Very often you can observe strange new growths on the surface of the skin, in addition to the usual moles or acne. The appearance of a growth of an undetermined nature should cause concern and become a pretext for an immediate visit to a dermatologist. Neoplasms can cause a number of problems, including the development of skin cancer. Even the most harmless wart should be checked by a doctor to ensure it is benign. What types of skin growths are there and what they pose as a threat.
Types of growths
Skin growths are divided into three main groups - benign, malignant and precancerous. And each group has its own subspecies.
Benign
Such neoplasms on the skin do not pose a direct threat to their carrier unless they are subjected to various types of mechanical influence.
Atheroma
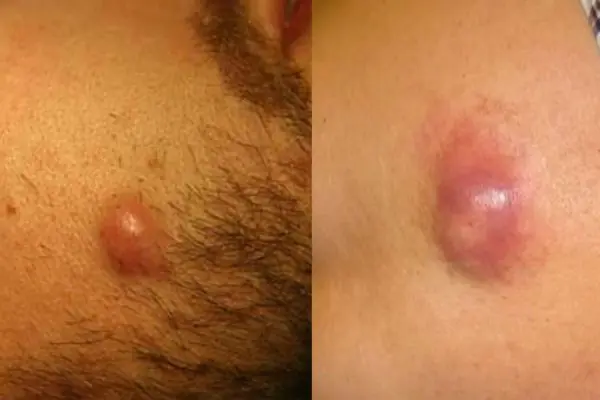
A skin tumor that forms as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands. Externally, the growth resembles a small dense bump, with a clearly defined contour. This cone feels very elastic and mobile to the touch. When palpated, it does not cause pain or other discomfort. The lump can fester and even burst. When a rupture occurs, a purulent-sebaceous fluid is released from the growth. During the period of inflammation, the temperature rises and the atheroma can hurt. The growth forms in places where there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands - on the scalp, neck, back, and groin area.
Hemangioma
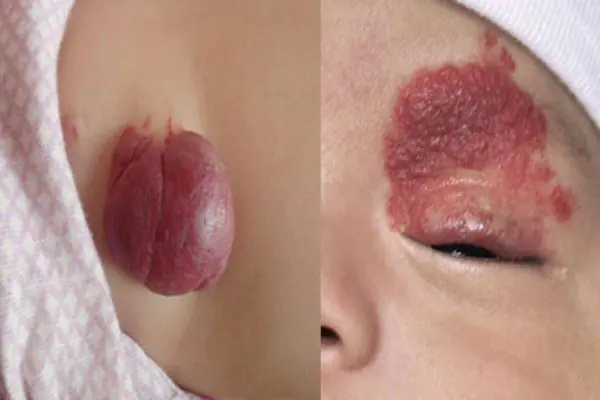
Hemangioma is a vascular tumor neoplasm, it can be:
- Capillary - a growth on the surface of the skin that can reach large sizes. Color from red to bluish. Often grows to the sides.
- Tricky - limited subcutaneous nodular growth. The skin in the area of a cavernous hemangioma usually turns red. Such tumors often appear in newborns in the neck and head area.
Lymphangioma
A tumor that develops on the walls of the vessels of the lymphatic system. The tumor is characterized by very slow growth. An inflated skin tumor grows in the area of the lymph nodes; it is painless. The neoplasm can be cystic, consisting of several isolated or combined cysts. The disease mainly affects children, but can also develop in adults. This disease usually occurs in the fetus during intrauterine development. The disease is not dangerous, but tends to grow instantly under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors. In this case, immediate surgical excision is required.
Lipoma or wen
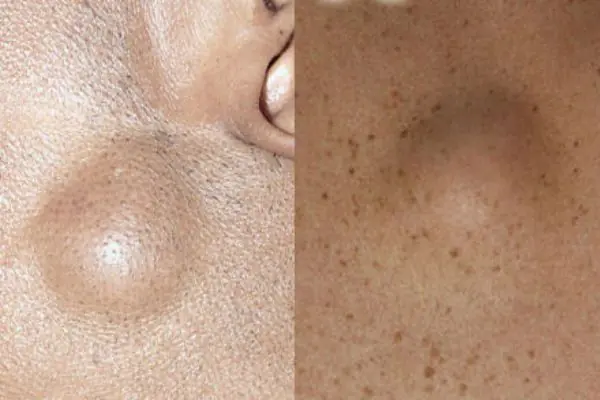
A neoplasm that develops under the skin from fatty tissue cells. Externally, the wen looks like atheroma. The subcutaneous lump is completely painless. It feels like a hard and moving ball when palpated. Lipoma can develop on any part of the body where there is subcutaneous fat. The growth can be single or multiple. One wen can grow in size from a large pea to a medium-sized apple. The tumor brings aesthetic discomfort to its owner.
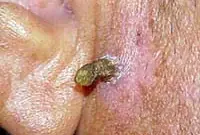
Papillomas and warts
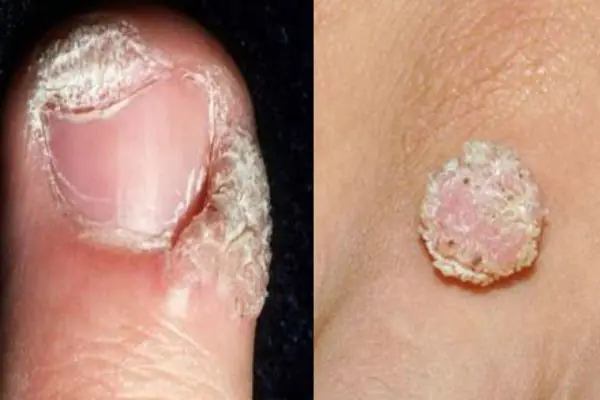
Growths on the skin that form from epithelial tissue. Such growths can be spherical (in the form of a papilla), horny (thread-like) or flat. The neoplasms are small and painless. They can develop on any part of the body. The color of the growths can be flesh-colored, brown, red and even black. The appearance of warts signals the presence of HPV (human papillomavirus) in the body.
Nevi and moles
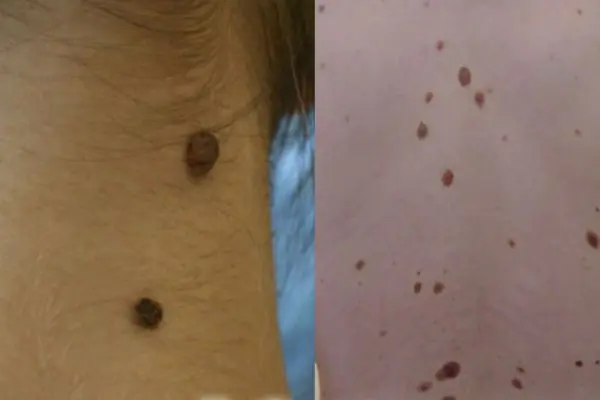
These are congenital or acquired flat neoplasms in the form of one or several spots. Such growths are a small or large accumulation of cells overflowing with the natural coloring pigment - melanin. New growths can vary in color (from beige to dark brown), texture, shape and size. Such growths do not pose any particular harm to health.
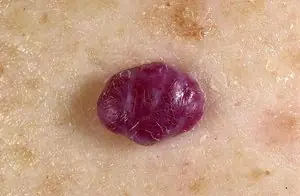
Fibroma
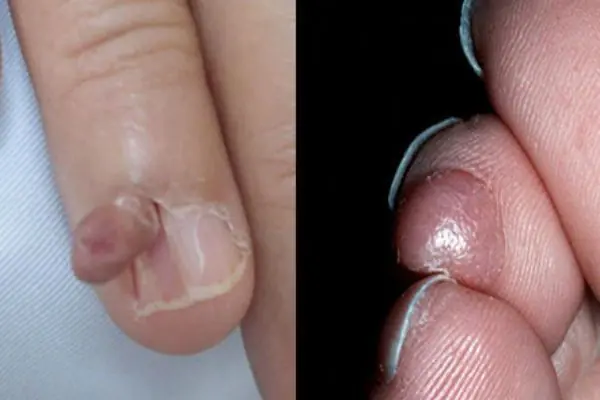
A growth that forms from an accumulation of connective tissue. Externally, fibroma resembles a wart on a thin stalk. The growth looks like a cluster of small spherical skin nodes. The surface of the fibroma can be smooth or loose. The color of the growth varies from flesh-pink to dark brown. Fibroma grows very slowly and does not cause discomfort (except for mechanical inconvenience caused by clothing or its location). If there is no effect on the fibroid, it is safe.
Neurofibroma
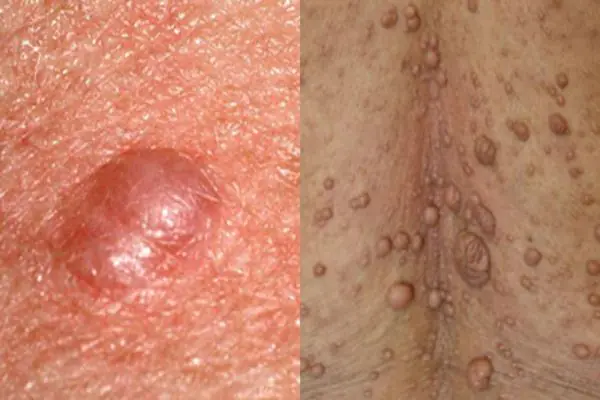
A skin neoplasm that forms from nerve cells. Most often it develops due to stress and nervous overexcitation. Often the growth is located in the area of subcutaneous fat and under the skin itself. Externally, the neoplasm is a dense tubercle, with a pigmented outer ball of skin. The growths quickly grow over the skin and are very rarely isolated. Most often it affects the back, neck, elbows and knees.
Malignant
This category of skin tumors often appears through the degeneration of a benign growth into a malignant one. Such growths require immediate identification and disposal.
Melanoma
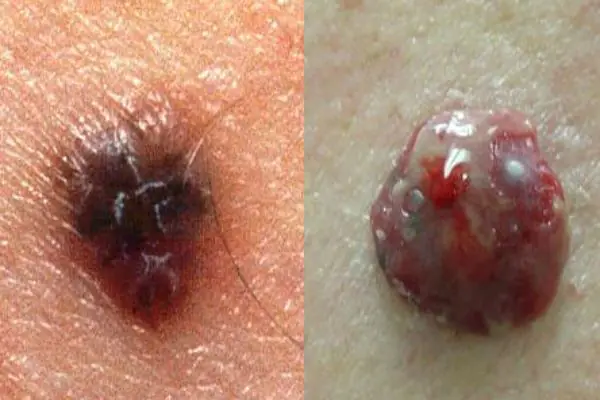
A neoplasm that occurs as a result of incorrect removal of a mole (nevus) or its degeneration into a malignant form. Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. The disease is very aggressive and quickly spreads throughout the skin. Such a tumor very soon metastasizes throughout the body, to internal organs and even to the brain.
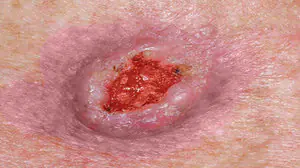
Basalioma
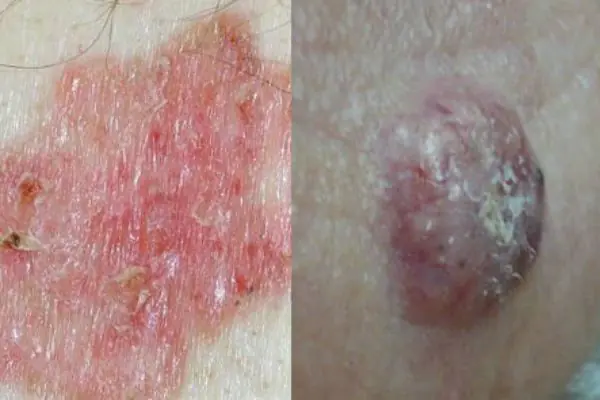
Squamous cell skin cancer, which is formed from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis, in the form of flat, single purulent wounds. Small nodular tumor wounds quickly progress and develop into mushroom-shaped ulcerative growths. Most often, wounds appear on the face, affecting the cheeks, wings of the nose, the area behind the ears and ears, and the lower eyelid. This type of cancer does not metastasize to internal organs and does not spread much throughout the skin.
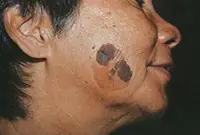
Kaposi's sarcoma
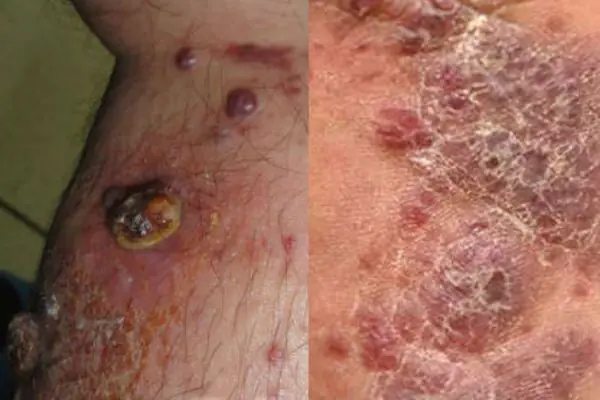
A malignant neoplasm on the skin in the form of extensive dark spots (from the color of boiled blood clots to black), which merge into large affected areas. The disease is diagnosed in most cases in HIV-infected people late in the course of the disease. Locations affected by sarcoma: hands, legs and feet. This disease is a consequence of serious problems with internal organs, it cannot be cured, you can only relieve the severe symptoms with a little medication.
Liposarcoma
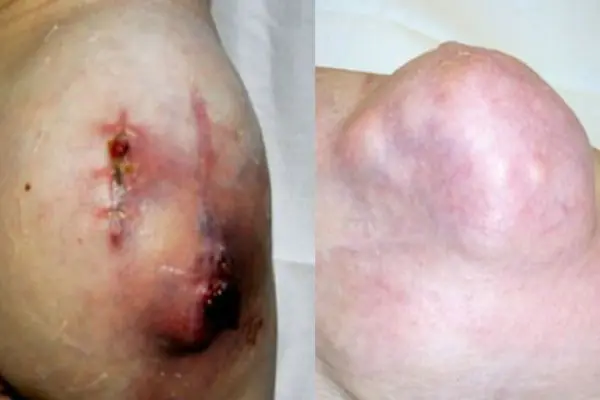
A tumor that occurs due to damage to adipose tissue. This is a large subcutaneous round growth (single node) that can grow up to 20 centimeters. The growth itself is uneven, with irregular outlines. When palpated, it may be hard and elastic. This growth often occurs in people over 50 years of age and mainly in men. Liposarcoma occurs through the degeneration of a lipoma or atheroma into a malignant tumor. The growth grows very slowly and does not spread metastases to internal organs.
Fibrosarcoma
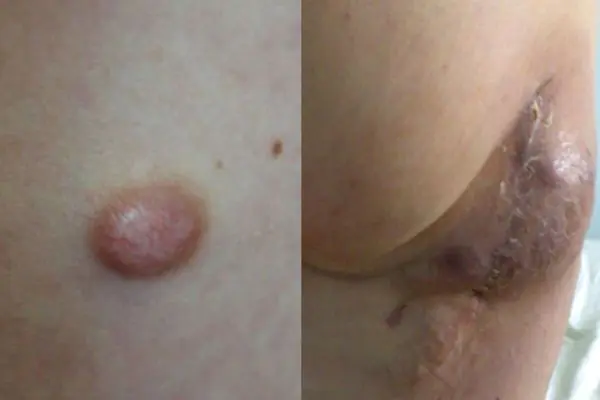
A neoplasm developing in connective soft tissues. Most often, the growth affects the skin of the lower extremities.
Fibrosarcoma can be located externally or subcutaneously. The cutaneous protrudes above the skin, such a growth has clearly visible boundaries and a dark blue or brown tint.
Subcutaneous fibrosarcoma is located deep under the skin and is hardly noticeable. We see only a small venous tubercle.
Precancerous
Despite the scary names of the category, most of these neoplasms, if quickly identified, can be removed and cured without serious harm to health.
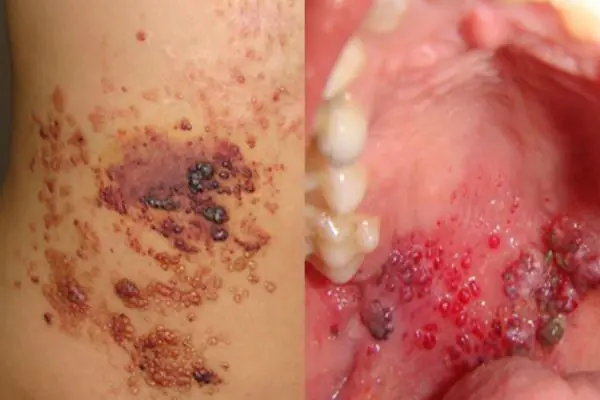
Bowen's disease
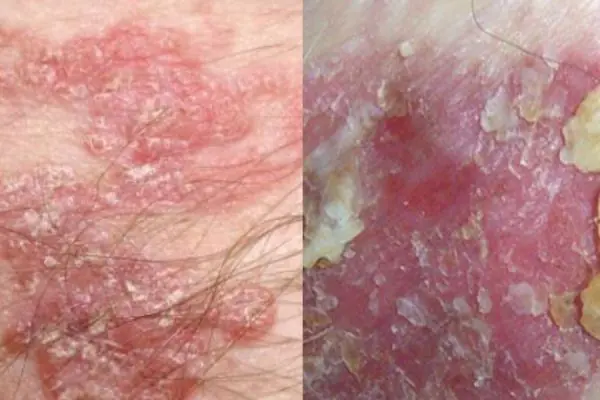
At the initial stages of tumor development, it is located in the upper layers of the epidermis. A clearly defined plaque of a brownish tint, with a flaky surface, appears on the skin. Beneath its surface is hidden a weeping purulent layer of the epidermis. The disease often develops after 40 years of age, mainly in men. Bowen's disease affects the genitals, skin of the face, hands, and oral mucosa. If the disease is not detected early and treatment is not started, it metastasizes and enters the stage of invasive cancer. Treatment is usually carried out locally, with medication.
Xeroderma pigmentosum
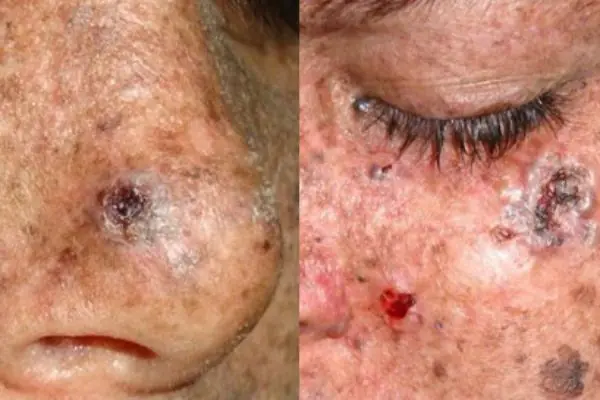
The disease develops through the degeneration of age spots. Occurs in people with increased sensitivity to the negative effects of solar ultraviolet rays on the skin. This pigmentation most often appears on the skin of the hands, face, back and chest. It densely covers the entire skin with dark brown spots. The spots may appear as growths above the surface of the skin and contain purulent blood.
Starcheskaya keratoma
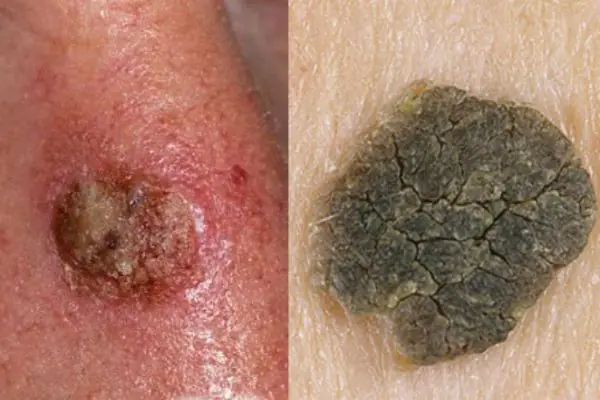
The growth looks like a rash at first, then like a cluster of small spherical skin nodules that unite into a common spot. Over time, the flat growth acquires a dense, loose crust on its surface. At the initial stage of development, the growth is flesh-colored; as it progresses, it darkens to brown. The upper scales of the keratoma may peel off, and the wound begins to bleed.
Cutaneous horn
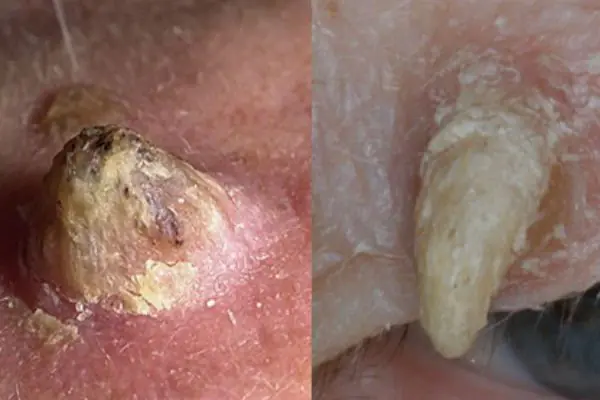
It is formed by the proliferation of epidermal cells of the spinous layer of the skin. A cone-shaped elevation is formed on the skin, which looks like a small horn. The horn has a multi-layered and scaly structure. Typically, dry growth appears in older people behind the ears, on the fingers and toes, feet and rough parts of the skin.

Skin neoplasms are the result of intensive division of epidermal cells and, by their nature, can be benign or malignant, capable of developing into skin cancer.
Moles, papillomas, nevi and many other skin growths are present on the skin of the vast majority of people.
Some growths do not pose a threat to health, but there are also those that, under the influence of negative factors, change and develop into malignant tumors. In order not to miss the moment when a harmless mole begins to transform into skin cancer, it is necessary to independently monitor the condition of all skin growths and regularly undergo medical examination.
Types of growths on the skin
All neoplasms developing from skin cells are classified into:
1. Benign, not posing a serious threat, but capable of causing physical and mental discomfort if extensively localized or located on areas of the body not covered by clothing.
2. Malignant, which is essentially a cancerous tumor. These growths quickly grow, affect the deep layers of the dermis and spread metastases throughout the body.
3. Borderline, potentially capable of transforming into a malignant form.
| Laser tumor removal | Prices, rub. |
|---|---|
| Laser removal of papillomas, warts - Cat. I. difficulties | 300 — 600 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. II. difficulties | 600 — 1200 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - Cat. III. difficulties | 1200 — 2400 |
| Laser removal of moles, papillomas, warts - IV category. difficulties | 2 400 — 5 000 |
| CO2 Laser callus removal (per unit) | 1000 — 3600 |
| Removal of atheroma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. I. difficulties | 6550 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Category II. difficulties | 8250 |
| Removal of atheroma, basal cell carcinoma, lipoma, fibroma, xanthelasma with laser - Cat. III. difficulties | 12 350 |
Make an appointment
Let's look at the features of these skin growths in more detail.
It is formed during blockage of the sebaceous gland and has the appearance of a compacted “ball” rising above the skin, which does not cause discomfort. Atheromas can form on any part of the body, including in the genital area; the neoplasm can be either single or multiple. In case of suppuration and inflammation, atheroma can be removed by surgical excision or laser.
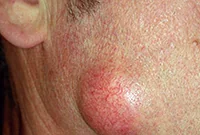
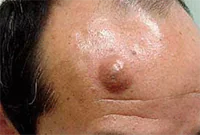
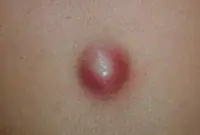
If the functioning of the ducts of the sebaceous glands is seriously impaired, then without special treatment of the underlying problem, they will be re-clogged and, as a result, atheromas will appear again and again, usually in the same place.
A vascular neoplasm that can be localized in both the upper and deep layers of the skin, as well as internal organs, and affect the vascular network. It has a burgundy or bluish-black tint and can reach large sizes. Treatment involves laser removal of hemangiomas, sclerotherapy or surgery.
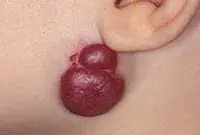
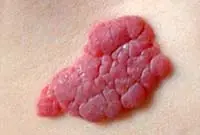
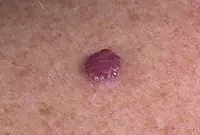
Hemangiomas most often occur on the body, but can sometimes develop on the scalp, face, neck, upper and lower extremities. The neoplasm itself is not dangerous, but it is very easy to injure. Injuries to hemangiomas are accompanied by heavy bleeding.
This type of tumor develops on the vessels of the lymphatic system and is characterized by slow growth. The disease occurs during intrauterine development of the fetus. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the tumor, as a rule, significantly increases in size, which becomes an indication for its surgical removal.
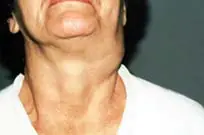
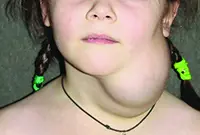

Lymphangioma primarily affects children and is easily diagnosed during the first year of a child’s life. The tumor itself is not dangerous, but its tendency to spontaneous and almost instantaneous growth can harm the child’s internal organs and even threaten his life.
A lipoma or wen is a benign tumor that develops under the skin from adipose tissue cells. The neoplasm can occur on almost any part of the body where, one way or another, subcutaneous fat is present. The neoplasm is felt under the skin as a small movable compaction; the tumor is absolutely painless.
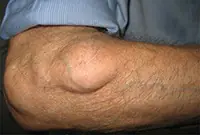

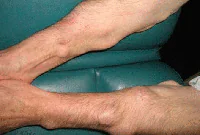
Lipomas can be single or multiple. The tumor is prone to growth. And, despite its benign quality, it causes aesthetic and, often, physical discomfort to the patient. That is why it is advisable to remove lipomas using modern methods. You can learn more about lipomas in the article “Lipoma or wen: what is it?”
5. Papillomas and warts
Warts and papillomas are benign neoplasms that develop from epithelial tissue. They have a similar viral origin, but different places of formation and development. The cause of the appearance of papillomas and warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is very common in the world.
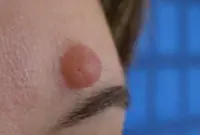
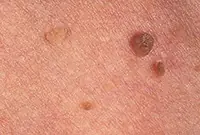

New growths are usually painless. Externally, they are small (up to several millimeters) horny outgrowths on the skin. The appearance of warts and papillomas most likely signals a weakened immune system, and the combination of antiviral therapy with correction of the immune system leads to complete elimination of tumors. Today, the most effective treatment method is laser coagulation; learn more about the removal of papillomas and the removal of warts using this method.
6. Nevi and moles
Nevi and moles are formed from melanocytes - cells containing the main coloring pigment of the body. As a rule, most of these tumors are not dangerous to health. However, their size and location can create some discomfort, especially if they are located on the face or open parts of the body.
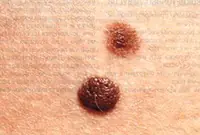
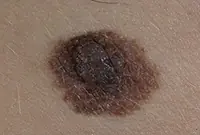

7. Fibroma
Fibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from connective tissue cells. The tumor has the appearance of spherical nodules protruding above the skin with a smooth or warty surface. The color of fibroids can be bluish-black, gray, or brown. More detailed information on fibroids can be obtained in the article "Skin fibroids. Description, symptoms, consequences. Laser removal."
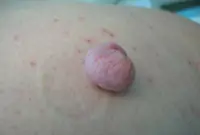
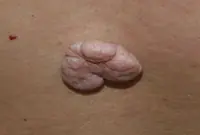
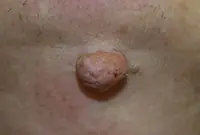
The tumor grows slowly, usually without causing much discomfort to the patient. Often, fibroma does not pose a threat to life, but when exposed to unfavorable external factors, as well as various carcinogens, it can develop into a malignant form - fibrosarcoma. The safest and most effective method for removing fibroids is laser therapy.
8. Neurofibroma
Neurofibroma is a benign neoplasm that develops from nerve cells. Most often, the tumor is located under the skin, in the area of subcutaneous fat. However, in some cases, it can also affect soft tissues, as well as the roots of the spinal cord.
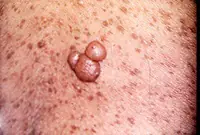

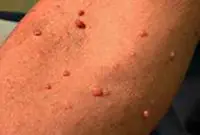
The neoplasm has the appearance of a dense tubercle with a pigmented surface. It can take on multiple forms and in this case requires treatment with medication or surgery.
Sign up for laser tumor removal
1. Melanoma
Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor; one of the types of skin cancer. Melanoma is often a consequence of the malignancy of certain moles and pigmented nevi. You can learn more about melanoma in our article “Skin cancer: melanoma.”.
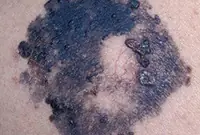
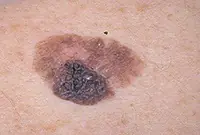
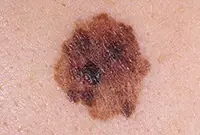
The disease is very aggressive. The tumor not only grows rapidly, but also metastasizes to almost all internal organs, including the brain. Of all the types of cancer known today, melanoma is one of the deadliest. The survival rate for patients with melanoma is very low.
2. Basalioma
Basalioma develops from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis; the neoplasm belongs to one of the types of skin cancer. The tumor is a nodular formation that, as it progresses, turns into mushroom-shaped growths or ulcers. More information about basal cell carcinoma can be found in the corresponding article "Bas cell carcinoma. Skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma.".
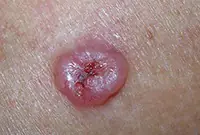
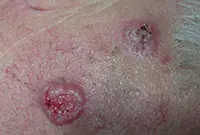
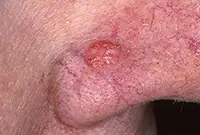
3. Sarcoma Galoshi
Multiple malignant skin tumors; dark spots that, as they grow, merge into large affected areas. The disease is often diagnosed in patients with HIV infection and has extensive statistics of deaths.
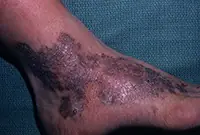
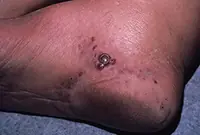
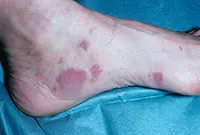
The tumor most often affects the feet, legs and hands. Since Kaloshi sarcoma is only a consequence of more serious internal diseases, its treatment is aimed solely at reducing symptoms.
Sign up for laser tumor removal
Precancerous:
1. Bowen's disease
At the initial stage, the tumor is localized in the upper layers of the epidermis, but without treatment it develops into invasive skin cancer and metastasizes. It looks like brownish plaques with a flaky surface, under which is hidden an area of weeping epidermis.
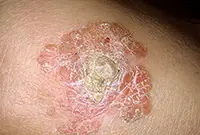
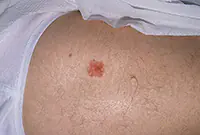
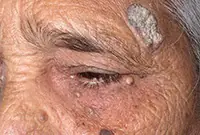
As a rule, the tumor develops in men over 40 years of age under the influence of various carcinogens. Mainly the genital organs are affected, as well as the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Treatment of the disease is usually local, and in case of extensive lesions, surgical intervention is also possible.
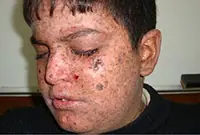
2. Xeroderma pigmentosum
An extremely rare disease that arises from age spots in people with increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. In the early stages it is treated with medication, in the later stages - surgically.
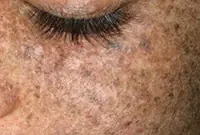
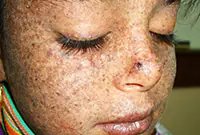
3. Senile keratoma
It looks like skin rashes consisting of scaly spots. The malignant form is characterized by the formation of compactions in the affected areas. Detailed information about keratomas can be found in our article "Keratoma. Description of pathology. Types of keratomas."
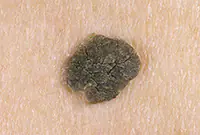
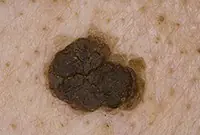
Senile keratoma occurs, as a rule, in older people. The likelihood of malignancy of this pathology is very high. As a rule, keratoma easily degenerates into squamous cell skin cancer. Modern technologies make it possible to easily and quickly remove keratoma using a laser.
4. Cutaneous horn
Proliferation of epidermal cells, forming a cone-shaped elevation with a multilayer scaly structure. It is most often diagnosed in older people and, without appropriate treatment, tends to develop into a malignant form. The skin horn is removed surgically or by laser coagulation.
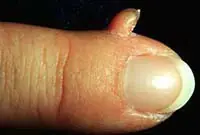

Sign up for laser tumor removal
Skin is the largest human organ. The skin protects the human body from environmental influences. The epidermis prevents germs and microorganisms from entering the body. Also, skin tissue is in daily contact with chemical, physical, environmentally aggressive and other factors.
The structure of the skin has three main layers. New growths appear on different layers. Therefore, the causes of formations are completely different reasons. Among those formed on the skin there may be moles, malignant oncological tumors, nevi and benign formations.
Based on statistical data, the largest number of formations that appear on the skin are malignant, in the form of melanoma, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
What are neoplasms?
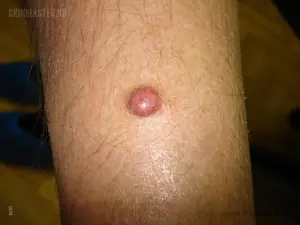
Unusual growth of skin cells is commonly called neoplasms. Experts cite exposure to ultraviolet rays as the main cause of neoplasms. The second cause of skin damage is carcinogenic substances. Any new formation that appears on the skin must be monitored and promptly consult a doctor - an oncologist. He will carry out all the necessary diagnostic procedures. And he will recommend what further actions you will need to take.
Classification of neoplasms
According to international standards, all neoplasms are divided into three types:
- Benign.
- Malignant.
- Borderline (precancerous).
Benign skin tumors
A characteristic feature of benign formations is their slow growth. These neoplasms do not infect adjacent skin cells. The formations are single and do not have additional lesions (metastasis). Benign neoplasms do not cause harm to the human body, but nevertheless they sometimes tend to degenerate into malignant ones.
Types of benign neoplasia:
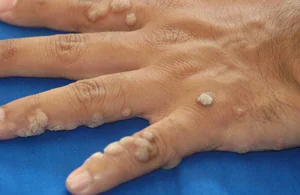
Papilloma. Benign warty growth of skin tissue. The surface of the papilloma is hairless, but nevertheless fleecy. It tends to increase in size, but this takes a long period of time. The color of the neoplasm ranges from brown to gray. The shape of papillomas is most often round, but can be absolutely any.- Seborrheic wart.
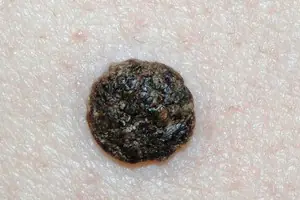
Another name for this neoplasm is senile papilloma. It looks like a clearly visible warty element. It has a color from brown to black. It appears most often in older people, hence the second name. The places where they form are most often the head, under the hair, or areas of the skin that are hidden under clothing. Seborrheic warts are formed when the placement of skin cells in the basal layer is disrupted. 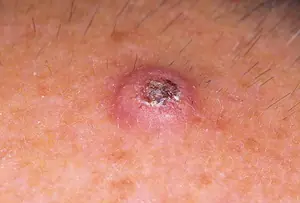
Keratoacanthoma - This is cancer of the skin of the face and hands, but benign. A dense formation is formed on the dermis, the central part of which is the horny mass. After the formation grows to three millimeters, it disintegrates on its own, but a small scar forms. This neoplasm is not capable of degenerating into cancer. In any case, such rebirths have not yet been encountered. The site of appearance of keratoacanthoma is most often a nevus. From the name it is clear that the formations consist of pigment cells of the epidermis. Pigmented nevi are dark in color due to the high content of melanocytes. There is no specific place for their appearance, since neoplasms occur in completely unexpected and different places. Some of the nevi that appear can turn into cancer. Most often, pigmented nevi that form on the soles of the feet, palms, and genitals degenerate.- Dermatofibroma. Newly formed tumor on the connective tissues of the skin. Visually it looks like a single or multiple nodular pigmented growth.
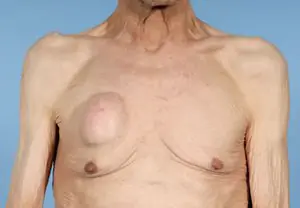
Lipoma. Formed in the fatty layer of the skin. The affected epidermal tissue appears soft and nodular. It can grow to a maximum size of ten centimeters. Mostly a single tumor is formed, but cases of multiple neoplasias have been observed that form on unprotected areas of the skin. Formed after insect bites and various minor injuries. The nodules are rich in color and do not develop into larger formations in the future.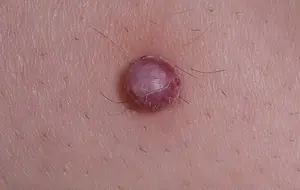
Angioma. A neoplasm that forms on the inner walls of blood vessels and the lymphatic system. It looks like spots on the skin that disappear when pressed. Angioma is quite difficult to diagnose in the initial stages, due to its location and appearance (visually the tumor follows the structure of the vessel). Neoplasia forms both on the surface of the skin and on internal organs.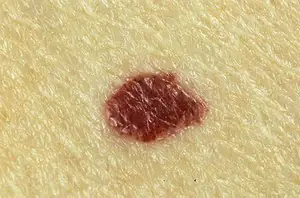
An angioma, having formed in a vessel, disrupts its functioning and, naturally, is dangerous to a person’s general health. The resulting angioma on the face is a pink to bluish spot. The surface of neoplasia is varied (i.e., it can be both smooth and lumpy). According to the place of formation of angiomas, they are divided into:- venous-cavernous
- mixed
- arteriovenous
Malignant neoplasms
Malignant tumors that appear on human skin behave very aggressively. This manifests itself in an accelerated increase in the size of formations, the formation of additional lesions, and infection of adjacent dermal tissues.
The most common types of malignant tumors:
Squamous cell carcinoma. This formation on human skin looks like a dense keratinized layer of the epidermis, which then degenerates into an ulcer that does not heal. Squamous cell carcinoma destroys the skin tissue adjacent to the ulcers and secondary foci of the disease form. Actinic keratosis can be a precursor to squamous cell carcinoma. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays and chemicals creates excellent conditions for this cancer. Like other types of malignant neoplasia, squamous cell carcinoma attacks neighboring skin cells, infecting them.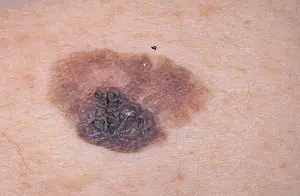
Melanoma. The fastest growing malignant neoplasm, which consists of lumpy papules. Sometimes, under bad conditions, they degenerate from moles. This is why you should closely monitor any changes in nevi on your skin. Pay close attention to moles that are located on the head under the hair or in the perineum. These are the areas where nevi are most often injured. As in other cases of low-quality tumors, try to spend less time in the sun.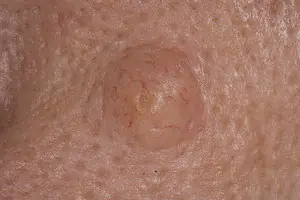
Basal cell carcinoma. The most common type of cancer. It got its name due to damage to the basal layer of the skin. Features that characterize basal cell carcinoma are no metastatic foci, penetration into neighboring skin cells, parasitic growth. The formation is a papule with blood flow from its center. Basalioma is a subtype of squamous cell carcinoma. The site of tumor formation is in areas of the skin that are usually under clothing.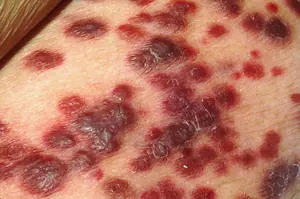
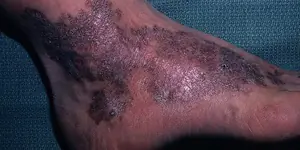
Fibrosarcoma. A malignant cancerous neoplasm forms in the connective layers of the epidermis. Education can be both external and internal. The external formation rises slightly above the rest of the skin and is brown with a blue tint. Fibrosarcoma is conventionally divided into:- Poorly differentiated. It is fraught with dangerous consequences in the future.
- Differentiated. The size gradually increases; additional tumor foci do not form.
Liposarcoma. The tumor consists of fat cells that have degenerated into malignant cancer cells. Formations reach significant sizes. Neoplasia grows slowly. The shape resembles a circle. Liposarcoma mostly affects older people. Sometimes metastases form.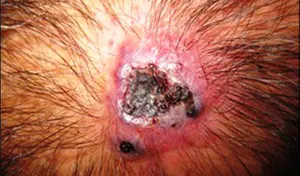
Angiosarcoma. A benign angioma tumor degenerates into a malignant angiosarcoma. This type of cancer is considered the most dangerous, as it often ends in death. Tumors appear in people with weak immune systems. Externally, this oncological disease looks like purple spots on which formations appear united with each other, transforming into ulcers in the future.
Borderline or precancerous skin conditions
Borderline or precancerous skin conditions are neoplasias that are in the stage of degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Types of precancerous neoplasms:
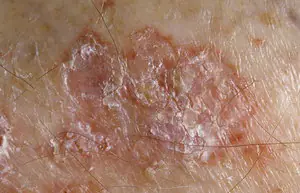
Bowen's disease. The disease is characterized by inflammation of skin cells and accelerated division of dermal cells, which subsequently leads to the development of squamous cell carcinoma. The lesion will most likely be on the skin of the temples, forehead, genitals or hands. Visually, the neoplasm looks like a rough pink to brown spot with slightly protruding edges. The tumor grows in size up to five centimeters. The human body can heal itself from this disease. But nevertheless, if the disease is left to chance, then in a few years you will become the owner of another more dangerous disease. You can determine the transition from Bowen's disease to one of the forms of cancer yourself, as it is quite simple. If ulcers appear on the surface of the neoplasia, degeneration into cancer has occurred.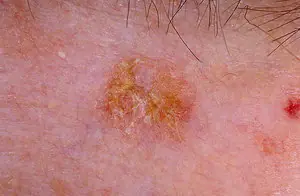
Actinic keratosis. This neoplasm appears most often in people aged forty-five years and older, but cases have been observed in young people with fair skin. It appears in skin that has been irradiated by solar radiation. The main danger from actinic keratosis is the progression to a more complex disease - squamous cell carcinoma. A sure sign of keratosis is rashes on those parts of the body and face that are not protected by clothing and hats. The formation looks like a round red plaque with a rough surface. Rashes occur in the following forms:- warty
- hypertrophic
- erythematous
- horny
- pigmented
Diagnosis of neoplasms
As soon as you discover a new skin formation on your body or face or a change in a mole, you need to contact an oncologist. A qualified specialist in appearance is able to determine an approximate diagnosis. And with the help of a biopsy, the goodness or malignancy of the neoplasm is determined. Therefore, do not try to diagnose a skin lesion on your own, but immediately contact a specialist.
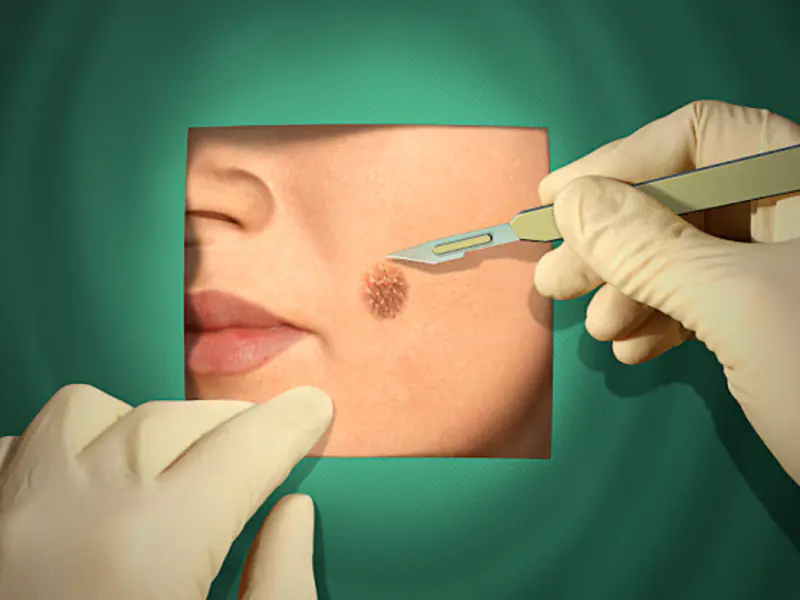
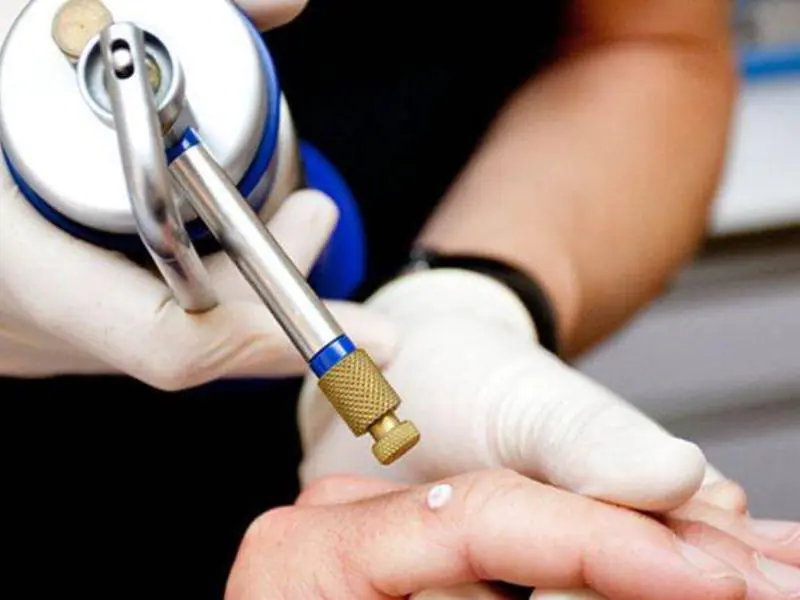
Treatment and removal methods
Only an oncologist has the right to choose the method of treatment for a new growth on your skin. He will make a choice based on a biopsy of your tumor, as well as the type, rate of growth, location and extent of the tumor.
Basic treatment and removal methods:
- Surgery. Removal of tumors is the most common treatment method. The tumor is excised completely, together with the surrounding healthy skin tissue and lymph nodes.
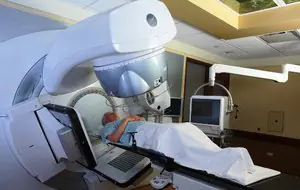
Radiation exposure. Used for small formations. The disadvantage of this method is that the surrounding uninfected skin cells are destroyed.- Cryogen. This removal method uses liquid nitrogen.
- Chemotherapy. Used when surgery is no longer possible. Chemotherapy is usually combined with radiation.
Your oncologist will determine which treatment method is right for you. They are all good in their own way.



