It's rare to see a person without small dark marks on their body. Is it worth paying attention to these points? Only a doctor will distinguish between dangerous and normal moles - malignant melanoma or harmless nevus - and give recommendations on what to do with them. Is it worth worrying about the appearance of new formations, when immediate contact with specialists is required, what are the signs of cancer development - the answers to these questions remain to be found out. No one is immune from disaster, and early diagnosis will protect you from severe consequences.
What is a mole
The first tiny spots may appear in children in infancy. A mole is a small formation on the skin - a nevus - that is considered benign and harmless. The basis for their appearance is melanocyte cells that accumulate the natural pigment melanin. Depending on its quantity, a difference in color is observed. Available colors:
The shape of the tumors depends on the location and concentration of melanin. They may have a stalk or be located under the skin, be flat and convex. The most common type is round, but there are exceptions. The development of neoplasms is provoked by ultraviolet radiation - natural from the sun, in a solarium. Hereditary factors cannot be excluded. A common cause of growth is hormonal imbalance, characteristic of periods:
- puberty;
- pregnancy;
- menopause.
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin– congenital, newly acquired;
- structure– pigment, vascular;
- place of education – in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin – flat – even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats – dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
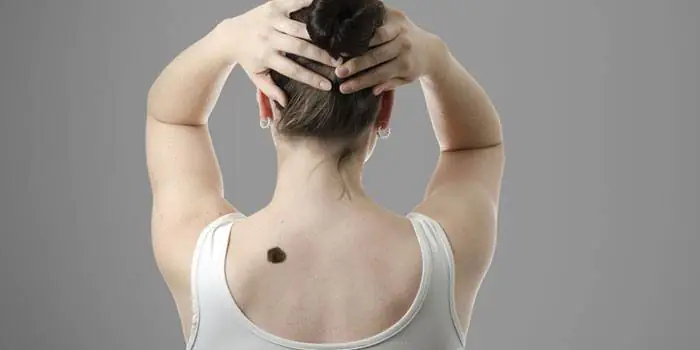
Safe moles
Those who have dark spots on their skin should be wary of their changes. In time, detected signs of degeneration into melanoma contribute to the timely removal of the formation and preservation of health. Safe moles are different:
- the presence of a stalk – it cannot be formed by malignant cells that grow randomly;
- long-term condition without changes.
Spots that appear soon after birth are not considered dangerous. It is important that they are small in size. Good – non-dangerous – signs of neoplasms include:
- flesh tone;
- unchanged pattern of the skin of the nevus and adjacent tissues;
- soft consistency;
- hair on the surface of the neoplasm - growing from the skin, indicates the absence of pathologies;
- diameter no more than 5 mm;
- symmetry;
- nevus in the form of a spot.
Which moles are dangerous?
Why do people with nevi on their bodies need to monitor their changes? There is always a threat of degeneration of non-dangerous tumors into a cancerous tumor. What moles are dangerous to health? Key signs you need to know:
- change in shades towards the dark side, the appearance of multi-color;
- rapid increase in size - exceeds two millimeters per year;
- occurrence of cracks;
- the formation of asymmetry due to uneven growth;
- lack of elasticity;
- the appearance of itching, burning;
- presence of discomfort.
The appearance of dangerous moles requires an immediate visit to a specialist to clarify the nature of the changes and the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Pathological transformations provoke:
- injury to the nevus due to negligence;
- self-removal;
- abuse of exposure to the sun, use of a solarium;
- location of the formation in places of frequent contact with clothing - on the neck, head, genitals, legs;
- placement in the hair, on the face, palms - where there is a high probability of injury;
- previously removed melanoma.
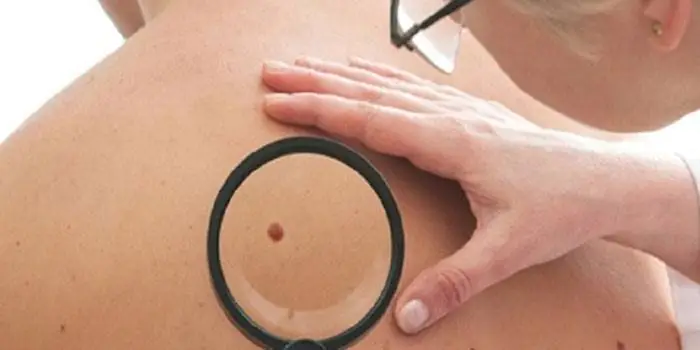
Why are moles dangerous?
Not a single person is protected from the sudden proliferation of cells of a harmless mole. Melanoma is an extremely serious disease. Changes not detected at the initial stage can result in death. The provoking factor is unsuccessful independent removal of tumors. Moles are dangerous because of their ability to:
- transform into an atypical – precancerous form;
- grow to large sizes;
- turn into cancerous;
- with minor external changes, metastases actively spread throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic channels.
How quickly does melanoma develop from a mole?
The transformation of a nevus into a cancerous formation can occur in different ways. The process depends on the stage of the disease and the type of tumor. Instant metastases are dangerous. Begins:
- growth of cancer (oncological) cells in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- their entry into the blood and lymph;
- penetration into the lungs, liver, kidneys;
- growth in these organs;
- complete damage to the body;
- death.
The growth phases of pigment cells are observed, along which melanoma develops from a mole. There are varieties:
- horizontal– damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs, lasting up to 10 years, but metastases do not appear;
- vertical– accompanied by the spread of cancer cells throughout the organs, can last two years, has an unfavorable prognosis;
- nodal – especially dangerous – characterized by deep spread within two months.
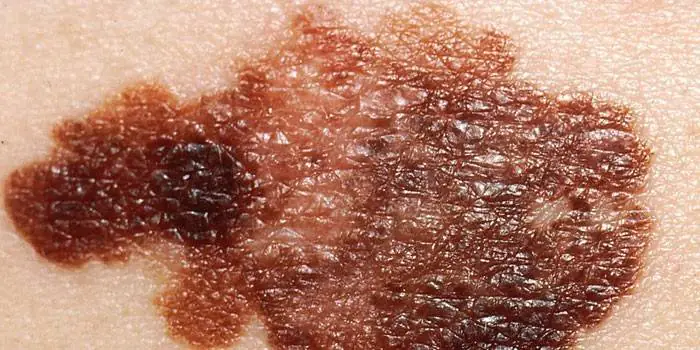
The first signs of melanoma
The patient can be assisted only when suspicious changes begin to be identified. The diagnosis, research, and referral for surgical treatment save a person’s life. The first signs of melanoma:
- increase in the height of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of discharge;
- redness;
- burning, itching;
- swelling of tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- the appearance of a crust;
- thickening;
- hair loss;
- expansion of pigmentation around the lesion.
With the further development of dangerous melanoma, the following are observed:
- significant change in size;
- the appearance of pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- surface ulceration;
- formation of new foci;
- bleeding from places of pigmentation;
- liquid separation;
- skin thickening;
- the appearance of an earthy tint;
- signs of metastases are chronic cough, weight loss, cramps, headaches.
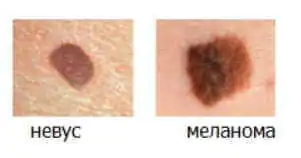
How to distinguish a mole from melanoma
To recognize which moles are dangerous and which are not dangerous, you need to know what they look like. A person with nevi, in order to avoid dire consequences, must constantly monitor the appearance of new formations and changes that occur. You can distinguish a mole from melanoma by its signs. Non-dangerous neoplasm:
- symmetrical;
- with smooth edges;
- uniform in color;
- with dimensions not exceeding 6 millimeters.
Features of dangerous melanoma that require seeking help from dermatologists:
- growth in a short time;
- pronounced asymmetry of shape;
- heterogeneity in color - the presence of inclusions of several shades;
- lack of clear boundaries - the contour line is blurred, jagged, and looks like a coastline on a geographical map;
- increased diameter over six millimeters;
- variability of any parameters - color, size, shape.
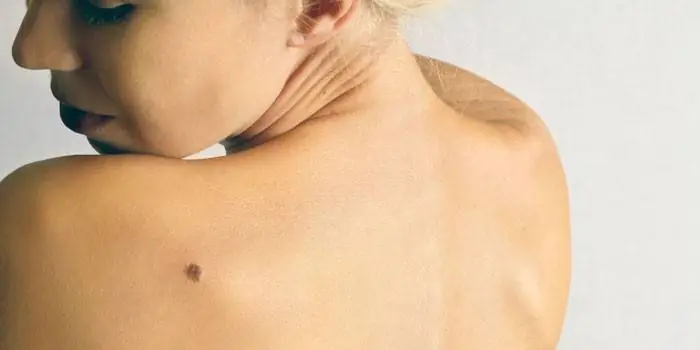
What dangerous moles look like
What do nevi that are subject to pathological changes look like? Only a doctor can correctly distinguish between non-dangerous tumors. Dangerous formations look like this:
- blue– compactions under the skin with clear boundaries, with dimensions no more than 10 mm;
- nodal– round, flat in shape, color – brown, black;
- cutaneous– often pale, convex;
- halo nevus – pigment surrounded by a light or white rim;
- spitz- looks like a dome-shaped tumor of pink shades, with the possible presence of a hole through which blood and liquid leak;
- connecting- connect individual entities into a whole.
Mole with jagged edges
One of the signs of a non-hazardous formation turning into a dangerous one is a change in contours. It often has blurred edges and scalloped borders. There are non-dangerous types of nevi - dysplastic. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis. A mole with uneven edges can be dangerous if there are additional signs of melanoma:
- accelerated changes in size;
- the presence of clearly defined asymmetry;
- the appearance of highly indented boundaries.
Rough mole
Such a neoplasm is harmless if its diameter is no more than 5 mm and remains constant in size. Often its appearance signals a lack of vitamins and nutritional disorders. Doctors advise coming for a consultation if it is discovered that:
- the smooth nevus turned into a rough one;
- bothered by burning, itching, tingling;
- irregularities and compactions appeared in the middle;
- areas with different shades formed;
- diameter has increased significantly.
A dangerous rough mole requires immediate examination if:
- the appearance of bleeding;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- rapid change in size;
- formation of asymmetry;
- formation of purulent discharge;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when touched;
- the emergence of an irregular shape, blurred boundaries, along the edges of the neoplasm.
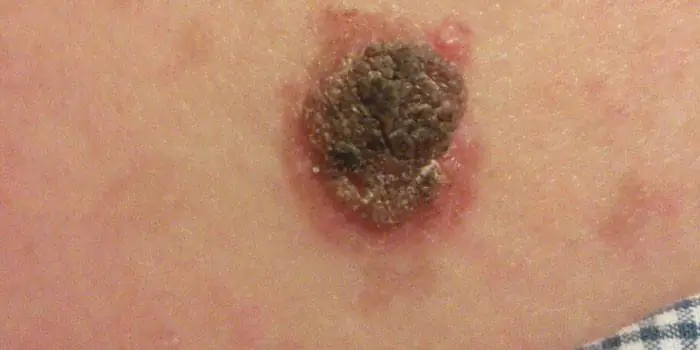
Large moles
Large formations on the skin are pigment spots. When they remain unchanged and do not cause inconvenience, this is not a dangerous phenomenon. It is important to constantly monitor their appearance, color, and size. To eliminate worries, you need to consult a dermatologist. During the visit, the specialist will conduct a diagnosis and give a forecast of the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm. Large moles become dangerous if they:
- injured;
- thickened;
- started to itch;
- were unsuccessfully removed independently;
- changed in size, shape;
- are bleeding.
What moles can be removed
Often nevi cause trouble for women when they are in a visible place - the face, neck. Even if they do not bother you, using removal will be the right decision - the appearance will improve significantly. After the procedure, the doctor must necessarily send the tissue for histological analysis to decide whether the mole is malignant or not. If the neoplasm is not dangerous, does not bother you, and does not change in size, surgery is not required. What moles cannot be removed? Experts believe:
- there are no contraindications;
- It is important to choose the right excision technique.
You should be careful about skin growths; it is unacceptable to remove them yourself. Only the doctor will determine whether a nevus is dangerous or not and decide what to do with it. You can delete it if:
- injured from clothing - on the neck, in the groin area, under the armpits;
- cause pain when touched;
- are located under the hair on the head and can be damaged when combing or cutting;
- change color, shape, outline;
- significantly increase in size;
- characterized by the presence of burning, itching;
- accompanied by inflammation and bleeding.
A birthmark is a “mark” for life. This is a “business card” that emphasizes the individual characteristics of each person. A mole does not affect your health in any way. But under some circumstances, it can degenerate into malignant melanoma, which leads to serious health problems. You need to be able to distinguish it from a birthmark and, if necessary, seek medical help.
What is a mole?
Almost every person has moles or nevi on their body. They are his “identification mark”; their location may vary. Sometimes nevi are found in the most unexpected places, causing some inconvenience to their owner.
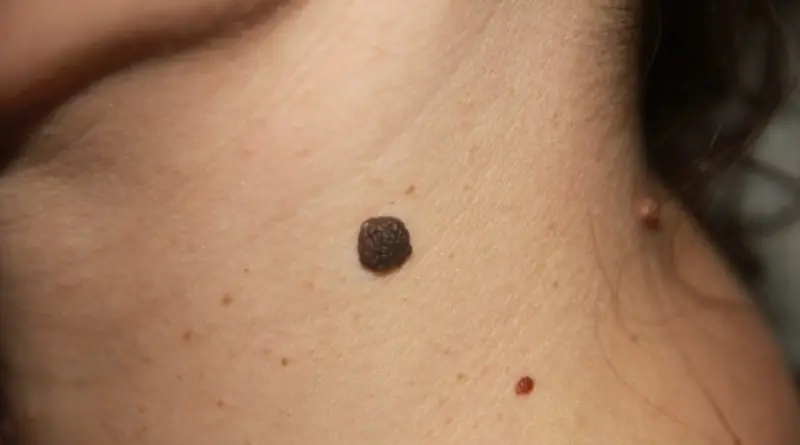
Birthmarks differ in size, color, and depth of penetration into the tissue. They are usually inherited and occur in the same areas of the body as in the parents. The color saturation of the nevus also depends on the ancestors and their genotype.
A mole is a collection of cells rich in melanin, a pigment that protects the skin from UV rays, so their normal color varies from beige to dark brown. We are talking about an abnormal accumulation, which is absolutely harmless and is considered melanoma-free until the birthmark degenerates into melanoma.
They look like flat spots of different sizes: from small (up to 1.5 cm) to large (more than 10 cm). There are also giant birthmarks that cover large areas of the skin. Their shape is varied: from round to the most unusual contours with uneven edges.
If brown spots that resemble plaques form on the skin, these are seborrheic dermatomas, hanging growths are acrochordomas, and red formations are hemangiomas.
Moles are also classified according to the depth of their location under the skin:
- border, located between the surface layer and the epidermis; they are smooth, but can grow and take on a convex shape with changes in hormonal levels or prolonged exposure to UV rays;
- epidermal, affecting the upper layer of the epidermis, flat or slightly convex;
- intradermal, which are localized in the lower layers of the skin, are distinguished by their convexity and rough surface; sometimes hairs grow from them.
There is also a gradation according to the risk of cancer:
- Dangerous ones include Ota's mole, blue and borderline nevus, congenital mole of enormous size, and atypical nevus. If the diagnosis confirms the presence of such forms of birthmarks, then you should prepare for their removal.
- All other species are classified as non-hazardous. Their malignant degeneration is possible only if the birthmark is damaged during shaving, by self-removal, or by rubbing clothes.
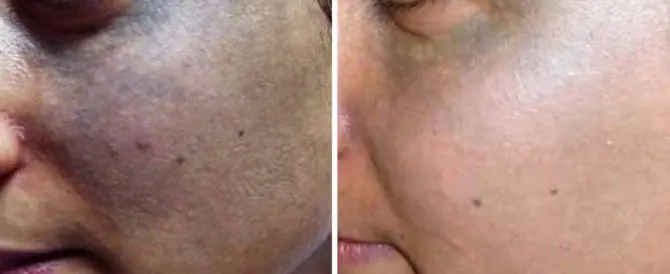
Moles occur not only for hereditary reasons. They can form due to intrauterine abnormalities in cell development, when the fetus experiences oxygen starvation or when hormonal levels change.
Characteristics of melanomas
Melanoma is one of the types of skin cancer. It is she who is called by oncologists “the queen of cancer” for her rapid growth rate and the rate of formation of metastases. It grows under the skin and on its surface in different directions and planes. Once in the inner layers of the dermis, melanoma cells are able to penetrate the bloodstream or lymph, spreading with the bloodstream throughout the body and gaining a foothold in certain organs. This is how metastases (clumps of diseased cells) form and the disease progresses quickly. Due to the rapid development, the percentage of deaths is quite high.
Among skin cancers, melanoma is the youngest, occurring even in infants and children. The female gender is more susceptible to its manifestation. A birthmark or age spots serve as a base platform, a source for degeneration into melanoma.
UV rays are considered to be the culprit of skin cancer.
Their influence increases:
- due to the thin ozone layer, the formation of “ozone holes”;
- as a result of people’s high sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- with prolonged exposure to the sun and regular sunbathing;
- with frequent visits to the solarium or hot exotic countries.
Sun exposure and solariums are especially dangerous for people who have many birthmarks on their bodies or a high tendency to pigmentation. You cannot avoid the consequences by covering moles with a band-aid or covering them with a towel: the “greenhouse effect” is harmful, increasing the risk of melanoma.
Sometimes cancer cells form “out of nowhere” for various reasons. On clean, disease-free skin, a dark-colored asymmetrical spot appears, which grows and becomes potentially dangerous. This is usually due to genetic factors and can be traced through the family tree.
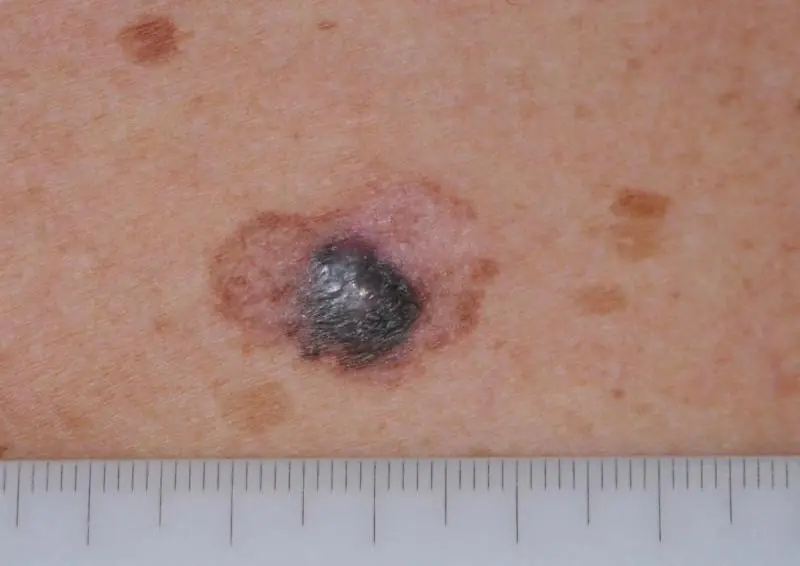
What is the difference between a mole and melanoma?
Most often, a person does not monitor the condition of pigmentation or moles that are familiar.
Meanwhile, when a birthmark degenerates, characteristic signs are noticeable:
- changing color to darker;
- lack of uniform color, peeling and loss of clear boundaries of the birthmark;
- redness along the contour of the mole as a result of its inflammation;
- surface growth and compaction;
- formation of dense nodules with signs of necrosis at the base of the nevus;
- irritation of the mole: it itches or there is a burning sensation;
- the formation of cracks and small ulcers, which may result in bleeding.
It is not so difficult to distinguish a nevus from a melanoma if you monitor the condition of the skin. If “metamorphoses” with birthmarks occur, consultation with an oncologist or dermatologist is required. It should be carried out as soon as possible, since the rapid development of melanoma leaves low chances of success.

It is not necessary to look for differences in all of the indicators mentioned. One change, for example, color or shape, is enough for it to become a signal to go to the doctor. An examination is required after visiting hot countries, if the nevus is injured or has significantly darkened.
Types of melanomas
Usually melanoma is a mole in the stage of degeneration.
There are different types of melanomas:
- Lentigo is usually seen in older people on the face or neck, protruding slightly above the surface of the skin.
- Nodular is the most aggressive manifestation of cancer. It is formed by small intertwined nodules that differ in color and volume. Raised above the epidermis and distinguished by shades of dark or purple color.
- Superficial is not much different from a regular birthmark. And since it is difficult to distinguish this type of melanoma, it is the most dangerous because it develops undetected.
- The nail is formed under the nail plate of the big toe. Every 10th melanoma patient experiences this type of pathology.
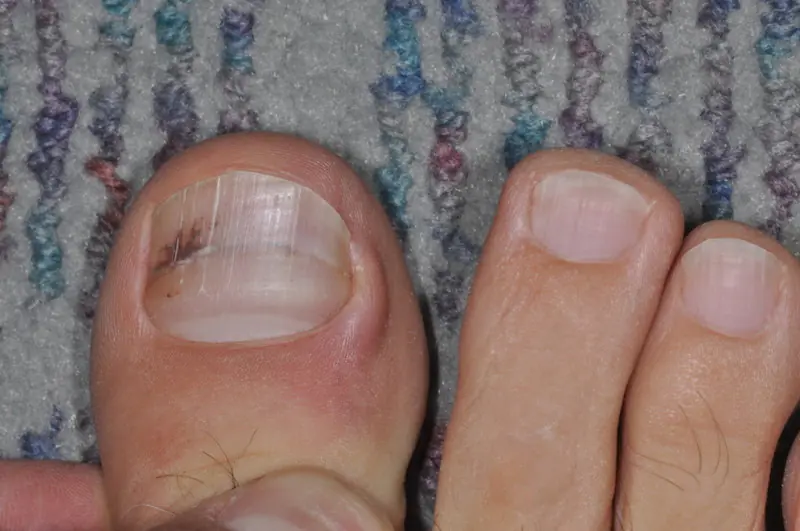
In detecting melanoma, the “black sheep” principle applies when one of the moles becomes different from the others in color, shape or other indicators. If an unusual spot is detected, you should undergo a medical examination.
Symptoms and signs of melanoma
How to distinguish malignant growth of cell mass from benign?
There are some signs that answer this question:
- if the nevus is conditionally divided into two parts, then asymmetry is noticeable;
- the birthmark loses its clear boundaries and becomes shapeless;
- the color not only changes, it becomes uneven, interspersed with different shades;
- noticeable rapid growth of the spot and redness at its borders;
- there is a burning and itching sensation.
When a nevus changes, when it begins to differ from a regular mole, the abbreviation ACORD is used (symmetry, edge clarity, color range, size, diameter are examined).
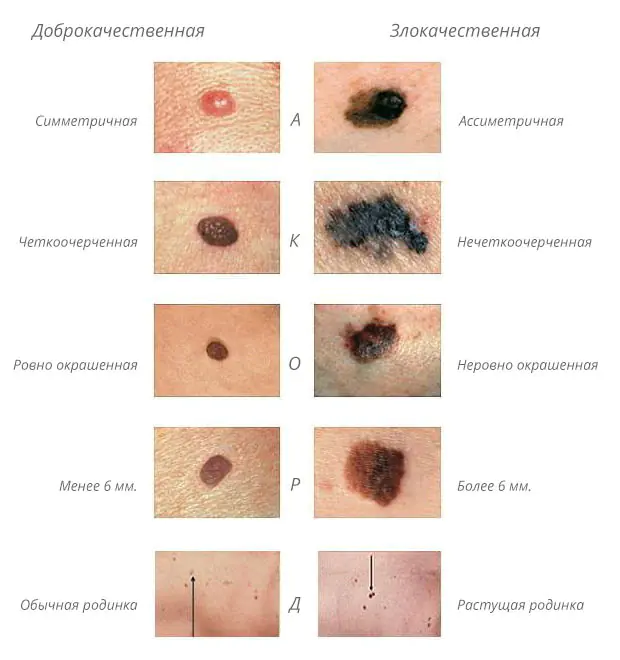
Note: To diagnose melanoma, an examination is carried out once every 3 months. It is advisable to involve another person, since moles are sometimes located in hard-to-reach places on the body. A thorough examination is carried out in the area of the legs, back, and scalp.
Reasons leading to the degeneration of moles
There are two main reasons leading to deformation of a mole: excess solar radiation and damage (irritating factors) to the nevus. Both of them are not fatal because they can be avoided. But it is generally accepted that tanning is good for health, and during the summer people try to get a beautiful skin tone.
Tanning has many negative manifestations. The skin ages prematurely and loses elasticity. Photoaging is observed: the epidermis becomes covered with pigment spots, and lentigo develops. When exposed to aggressive sunlight during the daytime, burns occur. If they are received in childhood, then at a more mature age the development of skin oncology is possible.
Tanning also leads to an abundance of age spots, which form and become clearly visible by the age of 30. At best, they are a cosmetic defect, and at worst, they lead to skin cancer.
It has been proven that people from sunny countries are more susceptible to cancer. Australia, Brazil and Israel have the highest rates of melanoma. In Europe, people in Finland and Switzerland are most likely to get sick because the level of melanin in the skin is low and it cannot protect the deeper layers of the dermis from UV radiation.
Risk factors
Based on a number of signs, each person can assess the risk of getting melanoma:
- light skin tones, poor in melanin;
- an abundance of birthmarks;
- freckles scattered all over the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- getting sunburned in childhood;
- age from 30 years;
- working in the sun or regular tanning, visiting a solarium;
- change in the appearance of moles.
People with hereditary albinism (lack of pigment in the epidermis), xeroderma, and keratosis are also at risk.
Note: Every year in Russia, 8,000 people develop melanoma. The figure is small, but those who become ill in advanced stages have a high mortality rate. Sometimes 2-3 years after removal of melanoma, metastases are discovered in the body, which complicates treatment and increases mortality.
Treatment methods for moles
If a birthmark is purely a cosmetic defect, then folk remedies are used or procedures are carried out in beauty salons. Traditional methods include lemon and garlic juice and celandine tincture.

Medical treatment includes surgery, laser removal, cryodestruction or cauterization with liquid nitrogen, and electrocoagulation.
The need to remove a nevus arises in the following cases:
- change in color or uneven tone;
- change in appearance;
- redness in the border zone;
- peeling, itching, separation;
- release of droplets of blood;
- hair loss from the birthmark;
- injury.
But if there is no special need, then the stain should be left alone and not disturb the skin again, which can lead to irreversible changes.
Treatment options for melanoma
The main methods of treating melanoma include its surgical removal. In the early stages, the disease is curable. Later ones will require radiation, chemotherapy, immunotherapy or biological treatment. Combination methods of fighting cancer are usually used.
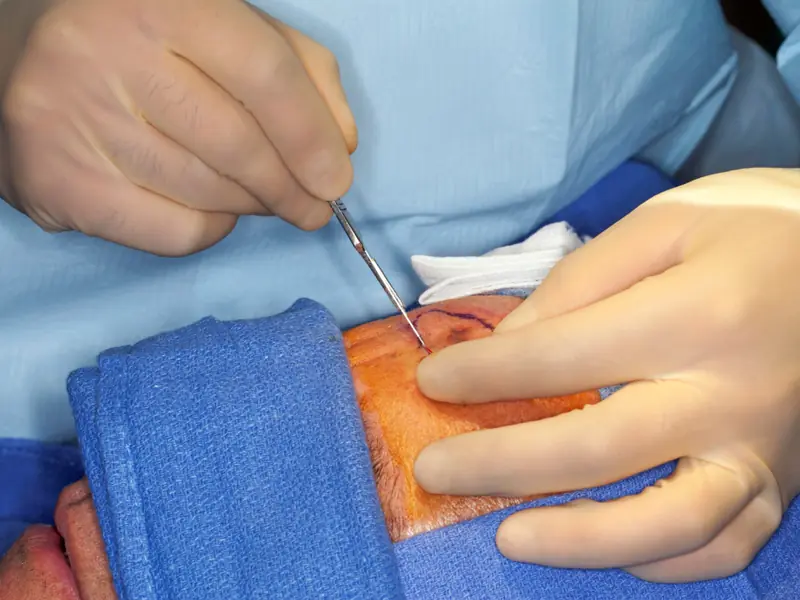
Once metastases appear, healing is impossible. In this case, the doctor aims to relieve pain and prolong the patient’s life.

Even if the tumor is removed at an early stage, the risk of relapse is quite high, when metastases are discovered in the organs after a few years.
Prevention
Prevention significantly reduces the risk of developing skin cancer.
It includes simple and accessible actions for everyone:
- Annual examinations by oncologists (dermatologists) if new spots appear or changes in the appearance of previous ones.
- Minimizing traumatic moments: do not try to get rid of moles without the help of a specialist.
- If sun exposure is necessary, use creams with UV filters to reduce the effect of sunlight on the dermis. It is undesirable to be outside on a sunny day from 10 a.m. to 5 p.m.
- After visiting exotic countries, be examined by a doctor.
- Avoid solariums, where artificial irradiation is much stronger than natural irradiation.

The rules are simple and achievable, but health is the same and it can be difficult to restore it. Therefore, take sunbathing in the morning, check the condition of your birthmarks and enjoy life, the right attitude towards which will give you many positive moments.
Every person has birthmarks of different types, textures, colors, and shapes on their body. These harmless formations arise in the epidermis from melanocytes and grow in clusters. The scientific name of a mole is nevus. This medical term applies to all skin abnormalities.
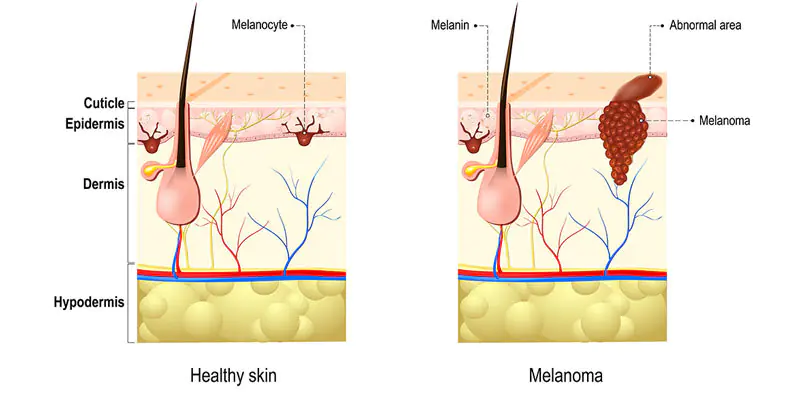
However, these so-called “floaters” can hide the most aggressive malignant tumor – melanoma. Therefore, you should know what dangerous moles are and be able to recognize the main differences between benign and malignant ones. Cancerous transformations most often occur on the basis of pigmented skin tissues.
What moles are dangerous?
Cancerous moles, like regular ones, consist of melanocytes. But this is an aggressive form of the tumor, prone to rapid spread and damage to other organs. In this regard, it is recommended to be careful with such pigmented skin formations as:
Atypical nevi
This type does not look like a regular birthmark because its size is larger than a pencil eraser, its shape is unclear, and its color is uneven. Moreover, the potential danger is posed by congenital formations, not acquired ones. Most of them are inherited and are larger than 1 cm.
Hutchinson's melanotic freckles (lentigo)
Appear as a flat spot containing two or more shades of darkening. They are quite common after the age of 50 and are localized particularly on the face. Gradually they become larger and darker, transforming into skin cancer.
Skin neoplasms of unknown etiology
Neoplasms that appear suddenly develop very quickly, are aggressive in appearance and do not at all resemble an ordinary “fly”. In 60% of all cases of melanoma, this type of pigmentation functions.
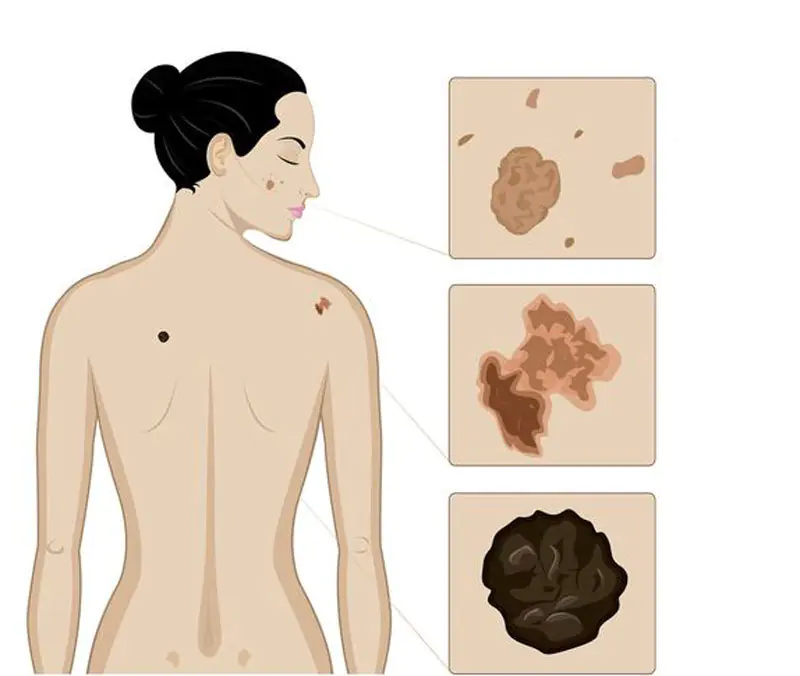
Dangerous moles: signs
Color Changes
A mole that has begun to change color is potentially cancerous. For example, one-color pigmentation has acquired some other spots around or in the middle.
Height change
An important feature is a change in the height of the previously flat spot and density (thickening).
Painful sensations
The mole hurts, the surface becomes larger, erosions appear, the release of fluid, purulent masses or blood appears.
Satellite pigmentations
The skin around the formation is also distinguished by redness, swelling or the presence of new color spots, the so-called. satellite pigmentations.
Itching and burning
There are sensations such as tingling, burning, and the mole itches.
Consistency changes
For example, a mole softens, is divided into small pieces that break off easily, or resemble scratches that do not heal.
Which moles are potentially dangerous?
There are certain categories of birthmarks that are prone to transform into a malignant form. All of them refer to abnormal skin lumps.
1. Nodular pigmented nevi: usually brown or black moles, round and flat.
2. Skin pigmented nevi: they have a raised appearance, pale color, and sometimes a hairy surface.
3. Connecting nevi combine elements of different formations.
4. Halo nevus is a pigmented area of skin surrounded by a discolored white ring.
5. Dysplastic nevus (otherwise known as Clark) is a specific neoplasm.
6. Spitz nevus: looks like a tumor-like growth on the skin. This spot is pink (but a combination of different colors is possible), dome-shaped, prone to bleeding. May have a hole through which liquid leaks.
7. Blue nevus has one of the shades of blue, shows well-defined borders, any size (but most often does not exceed 1 cm), looks like a lump under the skin.
THE MAIN DIFFERENCES OF BENIGN MOLES FROM MALIGNANT MOLES
A number of characteristics allow you to accurately determine which moles are dangerous. The benign formation is not asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle, then both sides will correspond to each other.
A cancerous lump does not meet these requirements.
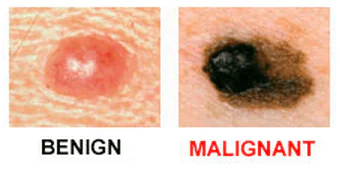
Unlike melanoma, a common pigmented spot has smooth, rather than jagged, borders.
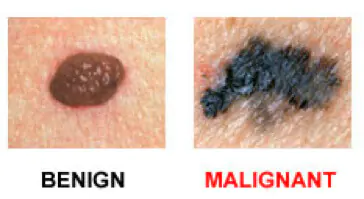
The presence of colors and brightness is another exciting symptom.
The formation changes size over time and becomes larger than 6 mm. Noncancerous nevi look the same. You need to be alert if a mole begins to grow or gives other unusual signals regarding its general condition.
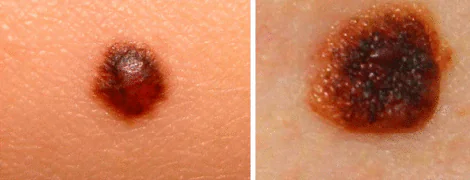
The only way to accurately establish a diagnosis and confirm or refute suspicions of cancer is to conduct a histological examination of cells using a biopsy.
Melanoma symptoms
Cancerous pigmentation can vary greatly in its symptoms. Sometimes a person is able to adequately assess only some of the features. You should pay attention to what a dangerous mole looks like. Uneven edges, but a fairly clear border with healthy tissue. Diameter – 10 mm.
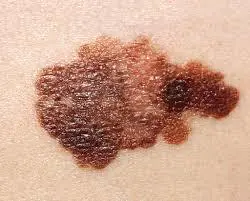
Blue-black newly formed melanoma that has irregular borders. It arose from a dysplastic nevus (pink-brown area in the upper left corner). Size about 12 mm.
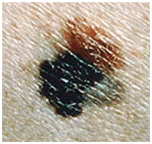
Oncological dysplastic nevus with black distant malignant extension, which was previously absent. It is only about 3 mm.
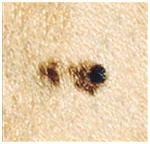
A malignant skin tumor consisting of three parts: a dark brown area on the left, a red area on the right and a light area on top. Size – about 15 mm.
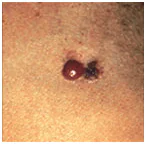
Photos of dangerous moles
Melanoma in a dysplastic nevus: irregular contours, bright color in a relatively small size (1/3 inch).
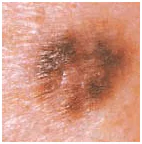
Transformation of a single atypical pigmentation with the presence of black, brown and pink colors (1/2 inch).
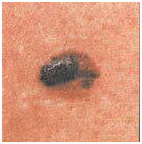
Tumor formation on the lower back demonstrates asymmetry, color saturation and changes in the zone bordering healthy skin.
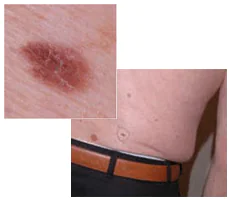
Every person should be attentive to the condition of their skin in order to diagnose dangerous moles in time and prevent possible consequences that are detrimental to health and life.
Remember that if detected early, skin cancer can be successfully treated. Published by econet.ru.
If you have any questions, ask them here
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consumption, we are changing the world together! © econet
Did you like the article? Then support us click:



