The eyes are the most important organ that allows us to fully perceive the world around us. For many people, this is a weak spot, often suffering from conjunctivitis, redness, and swelling. Eye ointments will help cope with ophthalmological problems. It is necessary to select a remedy depending on the type of pathology. Let's look at some of the most popular drugs in this category.
In what cases are eye ointments used?
In ophthalmological practice, various inflammatory processes involving the eyelid and the eyeball itself are often encountered. They bring a lot of discomfort and require immediate treatment. In most cases, complex drug therapy is indicated, which usually includes special ointments. For an eye suffering from the negative effects of an irritant, the drug is prescribed after the etiology of the disease has been established.
When should you use eye ointments? Medications in this form will help in the following cases:
- for conjunctivitis of viral, allergic, bacterial or fungal origin;
- with keratitis;
- with blepharitis;
- after surgery;
- for thermal and chemical burns of the cornea;
- with barley;
- after eye injuries;
- with demodicosis lesions of the skin around the eyes;
- with herpes infection.
Which ointment to choose for eye inflammation?
Inflammation of the eyes causes redness, itching, increased tearing, swelling, and purulent discharge. In order to eliminate these unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to establish the type of causative agent of the pathological process. Most often, patients suffer from viral and bacterial conjunctivitis, which manifests itself with the following symptoms. Eye ointments will help overcome the disease within a few days.
For bacterial infection, the following drugs will be effective:
Eye ointment for inflammation of viral origin may contain antibacterial components. This allows, along with treating the disease, to prevent the development of a secondary bacterial infection. Because the inflamed mucosa becomes especially susceptible to the effects of pathogenic pathogens. For viral conjunctivitis, ointments such as Acyclovir, Solcoseryl, Hydrocortisone, and Oxolin should be used. They will help quickly eliminate swelling, itching and tearing.
Tetracycline eye ointment: instructions
Tetracycline ointment is an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of effects. In the treatment of ophthalmic pathologies, the drug is used if a bacterial infection has occurred. This can be determined by the characteristic symptoms - the appearance of purulent discharge from the eyes and severe burning.
Indications for the use of the ointment are blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, bacterial lesions of the cornea, trachoma. Staphylococci, Shigella, Klebsiella, and streptococci exhibit sensitivity to the antibacterial component in the drug.
Destination Features
Tetracycline ointment is not used for the treatment of ophthalmological diseases in pregnant women, children under 8 years of age, and patients suffering from diseases of the circulatory system, liver and kidneys. Even in the absence of contraindications, using antibacterial eye ointment without prior consultation with a specialist can be harmful. Therefore, self-medication is highly not recommended.
What ointment will help get rid of puffiness under the eyes?
Bags and puffiness under the eyes appear, regardless of age. This may be due either to fatigue or to disturbances in the functioning of the body. If the real reason lies in lack of sleep, then eliminating the cosmetic defect will be much easier.
Heparin ointment under the eyes can be used as an emergency aid. Reviews say that this is one of the most effective and safest remedies. However, do not forget that this is primarily a medicine and it is not advisable to use it without consulting a doctor.
What is included in heparin ointment?
The main active ingredient in the external product is sodium heparin. This substance is a complex protein that improves blood circulation and eliminates tissue swelling. Benzyl nicotinate is another active anticoagulant substance necessary for better penetration of heparin.
Heparin ointment also contains components that can cause an allergic reaction. Therefore, it is necessary to use the product under the eyes with extreme caution.
Mode of application
Heparin ointment has long been considered the best remedy to help cope with bags under the eyes at home. You can see a positive result from use after several applications throughout the day.
Most often, skin care products are used in their pure form. The ointment should be applied in a thin layer to the delicate skin under the eyes. The dermis must first be cleaned of makeup. The manipulation can be repeated no more than twice a day. The maximum period for using the ointment as a cosmetic product is 10 days.
Another effective way to use it is as a mask. To do this, apply a mixture of ointment (about 2 peas), a few drops of peach and argan oil with patting movements to cleansed skin, leave for 10 minutes and remove the residue with a cotton pad. Repeat the procedure every day, before bed, for two weeks.
What do cosmetologists say?
Heparin ointment for swelling under the eyes is often replaced with other drugs that have a similar mechanism of action. Such drugs include “Troxerutin”, “Lioton”, “Troxevasin”, “Relief”. You can use any of them only if there are no contraindications specified in the instructions.
Reviews from cosmetologists say that such pharmaceutical preparations cannot be used to eliminate swelling and dark circles under the eyes. They have only a temporary effect and very often cause a number of negative consequences: increased dryness of the dermis, the appearance of fine wrinkles, itching, burning. They can be used only in extreme cases and in the absence of hypersensitivity.
In ophthalmology, ointments are often used to treat eye diseases. Self-prescription of drugs is not acceptable. Such treatment can be dangerous, have irreversible consequences, or simply be useless. It is for this reason that if complaints arise, you need to consult a doctor. Only he is able to determine which eye ointment is suitable in each specific case. When prescribing a medicine, the doctor relies on the pathogen that caused the disease.
This article provides detailed information on the types of ointments, their use, indications and method of application.
What are they?
According to the nature of inflammation and eye diseases, ointments can be divided into 5 main groups, let’s also figure out what they are called:
- If personal hygiene is not observed, washing with dirty water, or rubbing the eyes with hands, there is a high probability of eye infection. Under the influence of bacteria, the mucous membrane is affected, infection and inflammation develop. Used for treatment
- "Erythromycin";
- "Tetracycline";
- "Ebetal";
- "Neladex";
- "Floxal".
- "Oksolin";
- "Zovirax";
- "Zirgan";
- "Bonafton";
- "Acyclovir";
- "Virolex".
However, for inflammation caused by allergies, hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments: hydrocortisone are more effective.
When affected by parasites, there is a high risk of infection spreading to the eyelids, which will lead to serious complications.
Therefore, when diagnosing this type of disease, treatment should be started in a timely manner and following all antiseptic rules. Proven themselves antiparasitic ointments:
- "Demazol";
- "Demalan";
- "Glycodem";
- "Dexodem - Phyto."
General rules of use
For any drug in this group, certain application requirements:
- The drug is prescribed strictly by the doctor according to indications.
- When prescribing several medications, for example, drops and ointment, they are not allowed to be used at the same time. Drops should be instilled and ointment should be applied after 5 to 10 minutes.
- Depending on the disease, its severity and the doctor’s recommendations, the ointment is used according to a specific course of treatment that must be followed.
- When wearing contact lenses, remove them before applying the ointment. Lenses can be installed after 15 minutes.
- Never apply the medicine with your hands; it is recommended to use a special glass rod, which must be washed thoroughly after each use.
- When treating with ointments, strictly observe personal hygiene and general rules of sterility.
- Medicines are stored in the refrigerator; use after the expiration date is prohibited.
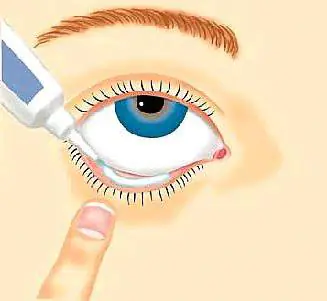
Instructions for use of eye products
Before carrying out the manipulation, you should prepare in advance. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap, prepare a thick cotton ball, medication, glass rod.
So, how to apply ointments:
- Having taken a sitting position, tilt your head back.
- Look up and pull the lower eyelid down with your left hand.
- Take the medicine with your right hand and apply the product along the entire length of the eyelid, but without touching the tip of the tube to the mucous membrane or eyelashes.
- Release the eyelid, close the eye, move the eyeball for a while for the best distribution of the product.
- When excess ointment appears, blot your eyes with a prepared cotton ball.
These are all the rules on how to smear and apply such products to the eyes.
Video on how to properly apply ointment to the eyes:
Indications
Depending on the nature of the pathogen, the doctor selects a drug.
Also there are contraindications and restrictions for use, the doctor takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
When making a diagnosis and conducting the necessary examination, the doctor will prescribe one of the medications listed below, and will also tell you how to apply eye medication:
- Antibacterial ointments prescribed for conjunctivitis, blepharitis, barley, abscesses, after injuries to the orbit, and eye surgery.
- Antiviral ointments: herpes, influenza, ARVI, diseases caused by adenovirus, retrovirus, cytomegalovirus.
- Anti-inflammatory non-hormonal: when getting used to contact lenses, after uncomplicated eye surgeries, with irritation of the mucous membrane, swelling, eye irritation. Anti-inflammatory with hormones are used for allergen damage, swelling, itching, redness.
- Antiparasitic: when diagnosing demodicosis or other parasitic diseases, there is a high probability of introducing the parasite into the eyelids, which can lead to serious complications on the organ of vision.
- Complex impact used daily as a skin care product, also for chronic blepharitis, to relieve irritation.
Conclusion
Ointments are used to treat diseases of the organs of vision. Ointments are divided into several groups, depending on the nature of the pathogen. After examination, tests, examinations, the doctor prescribes the most effective and efficient drug.
Without medical participation, the use of the medicine is unacceptable. The article presents popular drugs for the treatment of eye diseases, describes general principles of use, provides brief instructions for applying medicinal ointments to the eyelids, and provides indications for treatment.
What eye ointments for children can be used from the first days of life
Often, not only adults are exposed to ophthalmological diseases, but sometimes this attack can also occur in very young children, including newborns.
Thus, the most common childhood eye diseases are: blepharitis (accompanied by inflammation of the eyelids, itching, redness of the eyes and loss of eyelashes), stye (characterized by inflammation of the sebaceous glands of the eyelid, which leads to the formation of pustules), conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyeball), etc.
Instructions for use of Erythromycin ophthalmic ointment: composition, action and method of application
There are many medications aimed at treating ophthalmic diseases of bacterial and viral origin.
One of the proven remedies in modern pharmacology is Erythromycin ointment.
What this drug is, we will consider in more detail in this article.
Types of creams and ointments for bruises under the eyes from a blow and other causes: rules of use
The problem of swelling and bruising under the eyes is relevant for many modern people due to the dynamic rhythm of life, which causes lack of sleep, regular stress, and irregular nutrition. All these factors have a negative impact on the dividing membrane of the eye, thereby causing swelling and bruising under the eyes.
Let's look at the most effective ointments to eliminate this problem.
Sodium sulfacyl ointment and eye drops: instructions for use
Sulfacyl sodium is used to treat infectious eye diseases. This essential product should be in every first aid kit at home. Read on to learn more about the features of this medicine, as well as dosages and side effects.
Pay attention to how to use this product correctly and what side effects it has. Also, do not remain silent about the fact that the product is approved for use by pregnant women and even children under 3 years of age.
Composition and purpose of hydrocortisone ophthalmic ointment
Hydrocortisone eye ointment is used to get rid of various types of inflammation. The product eliminates inflammation and allergic reactions. Let's consider its composition, rules of use and side effects.
The eyelids protect the eyeball from exposure to adverse external factors, ensure uniform hydration of the cornea, and help focus the pupil. Eye ointments are effective for treating all types of eye pathologies.
Causes of eyelid inflammation
The symptoms of pathological processes, regardless of the cause, are largely similar.
With inflammation of the eyelids, the following are observed:
- redness/pallor;
- edema;
- itching;
- pain in the eyelid, eye.
In addition to these symptoms, there may be purulent discharge, headache, thickening of the eyelid, epithelial detachment, and abscess.
Infection, traumatic injury, allergic reaction, unfavorable external environment are the main causes of disease of the upper or lower eyelid in one or both eyes:
Inflammation of the edges of the eyelids (blepharitis) may be due to infection:
- Bacteria.
- Fungi.
- Ticks (demodex);
- From foci of chronic infection:
- for caries;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasal sinuses;
- Bladder.
There are anterior, posterior marginal and angular blepharitis.
Mechanical trauma in the absence of disinfection of the damaged area of the eyelid serves as a “gateway” for all types of pathogens.
The appearance of small blisters with liquid on the eyelid, burning, itching, then opening of the blisters, drying out with the formation of crusts are characteristic signs of herpes infection.
When the eyelash follicle or the sebaceous gland connected to it becomes inflamed, stye forms on the edge of the eyelid (upper or lower). The cause of suppuration is bacterial infection.
As a result of chronic inflammation of the sebaceous gland, a compaction forms in the thickness of the eyelid, which can suppurate and burst - a chalazion.
A provocative factor for the onset of the pathological process is conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye).
In the absence of treatment, visual function may suffer, since the eye membranes (cornea, iris), nearby meibomian glands, hair follicles, and optic nerve may become infected.
For inflammation of the eyelids and redness, medications of various forms and contents are used.
Treatment of inflammation of the eyelids with ointments
Prescriptions for the treatment of eye diseases of any etiology should be made by an ophthalmologist. The specialist will determine the cause of the pathology, the severity, and take into account the patient’s health status and age.
The main method of eye therapy is conservative, using drugs for external and local use. Eyelid ointments are among the most effective products due to their thick consistency and high concentration of the active substance, which ensures long-lasting effects. They can be used as a monomedicine or as part of a complex treatment, depending on the diagnosis.
The therapeutic effect of their use is:
- in pain relief;
- disinfection;
- restoration of skin and mucous membranes;
- relieving inflammation.
Contraindications for prescribing ophthalmic agents: retinal injury, allergic reaction to the active substance. During pregnancy, lactation, and childhood, eye medications containing hormones, NSAIDs, and antibiotics are prescribed with extreme caution.
Use may be accompanied by confusion, headache, allergies, and decreased visual acuity.
Types of ointments
Pharmacology offers a wide selection of eye ointments for inflammation and redness.
The list of eye products includes:
- universal;
- specialized (antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal);
- anti-inflammatory.
The active ingredients used are:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiparasitic;
- antivirus components;
- antibiotics;
- hormones.
Auxiliary products – glycerin, petroleum jelly, lanolin. To prevent dry eye syndrome, artificial tear preparations, for example, Vidisik eye gel, are simultaneously prescribed.
Antibacterial ointments
Eye ointments with broad-spectrum antibiotics:
- Tetracycline is a bacteriostatic agent, contains 1% tetracycline. Directions for use: placed behind the lower eyelid during the day: 2-4 times. Does not enter the general bloodstream. A rash and itching may occur around the eye. Purpose: treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, barley.
- The external ophthalmic drug Neladex contains neomycin (an antibiotic), dexamethasone (NSAID), polymyxin (a substance with antimicrobial properties). Used for the treatment of chronic blepharitis, conjunctivitis. Contraindicated for fungal, viral, tuberculosis, purulent eye infections.
- Erythromycin. The ophthalmic bacteriostatic drug is effective against most types of bacteria and has no side effects. Used in the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, barley. Disadvantages: rapid addiction to erythromycin and reduced therapeutic effect. The treatment procedure involves placing the medicine behind the lower eyelid.
- Terramycin is used to treat eye diseases. Ingredients: oxytetracycline. Has properties similar to Tetracycline ointment.
- Phloxal. The active substance is ofloxacin. The main purpose is chlamydial eye damage.
- Tobrimed eye ointment, which contains the antibiotic Tobramycin, is prescribed for the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and barley.
- Eubetal. The eye product contains antibiotics (tetracycline, chloramphenicol, sodium colistimethate) and a glucocorticosteroid (betamethasone).
- Nettavisk eye ointment contains the antibiotic netilmicin. The drug is used for bacterial infections of the eyelids, cornea, and iris.
- Collargol, which contains colloidal silver and albumin, has an anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effect. For chalazion, Collargol ointment is rubbed into the skin of the eyelid.
The drug is also used to treat:
- blepharitis;
- blepharoconjunctivitis;
- bacterial and allergic conjunctivitis;
- after injury and surgery.
Contraindications are purulent lesions of the cornea, conjunctiva, eyelids, barley, scratches on the cornea, tuberculosis, mycosis of the eyes.
Antiviral ointments
Antiviral eye medications include:
The drugs are prescribed for inflammation of the eyelids caused by the herpes virus.
Antifungal ointments
Infection with fungi is less common, more difficult to cure, and has relapses.
Ophthalmic antimycotic agents:
- universal ointment Pimafucin;
- Clotrimazole (for yeast, mold fungi);
- Fungoterbin (for fungi and lichen).
Application: apply a thin layer to cleansed and dry skin of the eyelids and rub in gently.
Antiallergic ointments
Swelling, redness of the eyelids, watery eyes are signs of an allergy. Symptom relievers include hormonal eye ointments and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Lorinden contain glucocosteroids and are prescribed for severe forms. NSAIDs – D-Panthenol, Levomekol, Fenistil.
For comparison: steroid drugs are more effective, but they are addictive, have more side effects, and are not used without medical advice.
Antiparasitic ointments
The activity of skin mites manifests itself when immunity decreases due to stress, overwork, or illness.
To combat demodicosis, eye ointments are used:
The products have an effect on mite reproduction and relieve symptoms: skin irritation, itching, inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory ointments
Anti-inflammatory eye ointment is used in case of external exposure or in combination with other ophthalmic agents to accelerate the relief of symptoms.
Factors influencing the condition of the eyelids:
- scratches, wounds;
- overwork of the eye muscles;
- contact lenses;
- bright light;
- cold exposure.
Eye ointments for non-infectious inflammation of the eyelids - Blefarogel, Teagel. Hyaluronic acid and aloe extract contained in Blefarogel affect blood circulation and metabolic processes. Teagel is a cosmetic product for permanent care of the skin around the eyes and behind the eyelids.
Actovegin ointment is used for eye inflammation. The drug promotes the regeneration of the skin, mucous membrane, cornea, and has no contraindications or side effects.
How to apply ointment behind the eyelid
How to apply eye ointment:
- With your left hand, pull the lower eyelid down.
- Raise your eyes up.
- Bring the tube to the eye and squeeze the required amount of medicine into the conjunctival sac.
- Move your eyes while closing your eyes.
The main requirements when applying medication to the eye are compliance with hygiene rules:
- clean hands;
- eyelids rubbed with boiled water or chamomile infusion;
- Do not touch the tip of the tube to the eyelid, eyelashes, or eyes.
The drug creates a film on the eye that reduces visual acuity for some time, which must be taken into account.