Keratosis (photo can be seen below) is the process of keratinization of epithelial and epidermal cells. Normally, this process occurs only in skin cells, and the mucous membranes of the body do not become keratinized. The appearance of horny scales on them is called keratosis, and excessive keratinization of the epidermis is called hyperkeratosis. These diseases have a similar nature, but their causes and symptoms can vary greatly.
Hyperkeratosis is excessive keratinization of the skin
Causes
The process of keratinization is characteristic of the epidermis (stratified keratinizing epithelium). Normally, skin cells gradually move from the lower layer to the upper layer, in the process accumulating keratin - a substance that makes them stronger and more resistant to external influences. The top layer of skin consists of completely keratinized cells - they lose their viability, but protect the living cells underneath them from temperature changes, mechanical damage, ultraviolet radiation and other unfavorable factors.
Disruption of this process is called hyperkeratosis. Healthy people may develop hyperkeratosis of the feet, less often - elbows or knees. The reason is that uncomfortable shoes, long walking and other types of pressure cause a defensive reaction - the skin thickens in those places where the mechanical influences on it are the strongest. Another example of a similar process is the formation of seals on the fingers of guitarists. This is considered a normal option if the seals are not painful and do not impair the function of the limb.
Pathological causes of hyperkeratosis:
- Disorders of metabolic processes in the skin (diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands);
- Hereditary skin diseases (ichthyosis, keratoderma);
- Inflammatory diseases (various types of lichen);
- Psoriasis;
- Disruption of the regeneration process at the site of injury;
- Neoplasms (benign and malignant).
Hyperkeratosis itself is never an independent disease - it is a sign of another, more serious pathology.
Classification
According to the characteristics of the course of the disease, they distinguish follicular hyperkeratosis, lenticular and disseminated forms of pathology.
- Follicular variant is a lesion of the hair follicles. It occurs more often in areas with dry skin. Causes: hereditary factors, vitamin deficiency, neglect of personal hygiene, inflammatory diseases of the skin and hair;
- The lenticular variant is the formation of small “plugs” on the hair follicles; they look like keratinized spots. Causes unknown, most often occurs in older men;
- Disseminated keratosis is not confined to a specific area of the body and can occur in any area;
- Seborrheic keratosis occurs on oily skin due to metabolic disorders;
- Warty – this form resembles warts in appearance, but without the participation of papillomavirus. Possible degeneration into a tumor, including malignant;
- Senile facial hyperkeratosis – affects older people of both sexes.
At-risk groups
Hyperkeratosis of the feet It occurs more often in people who are overweight, have flat feet, poor posture, and lameness. This is due to increased or uneven distribution of load on the epidermis. Pathological hyperkeratosis most often occurs in people with serious pathologies of the endocrine system organs and suffering from skin diseases. There is no direct connection with the characteristics of personal hygiene - clean people suffer from hyperkeratosis with approximately the same frequency as those who neglect regular washing. Lenticular hyperkeratosis has a definite connection with excessive sun exposure.
Symptoms
The main symptom of the pathology is thickening of the skin in areas where strong pressure occurs. The affected areas look like lumps, sensitivity in them is reduced, and the skin color may change to lighter or darker. At an early stage, the skin simply appears rougher than the surrounding tissue, then thickening appears. Severe foot hyperkeratosis can impair gait.
Follicular keratosis manifested by the appearance of epidermal scales on dry skin in the area of hair follicles (“goose bumps”). It is quite difficult to see the affected areas if they are single - these are small white or brown dots. If they are removed, normal skin is revealed underneath and they do not affect hair growth. Multiple keratosis pilaris can greatly spoil the appearance.
Symptoms in children
In children, this pathology usually accompanies other childhood skin problems, most often atopic dermatitis. The mechanism of development is quite simple - inflamed skin is much more sensitive to external influences, especially if the child constantly scratches it. That is why skin lesions are typical for scratching areas. After puberty and hormonal changes in the body, this pathology can go away on its own.
Treatment
There are several ways to get rid from keratosis – cosmetic, medicinal and surgical. Cosmetic treatment is suitable for the early stages, when the skin is just beginning to harden. It includes the use of nourishing, moisturizing and softening creams, foot baths, foot steaming and pumice. It is imperative to select comfortable shoes that will not rub. Folk remedies that have proven themselves to be effective are baths with chamomile, calendula, pine bark and pine needles. They not only soften the skin, but also eliminate bacteria that support the inflammatory process.
Drug treatment requires an integrated approach. The first thing to do is to find out the causes of keratinization of the skin and cure the underlying disease or achieve remission. Among the universal recommendations, they usually advise choosing a balanced diet, normalizing weight, and taking vitamin complexes. To make you feel better, it is recommended to use essential oils of lavender, pine or lemon balm.
To combat keratosis directly, keratolytic agents are used. ointments. These products contain components that break down the stratum corneum and have an antiseptic effect. Additionally, an antifungal or anti-inflammatory component may be added. The ointments contain enzymes, caustic substances (sulfur, urea, phenol), weak acids or alkalis.
The use of keratolytic ointment occurs in several stages:
- You need to wash the affected part of the body, you can pre-steam the skin;
- Apply ointment to clean, dry or slightly damp skin;
- Wait about 10 minutes (more precisely indicated in the instructions for each ointment);
- Wash off the ointment and remove dead skin using cutting instruments.
Seborrheic keratosis They are treated with several types of ointments - keratolytics (mozolin, acriderm), agents with a drying effect (salicylic acid), antiseptic drugs and agents that normalize oily skin are used. Be sure to choose the right care and follow the rules of personal hygiene - this is the only way the skin will regain its original appearance.
Severe hyperkeratosis is treated surgically. Indications are large areas of keratinization that cause pain, interfere with walking or disturb the appearance of the skin, but are not amenable to drug treatment. To remove the affected areas, liquid nitrogen, laser or radiosurgery are used. Especially large areas are removed with a scalpel.
To cure keratosis pilaris on various parts of the body, peelings are used - medium or deep. In this case, this is not a cosmetic, but a medical procedure that completely removes the upper layer of the epidermis, after which it is restored again. The skin after peeling requires special care.
Complications and prognosis
More often hyperkeratosis (photo below) does not pose a threat to the life and health of the patient, and is only an aesthetic problem. It does not cause complications, and the prognosis is favorable. Getting rid of “normal” hyperkeratosis is relatively easy with proper skin care.
The most common complication of hyperkeratosis is calluses. This is a formation from the stratum corneum, which is torn away from the skin with an inflammatory reaction and the formation of a bubble with liquid. Everyone has encountered calluses, and the treatment of such processes is quite simple - you need to puncture the vesicle, release the liquid from it and seal it with a bactericidal or keratolytic plaster. Calluses do not pose a danger to life and health.
Follicular keratosis, which affects a specific area of the body, can create problems with appearance, especially if it is on the face. This can be corrected with the help of peelings, so the prognosis for life and ability to work can be called favorable. However, if the disease constantly recurs, it reduces the patient's quality of life.
Seborrheic keratosis, which is most often a sign of a more serious pathology, is not assessed as an independent disease. It can expand the affected area and impair quality of life due to deterioration in appearance. However, the prognosis for keratosis itself is favorable.
The only type of keratosis that you should be wary of is verrucous. Especially if the neoplasm on the skin becomes covered with cracks, is constantly exposed to traumatic influences, or suddenly changes its appearance. Warty keratoses are prone to degeneration into benign and malignant tumors.
Prevention
“Normal” keratosis is relatively easy to prevent. To do this, you need to be careful when choosing shoes - they should be comfortable, not chafe, and not create excess stress on your feet. People who have risk factors - walking or working on their feet a lot, being overweight, pathologies of the feet and posture - should pay attention to foot care. Baths and cream should be used every day, and the stratum corneum should also be scraped off daily - this will help avoid its thickening. For large corns and calluses, keratolytic treatment will help ointment.
To prevent seborrheic keratosis, attention should be paid to skin care in general, as well as the state of the immune and endocrine systems. Regular showering, the use of body creams and gels that normalize sebum production, as well as a healthy diet with a sufficient supply of vitamins will help to avoid this pathology. If peeling of the skin appears, you should consult a doctor to get examined - perhaps the cause is a serious illness.
If warty hyperkeratosis appears, you should immediately begin treatment, since this type of excess keratinization poses a health hazard. Avoid appearance
This pathology is difficult because its causes are not fully known.
Other types of hyperkeratosis - follicular, senile, lenticular - are difficult to prevent due to the lack of accurate data about their causes.
Problematic skin is an unpleasant phenomenon that creates internal discomfort. One of the common skin diseases is keratosis pilaris, popularly called “goose bumps”. Find out what causes a rare disease, what its types are, symptoms and treatments.
What is hyperkeratosis
Cutaneous hyperkeratosis is a disease that occurs when the upper stratum corneum of the epidermis thickens excessively. Epidermal cells rapidly divide, which, combined with disturbances in the desquamation process and the appearance of keratin, immediately leads to thickening. Signs of the disease are the formation of nodules of varying sizes, protrusions, spines, and keratinized plates. The skin becomes dry, rough, and there is a significant decrease in sweating. Hyperkeratosis often appears during puberty and weakens with age, but there are cases of the disease in adults.
Follicular hyperkeratosis
Damage to the stratum corneum, in which the cells of the surface of the epidermis do not have time to renew themselves and begin to become coarser, has its own name - follicular hyperkeratosis. The keratinized scales can clog the hair follicles, leading to small rashes. The areas of localization of the disease, as a rule, are the following areas of the body:
When the action of an infection is connected to local inflammation, follicular dermatitis occurs. As a result, there is an increased secretion of the protective protein keratin by the skin, which prevents the normal separation of keratinized cells. Increased keratin production can cause irritation, lumpy, dry, and unpleasant appearance.
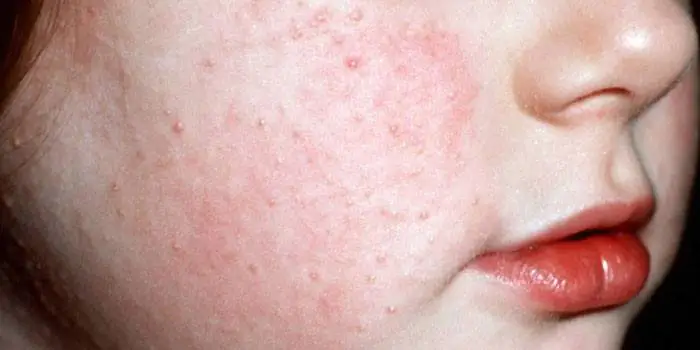
The likelihood of developing hyperkeratosis of the facial skin is high in patients with dry skin. The skin begins to peel off and become covered with a crust, bursting from facial wrinkles. Often the disease affects the lips, which is manifested by the formation of a flat surface with grayish-white scales around the edge. Scabs and wounds form, causing discomfort. Often young women mistakenly perceive pilar keratosis of the face only as an external defect, not knowing about the possibility of its degeneration into precancerous diseases.
Thickening during foot hyperkeratosis occurs over the entire surface of the skin, especially noticeable on the heel and sides of the big toe. There is a change in the color of the limb - the skin becomes whiter, looks flaky, and excessively dry. Cracks, minor hemorrhages, and calluses appear. Horny skin on the feet often occurs due to wearing uncomfortable shoes and excess weight, which puts excess pressure on the feet.
The skin of the elbows is characterized by increased density and dryness, since it has almost no sebaceous glands. Often people, sitting at the table, rest their elbows on it. This makes the epidermis rough, leads to the appearance of cracks and can provoke hyperkeratosis of the elbows. The disease can manifest itself as a small red rash and the appearance of papules (nodules raised above the skin).
Symptoms of follicular hyperkeratosis
The disease is popularly called “goose bumps”, due to the similarity of symptoms with rough red bumps on the skin of a bird. In dermatology, the following symptoms of follicular hyperkeratosis are distinguished:
- dryness, roughness in certain areas;
- coarsening in those parts of the body that are subject to mechanical stress (feet, elbows, knees, buttocks);
- the formation of small red rashes, bumps, papules, plaques, cracks;
- the appearance of dense spiny nodules at the base of the hair follicles.
Causes of follicular hyperkeratosis
Dermatologists believe that keratosis pilaris is often not an independent problem of the body, but a concomitant symptom of other diseases:
- ichthyosis;
- psoriasis;
- endocrine disorders;
- diabetes mellitus;
- atopic dermatitis.
It happens that the disease manifests itself in healthy people - then the causes of follicular hyperkeratosis are:
- Lack of vitamins. A deficiency of vitamin C, which is responsible for the production of collagen, leads to peeling and irritation, and loss of skin elasticity. A lack of vitamins A and E makes the skin flabby, rough, and inflamed.
- Taking hormonal drugs. Hormones accelerate the process of cell renewal, keratinized scales do not have time to peel off, and the skin thickens.
- Poor nutrition. An unbalanced diet can lead to intestinal dysbiosis and cause irritation.
- Stress, emotional tension. Problems of the nervous system negatively affect the condition of the skin - dullness, dryness, and loss of moisture appear.
- Genetic predisposition. If the parents suffered from hyperkeratosis, then it is likely that the disease will be detected in the child.
- Cold. Low temperatures dry out, causing cracks and roughness.
Treatment of keratosis pilaris
If you experience symptoms of goose bumps, you should seek help from a medical facility. A dermatologist, endocrinologist and cosmetologist will conduct a thorough diagnosis of your skin and prescribe an appropriate course of treatment for keratosis pilaris. Do not try to get rid of the disease at home - this can only worsen the situation. The disease cannot be completely cured, but it is possible to reduce the inflammatory process and return the skin to a healthy appearance by adhering to the following recommendations:
- Do not perform unprofessional mechanical facial cleansing. Use soft masks and surface peels based on acids - lactic, glycolic, salicylic.
- To prevent the localization of keratosis from increasing, take baths with the addition of milk or decoctions of medicinal herbs.
- Avoid sun exposure, as tanning makes the layers of the epidermis dry and thin.
- Choose care cosmetics carefully - soaps and gels with a drying effect will only aggravate the disease. Give preference to gentle moisturizers.
- Do not squeeze out the rash - this can lead to inflammation, infection, and scarring.
- Prevent hypothermia and overheating of the skin.
- Try to wear loose clothing and shoes that fit properly.
- Eat right, eat more vegetables and fruits, which will saturate your body with the missing vitamins.

When treating follicular hyperkeratosis with drugs, patients are prescribed tretionin, ascorbic acid, vitamin A, drugs based on salicylic acid, and sometimes topical corticosteroids. Often, a dermatologist prescribes LacHydrin, a cream lotion containing lactic acid that helps moisturize the skin. To soften it is recommended to use:
- Castor oil;
- glycerol;
- baby cream;
- fish fat.
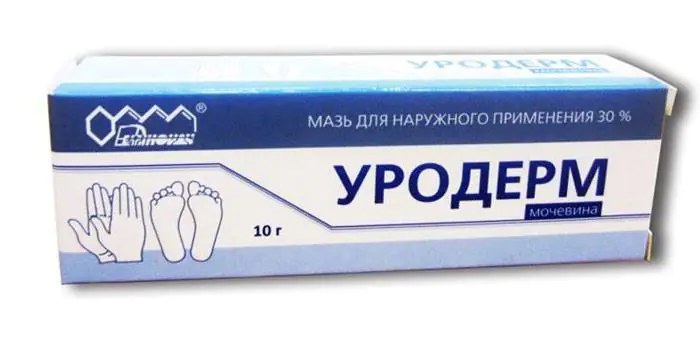
Treatment of hyperkeratosis often occurs with the use of ointments containing isotretinoin. "Uroderm" is an ointment for follicular hyperkeratosis, consisting of 30% urea. This element effectively breaks down the protein bonds that hold together the keratinized particles of the epidermis, creating additional conditions for exfoliation of horny layers in keratosis. Urea retains moisture in the intercellular space, preventing the skin from drying out. Using the drug for two weeks reduces dryness and keratinization.
Forecast and prevention of follicular hyperkeratosis
“Goose bumps” do not have a negative effect on the patient’s internal organs. The prognosis and prevention of follicular hyperkeratosis indicate that the disease does not pose a particular danger. To reduce the risk of keratosis pilaris, you should follow several rules:
- eat well, take vitamins;
- use non-hormonal contraception;
- strengthen immunity;
- Take good care of your skin using high-quality cosmetics.
Video: Hyperkeratosis of the skin of the legs
Reviews
Tatyana, 22 years old I have been suffering from goose bumps on my face for several years. The disease appeared in adolescence and still does not go away. I hope that after childbirth the body will be rebuilt and the skin will become normal. I use gentle baby soap, make honey masks and light peelings based on fruit acid. The redness is decreasing, but the bumps are not completely gone yet.
Evgeniy, 37 years old My elbows are terribly dry - my wife gave me moisturizer, but it didn’t help much. When it got to the cracks, I went to the hospital. I work in an office, at a desk all day, sometimes I rest on my elbows - they said this is the cause of my illness. They prescribed vitamin A and healing ointment - it helps well, keratosis pilaris on the elbows is almost gone.
Alla, 53 years old My daughter was diagnosed with manifestations of hyperkeratosis when she was fourteen, rashes everywhere - face, back, arms, thighs. The LacHydrin product helped a lot - the skin became softer, the redness went away. They also used Retin-A, which is also an effective drug. Now everything is fine, adolescence has passed - the disease has disappeared.
Goose bumps or follicular hyperkeratosis is a fairly common phenomenon that worries many people. The defect is not accompanied by pain or other symptoms, but it looks unpleasant. Often this problem causes self-doubt in women when the disease manifests itself on visible parts of the body. Parents worry about the baby’s health if he suddenly develops similar rashes on his legs or torso. For these and other reasons, you should know what hyperkeratosis is called and how it is treated.
A little about the disease
In a healthy person, the epidermis is constantly renewed, and the death of cells goes unnoticed. With pathology, changes occur in the structure of the skin, which is reflected in their appearance. The dermis on the face and body becomes denser and becomes covered with scales or dots. The reason is accelerated cell division, disrupted desquamation and the occurrence of keratosis. In simple words, we can say this: dead particles do not exfoliate, but remain on the surface and clog the hair follicles. Having examined the integument, it is possible to notice various rashes, nodules and small tubercles. Dryness and roughness are noted, and sweating in the affected areas is increased. The problem is localized in the following areas:
- legs – feet, calves and knees;
- arms - shoulders, elbows and palms;
- back.
Follicular hyperkeratosis is most often diagnosed in children, adolescents and people with weakened immune systems. The disease is not considered dangerous, but it must be treated. Untimely therapy spreads over large areas, causes severe itching and looks very unpleasant. If you scratch the inflamed areas, a bacterial infection may occur.
In the international classification of diseases it has the following code: ICD 10: L11.0.
Causes
Experts identify several main reasons that provoke the development of follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin. Hereditary factors and weakened immunity play a huge role. Vitamin A deficiency contributes to the development of type I disease, and vitamin C deficiency contributes to type II pathology. In addition, the disease can be caused by:
- hypothermia or chapping of the epidermis during cold weather;
- unbalanced diet;
- wearing clothes and shoes made of low-quality materials;
- contact with household chemicals (soaps, shampoos and gels that dry the dermis);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- use of certain medications, such as hormonal contraceptives;
- unfavorable situation in the family and work team or other nervous situations.
Some dermatologists are of the opinion that follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin signals the development of psoriasis, ichthyosis, thyroid pathologies and hormonal imbalance, as well as atopic dermatitis. For this reason, during the examination, they try to confirm or exclude such disorders.
Manifestation of the disease in adults and children
Disease in children
The very first and brightest signs are a rough surface with small convex dots. Sometimes they are invisible to the eye and can only be detected by touching the skin. In most cases, the inflamed dermis turns pink and becomes covered with pimples, which is why many people call the defect “goose bumps.” The pathology develops slowly, but causes noticeable redness, an itchy rash and spread to the abdomen, thighs and genitals. This requires several months or even years. However, if a person is in favorable conditions for the development of hyperkeratosis, then the situation quickly worsens.
Vitamin A deficiency will be indicated by speckles that form on the limbs, buttocks and in the area of the extensor joints. They do not differ in color from the rest of the body, but are very rough to the touch. In some cases, the touch feels more like sandpaper than skin. Vitamin C deficiency manifests itself in another way: damage affects the abdomen, genitals and thighs. The pimples are red with blood spots.
As a rule, the rashes are small and dense (there is never liquid inside them) and are localized around the hair follicle. In the middle it is a little lighter than the contours. The edges of the spot are clear and red. Below you can see what the lesion looks like in a photo in a person. The disease begins with pimples on the sides of the arms or legs, then spreads to the rest of the body. The size of the bubbles is small - the plaques are smaller than a match head. Only the generalized type of follicular hyperkeratosis of the skin affects the entire body.



