
- Reasons for appearance
- What do papillomas on the clitoris look like?
- Treatment options
- Folk remedies
- Medicines
- Removal of papillomas on the clitoris
Papilloma on the clitoris is a so-called genital formation, in most cases benign. It is localized in the intimate area, so it creates certain inconveniences when walking and during sexual activity. This growth can appear not only in sexually active women, but also in those who have not had many partners.
Causes of papilloma on the clitoris
The appearance of papilloma on the clitoris is provoked by a virus of the same name, mainly types 6 and 16. Infection usually occurs through sexual contact, and a condom is not always able to protect against this, since, firstly, it can tear, and secondly, it does not completely cover the phallus. As a result of its friction against a woman’s mucous membrane, HPV can pass to her.
The likelihood of the virus entering the body increases if there is damage in the clitoral area. The danger of this exists especially for those who have sexual intercourse for the first time in their lives, since this usually does not happen without the appearance of blood. Together with it, HPV can move further and infect a large number of healthy cells, including in intimate places, which creates optimal conditions for the occurrence of papilloma on the clitoris.
We should not exclude the household route of transmission of the virus, which is characterized by its transfer between people when using contaminated things - dishes, towels, toothbrushes, razors, washcloths, etc. But this happens extremely rarely, and in order to become a carrier of HPV in this way, you need to live with the patient in the same house for a long time. Therefore, in this case, the main threat to a woman is her husband, parents, siblings.
One of the ways to spread the genital type of papilloma virus is through examination by a gynecologist using instruments that are not well sterilized. Here we mean only those that are used repeatedly, that is, not disposable. We are talking mainly about a special gynecological speculum.
Papilloma on the clitoris can also occur when visiting unscrupulous dentists, gastroenterologists, proctologists, who are also not responsible for the sterilization of medical instruments. But to do this, they must first be used to examine an already infected person, as a result of which traces of the virus remain on them.
After entering the body, HPV may not make itself known for a long time, remaining in a passive state. Its activation occurs due to a disruption of the immune system, which is provoked by many different factors. The stronger it is, the longer the latent period will be. On average, it lasts from 2 weeks to 2-3 years, and in some women the virus remains in the body all their lives, but does not produce symptoms in the form of formations on the clitoris.The following problems increase the likelihood of clitoral papilloma formation in this intimate place:
- Intoxication. Poisoning with nicotine, alcohol and even ordinary food may well worsen the state of health and reduce the degree of protection of the body, thereby provoking the process of proliferation of the epithelium. “Heavy” drugs made from harmful synthetic substances also pose a threat.
- Hormonal disorders. The cause of such failures is a lack or excess in the blood of FSH, estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, TSH, adrenaline and a number of other hormones of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and ovaries. Mostly women who have reached the age of 40 experience clitoral papilloma, since the first signs of menopause appear around this age. At this time, an acute deficiency of estrogen occurs, which is gradually replaced by estrol, which to some extent negatively affects the protective functions of the body.
- Avitaminosis. Clitoral papilloma is caused by a lack of ascorbic and folic acid, cyanocobalamin, alpha-tocopherol, iron, zinc and many other vitamins, macro- and microelements in the diet. These problems arise due to limited consumption of fresh fruits, vegetables, berries, as well as fish, meat, and dairy products. They mostly make themselves known in late autumn, winter or early spring.
- Gastrointestinal diseases. Women who have been diagnosed with gastritis, which is an inflammation of the walls of the stomach, are most susceptible to the formation of papillomas on the clitoris. In this case, the process of absorption of nutrients from food is disrupted, which is why vitamin deficiency most often develops and the level of hemoglobin decreases. As a result, the body’s resistance to HPV decreases, it becomes more active and destroys healthy cells.
- ENT diseases. The danger comes from tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, frontal sinusitis, tracheitis and other similar diseases of bacterial origin. The active activity of these pathogenic microorganisms negatively affects the state of the immune system and sooner or later puts it out of order, provoking serious malfunctions and the formation of papilloma on the clitoris.
- Unfavorable factors. These include, first of all, bad habits - using drugs and drinking alcohol, smoking tobacco. Poor environmental living conditions are also very harmful to the immune system. First of all, this is worth thinking about for those who spend most of their time in large cities with actively developing industry.
- Long-term medication use. This applies mainly to those who abuse antibiotics, taking them without medical supervision and in high dosages not provided for in the instructions. Their danger lies in the fact that they help suppress the activity of beneficial bacteria and provoke the development of pathogenic microflora. Due to such an overweight, the immune system suffers and the body’s protective properties deteriorate, resulting in an increased likelihood of papilloma formation on the clitoris.
- See also the causes of warts on the labia
What do papillomas on the clitoris look like?
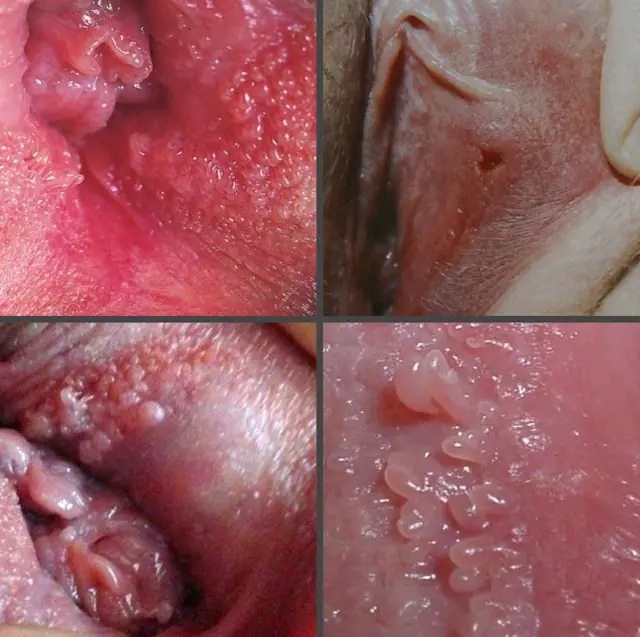
Photo of papillomas on the clitoris
In the photo, papillomas on the clitoris look like small dots, reminiscent of a nettle or boiling water burn. Basically, they form lesions up to 3-5 cm in size, in which numerous spots are grouped. Outwardly, they are first mistaken for a rash that occurs, for example, as a result of irritation of the mucous membrane. But over time, as the virus activates, the diameter of the formations gradually increases. Eventually, they often take on the appearance of a cockscomb or cauliflower.
The following types of papillomas may appear on the clitoris:
- Vulgar. They are dense nodules covered with a keratinized layer of epithelium. Their surface is usually ribbed, their shape is round or oval, with slight deformation, their diameter is up to 0.6 cm, their color is flesh-colored.
- Flat. Such growths practically do not stand out against the general background, representing a small compaction with a diameter of 0.3-0.6 cm. Sometimes they are confused with moles, but since the latter usually do not appear on the clitoris, recognizing flat tumors is not particularly difficult.
- Pointed. Clitoral papillomas are usually called condylomas, and they are the ones that most often arise here. These growths are the largest in size, reaching 1-2 cm in diameter. They are distinguished by uneven edges and an unsmooth surface; their color is usually deep red and pale pink; such tumors are rarely flesh-colored.
- Acrochords. Compared to genital warts, vulgar warts and flat growths, such papillomas on the clitoris are rare. Their peculiarity lies in their single location; only sometimes 2-3 tumors can be seen here. A characteristic feature of acrochords is the presence of a dense, strong “leg”, which is their root.
Among the symptoms of papilloma on the clitoris, severe itching should be highlighted first. When scratching problem areas, the virus spreads across the surface and destroys other cells. Because of this, the lesion increases in size, and the formations may begin to grow.
Among other signs, it is worth paying attention to possible bleeding, which is the result of a violation of the integrity of the papilloma as a result of mechanical impact on it, for example, during sexual contact. When infection penetrates inside through wounds, inflammation and redness of the mucous membrane often appears. It is also quite possible that irritation and hyperemia may occur due to constant contact with underwear made of synthetic fabrics.
One of the obvious signs of the appearance of papilloma on the clitoris is a certain discomfort during sexual intercourse and a burning sensation, sometimes it even leads to pain. Quite often it intensifies when walking and rubbing against underwear. An unpleasant odor and various vaginal discharge may also indicate such a formation.Methods for treating papillomas on the clitoris
Before carrying out therapy, it is logical to perform a thorough diagnosis. Here, a PAP test will be relevant, which allows you to determine the type of virus that caused the formation. A biopsy of the growth will also be required to rule out its malignancy. The treatment regimen itself usually includes taking immunostimulants and antiviral drugs, as well as the use of external medical and folk remedies for clitoral papilloma.
Folk remedies for treating papillomas on the clitoris

Castor oil is very effective against such growths, in which you should soak a cotton pad and wipe the formation. Such procedures should be performed at least 2-3 times a day. The optimal duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
This oil can be replaced with sea buckthorn, coconut, lavender, and olive oil. The main thing here is that they should be cheese-pressed, otherwise their effectiveness will decrease. Before use, all this can be heated, but so as not to burn the mucous membrane.
Here are other, no less effective folk remedies for clitoral papilloma:
- Aloe juice. Cut a leaf from this plant, grind it into a paste and squeeze the mass through cheesecloth. Wipe the papilloma with the resulting juice 3-5 times a day using a cotton pad. This procedure should be carried out within 1-2 weeks. It is necessary to prepare the product just before use so that its benefits do not disappear.
- Green tea. Brew its leaves (1 tablespoon) in boiled water (200 ml), cover them with a lid and keep under it for about 15 minutes. Then strain the mixture, soak a cotton pad in the resulting infusion and wipe the formations well. Repeat these steps 2-3 times a day until the clitoral papilloma goes away.
- Potato juice. To prepare it, peel the tubers of this plant, then grind them in a meat grinder or grater. Next, place this mass on cheesecloth and press well with your fingers. The liquid that has drained during this time should be used to treat papilloma twice a day. Treatment is usually carried out over 2-3 weeks.
- Chamomile. Pour this dried herb (3 tablespoons) with boiled water (300 ml), cover with a lid and let it stand for about 3-4 hours. Then strain the mixture and use the resulting liquid to wipe the clitoral papilloma 3-5 times a day. To do this, soak a cotton pad in it, with which the growths are treated.
Treatment of papillomas on the clitoris with medications
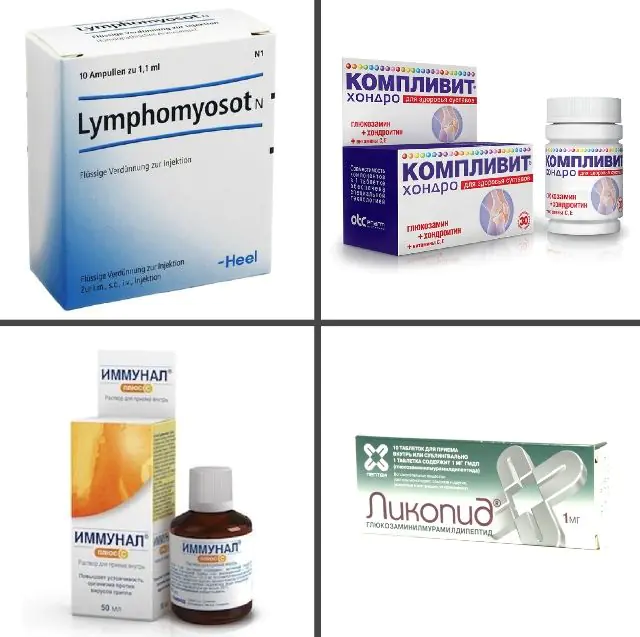
In the photo are preparations for papillomas on the clitoris
It is not recommended to use Ferezol, Verrukacid and other cauterizing agents with an aggressive effect to eliminate papilloma on the clitoris. They can cause burns, burning and itching of the mucous membranes, so it is better to choose the safer Super Clean product instead. It is sold in the form of a solution, in 3.6 ml bottles, the cost is about 100 rubles. (30 UAH). The composition should be applied to the clitoral papilloma using an applicator, 1-2 times in total.
Here are the drugs prescribed in addition to external agents:
- Immunostimulants. Lymphomyosot, which is a natural food supplement available in liquid form, has performed well. It is taken 30-40 drops per day, washed down with water, for a month. The cost of the drug is 450 rubles. (200 UAH). It has excellent analogues - Immunal and Imudon, which are sold in tablet form. On average, treatment for clitoral papilloma lasts 2-3 weeks.
- Vitamins. The most effective drugs are those from Doppelhertz Active, Solgar, Complivit, Perfectil, Alphabet. If we talk about supplements intended specifically for women, then it is worth highlighting the Opti Women Optimum Nutrition tablets, the cost of which is 1000 rubles. (450 UAH). On average, they are drunk for 2-4 weeks, 1-3 capsules per day.
- Antiviral. First of all, doctors recommend paying attention to the drug “Likopid”, which perfectly fights various types of HPV. It should be taken for 5-7 days, 1 tablet per day, the cost of the medicine is 600 rubles. (250 UAH). It has good analogues - Cytovir-3 and Kagocel.
For successful treatment of clitoral papilloma, it is necessary to combine the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, immunostimulants and vitamins. In addition to this, you need to use antiviral ointments, for example, Oxolinic or Salicylic. They must be applied in a thin layer 2-3 times a day throughout the week and left until absorbed.
Removal of papillomas on the clitoris
If the formation is large and cannot be treated with therapeutic methods, then the question of surgical removal may arise. To do this, a mini-operation is performed to excise the growth under general anesthesia. On average it lasts 20-30 minutes, but after this the patient is usually left in the hospital for several days to recover.
Among the physiotherapeutic methods of eliminating papilloma on the clitoris, the following should be especially noted:
- Cryotherapy. To eliminate the formation using this technique, liquid nitrogen is used, which is applied to the growth and kept on it for some time. Thanks to this, it dries out and after a few days falls off along with the scab and root. This method is unique in that it eliminates scars and burns. The price of cryodestruction is 360 rubles (150 hryvnia).
- Radio wave removal. To do this, use a special knife that prevents direct contact with tissue. Due to this, it is possible to remove only the clitoral papilloma itself, without affecting healthy areas of the skin. The procedure is carried out without pain, but analgesics are still used just in case. The price of radiosurgical removal is 3,000 rubles (1,200 hryvnia).
- Electrocoagulation. This method requires exposure to the formation of a current of a certain frequency. It ensures reliable cauterization of the growth, resulting in the formation of a dense crust after the procedure. Eventually, the scab disappears, and along with it the tumor itself disappears. The price of electrocoagulation is 590 rubles (250 hryvnia). This method for papilloma on the clitoris is used less frequently than cryotherapy and radioknife.
- Laser therapy. This is a safe method of atraumatic removal of a formation, which is carried out by destroying its cells with a beam of certain parameters. Its main advantage is the ability to penetrate deep into the tissue and eliminate the growth the first time along with the root. The price of laser therapy is 2900 rubles (1300 hryvnia).
Read also how to treat the skin after removing papilloma with liquid nitrogen.
When considering the problem of such formations, you need to understand that in principle a papilloma on the clitoris cannot come out in one day. It’s just that in most cases no one pays special attention to the first symptoms of its appearance - and these are itching, redness, swelling and burning in the mucosal area. Once the formation reaches a certain size, it becomes more difficult to eliminate it. That is why it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all his recommendations.
- Related article: Examination by a gynecologist for papilloma in intimate places



