It's rare to see a person without small dark marks on their body. Is it worth paying attention to these points? Only a doctor will distinguish between dangerous and normal moles - malignant melanoma or harmless nevus - and give recommendations on what to do with them. Is it worth worrying about the appearance of new formations, when immediate contact with specialists is required, what are the signs of cancer development - the answers to these questions remain to be found out. No one is immune from disaster, and early diagnosis will protect you from severe consequences.
What is a mole
The first tiny spots may appear in children in infancy. A mole is a small formation on the skin - a nevus - that is considered benign and harmless. The basis for their appearance is melanocyte cells that accumulate the natural pigment melanin. Depending on its quantity, a difference in color is observed. Available colors:
The shape of the tumors depends on the location and concentration of melanin. They may have a stalk or be located under the skin, be flat and convex. The most common type is round, but there are exceptions. The development of neoplasms is provoked by ultraviolet radiation - natural from the sun, in a solarium. Hereditary factors cannot be excluded. A common cause of growth is hormonal imbalance, characteristic of periods:
- puberty;
- pregnancy;
- menopause.
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin– congenital, newly acquired;
- structure– pigment, vascular;
- place of education – in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin – flat – even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats – dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
Safe moles
Those who have dark spots on their skin should be wary of their changes. In time, detected signs of degeneration into melanoma contribute to the timely removal of the formation and preservation of health. Safe moles are different:
- the presence of a stalk – it cannot be formed by malignant cells that grow randomly;
- long-term condition without changes.
Spots that appear shortly after birth are not considered dangerous. It is important that they are small in size. Good – non-dangerous – signs of neoplasms include:
- flesh tone;
- unchanged pattern of the skin of the nevus and adjacent tissues;
- soft consistency;
- hair on the surface of the neoplasm - growing from the skin, indicates the absence of pathologies;
- diameter no more than 5 mm;
- symmetry;
- nevus in the form of a spot.
Which moles are dangerous?
Why do people with nevi on their bodies need to monitor their changes? There is always a threat of degeneration of non-dangerous tumors into a cancerous tumor. What moles are dangerous to health? Key signs you need to know:
- change in shades towards the dark side, the appearance of multi-color;
- rapid increase in size - exceeds two millimeters per year;
- occurrence of cracks;
- the formation of asymmetry due to uneven growth;
- lack of elasticity;
- the appearance of itching, burning;
- presence of discomfort.
The appearance of dangerous moles requires an immediate visit to a specialist to clarify the nature of the changes and the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Pathological transformations provoke:
- injury to the nevus due to negligence;
- self-removal;
- abuse of exposure to the sun, use of a solarium;
- location of the formation in places of frequent contact with clothing - on the neck, head, genitals, legs;
- placement in the hair, on the face, palms - where there is a high probability of injury;
- previously removed melanoma.
Why are moles dangerous?
Not a single person is protected from the sudden proliferation of cells of a harmless mole. Melanoma is an extremely serious disease. Changes not detected at the initial stage can result in death. The provoking factor is unsuccessful independent removal of tumors. Moles are dangerous because of their ability to:
- transform into an atypical – precancerous form;
- grow to large sizes;
- turn into cancerous;
- with minor external changes, metastases actively spread throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic channels.
How quickly does melanoma develop from a mole?
The transformation of a nevus into a cancerous formation can occur in different ways. The process depends on the stage of the disease and the type of tumor. Instant metastases are dangerous. Begins:
- growth of cancer (oncological) cells in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- their entry into the blood and lymph;
- penetration into the lungs, liver, kidneys;
- growth in these organs;
- complete damage to the body;
- death.
The growth phases of pigment cells are observed, along which melanoma develops from a mole. There are varieties:
- horizontal– damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs, lasting up to 10 years, but metastases do not appear;
- vertical– accompanied by the spread of cancer cells throughout the organs, can last two years, has an unfavorable prognosis;
- nodal – especially dangerous – characterized by deep spread within two months.
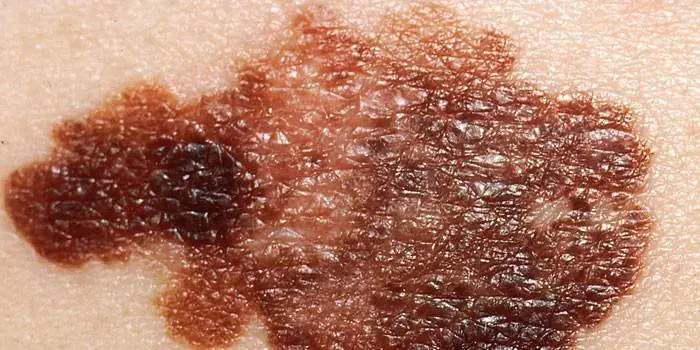
The first signs of melanoma
The patient can be assisted only when suspicious changes begin to be identified. The diagnosis, research, and referral for surgical treatment save a person’s life. The first signs of melanoma:
- increase in the height of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of discharge;
- redness;
- burning, itching;
- swelling of tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- the appearance of a crust;
- thickening;
- hair loss;
- expansion of pigmentation around the lesion.
With the further development of dangerous melanoma, the following are observed:
- significant change in size;
- the appearance of pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- surface ulceration;
- formation of new foci;
- bleeding from places of pigmentation;
- liquid separation;
- skin thickening;
- the appearance of an earthy tint;
- signs of metastases are chronic cough, weight loss, cramps, headaches.
How to distinguish a mole from melanoma
To recognize which moles are dangerous and which are not dangerous, you need to know what they look like. A person with nevi, in order to avoid dire consequences, must constantly monitor the appearance of new formations and changes that occur. You can distinguish a mole from melanoma by its signs. Non-dangerous neoplasm:
- symmetrical;
- with smooth edges;
- uniform in color;
- with dimensions not exceeding 6 millimeters.
Features of dangerous melanoma that require seeking help from dermatologists:
- growth in a short time;
- pronounced asymmetry of shape;
- heterogeneity in color - the presence of inclusions of several shades;
- lack of clear boundaries - the contour line is blurred, jagged, and looks like a coastline on a geographical map;
- increased diameter over six millimeters;
- variability of any parameters - color, size, shape.
What dangerous moles look like
What do nevi that are subject to pathological changes look like? Only a doctor can correctly distinguish between non-dangerous tumors. Dangerous formations look like this:
- blue– compactions under the skin with clear boundaries, with dimensions no more than 10 mm;
- nodal– round, flat in shape, color – brown, black;
- cutaneous– often pale, convex;
- halo nevus – pigment surrounded by a light or white rim;
- spitz- looks like a dome-shaped tumor of pink shades, with the possible presence of a hole through which blood and liquid leak;
- connecting- connect individual entities into a whole.
Mole with jagged edges
One of the signs of a non-hazardous formation turning into a dangerous one is a change in contours. It often has blurred edges and scalloped borders. There are non-dangerous types of nevi - dysplastic. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis. A mole with uneven edges can be dangerous if there are additional signs of melanoma:
- accelerated changes in size;
- the presence of clearly defined asymmetry;
- the appearance of highly indented boundaries.
Rough mole
Such a neoplasm is harmless if its diameter is no more than 5 mm and remains constant in size. Often its appearance signals a lack of vitamins and nutritional disorders. Doctors advise coming for a consultation if it is discovered that:
- the smooth nevus turned into a rough one;
- bothered by burning, itching, tingling;
- irregularities and compactions appeared in the middle;
- areas with different shades formed;
- diameter has increased significantly.
A dangerous rough mole requires immediate examination if:
- the appearance of bleeding;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- rapid change in size;
- formation of asymmetry;
- formation of purulent discharge;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when touched;
- the emergence of an irregular shape, blurred boundaries, along the edges of the neoplasm.
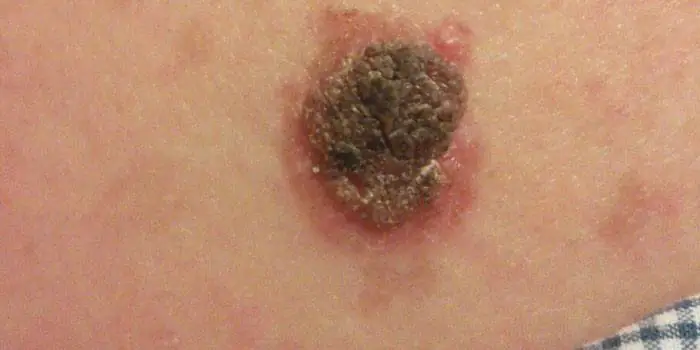
Large moles
Large formations on the skin are pigment spots. When they remain unchanged and do not cause inconvenience, this is not a dangerous phenomenon. It is important to constantly monitor their appearance, color, and size. To eliminate worries, you need to consult a dermatologist. During the visit, the specialist will conduct a diagnosis and give a forecast of the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm. Large moles become dangerous if they:
- injured;
- thickened;
- started to itch;
- were unsuccessfully removed independently;
- changed in size, shape;
- are bleeding.
What moles can be removed
Often nevi cause trouble for women when they are in a visible place - the face, neck. Even if they do not bother you, using removal will be the right decision - the appearance will improve significantly. After the procedure, the doctor must necessarily send the tissue for histological analysis to decide whether the mole is malignant or not. If the neoplasm is not dangerous, does not bother you, and does not change in size, surgery is not required. What moles cannot be removed? Experts believe:
- there are no contraindications;
- It is important to choose the right excision technique.
You should be careful about skin growths; it is unacceptable to remove them yourself. Only the doctor will determine whether a nevus is dangerous or not and decide what to do with it. You can delete it if:
- injured from clothing - on the neck, in the groin area, under the armpits;
- cause pain when touched;
- are located under the hair on the head and can be damaged when combing or cutting;
- change color, shape, outline;
- significantly increase in size;
- characterized by the presence of burning, itching;
- accompanied by inflammation and bleeding.
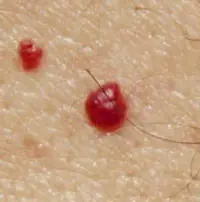
Many people have red dots on their bodies, like moles. Large, small, multiple and single, convex and flat - such neoplasms can have a completely different character. But for the most part they are benign and do not pose a particular threat to health.
However, this does not mean that they are absolutely safe. Angiomas on the body can also cause harm if they are often subjected to mechanical stress and become inflamed. In view of this, many angiologists and oncodermatologists recommend getting rid of such growths as soon as they are noticed.
But what does it mean if red moles appear on the body? How can they affect health, and what methods of treatment does modern medicine have?
What is angioma, what can it be, and why is it dangerous?
What do red moles on the human body mean? Angiomas are neoplasms that form from blood vessels. Blood circulates inside them, so if they are injured, intense bleeding can occur, which is sometimes very difficult to stop.
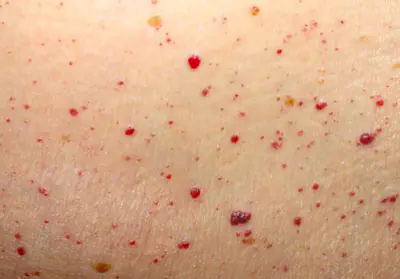
Red moles are mostly benign in nature, but still, they require special attention due to the fact that:
- when injured, they become easily inflamed;
- they are prone to overgrowth;
- new growths may appear on the body throughout a person’s life;
- some types of angiomas, in particular hemangiomas, can become malignant (rare, but still possible).
Angiomas have their own classification, according to which they are divided into:
- Pineal. Such a vascular mole is a small convex neoplasm, which can be clearly seen due to the fact that it protrudes sharply above the surface of the skin.
- Nodular, the main feature of which is the complete absence of capillary branches. This growth looks like a red dot on the skin, like a mole, and occurs when a blood vessel comes to the surface of the skin.
- Branched (spider-like). The appearance of such red moles on the body is a consequence of the branching of blood vessels from the main, “maternal” angioma.
- Flat. These red moles on the skin look like small lumps or dots.
On a note. If the neoplasm appears due to an abnormal development of blood vessels and their plexus, then it is called a hemangioma. It looks like a red convex mole, and it is this mole that is most susceptible to mechanical damage, followed by bleeding and inflammation.
A rarer type of such tumors is lymphangioma. It appears due to disruption of the human lymphatic system.
Causes of angiomas on the body
There are several reasons for the appearance of red moles on the body. They are often associated with processes occurring in the human body - both pathological and physiological. External factors rarely lead to the formation of vascular moles.
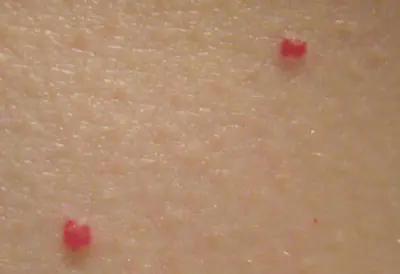
As practice shows, a large number of such growths are congenital. However, for some people they may appear in childhood, for others during adolescence, for others throughout adulthood.
So, why do red moles appear on the body? The most common provocateurs of such growths are described below.
Changes in hormonal status
The reasons for the appearance of angiomas on the body in women very often lie in changes affecting the hormonal balance. Of course, they occur mainly during pregnancy, during perimenopause and menopause.
But the balance of hormones can also change for pathological reasons, so non-pregnant women, as well as men and children who have such growths, should consult a doctor. In this case, only a specialist will be able to understand what kind of red moles are on the patient’s body and decide whether they need to be removed.
Mechanical damage to the skin
Despite the fact that external factors rarely provoke the appearance of small red moles on the body, this case is an exception. During shaving, when mechanical damage to the skin and capillaries occurs, subcutaneous hemorrhage may occur, followed by improper fusion of blood vessels. As a result, red formations appear on the skin in the form of a mole. And this applies not only to the face, but also to other areas of the body (especially in women) where there is unwanted hair that can be removed by shaving.
Disorders of the liver or pancreas, gastrointestinal diseases
The reasons why red moles appear on the body can be diseases of the digestive tract, as well as malfunctions of the liver or pancreas. It is possible to understand that it was these problems that provoked the formation of angiomas by looking at the location of the latter. If they occur in the upper part of the body - on the stomach or chest - then it is quite possible that similar pathologies are the cause. With such suspicions, you need to go to either a therapist or a gastroenterologist.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
In middle-aged and elderly patients, the appearance of red dots on the body that look like moles is often caused by cardiovascular disease. Hypertension, ischemia, previous heart attacks or strokes, atherosclerotic disease, etc. - this is just a small list of those pathologies of the cardiovascular system that can provoke a plexus of blood vessels with the subsequent formation of angiomas.
If this is really the case, then red moles will be localized mainly on the chest.
Other reasons
If a regular mole turns red, it means that it is inflamed. This can happen when its surface rubs against clothing, or when it is overexposed to UV radiation (in the sun and in a solarium).
The appearance of new tumors in some patients is due to autoimmune pathologies, lipid metabolism disorders in the body, or heredity. This process can also be affected by kidney pathologies, in particular pyelonephritis.
Thus, the reasons for the formation of angiomas and hemangiomas are completely different, and there are many of them. Therefore, it is often difficult or even impossible to understand them on your own.
On a note. Even if the growths do not cause concern, it is better to show them to a doctor. The specialist will tell you whether it is possible to remove red moles that are present on the body of a particular patient.
Ways to deal with red moles on the skin
Removing red moles using instrumental or surgical methods is a last resort. Although, if the neoplasm is truly benign, then the patient can get rid of it at his own request. Especially if it is located on the face and causes aesthetic discomfort.
Other indications for removing red raised spots on the body are:
- frequent friction and inflammation of tumors;
- rapid increase or proliferation of spots;
- the addition of secondary unpleasant symptoms: itching, peeling, burning, swelling.
Important! Under no circumstances should you try to get rid of red moles using home methods! It is especially dangerous to burn them with acid or alkalis. Such rash actions can lead to serious damage to its cells, which can subsequently develop into cancer.
If a red mole on the chest, neck, face or other part of the body is problematic, that is, it gets wet, turns purple, and often becomes inflamed, then it is advisable to consult a dermatologist-oncologist rather than a regular dermatologist. An experienced specialist will be able to assess the nature of the tumor even by eye, and will prescribe the necessary tests in order to be absolutely sure that the growth is benign.
What to do?
So, how to get rid of red moles? Modern medicine offers several options for solving an unpleasant problem.
- Laser coagulation. With the help of a powerful, correctly focused light beam, the bulge is excised. The method is absolutely bloodless, since during the removal of a vascular tumor, the capillaries in the area of healthy skin are immediately sealed (coagulated) with a laser.
- In addition to coagulation, laser vaporization can also be performed - a procedure that has the same principle, but the neoplasm is not burned out, but “evaporated.” That is, under the influence of the beam, all the liquid evaporates, the growth dries up and falls off. This method of instrumental treatment of benign skin tumors is especially good for large hemangiomas.
- Radiofrequency ablation. Using a special device, microwaves are supplied through a radio knife, which destroy the structure of the angioma, thereby provoking its death.
- Cryotherapy. Freezing growths with liquid nitrogen for angiomas or hemangiomas is rarely done. Firstly, this is a very unpleasant, even painful, procedure (although some patients claim that they did not feel pain). Secondly, cryodestruction is less effective for these types of tumors than laser coagulation or vaporization. Thirdly, when removing a growth with a laser, tissue can be collected for histological examination. Cryotherapy does not provide such an opportunity.
Some hemangiomas can be removed through surgery. As a rule, this method of treatment is resorted to when there is a risk of tumor degeneration.
Before excision of angiomas, as well as after it, a histological examination of the tissue obtained during therapeutic manipulation is carried out. Results are ready in approximately 2 weeks.
Many laboratories work on the principle: if everything is fine, no one bothers the patient, the results simply do not come. If there is a risk of malignancy of the growth, the patient must undergo a series of other diagnostic studies, based on the data of which a decision on further treatment will be made.

Skin neoplasms are the result of intensive division of epidermal cells and, by their nature, can be benign or malignant, capable of developing into skin cancer.
Moles, papillomas, nevi and many other skin growths are present on the skin of the vast majority of people.
Some growths do not pose a threat to health, but there are also those that, under the influence of negative factors, change and develop into malignant tumors. In order not to miss the moment when a harmless mole begins to transform into skin cancer, it is necessary to independently monitor the condition of all skin growths and regularly undergo medical examination.
Types of growths on the skin
All neoplasms developing from skin cells are classified into:
1. Benign, not posing a serious threat, but capable of causing physical and mental discomfort if extensively localized or located on areas of the body not covered by clothing.
2. Malignant, which is essentially a cancerous tumor. These growths quickly grow, affect the deep layers of the dermis and spread metastases throughout the body.
3. Borderline, potentially capable of transforming into a malignant form.
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
|---|---|
| Laser removal of papillomas, warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 300 — 600 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 600 — 1200 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1200 — 2400 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 2 400 — 5 000 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 1000 — 3600 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6550 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 8250 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 12 350 |
Make an appointment
Let's look at the features of these skin growths in more detail.
It is formed during blockage of the sebaceous gland and has the appearance of a compacted “ball” rising above the skin, which does not cause discomfort. Atheromas can form on any part of the body, including in the genital area; the neoplasm can be either single or multiple. In case of suppuration and inflammation, atheroma can be removed by surgical excision or laser.
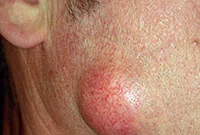
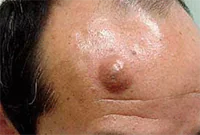
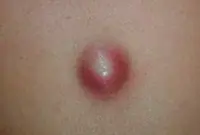
If the functioning of the ducts of the sebaceous glands is seriously impaired, then without special treatment of the underlying problem, they will be re-clogged and, as a result, atheromas will appear again and again, usually in the same place.
A vascular neoplasm that can be localized in both the upper and deep layers of the skin, as well as internal organs, and affect the vascular network. It has a burgundy or bluish-black tint and can reach large sizes. Treatment involves laser removal of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy or surgery.
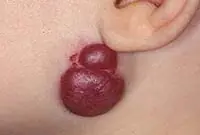
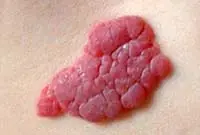
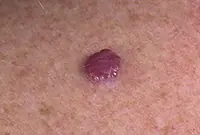
Hemangiomas most often occur on the body, but can sometimes develop on the scalp, face, neck, upper and lower extremities. The neoplasm itself is not dangerous, but it is very easy to injure. Injuries to hemangiomas are accompanied by heavy bleeding.
This type of tumor develops on the vessels of the lymphatic system and is characterized by slow growth. The disease occurs during intrauterine development of the fetus. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the tumor, as a rule, increases significantly in size, which becomes an indication for its surgical removal.
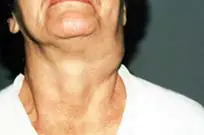
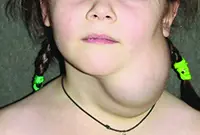

Lymphangioma primarily affects children and is easily diagnosed during the first year of a child’s life. The tumor itself is not dangerous, but its tendency to spontaneous and almost instantaneous growth can harm the child’s internal organs and even threaten his life.
A lipoma or wen is a benign tumor that develops under the skin from adipose tissue cells. The neoplasm can occur on almost any part of the body where, one way or another, subcutaneous fat is present. The neoplasm is felt under the skin as a small movable compaction; the tumor is absolutely painless.
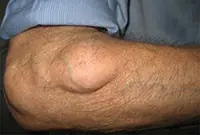

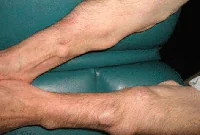
Lipomas can be single or multiple. The tumor is prone to growth. And, despite its benign quality, it causes aesthetic and, often, physical discomfort to the patient. That is why it is advisable to remove lipomas using modern methods. You can learn more about lipomas in the article “Lipoma or wen: what is it?”
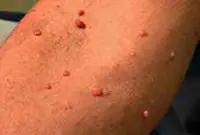
5. Papillomas and warts
Warts and papillomas are benign neoplasms that develop from epithelial tissue. They have a similar viral origin, but different places of formation and development. The cause of the appearance of papillomas and warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is very common in the world.
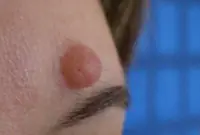
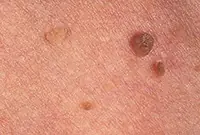

New growths are usually painless. Externally, they are small (up to several millimeters) horny outgrowths on the skin. The appearance of warts and papillomas most likely signals a weakened immune system, and the combination of antiviral therapy with correction of the immune system leads to complete elimination of tumors. Today, the most effective treatment method is laser coagulation; learn more about the removal of papillomas and the removal of warts using this method.
6. Nevi and moles
Nevi and moles are formed from melanocytes - cells containing the main coloring pigment of the body. As a rule, most of these tumors are not dangerous to health. However, their size and location can create some discomfort, especially if they are located on the face or open parts of the body.
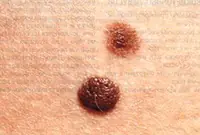
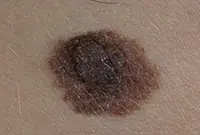

7. Fibroma
Fibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from connective tissue cells. The tumor has the appearance of spherical nodules protruding above the skin with a smooth or warty surface. The color of fibroids can be bluish-black, gray, or brown. More detailed information on fibroids can be obtained in the article "Skin fibroids. Description, symptoms, consequences. Laser removal."
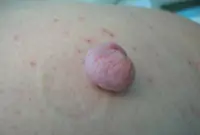
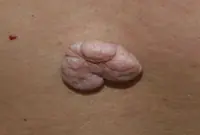
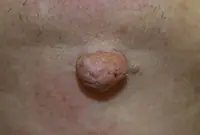
The tumor grows slowly, usually without causing much discomfort to the patient. Often, fibroma does not pose a threat to life, but when exposed to unfavorable external factors, as well as various carcinogens, it can develop into a malignant form - fibrosarcoma. The safest and most effective method for removing fibroids is laser therapy.
8. Neurofibroma
Neurofibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from nerve cells. Most often, the tumor is located under the skin, in the area of subcutaneous fat. However, in some cases, it can also affect soft tissues, as well as the roots of the spinal cord.
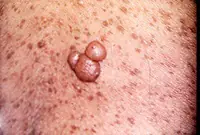

The neoplasm has the appearance of a dense tubercle with a pigmented surface. It can take on multiple forms and in this case requires treatment with medication or surgery.
Sign up for laser tumor removal
1. Melanoma
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor; one of the types of skin cancer. Melanoma is often a consequence of the malignancy of certain moles and pigmented nevi. You can learn more about melanoma in our article “Skin cancer: melanoma.”.
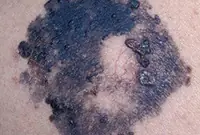
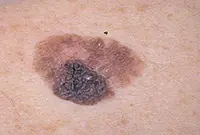
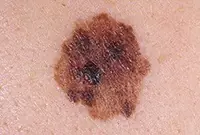
The disease is very aggressive. The tumor not only grows rapidly, but also metastasizes to almost all internal organs, including the brain. Of all the types of cancer known today, melanoma is one of the deadliest. The survival rate for patients with melanoma is very low.
2. Basalioma
Basalioma develops from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis; the neoplasm belongs to one of the types of skin cancer. The tumor is a nodular formation that, as it progresses, turns into mushroom-shaped growths or ulcers. More information about basal cell carcinoma can be found in the corresponding article "Bas cell carcinoma. Skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma.".
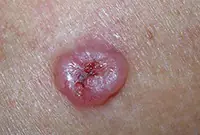
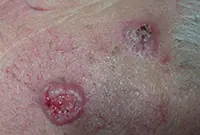
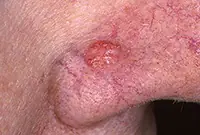
3. Sarcoma Galoshi
Multiple malignant skin tumors; dark spots that, as they grow, merge into large affected areas. The disease is often diagnosed in patients with HIV infection and has extensive statistics of deaths.
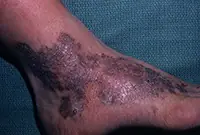
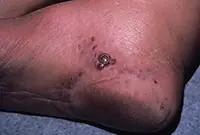
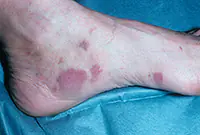
The tumor most often affects the feet, legs and hands. Since Kaloshi sarcoma is only a consequence of more serious internal diseases, its treatment is aimed solely at reducing symptoms.
Sign up for laser tumor removal
Precancerous:
1. Bowen's disease
At the initial stage, the tumor is localized in the upper layers of the epidermis, but without treatment it develops into invasive skin cancer and metastasizes. It looks like brownish plaques with a flaky surface, under which is hidden an area of weeping epidermis.
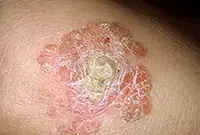
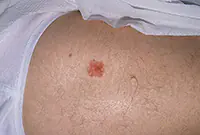
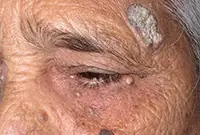
As a rule, the tumor develops in men over 40 years of age under the influence of various carcinogens. Mainly the genital organs are affected, as well as the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Treatment of the disease is usually local, and in case of extensive lesions, surgical intervention is also possible.
2. Xeroderma pigmentosum
An extremely rare disease that arises from age spots in people with increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. In the early stages it is treated with medication, in the later stages - surgically.
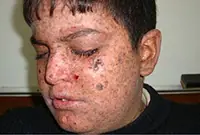
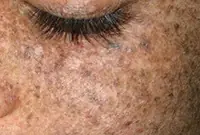
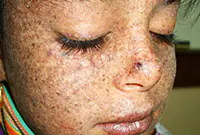
3. Senile keratoma
It looks like skin rashes consisting of scaly spots. The malignant form is characterized by the formation of compactions in the affected areas. Detailed information about keratomas can be found in our article "Keratoma. Description of pathology. Types of keratomas."
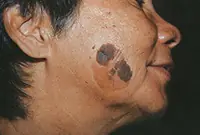
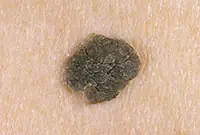
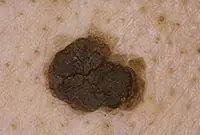
Senile keratoma occurs, as a rule, in older people. The likelihood of malignancy of this pathology is very high. As a rule, keratoma easily degenerates into squamous cell skin cancer. Modern technologies make it possible to easily and quickly remove keratoma using a laser.
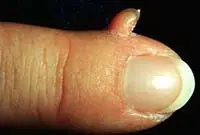
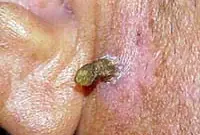
4. Cutaneous horn
Proliferation of epidermal cells, forming a cone-shaped elevation with a multilayer scaly structure. It is most often diagnosed in older people and, without appropriate treatment, tends to develop into a malignant form. The skin horn is removed surgically or by laser coagulation.

Sign up for laser tumor removal



