape of a hemisphere. Often, nodules then form, and when pressed, a plug of curdled consistency emerges.
The red spots do not itch or flake, and they are also not painful. The genital form of the disease does not require treatment. In most cases, the rash disappears on its own within 2-3 months after its appearance.
If the spots are located in such a way that they are often injured, your doctor may recommend removing them in one of the following ways:
- curettage;
- cryodestruction;
- husking;
- laser excision;
- electrocoagulation.
Such treatment is carried out only in extreme cases. This is due to the fact that scars remain on the skin after the intervention.

Genital herpes
Carriers of the virus are 90% of the world's population. The pathogen, as a rule, is in a dormant form and is activated only when the body’s defenses are weakened.
Provoking factors are:
- hypothermia or, conversely, overheating;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- venereal diseases;
- avitaminosis.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, a person’s body temperature rises, insomnia bothers them, sleep and appetite are disturbed. Then painful sensations arise in the intimate area and rashes appear. Red spots on the pubic area itch, and a burning sensation is also bothersome. Gradually, bubbles filled with pathological fluid form at the site of the rash. After about 5 days they open, and crusts form in their place.
Treatment of genital herpes involves external use and the use of antiviral medications and immunomodulators. Ignoring the disease leads to complications: damage to the nervous system, blurred vision, and prostate pathologies.

Seborrheic dermatitis
If the red spots on the pubis are peeling, the doctor may suspect this pathology. Externally, the disease manifests itself as plaques, which are covered with scales of different sizes. Inflammations are localized in areas where the sebaceous glands are most developed.
The causative agent is a fungus. The process of its active reproduction is triggered by the following factors:
- Long-term use of certain medications.
- Living or staying for a long time in a region with high humidity.
- Overwork.
- Regular exposure to stressful situations.
- Unbalanced diet.
The treatment regimen for seborrheic dermatitis on the pubis includes taking antifungal drugs, as well as topical use of zinc pyrithione-based products. Additionally, medications of other effects may be prescribed. The choice of remedy depends on the form of seborrheic dermatitis.
Causes not associated with diseases
Most often, rashes on the pubis indicate the development of a pathological process. Less often, they do not cause any harm to the body. For example, sometimes red spots appear on the pubic area after shaving. This occurs due to the formation of small cuts on the skin. In this regard, it is necessary to change the blades in a timely manner. If stains appear after shaving, it is important to treat them with an antiseptic.
In addition, the following conditions may be the causes of rashes:
- Excessive sweating.
- Wearing tight underwear or items made of synthetic materials.
- Allergic reaction to hygiene products.
- Excess weight.
- Insufficient adherence to hygiene rules or their disregard.
If a rash appears on your pubic area, it is important to see a doctor immediately. Only a specialist can determine the cause of red spots on the pubis.

Finally
Any rash in the intimate area causes discomfort. Most often, red spots are a symptom of the development of a disease. To make a diagnosis, you should contact a gynecologist, urologist or dermatovenerologist. The specialist will prescribe a comprehensive examination and, based on its results, will draw up a treatment plan.
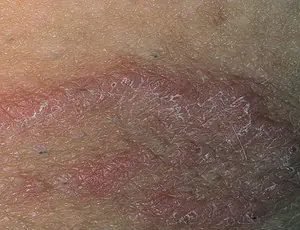
Today, skin fungus is one of the most common infectious diseases. This is caused, first of all, by a significant decrease in immunity and poor awareness of the population about the source of the disease, methods of its spread and preventive measures. Most often, patients seek help from a medical facility already having an advanced form of fungal infection. The fungus affects body folds, skin, internal organs, mucous membranes and nails.
Athlete's inguinal
Men are more likely to get groin fungus. The infection is transmitted contact-household method (through household items and clothing).
Factors that provoke the development of the disease are: diabetes mellitus, obesity, increased sweating, the use of external glucocorticoids for a long time, constant exposure to conditions of high humidity, wearing tight clothing.
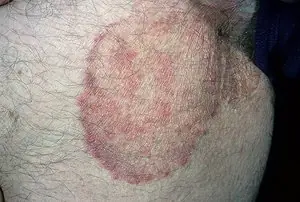
The disease affects the folds under the mammary glands, intergluteal, inguinal, axillary folds, and sometimes the popliteal folds. Inguinal dermatophytosis is characterized by damage not only to the inguinal folds, but also to adjacent areas of the skin and pubis.
Clinic of the disease
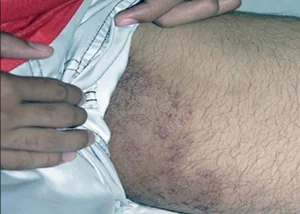
Appear first pinkish-red spots, the size of a coin. The lesion is surrounded at the edges by a small cushion, slightly rising above the level of the skin. Over time, inflammation spreads beyond the skin fold. The inflammatory lesion has wavy or jagged edges. The area of skin surrounding the affected area becomes red, cracks, dryness and peeling appear.
Allergic reaction to antigens Epidermophyton floccosum causes the appearance of vesicles and papules on the affected area. The addition of infection promotes the transformation of vesicles into pustules (vesicles with purulent contents). With a large number of rashes, skin erosion occurs and weeping appears. All this is accompanied by severe itching. Itching may spread to the anus and genitals, but this is extremely rare.
If you find the above signs, you should immediately contact a specialist. The doctor, having examined the patient and familiarized himself with the medical history, will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Treatment of groin fungus
Treatment of the disease must begin immediately after detection, otherwise the fungus will become chronic and it will be more difficult to cure. If the inguinal fungus does not spread to the hair and nails, then you can use external antimycotic preparations that have a fungistatic and fungicidal effect.
The main task of the first group of drugs is to prevent mycotic proliferation, the second group is designed to destroy the fungus itself. In practice, complex action drugs have shown themselves to be effective - Terbinafine and its analogue Termicon, which have antipruritic, drying, fungicidal, fungistatic and antiseptic effects. The drug is available in the form of a spray, which greatly facilitates its use.
In addition, to get rid of the fungus you can do lotions with the following drugs:
- ethacridine;
- furatsilin;
- nitrofungin;
- manganese (potassium permanganate);
- chlorhexidine;
- resorcinol.
In order to heal as quickly as possible, papules can be pierced with a needle yourself, without waiting for an opening.
But (!) take precautions so as not to provoke infection - the puncture site must be treated with fucorcin, brilliant green or iodine.
The following ointments can be used, which are applied to the damaged area of the skin:
sulfuric;- tar and boron-tar;
- ketonazole;
- naftifine;
- lamisil;
- oxiconazole;
- salicylic ointment.
The course of treatment with any antimycotic drug is 7-10 days. Its further use does not make sense, since the fungus gets used to the drug and develops immunity to its active components. Complete cure of a mild, uncomplicated form of the disease occurs in 1.5-2 months.
Treatment of athlete's foot in women
It is worth talking separately about the treatment of inguinal fungus in women. Female athlete's foot often acts not as a separate disease, but has a mixed formTherefore, treatment must cover the disease in all its variations. The affected area must be clean-shaven, since hair in the groin and pubic area prevents the complete destruction of the fungus.
Traditional methods of treating inguinal fungus
To effectively combat a fungal disease, it is recommended to take a shower more often, then thoroughly dry the affected area and apply an astringent-disinfectant to it. Can use the following herbs:
chamomile;- sage;
- series;
- celandine;
- willow and oak bark;
- calendula;
- birch leaves.
Decoctions of these herbs have a powerful antipruritic and drying effect. Lotions are applied to inflamed areas of the skin. Birch tar, which is the basis of tar soap, has a particularly strong healing effect, and is also the main component of ichthyol ointment, Vishnevsky and Wilkinson liniment. It should be noted that during the treatment of a fungal disease, it is best to use tar soap to wash your hands and body.
Natural pure tar, purchased at a pharmacy, can be used as part of a medicinal mixture or as an independent remedy. For example, following one interesting recipe, you need to mix rendered lard and tar in a 50/50 ratio and lubricate the inflamed areas with the resulting composition. Another equally interesting recipe suggests using egg white, castor oil and tar for a compress. All ingredients are mixed in equal quantities and the resulting mixture is applied to the affected skin (preferably at night).
Important. You should not use tar alone, as this can cause an allergic reaction in the inflamed area of the skin, which will further aggravate the situation and slow down treatment.
Traditional methods are only auxiliary treatment, which is used in combination with the main one.
Dark spots in the groin area
Men should not ignore darkening of the skin that appears in their groin. Although this phenomenon at first glance is quite harmless and does not cause any inconvenience, it may be the first sign of the onset of a serious illness.
Causes of spots in the groin folds
Pigment spots that appear in the groin can take on different shapes and shades. In some cases, their appearance is accompanied by swelling and pain. But it also happens that pigmentation occurs completely unnoticed.
There are the following causes of dark spots in the groin area:
- Wearing clothes that are too tight can cause the formation of microtraumas of the skin, and as a result, the appearance of pigment spots in the groin area.
- The appearance of dark spots may be due to professional activities. Men whose occupation involves constant exposure of the body, as a rule, try to remove excess vegetation, thereby damaging the protective layer of the skin. As a result of microtrauma of the epidermis, which is responsible for the production of melanin, pigmentation occurs.
- Liver and gallbladder diseases can also cause discoloration of the skin in the groin area.
- Excessive pigmentation in the inguinal folds may appear with Addison's disease. This is a disease in which the adrenal glands stop producing enough hormones to ensure the normal functioning of the body. As a result, dark spots appear in the groin, armpits and nipples.
- Dense, velvety-to-touch black or dark brown spots may indicate the presence of stomach cancer.
- The appearance of pink pigment spots in the groin folds most often indicates the presence of pityriasis versicolor or a fungal disease. In this case, painful sensations, itching and peeling of the skin occur in the groin. If the disease is not treated, the inflammation spreads to the legs and buttocks.
- Chemical poisoning, usually associated with professional activities in hazardous industries, can also lead to discoloration of the skin in the groin area.
Prevention of dark spots in the groin area
To avoid the appearance of excessive pigmentation in the groin, as well as to stop the spread of existing spots, a man needs follow the following rules:
- When visiting a public bath or sauna, try not to touch shelves and benches with your bare skin.
- Maintain hygiene and keep your body clean.
- Do not use another person's personal items.
- In order to combat excessive sweating, treat the groin area with special preparations.
- Avoid obesity.
- Buy underwear only from natural fabrics, avoid wearing tight synthetic clothing.
- Avoid microtrauma of the skin.
Compliance with these simple rules, of course, cannot prevent organic changes in the body or the appearance of systemic diseases. But by contacting the clinic in time, you can stop development any serious illness at an early stage.
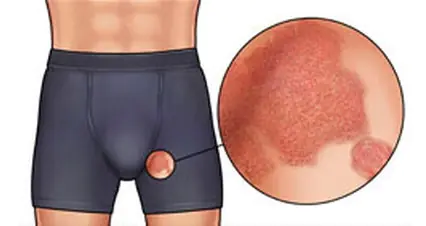
Athlete's groin is a chronic disease caused by a fungus that affects the epidermal layer of skin mainly in the groin area. The main morphological element of pathology is a scaly pink spot with pustular rashes located along the periphery. The lesions itch and cause discomfort to patients. Athlete's groin is a delicate disease that leads to sexual dysfunction, decreased libido and sexual arousal.
The disease affects men more often than women. In children and adolescents, the pathology develops extremely rarely. The spread of fungal infection occurs through household contact through direct contact, through household items, personal hygiene products, and cosmetics. With a decrease in the general resistance of the body, a primary focus is formed at the site of entry of the pathogen, which gradually grows along the periphery and spreads to healthy skin. The main location of the fungus is the inguinal folds. In more rare cases, the disease can affect the skin of the buttocks, scrotum, perineum, penis, inner thigh, and pubic area. In women, the skin under the mammary glands, in the armpit and popliteal fossa often becomes inflamed.
Fungi of the genus Epidermophyton floccosum settle in the epidermis of the skin, destroy and utilize collagen, which leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the skin. Microorganisms have a low degree of pathogenicity, therefore the disease rarely develops in healthy people with complete immune protection.
The diagnosis of pathology is made after microscopic detection of fungal mycelium in scrapings from the surface of spots and obtaining the results of bacteriological examination of biomaterial from patients.
Groin fungus requires a patient and careful approach. Causal treatment involves the use of antimycotic drugs that can completely cure the disease.
Etiology
Athlete's foot is a dermatomycosis caused by the fungus Epidermophyton floccosum. This is an anthropophile that grows and develops only on the human body. It is located in the scales of the epidermis and nail plates. Under a microscope, fungal spores and well-branched mycelium are determined in skin scrapings. After isolating a pure culture, the mycelium becomes yellow and the spores look larger.
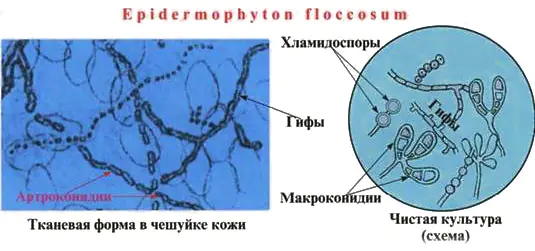
Fungi are resistant to environmental factors. They grow and develop quickly at high humidity and temperature.
The infection spreads through contact and household contact through contaminated household items, as well as through touching and shaking hands. For rapid growth and development of fungi, moisture is necessary. Excessive sweating in a patient significantly increases the risk of infection.
In medical, preventive and public institutions, neglect of sanitary norms and rules can provoke an entire epidemic of mycosis.
Factors contributing to infection:
- Hyperhidrosis,
- Stress,
- Skin microtraumas
- Tight clothes,
- Obesity,
- Failure to comply with sanitary rules and regulations,
- Decreased immunity
- Hormonal disbalance,
- Metabolic disorders.
Symptoms
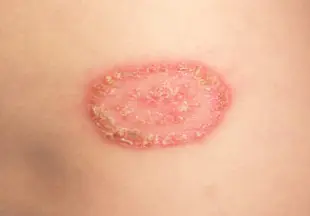
single spot of athlete's foot
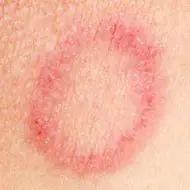
With inguinal athlete's foot, pink or red-brown spots appear on the skin, having a round shape and a diameter of no more than one centimeter. The spots are located symmetrically, itch, peel and gradually grow. Along the periphery of the spot on hyperemic and edematous skin, multiple blisters, pustules, suppurations, crusts and small flaky inclusions appear. Foci of inflammation are limited to an edematous ridge. Plaques can merge with each other, forming a single erythematous area that spreads to surrounding tissues. Itching and burning are especially felt when walking, squatting and while bathing.
As the inflammatory process subsides, the central part of the spot becomes clear, pale and slightly sunken. This gives foci of epidermophytosis a special appearance of rings and is a pathognomonic sign of pathology. Fungus in the groin in men itches and burns, and severe discomfort occurs when walking. The areas are painful to the touch. Vesicles and pustules can burst, forming erosions and ulcers. When a secondary bacterial infection occurs, severe complications develop.
Photo: inguinal athlete's foot in men and women
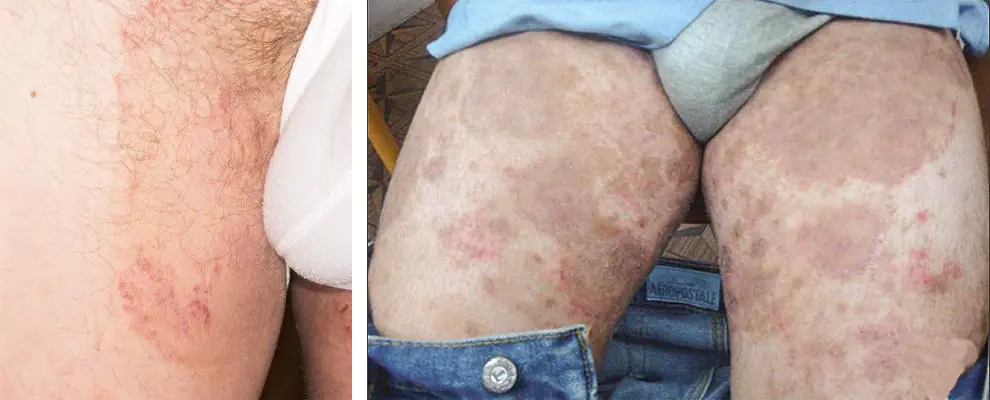
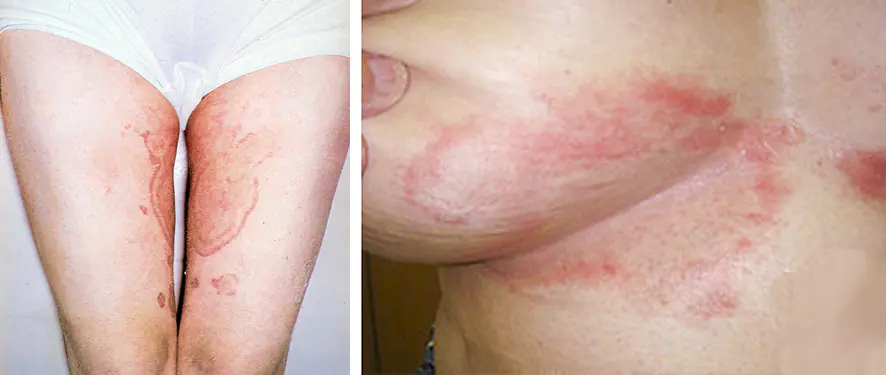
Additional symptoms of athlete's foot include swelling of the groin area, hyperemia of nearby skin, and the appearance of specific blisters with turbid serous fluid. With epidermophytosis, not inflammatory, but allergic rashes - epidermophytide - may appear on the skin. They are located symmetrically, do not contain fungi and disappear on their own after undergoing antimycotic treatment.
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the disease can last for years. Athlete's disease is characterized by an acute or subacute course with pronounced signs of inflammation. The disease quickly becomes chronic and takes on a wave-like course, during which periods of remission are replaced by exacerbations, forming from time to time new foci of skin lesions. Even after complete recovery, the disease can recur.
Constant stress, friction in the affected area and hyperhidrosis complicate the course of the pathology.
Stages of the disease
- The initial stage is characterized by increased proliferation of the fungus in the epidermis and the appearance of pink spots with papules and vesicles on the skin.
- Clinical signs of the acute stage are weeping spots that grow, itch and are replaced by rings with scalloped edges.
- Chronic stage - lesions on the skin periodically lighten, and then become inflamed again under the influence of unfavorable factors.
- The advanced stage develops with a complicated course of the pathology. If left untreated, large blisters appear on the skin, which become infected when damaged. The blisters are opened, necrotic tissue is removed and the wound is treated.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis and treatment of fungus in the groin area is carried out by dermatologists and mycologists. After collecting a history of the disease and listening to the patient’s complaints, they begin an external examination of the lesion and laboratory research methods. In some cases, consultation with an infectious disease specialist, venereologist, or immunologist may be required.
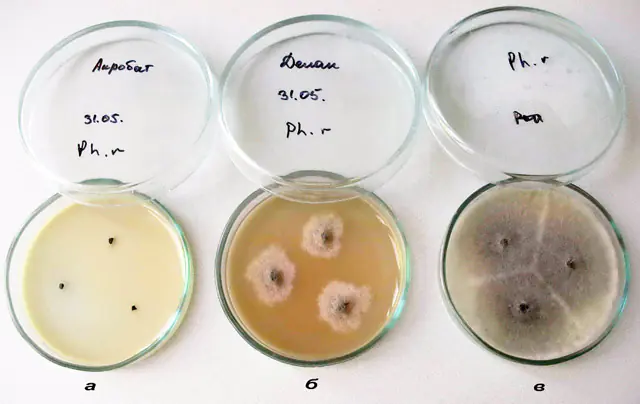
To confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a microscopic and bacteriological examination of the scraping from lesions to pathogenic fungi. To do this, prepare a smear for microscopy and inoculate the test material on Sabouraud’s selective medium. The crops are incubated in a cooling thermostat at 22 degrees for 5 days. Saburo produces cream or yellow colonies with a round shape and fluffy consistency. Microscopy reveals septate branching short mycelium and chains of rectangular spores.
Examination under a Wood's lamp will help exclude other diseases with a similar clinical picture.
Treatment
Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot is predominantly etiotropic. Since the disease is fungal, it is necessary to start taking antifungal agents. Currently, the pharmaceutical industry produces a large number of effective ointments and creams. Modern antifungal drugs - Lamisil, Mycoseptin, Clotrimazole. You can use Nystatin, Ciclopirox, Ketoconazole, Oxiconazole, Econazole. Complex ointments with an antifungal component and glucocorticosteroids are used in especially advanced cases. They have a pronounced antipruritic, fungicidal, drying and antiseptic effect.

Treatment of inguinal fungus is carried out in the acute period, when the patient suffers from itching and burning. They come to the rescue antihistamines, which eliminate irritation and discomfort in the groin - “Cetrin”, “Zyrtec”, “Zodak”, “Diazolin”.
After eliminating the symptoms of inflammation, the foci of epidermophytosis are treated with a Fukortsin solution, which has a fungicidal and antimicrobial effect. Patients are prescribed lotions with Resorcinol, sulfur-tar, Wilkinson and zinc ointments, Triderm. A silver solution will help cope with inflammation and serous blisters. Local preparations are applied to inflamed areas 2 times a day. If the blisters reach large sizes, they are opened with sterile instruments. Fungus in the groin should be treated for a long time, until the symptoms disappear completely.
During illness, the patient's immunity is greatly reduced. To strengthen it, it is recommended to use mild immunostimulants – “Immunal”, “Imunorix”, “Licopid”. Complications of bacterial origin require treatment with antibiotics.
In the presence of extensive lesions, desensitizing therapy, antibiotic therapy, vitamin therapy, and autohemotherapy are carried out in a hospital setting.
If personal hygiene is not observed, drug treatment does not give a positive result. Patients need:
- Wash daily, paying special attention to the treatment of skin folds;
- Take baths with infusions of medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects;
- Wear loose underwear made from natural fabrics.
ethnoscience
Currently, there are a large number of traditional medicine recipes intended for the treatment of inguinal epidermophytosis at home.

Infusion of St. John's wort, chamomile and lingonberry leaves is taken 100 ml daily for a month.- Lotions made from a decoction of string, yarrow, and oak bark give good results. After the procedure, zinc ointment is applied to the skin.
- Radish seed pulp is applied to the affected areas of the skin.
- An alcohol tincture of poplar and birch buds is used to treat inflamed areas.
- Crushed celandine is applied to the lesions of inguinal athlete's foot for half an hour.
- Onion gruel helps get rid of pathology.
- A thick paste is prepared from soda, which is rubbed onto the affected skin.
- Ointment with essential oils is rubbed into the affected areas daily.
- Almond essence will help cure athlete's foot in the groin.
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid the appearance of fungus in the groin:
- Disinfection of patient care items and common areas,
- Boiling and ironing linen, socks, shoe treatment,
- Use of removable shoes in baths and saunas - slates or rubber slippers,
- Fighting sweating
- Regular hygiene procedures,
- Wearing underwear made from natural fabrics in hot weather,
- Daily treatment of skin folds with cologne, salicylic alcohol, resorcinol and powdering them,
- Examination of contact persons,
- Prevention of stress,
- Strengthening the immune system.
Without adequate treatment, the spots will not disappear, and the disease will only progress. At the first symptoms of inguinal athlete's foot, you should consult a specialist. Pathogenic fungi and foci of epidermophytosis on the skin grow rapidly.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable. Acute and chronic stages of inguinal athlete's foot respond well to therapy. Modern antimycotic drugs can prevent relapse and re-infection.



