
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment with medications
- Treatment with traditional methods
- Prevention
- Complications
Gonorrheal folliculitis is a disease caused by a complication of untreated, complex and long-lasting gonorrhea. The causative agent of the disease is gonococci. Localization - genitals (in men - the foreskin, in women - the perineal area). Manifests itself in the form of rashes. Treatment is effective only after getting rid of gonorrhea.
Causes of gonorrheal folliculitis
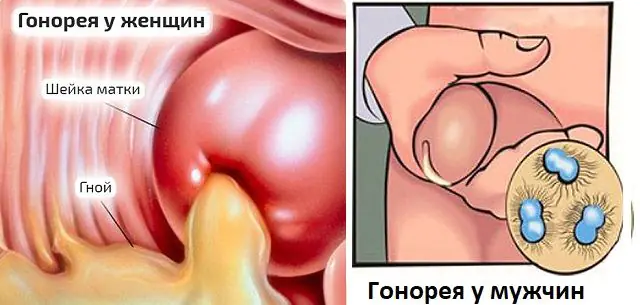
The main causes of gonorrheal folliculitis:
- A complication of long-term gonorrhea.
- Untreated gonorrhea.
The likelihood of developing gonorrheal folliculitis is much higher in people with existing skin diseases (eczema, scabies, Dühring's dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis). Patients with diabetes mellitus and HIV infection are also prone to developing folliculitis.
Gonorrheal folliculitis develops against the background of penetration of gram-negative bacteria or pseudomonads into the hair follicle, which are detected after taking infected hot baths. The bacterium enters the hair follicle most often through a small break in the skin. When scratching the pustules, the rash spreads to adjacent areas of the skin.
- Read about the causes of bacterial folliculitis
Symptoms of gonorrheal folliculitis
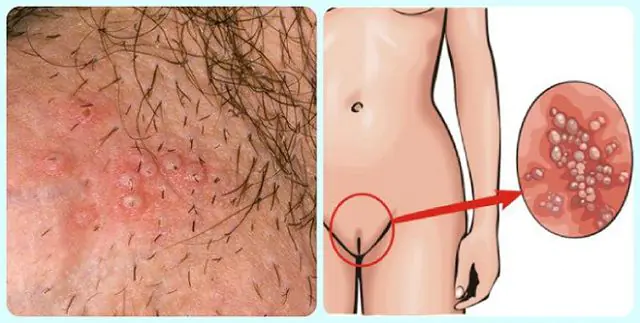
Gonorrheal folliculitis does not have any special symptoms. Considering that the disease develops secondary (after gonorrhea), the localization of papules and the extent of damage depend on the predisposing causes. The disease affects the foreskin in men and the surface of the perineal skin in women.
The primary features of folliculitis are manifestations in the form of a red purulent rash accompanied by ulcers. Threads of the hair follicle may pass through some ulcers. Inflammatory papules appear in small or large groups, accumulating in clusters. The infection can be superficial or deep. If treatment is not started in time, pus with blood clots will begin to come out of the blisters.
- Read about the symptoms of folliculitis decalvans
Diagnosis of gonorrheal folliculitis
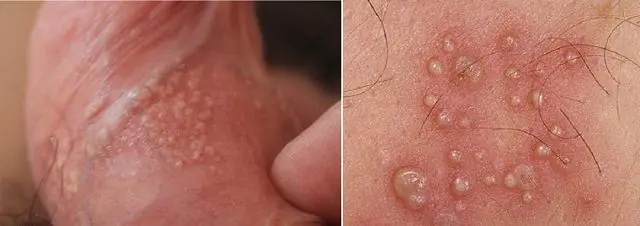
Pictured is gonorrheal folliculitis in men and women
If you suspect folliculitis, you should contact a dermatologist and infectious disease specialist. It is important to determine the source of the pathogen and perform differential diagnosis with other dermatological diseases that have similar manifestations.
The course of gonorrheal folliculitis is similar to other diseases:
- Common acne.
- Rosacea.
- Follicular keratosis.
- Inflammation of the hair follicles of a non-infectious nature.
- Exposure to chemicals.
- Toxicoderma of drug origin, which can be caused by corticosteroids, lithium and bromine preparations.
- Ingrown hair.
- Kirle's disease.
To clarify the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment method, the doctor must take the following steps:
- Inspect the rash.
- Conduct a laboratory test of the hair follicle.
- Identify concomitant pathology.
- Perform dermatoscopy.
- Send the contents of the pustules for microscopic examination.
- Prescribe a bacteriological culture test.
- Rule out the specific etiology of the disease (gonorrhea, syphilis) by prescribing a PCR diagnostic or RPR test.
- If necessary, prescribe an immunogram, blood sugar test and other examinations.
Find out if folliculitis can be spread from person to person.
Treatment of gonorrheal folliculitis with medications
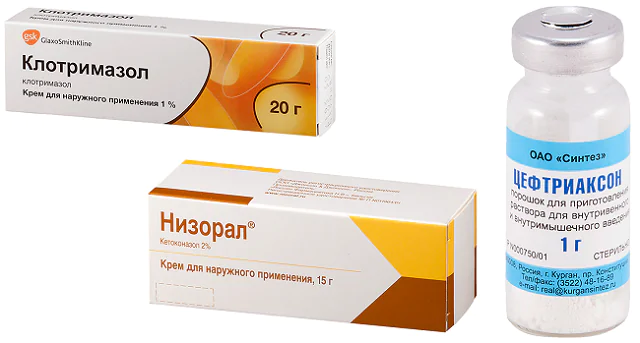
Treatment of folliculitis should correspond to the genesis of the disease. Typically, treatment for gonorrheal folliculitis consists of treating the bacterial infection and the causes that provoked the disease. At the first signs of the onset of the disease, the patient is prescribed antifungal ointments and solutions as therapeutic measures:
- Ointment or gel Clotrimazole 1%.
- Nizoral cream 2%.
- Amphotericin ointment (30,000 units/g).
Also, at the initial stage of the disease, in order to prevent the development of bacteria, the affected area is treated with alcohol solutions (diamond green, fucorcin, 2% camphor or salicylic alcohol). If the disease is of a deep form with a large accumulation of pus, the pustules are opened to remove the pus and treated with alcohol solutions.
In addition, treatment of the disease that caused the appearance of gonorrheal folliculitis - gonorrhea - should be continued. The main therapy is antibiotics. Treatment is prescribed taking into account:
- Form of the disease.
- Localization of the inflammatory process.
- Complications.
- Concomitant infection.
- Sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics.
For the treatment of gonorrhea of the pelvic organs with complications, therapy is prescribed for 7 days:
- Spectinomycin 2 g intramuscularly every 12 hours.
- Ceftriaxone 1 g intramuscularly or intravenously every 24 hours.
Local therapy includes instillation of a 1–2% protargol solution or a 0.5% silver nitrate solution into the urethra and vagina.
During treatment, they abstain from sexual intercourse until the disease disappears completely and follow a diet. Alcohol, sweets, pickles, preserves, and smoked foods are excluded from the diet. They introduce more fresh fruits, vegetables, vegetable fiber, cottage cheese, beef, and sea fish into the menu. Drink 200 ml of water on an empty stomach and before bedtime.
To strengthen weakened immunity, vitamin therapy is carried out against the background of antibiotic therapy. Immunomodulators are prescribed: Timalin, Immunal, Vitaferon.
Treatment of gonorrheal folliculitis with traditional methods

Traditional medicine has proven itself well in the treatment of gonorrheal folliculitis. The following products demonstrate positive and effective dynamics.
- Calendula decoction. 200 ml of boiling water is poured into 5 g of calendula, left for 20 minutes and filtered. Used to lubricate diseased areas of the skin 3-4 times a day.
- Tea tree oil. They lubricate the affected areas of the skin 3-4 times a day.
- Thistle. Crushed leaves of freshly picked thistle are pounded to a paste consistency. The resulting mass is applied to the diseased areas, covering the top with a gauze bandage. The procedure is repeated several times a day.
- Chamomile decoction. 20 g of plant leaves are poured into 200 ml of boiling water, left for 20 minutes and filtered. Use to lubricate affected areas 3-4 times a day.
- Viburnum, rosehip and nettle. Combine 200 g of viburnum and rose hips, 100 g of dried nettle and 10 g of crushed walnut shells. All components are mixed and 6 tbsp. l. pour 0.5 liters of boiling water into the mixture. The broth is boiled for 10 minutes, left covered for 24 hours and filtered. 50 ml of decoction is combined with 50 g of honey and cottage cheese. Use for compresses 3 times a day for 20 minutes.
Before using any folk remedy, you should first discuss treatment with your doctor.
- Read also about treatment of itching due to folliculitis with folk remedies
Prevention of gonorrheal folliculitis

To speed up the recovery process and avoid relapse of gonorrheal folliculitis, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene:
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Disinfect skin care items.
- Get rid of expired and open lotions and creams.
- Take a shower with baby soap 2 times a day.
- When taking a shower, wash with laundry soap.
- Do not use substances with a high concentration of alkali for washing and treating leather.
- Do not take hot baths.
- Do not visit swimming pools and saunas.
- Do not swim in open waters.
- Change bedding and clothes in a timely manner.
- Do not use other people's hygiene products and bath accessories.
- Monitor the integrity of the skin. For microtraumas, use wound-healing drugs.
- Wear clean clothes every day.
- Increase the body's immune defense.
- Sensitive and irritated skin should be disinfected.
- For other diseases (diabetes mellitus, gastrointestinal pathology, endocrine disorders, immunodeficiency), carry out proper treatment of the underlying disease.
Complications of gonorrheal folliculitis
Complications of gonorrheal folliculitis arise due to the lack of treatment for the underlying disease - gonorrhea, as well as with weak immunity and improper hygiene. Complications can be in the form of an abscess, carbuncle, boils, or the formation of follicular scars. In advanced and severe forms of the disease and with reduced immunity, meningitis, nephritis and serious forms of pneumonia occur.
- Related article: How to distinguish folliculitis from a boil



