What it is?
Acne is a skin pathology expressed in the appearance of a specific rash on the face or other parts of the body. 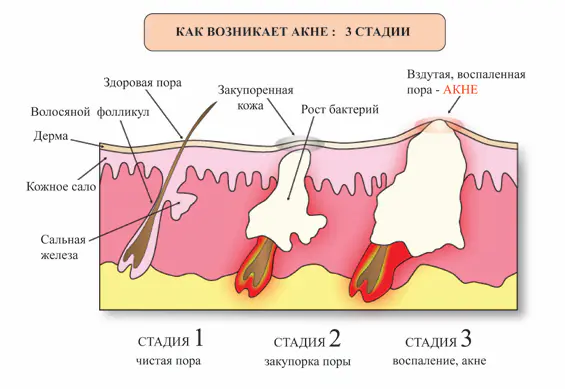
Acne appears externally rashes, they come in several types:
- acne blackheads, visible when examining the pores;
- acne-like whiteheads, small bumps above the surface of the skin;
- papules, small inflamed areas of skin, without accumulation of exudate inside;
- pustules, hollow formations with liquid contents inside them (clear or purulent effusion);
- nodes, dense subcutaneous lumps;
- cysts, areas with clear boundaries, inside which a large amount of pus accumulates.
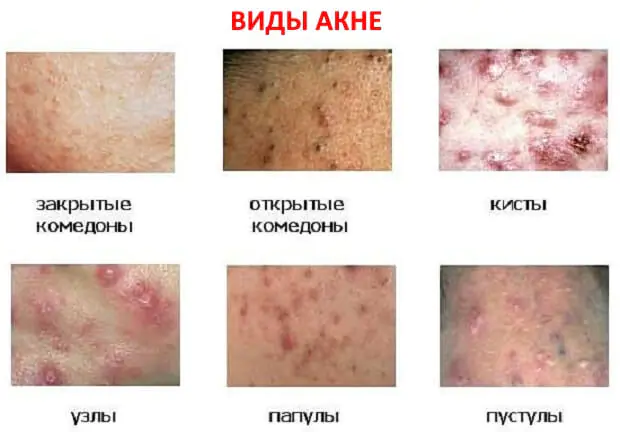
Photos of types of acne rashes
Since the disease is characterized by a wide variety of skin rashes (often a combination of them), methods of its treatment are selected individually by a dermatologist. How to treat acne correctly depends on the type, prevalence and course of the disease.
For some forms of the disease, it will be enough to properly organize daily skin care activities and select suitable products for facial and body hygiene; for others, intensive antibacterial treatment, selection of medications to resolve scar changes and improve the nutrition of the epidermis may be necessary.
ICD-10 code
Medical science has systematized the types of acne. The International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10) combines it into a separate group of skin diseases with the code - L70.0–9.
Scientists explain what it is in people and reveal clinical features every type of disease:
1. Acne ordinary. Most often it affects teenagers and young men, localizing on the face in the area of the wings of the nose, cheeks and chin.
2. Globular acne. The disease manifests itself in young men in the form of formations on the skin that resemble cherries. Inside, these cysts are filled with pus; when they are torn, the walls of the cysts fall off and stick together, and as the wounds heal, scars form.
3. Smallpox acne. It is characterized by the formation of numerous, centrally necrotic, bright pink (red or purple) nodules. Most often, the disease is found in people over 40-45 years of age.
4. Tropical acne. It affects travelers (lovers of hot countries), manifests itself as widespread and isolated acne throughout the body (back, abdomen, chest), the rash can go away without treatment or fester.
5. Baby acne. Formed, as a rule, due to metabolic disorders in children, it is characterized by the formation of small papules or pustules, very similar to an allergic rash.
Causes
The pathogenesis (emergence and development) of the disease occurs in several stages:
- increased production of sebum by the glands due to the active work of the adrenal glands, releasing a large amount of androgens (male sex hormones) into the blood;
- accumulation of desquamated (dead) cells in the skin lumens (epithelial keratosis) and clogging of pores;
- inflammation of the affected areas and the formation of acne vulgaris;
- suppuration of the rash;
- rupture of abscesses and scar formation.
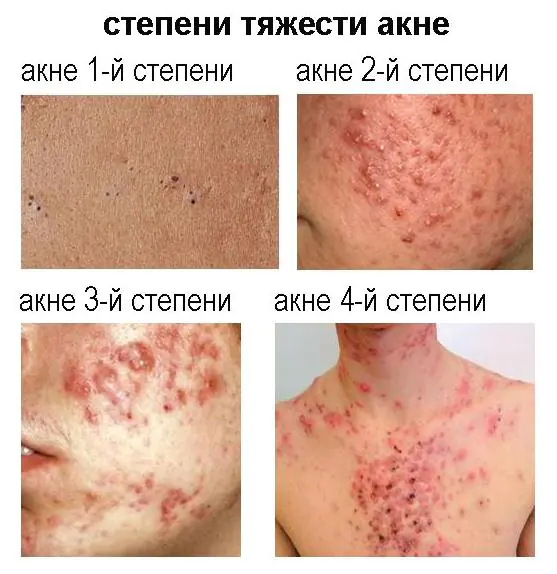
Sometimes incompetence and impatience lead to the fact that patients themselves introduce an infection to the skin and the disease goes from a mild form to a complicated one.
Factors that provoke the development of this pathology include:
- changes in hormonal levels in the body (during puberty, menopause, infancy, pregnancy, endocrine pathologies, metabolic diseases);
- excess corticosteroids in people with long-term treatment with hormones or systematic use of drugs that stimulate muscle growth (steroids);
- disorders of the digestive system (diseases of the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas);
- severe emotional distress or chronic stress;
- thermoregulation disorders;
- skin pathologies of bacterial or fungal origin;
- hereditary predisposition;
- poor hygienic skin care.
Newborn acne
The appearance of acne in children always worries parents.
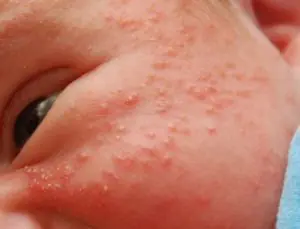
Newborn acne: photos
Often mothers blame themselves for eating disorders and eating sweet or fatty foods. Therefore, in the heat of the moment, mistakes can be made in caring for a child; their skin begins to be lubricated with baby creams and powders are often used. But acne is caused by clogged pores, so all these procedures only increase the formation of the rash. If acne in a child does not fester, it is not a pathology.
Video (about acne in infants – see from 12:20):

What should parents do if they see acne in their child:
- consult a doctor;
- keep the child clean.
This is quite enough to give the newborn time to adapt to new living conditions; acne in these cases goes away on its own, without taking medications.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease is carried out according to a general scheme, mostly using local remedies. Sometimes specialized means are used to normalize hormonal levels; in case of suppuration, a course of antibiotics is prescribed; in the presence of residual pigmentation and scars, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and biostimulants is necessary.
General strengthening and hygienic treatment methods are actively used in acne therapy.:
1. Shower daily using neutral detergents. Cleanses the skin of excess sebum and dead cells.
2. Gymnastics classes. Normalizes peripheral blood circulation and delivery of nutrients to epidermal cells.
3. Facial massage. Allows you to improve lymphatic drainage and reduce the manifestations of inflammatory reactions. It is not performed during purulent processes (due to the risk of infection spreading into the deeper layers of the skin).
4. Walks, hiking trips at the place of residence. These activities enrich the body with oxygen and strengthen the human immune system.
It is important to remember that during treatment for acne it is undesirable:
- abuse cosmetics, do home and salon skin peeling;
- take a long steam bath, sunbathe;
- use fatty creams for face and body care.
Drugs
1. Benzoyl derivatives (Oxygel, Baziron-gel, Proderm-cream, etc.). Bactericidal agents that inhibit the growth of microorganisms in hair follicles.
2. Salicylates (Clerasil, Delax acne gel). Lotions, gels, and ointments based on them can dissolve plugs in pores (blackheads) and disinfect the skin.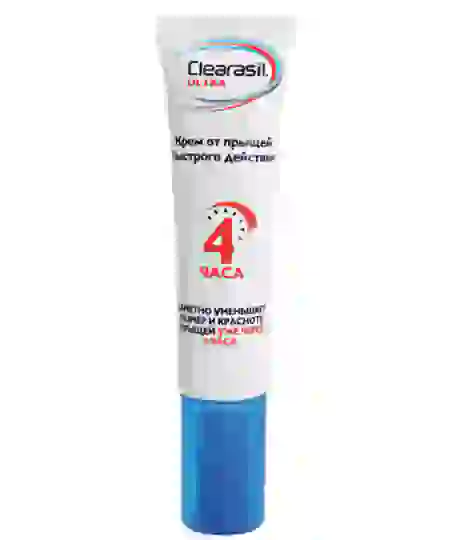
3. Retinoid products (containing vitamin A). Airol, Zorak, Klenzit and other drugs are excellent prevention of the formation of blackheads and a medicine that helps to destroy them.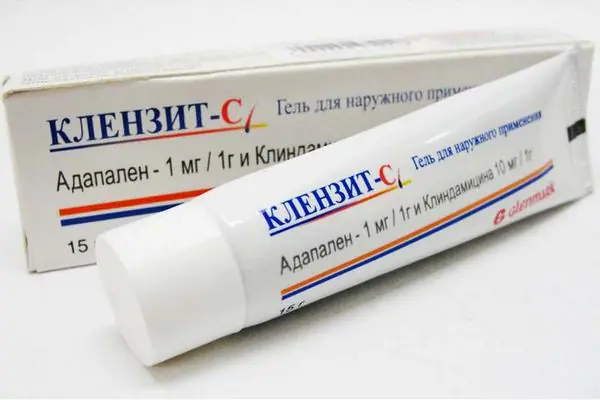
4. Azelaines (Azogel, Skinoren, Acne-derma). Products based on them help to quickly cleanse the skin of keratinized scales and destroy pathogenic flora on the skin.
5. Sulfur ointment. Used to reduce redness and swelling of acne.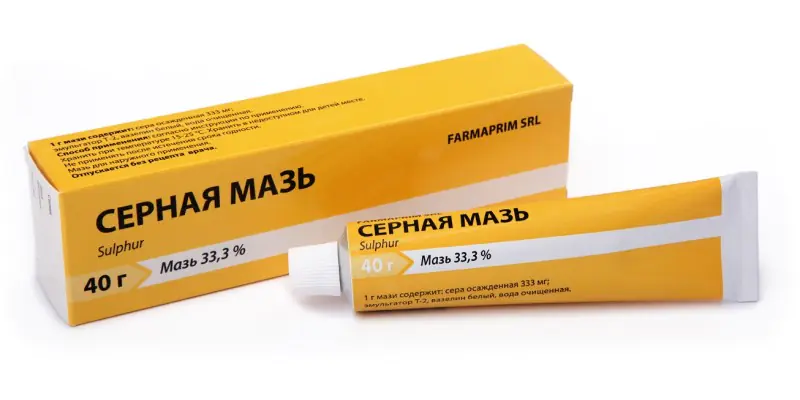
6. Antibacterial agents (Klindovit, Zinerit, Dalatsin), drugs that destroy pathogens of skin infections. Creams and gels containing them are widely used.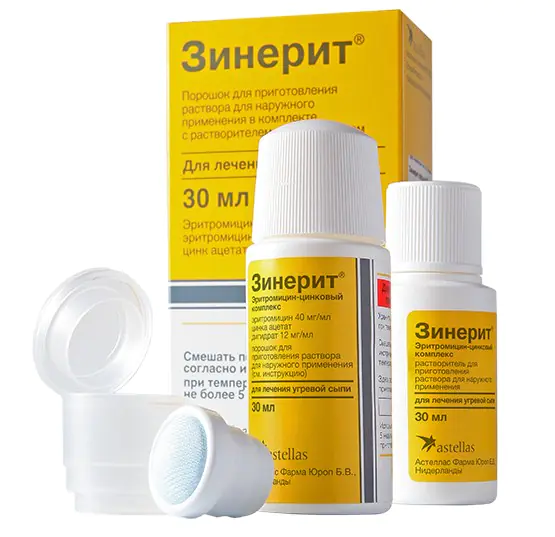 
Antibiotic ointments for acne are rarely used due to their heavy texture, and oral tablets are prescribed for generalized (extensive) purulent process or cyst formation.
Laser treatment
Laser treatment is an effective additional method to drug therapy for acne; patient reviews of it are mostly positive. In addition to affecting papules and pustules, pimples and blackheads, this method allows you to get rid of the consequences of suppuration and scarring.
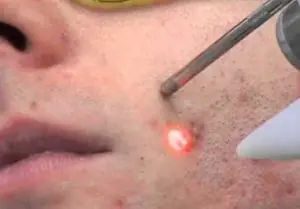
Anti-acne (laser acne removal): photo
Procedure Anti-acne used by dermatologists for more than 30 years, it is based on laser penetration into the deep layers of the skin, while creams and ointments act superficially. The radiation, which patients experience as a slight tingling sensation and a feeling of warmth, kills bacteria, cleanses pores, and stimulates the regeneration processes of epidermal cells. Laser sessions of 15-20 minutes are carried out 2 to 6 times, with an interval between them of 3-4 weeks. The treatment is practically painless (a slight burning sensation is felt upon contact with the laser beam), and in the areas of exposure, after the procedure there remains slight redness and swelling, which disappear within a few days.
Diet
Without changing your usual diet, pimples and blackheads on the face are difficult to cure at home.
All therapeutic efforts and the use of advanced methods may not be effective if you do not limit a number of foods in your diet that stimulate the sebaceous and sweat glands.
Therefore, with acne it is important:
- give up sweet, spicy, hot, salty, smoked, fatty, fried foods or consume such foods in minimal quantities;
- do not abuse alcohol and carbonated drinks;
- It is good to include in your diet seafood rich in omega-3 acids, vegetables, herbs and fruits containing vitamins A, E, B;
- it is necessary to maintain an increased water regime, drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day (to enhance the removal of unnecessary substances).
- red fish;
- squid;
- seaweed;
- lean beef;
- oranges, carrots, mangoes, spinach, celery, tomatoes.
- sandwiches, hot dogs, burgers, french fries;
- beer, liqueurs, champagne;
- chocolate, cocoa, coffee, baked goods.
There is no single and complete classification of acne (acne). This is a multifaceted problem, both in terms of the reasons for its occurrence, the mechanism of its development, and the individual characteristics of each person.
At the same time, on the Internet you can find many words that people use to call this kind of rash: in addition to the term “pimples”, such words as “acne”, “blackheads”, “acne”, “comedones” are widely used. What is hidden under all these names, we will try to understand in this article.
What are comedones, pimples, acne
As noted above, there are several names by which we call rashes on the face and body. The common term “acne” is a collective term for inflammatory diseases of the sebaceous glands; it is simply most often used to refer to pimples and blackheads.
If I may say so, in most cases it all starts with comedones – when the mouth of the hair follicle becomes blocked with dead epithelial cells mixed with sebum, a plug is formed. It is called “comedone”.
If this element becomes inflamed (infected), papules (nodules) or pustules (pustules) form.
When the pus comes out, we see pimples (acne). After healing of very large ulcers, scars may remain.
Pimples and blackheads are common manifestations of acne and are characterized by inflammation of the sebaceous glands.
Nature of manifestation
According to the nature of the manifestation, rashes on the face and body can be divided into:
- non-inflammatory manifestations;
- inflammatory manifestations;
- dermatoses with acneiform rashes.
These include black and whiteheads (comedones).
Blackheads also called blackheads, open comedones. These blackheads form when a blockage of dead epidermal cells and sebum occurs at the top of the pore.
At first, this plug is white in color and has a certain transparency, but over time the lard begins to harden, forming a white or yellow dense lump. Under the influence of oxygen, the sebum in the open pore oxidizes and a black head (blackhead) appears.
Whiteheads also called wen, whiteheads, closed comedones, microcysts, milia. These blackheads form when a congestion of dead epidermal cells and sebum forms deep under the skin, that is, at the bottom of the pore. The ducts of the sebaceous glands expand and a wen (cystic thrombus) is formed, consisting of sebum, which has no way to reach the surface.
Some closed comedones clearly rise above the surface of the skin, others can be felt with your fingers and look like small tubercles. They are best visible when the skin is stretched. These white nodules can vary in size. Elements similar in size to millet grains are called milia, and people call them “millet grains.”
As we noted above, when a comedone gets infected, it becomes inflamed, forming papules or pustules.
Papule looks like a nodule that has clear boundaries and usually rises slightly above the surface of the skin. The diameter of papules can be from 1 mm to 3 cm. According to the Western classification, elements with a diameter of more than 1 cm are called “nodes”.
This type of inflammatory acne is usually red in color (shades ranging from bright red to purple) and is accompanied by swelling of the area of the surrounding skin. When you press on the papule, its color becomes paler. Unlike a pustule, there is no white pustule in it.
As a rule, the formation of papules occurs from closed comedones. In the case of formation from open elements, we can observe on the surface of the papule an expanded mouth of the hair follicle and a dark-colored plug.
Pustule is an acute inflammatory element containing purulent contents. The cause of pustules is a purulent process in the skin.
Pustules can form either on their own or from papules when pathogenic microflora develops there. The size of the pustule is from 1 mm to 1 cm. The shape is a hemisphere, cone or flat formation. The contained pus forms a loose head on the surface of the skin (sometimes it can burst), along the edges of which the skin is red and inflamed.
The pus contained inside may be white, yellow, grayish or greenish. If the color is yellow or green, it can be said that a secondary infection has occurred.
Rosacea
With such rashes there are no comedones. The acneiform group includes a large number of dermatoses: from rosacea And rosacea, which many people have heard of, to perioral dermatitis, skin tuberculosis, small nodular sarcoidosis of the face. This also includes drug rash.
In the case of acneiform rashes, the pilosebaceous follicle becomes inflamed first. For diagnostic purposes, it is necessary to distinguish such dermatoses from acne.
Acne: classification of acne
Very often, acne is called “acne” or “acne vulgaris” in various sources, but these are not synonyms. As mentioned above, the term “acne” refers to a particular manifestation of the disease – external rashes on the skin. However, the entire clinical picture of the disease is not reflected.
Acne can develop for various reasons and, depending on the age of the patient, has its own characteristic features. According to the most common classification proposed by scientists Plewig and Kligman, the following acne is distinguished:
- children's;
- youthful;
- adults;
- caused by mechanical factors;
- exogenous.
Childhood acne
Such manifestations, in turn, are divided into acne:
- newborns. This is a borderline physiological state of this period, caused by a sexual (hormonal) crisis. Other manifestations of this: an increase in size and pain (engorgement) of the mammary glands, hydrocele, physiological vulvovaginitis. The reason is the effect of maternal hormones that the fetus received during the prenatal period. Acne in newborns is a closed comedones in the form of white or yellowish papules. Places of rashes: nose, cheeks, chin, forehead. Such rashes, as a rule, disappear on their own within one and a half to two weeks;
- children. Manifestations between the ages of 3 and 6 months are considered childhood. Moreover, such acne can provoke severe, protracted forms of acne. The cause may be acute congenital pathologies such as hyperplasia (pathological tissue growth) or adrenal tumors. To identify the cause, the child must be carefully examined.
Juvenile acne
According to statistics, 1/3 of teenagers face this problem. Girls - more often than boys. In the vast majority of cases (up to 75%), the face is affected, in the remaining cases (15%) - the face and back. Typically, juvenile acne goes away by age 18–20. However, in some cases the disease is long-term, sometimes up to 40–60 years. This physiological acne is considered adult acne.
Among juvenile acne there are:
Comedones
- comedones. What are comedones, you can read above. We only note that when they are weakly expressed, they are considered a physiological norm. As for acne, its initial manifestation is microcomedones, which do not manifest themselves clinically. Then comes the formation of closed comedones, in which inflammation is not expressed, but there are conditions favorable for this. As a result of further accumulation of sebum in them, nodules are formed and closed comedones are transformed into open ones (blackheads);
- nodular cystic acne. With this form of acne, purulent cystic cavities and infiltrates form deep in the dermis. Then they merge, forming conglomerates of inflammation. The healing of such acne is always accompanied by scars. As a rule, nodular cystic elements are a long-term, long-term problem, even if the process is of moderate severity;
Nodular cystic acne
- lightning acne. They are the rarest and at the same time the most clinically severe form of acne. Typically, such acne develops in adolescents aged 13 to 18 years who have nodular cystic or papulopustular acne. Acne fulminans appear suddenly in the form of ulcerative-necrotic areas on the body, with a constant increase in intoxication symptoms (increased body temperature above 38 degrees, pain in muscles and joints, abdominal pain, anorexia, etc.). In its course, such acne is close to the gangrenous form of pyoderma (purulent skin lesions). The reasons are not fully understood. Most often, people with such acne have severe damage to the digestive system, and fulminant manifestations can also be caused by taking certain medications. Places of fulminant acne are the torso and upper limbs. After healing, scars are formed, including keloids (for more information about keloids and other types of scars, read “Removing scars on the face”);
Papulopustular acne
- papulopustular acne. Most often they are formed due to the attachment of the inflammatory process to open or closed comedones. The papules (nodules) or pustules (pustules) already described above form. The mild form of such acne usually heals without a trace, but if the deep dermal layers are involved in the process and the structure of these acne is damaged, scars may remain after healing.
The most common comedones and acne are in the form of papules or pustules. Other forms are less common and require more complex treatment.
Adult acne
If acne persists into adulthood, it is referred to as the adult form. This problem occurs between 3 and 5% of people aged 40–50 years. Often they are a “recurrence” of juvenile acne.
Among them are:
- late acne. Most often found in women, in 20% of cases - before the menstrual cycle. In this case, they disappear on their own at the end of menstruation. But late acne can also have a permanent “registration”, usually in the form of papules, pustules or nodules. The most likely causes are polycystic ovary syndrome with complications such as hirsutism (excessive growth of dark hair on the face and body) and anovulatory menstrual cycle (lack of ovulation). If such acne occurs, you must be thoroughly examined by a gynecologist, as well as adhere to a certain diet, which you can read about here:
Acne conglobata
- globular or clustered comedones. Acne conglobata is one of the most severe forms of acne. Men suffer from it due to severe seborrhea. Externally, these are numerous nodular cystic elements and large comedones, which can be located not only where seborrhea is, but also in other places. As these acne heal, they form scars. Occurring in adolescence, they persist, as a rule, up to 40 years or even more;
- acne inversa. The reason is the secondary involvement in the inflammatory process of the sweat glands of the armpits, perineum, navel, pubis, etc. Predisposing factors are high body weight, scratching areas and wearing tight clothing. Externally, inverse acne looks like tubercles filled with pus or purulent-bloody contents. Then they merge into conglomerates. As they heal, they form fistulas and scars. Inverse acne is characterized by a chronic nature and frequent relapses;
Pyodermatitis
- skin pyodermatitis. Many experts consider pyodermitis to be a manifestation of rosacea (dermatosis with acneiform rashes), and not acne. Most often, pyodermatitis affects women aged 20 to 40 years. First, persistent erythrema (severe redness) appears on the face, and then rashes rapidly form in the form of papules, pustules and nodules. Then these phenomena merge into purulent conglomerates. The rashes are localized mainly on the face, heal slowly - within a year or even more;
- bodybuilding acne. The main reason is the use of androgens or anabolic steroids. Against the background of developing hyperandrogenism, sebum production increases. Long-term use of glucocorticoids can also lead to this effect. Since cocktails with B vitamins are often taken along with steroids, this leads to the formation of nodular cystic acne. To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude the presence of endocrine disorders.
Acne caused by mechanical factors
Such acne is a consequence of mechanical blockage of the ducts due to pressure or friction. For example, they can occur due to a tight headdress, excessive sweating, wearing a cast, etc.
Read about methods to get rid of excessive sweating:
Treatment of hyperhidrosis
Exogenous acne
This could be acne:
- toxic (professional)that appear in people due to contact with chemical compounds (chlorine, lubricating oils, etc.);
- cosmeticresulting from excessive or improper use of cosmetics (creams, masks, etc.);
- from detergents, as a result of exposure to detergents;
- sunny, in the form of acne due to the hot and humid climate.©
Acne treatment
Treatment directly depends on the type of rash and the severity of the process. In the treatment of acne, both various medications for oral administration and superficial agents (lotions, ointments, etc.) can be used. There are also special cosmetic procedures, for example:
- mesotherapy, ozone therapy, darsonval, ozokerite therapy, magnetotherapy, phototherapy, ultraphonophoresis, naphthalene therapy, carboxytherapy, plasma lifting, etc.;
- peelings: acid, chemical, microdermabrasion (diamond), ultrasonic, gas-liquid;
- cleaning: ultrasonic, manual, laser, non-hardware instrumental, liquid nitrogen;
- massages: pinch massage according to Jacquet, ultrasound, cryomassage;
- masks: clay, thermoplastic;
- colon hydrotherapy (enemas);
- baths: iodine-bromine, subaqueous intestinal.
August 28, 2017 at 03:18 pm
I don’t know about such a serious disease, as shown in the picture, but the Clearvin complex (lotion and cream) helps well with youthful pimples. Cleanses and nourishes the skin well. Natural composition and affordable price. I've been using it for several months now and really like it.
October 9, 2017 at 12:14 pm
Based on personal experience, I came to the conclusion that you can get rid of acne, but it takes some effort. Firstly, watch your diet, and secondly, take proper care of your skin and avoid stress. I am currently using Elon ointment with essential oils and seeing great results. The face is clean, and the skin is no longer as oily as before.
July 8, 2018 at 10:45 pm
All you need to do is go to a dermatologist. Oral antibiotics, antibiotic gel for washing the face, antibiotic cream and then cleansing.
The main thing is to wash your face regularly, at least twice a day.
Acne on the face (4 types) – TOP treatment methods
Facial acne or acne is a disease of the pilosebaceous structures of the skin, which is based on blockage and inflammation of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle.
There are several types of these rashes: milia (nodular, white, with clear boundaries), comedones (black), pustules and subcutaneous cysts (inflamed red, with purulent contents), papules (nodular rash without a white purulent dot).
Etiology and pathogenesis (11 reasons)
The causes of acne on the face are varied. An important role in the occurrence of the problem is played by:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal changes;
- endocrine disorders;
- contact with chemicals;
- excessive pressure or friction (eg, tight headgear);
- errors in nutrition;
- using inappropriate cosmetics;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- skin damage and infection;
- insufficient hygiene;
- taking hormonal drugs.
Increased sebum secretion is a prerequisite for the proliferation of bacterial infections, the development of inflammation and acne.
Acne is accompanied by increased keratinization of the epithelium in the hair follicles. When the horny scales do not have time to peel off, the ducts of the sebaceous gland become clogged and the release of its secretion to the outside is disrupted.
As a result, sebum and dead cells accumulate at the mouth of the hair follicle, clog the pore and form a blackhead.
Further, the process worsens, the amount of secretion that does not come out increases, which leads to the expansion of the hair follicle, pores, and atrophic processes in the sebaceous gland.
Favorable microflora for pathogenic microorganisms is formed inside. The reproduction and release of waste products of bacterial agents irritate the tissues, causing local inflammation.
Age range of the disease (3 categories)
Acne occurs at almost any age: from birth to old age. Previously, this problem was considered a teenage problem, but today it can be a concern regardless of a person’s age and gender.
Based on this, pathology is classified into the following categories:
- Baby acne (3-6 months). They arise against the background of the action of maternal hormones that were obtained during intrauterine development. Less commonly, they occur against the background of congenital diseases (for example, adrenal tumors). Features: closed, often located on the forehead, nose, chin, look like white or yellowish papules (milia), disappear on their own.
- Juvenile acne (12-17 years old). They occur more often against the background of hormonal changes. With properly selected skincare cosmetics and cosmetic procedures, they disappear on their own by the age of 20.
- Acne in adults. This category includes rashes that occur even at 40-50 years of age. May bother men and women. The causes and treatment methods for facial acne are varied.
The problem can arise in adulthood due to hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, breastfeeding, menopause, taking hormonal contraceptives, abortion, etc.). In this case, acne disappears on its own after hormonal levels normalize.
If late acne is constantly present, then perhaps the problem lies in a disruption of the urinary and/or reproductive systems (for example, ovarian cysts, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs), infectious parasites, poor diet, long-term use of potent medications, etc.
For therapy to be effective, the cause of the problem must first be identified and eliminated.
Symptoms of different types of acne
There are different types of acne, and they all have their own characteristics:
- Milia - sebaceous gland cysts in the form of a small white grain. They consist of thick sebum and keratin. Dense in consistency, not accompanied by inflammation or discomfort. They form slowly. Their size varies from 0.5 to 3 mm. They have a clear boundary, resemble millet grain, which is why they are popularly called “millet grain”. They can be localized singly, but more often multiplely in the area of the nose, cheeks, cheekbones, and eyelids.
- Comedones look like blackheads. These are open acne that most often occur on oily skin with enlarged pores. Their development begins with insufficient facial hygiene. The black contents consist of dead epidermal cells, dust, and altered sebum. The skin around the formations becomes rough, becomes prone to peeling, and takes on an unhealthy appearance (with a green or gray tint). Treatment of such acne is still possible at home.
- Papules - inflammatory red nodules, in the center of which a small infiltrate forms. The formations have a hemispherical shape (2-5 mm). Rashes that bother you for a long time take on a bluish, purple tint.
- Pustules or pustules - rashes resulting from a purulent-inflammatory process in the skin. There are superficial and deep. The first ones disappear without a trace, their purulent contents dry out and fall off over time, leaving behind temporary pigmentation. The latter leave scars because they are located deep in the dermis. They can have different shapes: spherical, flat, cone-shaped.
Question answer
Do you need to moisturize your acne-prone skin?



