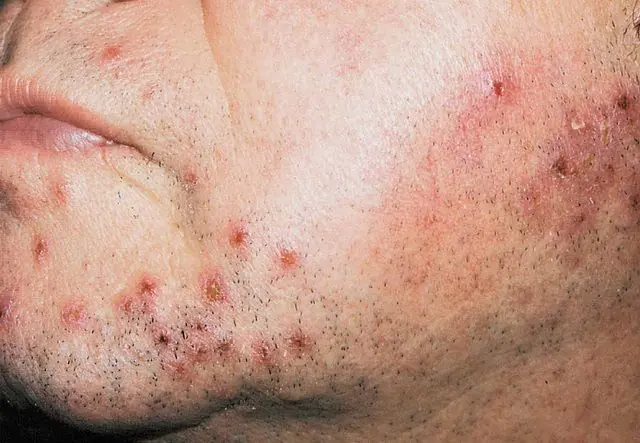
- Clinical form
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Treatment
Superficial folliculitis is a form of purulent inflammation of the upper sections (only the mouth) of the hair follicle, which is caused by staphylococci. These microorganisms are present on the skin of the majority of the population. They are also present in the environment: dust, air, soil. Most types of staphylococci that live on human skin do not cause disease. And only 10% of people have pathogenic strains. The disease often develops due to excessive sweating, scratching, dirt and irritation of the skin.
Clinical form of folliculitis
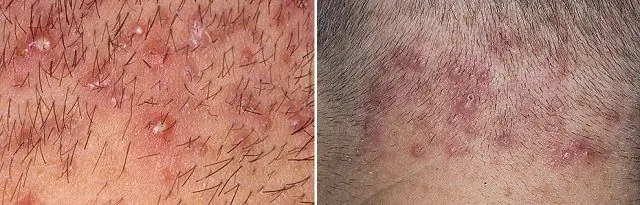
Folliculitis is distinguished between superficial and deep:
- In some cases, staphylococcal folliculitis begins with ostiofolliculitis - superficial inflammation of the pilar funnel (superficial folliculitis), covering only the mouth.
- The infection then spreads below the funnel into the depths of the follicle (deep folliculitis) and a complication may form an abscess or boil.
In this article we will talk about the causes, symptoms and treatment of superficial folliculitis (ostiofolliculitis).
Symptoms of superficial folliculitis
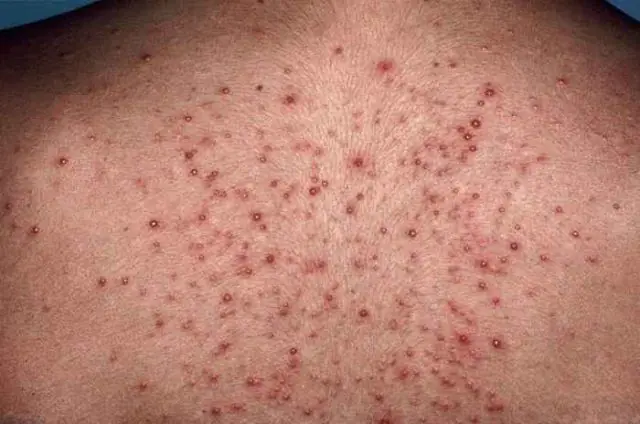
The photo shows superficial folliculitis on the back
Superficial folliculitis (ostiofolliculitis) begins with redness and the development of a small hemispherical abscess, ranging in size from a pinhead to a small pea. The pustules are filled with thick yellowish pus and are surrounded by a corolla of hyperemia with a narrow vellus hair pierced in the center. After 2–3 days, the contents of the abscess dry out and become covered with a crust, which quickly falls off, leaving no scars. The process of development of inflammation of one follicle until its resolution takes up to 1 week.
More often, folliculitis is multiple in nature. The number of pustules can reach many dozens. They are usually located on areas of the skin with hairy covering: on the face, head, groin, armpits, legs. Pustules are sometimes accompanied by pain, itching and burning sensations of varying severity. In the absence of proper treatment and compliance with hygienic standards, complications arise, and folliculitis develops into a deep form with the development of a boil, abscess, or carbuncle.
Causes of superficial folliculitis
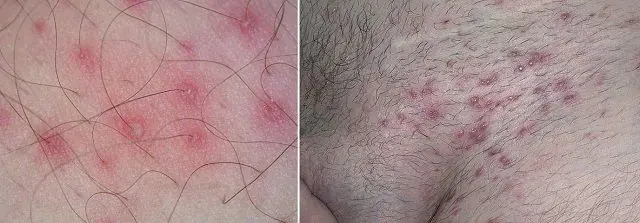
Staphylococcal superficial folliculitis most often affects men on the face in areas of stubbly hair growth (chin and skin around the mouth) after shaving. In women, folliculitis occurs less frequently, and the rashes are localized on the legs and thighs after the depilation procedure. The disease often occurs in people living in hot countries with high humidity and high air temperatures. High incidence rates occur among socially disadvantaged segments of the population who live in unsanitary conditions. Predisposing factors can also provoke folliculitis:
- Pseudomonas, viruses, fungi, gram-negative bacteria. They usually occur in immunodeficient states.
- Diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Hyperandrogenism (impaired functioning of the adrenal glands or ovaries in women).
- Lack of protein in the body.
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Hypovitaminosis A and C.
- Chronic diseases (malignant tumors, tuberculosis, digestive system).
- Acute infectious diseases (respiratory infections and influenza).
- Injuries (abrasions, scratches, burns, scratches).
- Long-term use of antibiotics.
- Improper skin care for a newborn.
- Hypothermia and overheating.
Treatment of superficial folliculitis
Treatment of folliculitis is carried out comprehensively:
- The lesions are treated with antiseptics.
- Prescribed medications for oral administration.
- Physiotherapy and herbal medicine are carried out.
- They fight concomitant diseases and eliminate chronic infection.
- Follow the rules of hygiene.
- Stick to proper nutrition.
If there is any reason for the appearance of follicles, then first of all it needs to be eliminated, and then proceed directly to the treatment of pustules. The pustules are opened and lubricated with a 1–2% alcohol solution (diamond green, salicylic, boric, camphor alcohol, etc.). The affected areas of the skin are also treated with alcohol, and pure ichthyol is applied to the nodule itself. If superficial folliculitis has progressed to a deep stage, then penicillin antibiotics are indicated. Chronic recurrent folliculitis is treated with autohemotherapy, toxoid, staphylococcus vaccine and vitamin therapy (A, C).
In the patient's diet, the amount of foods containing protein (including animal origin), plant fiber, bran and vitamins (especially carrots, black currants and rose hips) is increased. Limit the consumption of animal fats, sweet carbohydrates (sugar, chocolate, flour baked goods), spices, alcohol, strong tea, coffee and iodized salt.
The patient must use separate accessories (bed, towel, clothing, personal hygiene items). During purulent processes, pillowcases and towels are often changed, washed with disinfectants and boiled. It is recommended that the patient wash his face with cool water, since hot water stimulates the secretion of sebum. Swimming in open reservoirs, pools, baths and saunas is prohibited. The patient washes in the shower with baby or tar soap and a special dermatological shampoo.
At home, treatment is supplemented with herbal medicine. They wash themselves with infusion of birch leaves, and wipe their face with plantain juice, infusions of calendula and St. John's wort. An infusion of burdock roots is taken internally, and the lesions are treated with homeopathic medicines (Trumeel C ointment).
- Related article: Aloe vera in the treatment of folliculitis



