Moles in medical terminology they are called nevi.
They can be found on the body of any person in the form of small round dots, small spherical formations that rise above the surface of the body, and large pigmented areas of the skin.
What it is?
Moles consist of specialized cells of the epidermis - melanocytes, responsible for the production of melanin in the body (a pigment that colors the skin in various shades of brown). Under the influence of external or internal factors, an excess amount of them accumulates in certain places of the skin - this is why moles appear on the body of an adult, child or elderly person.

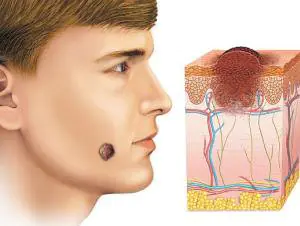
In some people, nevi remain unchanged on the skin all their lives, in others they disappear, in others they grow or change their shape and color. The latter become dangerous and can degenerate into malignant formations.
- Common moles have a rounded symmetrical shape, depending on the concentration of melanin in them, nevi are colored beige, brown or black.
- Meet and red dots on the body as moles, for the most part this phenomenon is associated with impaired skin pigmentation due to hepatic or endocrine pathology, as well as natural age-related changes (i.e. as a result of aging).
The difference between these spots and moles is that they usually appear in groups on a limited area of the skin. When metabolic processes are restored, the red spots disappear.
In adults, the appearance of nevi is associated with hormonal crises due to illness, menopause or nervous exhaustion. The appearance of moles in them can be observed constantly or appear spontaneously, in response to a certain stimulus. In childhood, science has noted the wavy growth of nevi.
Periods when moles appear in children:
- 6 months - six months, at this moment the child’s endocrine system adapts to external conditions;
- 5-7 years, the stage of active growth of the skeletal system and skeletal muscles, requiring rapid metabolic reactions;
- 12-16 years, puberty with significant changes in the functions of the whole organism.
Why do they appear?
Nevi are essentially benign skin formations.
Some people get scared when they see many moles on their body. What does this mean for a specialist? Only that the patient’s body is prone to accumulation (accumulation) of melanin in the surface layers of the epidermis.
The reasons for the appearance of numerous or single nevi are varied.:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation, one of the most common factors in the formation of moles due to increased melanin levels during tanning;
- traumatic damage to the epidermis, systematic violations of the integrity of the skin contribute to the appearance of pathological changes in it;
- exposure to radiation, which rapidly changes normal skin cells;
- consumption of harmful products (GMOs, fast food, alcohol) and smoking, these habits negatively affect metabolic processes in the body.
- endocrine disorders and diseases, any changes in hormonal levels can cause the appearance of skin pathologies, pigmentation, moles;
- hereditary predisposition, the presence of various nevi in the family.
Classification and photo
1. A flat nevus or birthmark is a pigmented island of skin with clearly defined boundaries. It can take the form of lentigo - multiple brown or brownish formations in the upper layers of the epidermis.
2. Convex nevus or mole. It has a diameter of up to a centimeter, a smooth or lumpy surface and rises above the level of the skin. Its color varies from beige to black, and a hair is usually located in the center of such a formation.
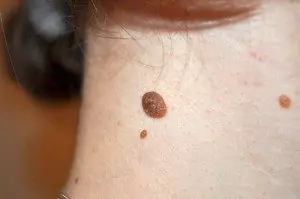
3. Blue nevus or blue mole. It looks like a smooth hemisphere, slightly raised above the skin, sometimes reaching a size of 2 cm. The color of this benign formation ranges from blue to dark blue.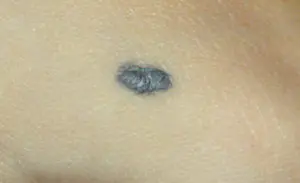
4. Giant nevus. It is a large spot on the body, gray, bright beige (sometimes brick), black or brown.
Dangerous and non-dangerous moles
Ordinary nevi do not cause any discomfort to their carriers; sometimes they even disappear without a trace. Their shape is stable, size and color remain unchanged.
But benign moles are sometimes removed to prevent their degeneration if they are of rather large size (pedunculated) and are located in areas of the body where a person constantly injures them (during vigorous activity or parts of clothing).

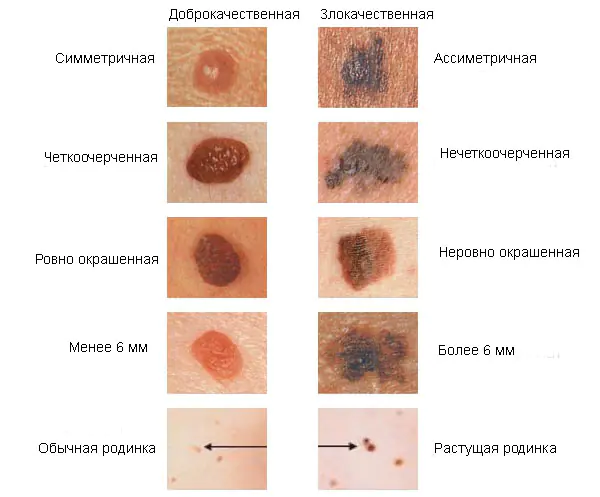
Remember dangerous moles in the photo and be vigilant!
If nevi degenerate into cancerous moles, this is dangerous, since such neoplasms quickly metastasize to other organs.
Therefore, it is very important to see signs of malignancy in time.:
1. The shape of the mole changes, it loses its symmetry and begins to grow in one direction.
2. The edges of the nevus become uneven (“cut up”, “torn”).
3. The color of the mole is uneven and contains yellow, red or black inclusions.
4. The nevus grows or “shrinks”, its size changes rapidly.
5. The texture of the mole becomes different, smooth becomes rough, bumpy becomes flat, etc.
6. Loss of hair growing from the nevus.
7. Itching, peeling and burning in the mole area.
There are several reasons why a nevus itches:
– pathological cells multiply;
– there are active processes of death of healthy tissues;
– the area around the formation becomes inflamed and swollen.
8. The appearance of microcracks and ulcerations.
9. Bleeding and soreness of the mole.
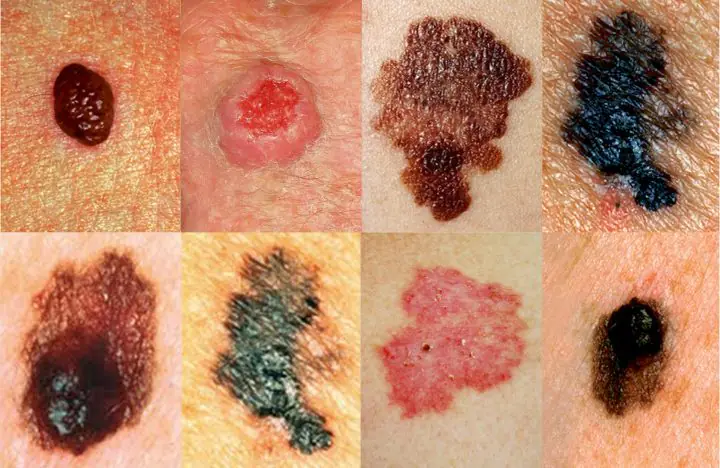
Cancerous moles (melanomas): photo
What happens if you rip off a mole?
You cannot remove a nevus yourself.
Firstly, it is dangerous, and secondly, it is simply ineffective. If the mole is located close to blood vessels, prolonged bleeding may develop. Often such self-medication leads to re-formation of the nevus, its growth or malignancy.
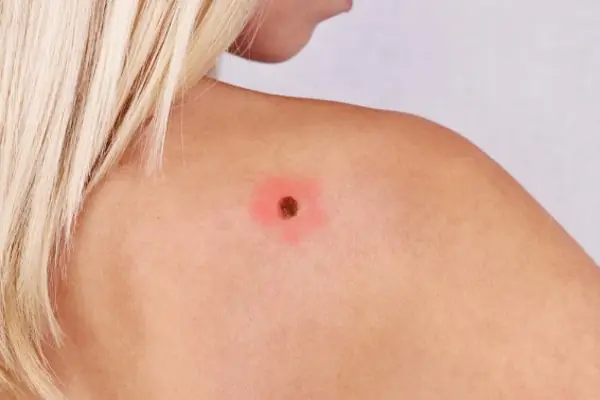
Therefore, it is difficult to predict what will happen if a mole is torn off. It may have no consequences, or it may cause serious complications for the health and life of patients.
Doctors warn that any trauma to the nevus is extremely undesirable, but pedunculated moles or small convex formations can be accidentally removed with nails or hard items of clothing.
What to do if you rip off a mole:
- cauterize the wound with an alcohol solution;
- stop the bleeding by applying a gauze bandage;
- come to see a specialist.
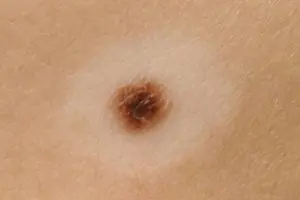
In cases of partial removal of a mole, do not touch the remaining formation, do not cut it off or tear it off.
Sometimes such pigmentation appears before the disappearance of a mole (as a sign of depigmentation), and in other cases it may signal its degeneration.
White spots around the mole appear as a characteristic sign of Setton's nevus. This formation is considered harmless in terms of degeneration into a more malignant form, however, melonomas (aggressive cancerous formations) can also have such a white rim, so the appearance of white spots is a reason to contact a medical specialist.
Diagnostics
Dermatologists and oncologists are involved in determining the type of nevus.
Using a dermatoscope, the doctor examines the formation and determines its nature (benign or malignant). Sometimes a histological examination (scraping method) is required.
Biopsy (tissue sampling) for nevi is not used due to their trauma during this procedure. And as you know, it’s better not to touch moles again!
Removal
Many people want to get rid of birthmarks and nevi not only in cases of malignancy (pathological change), but also to correct a cosmetic defect.
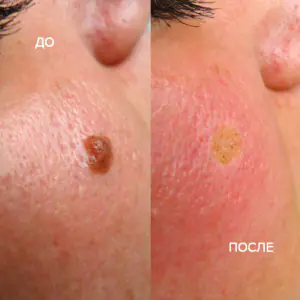
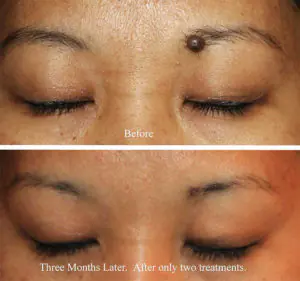
However, removal is carried out at the oncology center for people with malignant tumors and with a high probability of degeneration of nevi.
Often the indication for surgery is the localization of moles on the body: on the scalp, on the neck, on the chin, in the area of the shoulder blades.
Methods for removing nevi (with information on how much it costs to remove them):
- surgical, using local anesthesia and a scalpel (in municipal surgical hospitals, according to indications - free of charge, in medical centers from 300-500 rubles)
- cryofreezing with liquid nitrogen (1000-1500 rubles);
- electrocoagulation - cauterization with electric current (600-1300 rubles);
- photodynamic - ultraviolet irradiation (1000-1200 rubles);
- laser - removal of moles with a beam (800-2000 rubles);
- radio wave, destruction of nevi by shock radio wave (RUB 700-1400)
The choice of method for removing moles is made by the doctor; prices for these procedures depend on the size and type of nevus.
Prevention of malignancy
Preventive methods for reducing the risk of malignancy of moles include:
- limited sunbathing, cancellation of visits to the solarium;
- minimizing skin trauma;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle (healthy eating and avoiding bad habits).
Nevi on the body are otherwise called birthmarks, moles, and are benign formations that appear on the skin. Moles are either at the same level with the skin or rise above it; the reasons for their appearance are varied, mainly genetic predisposition and a certain skin type. The sizes of the nevi shown in the photographs below vary from very small (1-2 mm) to large (15-25 cm).
The color, depending on the cells that formed it, can be:
Benign formations can occur not only on the skin, but also on mucous membranes (for example, in the vagina), connective membranes, edges of the lips, blood vessels of the eye as a spot, a skin phenomenon consisting of nevoid cells.
Nevi can be congenital or acquired. Educational cells appear in the prenatal state of the developing human body. They originate in the neural crest, a “cellular reservoir” that serves as the basis for the formation of various anatomical structures.
According to statistics, almost 80% of white-skinned representatives of the world's population have nevi on their bodies. In adults, the number can be 30 pieces or more. In childhood, they may not exist, but during puberty, during pregnancy, under the influence of sun activity, nevi appear on the skin.
A benign formation, developing, goes through several phases:
- intraepithelial (initial);
- border;
- intradermal (at the age of 30 years);
- reverse (in old age, the cells “return” to the layers of the skin).
Nevi are accumulated nevocytes containing large amounts of melanin. Neocytes are called changed melanocytes - cells that determine the shade of human skin. When exposed to sunlight, melanin appears in them, giving the skin a tan color.
It is important to know! The shapes and sizes of birthmarks are so diverse that they are confused with some dermatological pathologies: “cutaneous horn” (fibroma), seborrheic keratosis, papillomas. Therefore, only a specialist is able to make an accurate diagnosis through differentiation. This often requires a histological analysis to study the taken tissue biomaterial.
Causes of nevi
Disturbed embryogenesis causes the development of congenital nevi. They can have hereditary traits and serve as proof of belonging to the same genus.
“Children’s” melanocytic nevi appear under the following predisposing conditions:
- the effects of toxic compounds and radiation on a woman carrying a child;
- the presence of pathologies in pregnant women that have developed in the urogenital tract;
- toxicosis, threats of abortion;
- hereditary unfavorable predisposition.
The following provoking factors contribute to the occurrence of acquired nevi:
- hormonal “explosion” during puberty;
- pregnancy period with hormonal fluctuations;
- oral contraceptives taken;
- skin pathologies of infectious and allergic nature;
- injury to the skin as a result of mechanical impact;
- insolation (exposure to direct solar radiation);
- influence of radiation and x-rays on the human body;
- diseases of viral etiology.
Types of nevi
Classification of nevi according to histological characteristics provides an assessment of the characteristic features of any type of formation, which contributes to an effective prognosis of the course of the disease. There are more than 50 types of birthmarks, of which ten nevi are common.
The conditionality of division into groups concerns tumors:
- Melanoma-hazardous (having a tendency to degenerate into malignant formations).
- Melanoma-hazardous (without a tendency to degenerate into malignant formations).
Melanoma formations include the following types of nevi:
Blue
Such a single formation, which is an accumulation of melancites, is in a precancerous state, although it is called benign. At the same time, it has no tendency to undergo oncological degeneration. The color of the nevus - bluish or blue-black - depends on the active production of melanin by the nevus cells. It has the correct shape, evenly outlined contours. Due to its elevation at the skin level, such a nevus can often be injured by items of clothing, jewelry, etc. Patients with such a birthmark should be regularly examined for preventive purposes to prevent degeneration into a malignant tumor.
| Blue nevus |
Borderline pigmented
This is a congenital formation that manifests its characteristics immediately in the first periods of a person’s life. The nevus develops along with the growing organism, even without the influence of any external factor. The brown/brown/black spot can reach a diameter of 1.5 mm to two to three or more centimeters. Such nevi “settle” on the palms and soles. Malignancy can manifest itself after injury or prolonged exposure to the sun.
| Borderline pigmented nevus |
Giant pigment
Nevus, reaching up to 50 cm in diameter, is a congenital formation. It differs from other formations in shades of gray/brown and rises above the skin level. The formation has cracks, grooves, warts, so there is a high risk of possible trauma and degeneration into a malignant tumor. In this case, the patient is recommended to solve the problem surgically.
| Giant pigmented nevus |
Nevus Ota
The manifestation of the skin phenomenon is directly dependent on the nervous factor. The spot, consisting of a large amount of melanin, is localized on the most exposed part of the body - the face. Black-blue formation of genetic orientation is found in representatives of the Asian race.
| Nevus Ota |
Dysplastic
Congenital nevus is registered in half of the registered cases. Spots of this type can be detected in members of the same family. Dark brown multiple formations are small in diameter: no more than half a centimeter. They are located throughout the body and have a smooth, flat surface. A high rate of transformation of dysplastic nevus into melanoma is recorded - 90-95% of cases.
| Dysplastic nevus |
Melanomic nevi , in turn, there are several types:
Intradermal pigment
These moles, which form in the dermal layer, under the skin, are mainly reported during adolescence. They are initially small in size, but grow and develop along with the teenager’s body. Nevi of this type are practically unable to degenerate into malignant ones. Only under the influence of certain factors there is a risk of melanoma.
Such formations can be located on the neck, in the groin area, armpits, under the mammary glands, sometimes on the upper and lower extremities, and the skin of the body.
| Intradermal pigmented nevus |
Papillomatous
This type of nevus has a repulsive appearance, being a cosmetic defect. A brown or pink mole in the form of a growth rises above the skin level, has a soft granular surface, and is painful when touched.
Such moles are found on the head under the hair, and are also found on the body. The growth of formations is slow, transformation into a malignant formation is practically not recorded.
| Papillomatous nevus |
Galonevus
This birthmark is also called Setton's nevus. It appears in people with weakened immunity due to hormonal imbalances and autoimmune pathologies.
Halonevus is characterized by an oval shape, large size, and elevation on the skin. The formation is localized on the trunk, upper and lower extremities. There are both single and multiple nevi, but they do not degenerate into malignant tumors.
| Galonevus |
Mongolian spot
A similar type of mole is observed in newborns, sometimes found in adults, appearing on the skin in the form of a fifteen-centimeter spot in diameter as a result of a hormonal pigment disorder. As the name suggests, this phenomenon is often recorded in Mongolia: in almost 92% of cases. The nevus is “located” on the child’s sacrum or buttocks. Conversion to melanoma is not observed. The stain may generally disappear over time.
| Mongolian spot |
Fibroepithelial
This type of congenital or acquired nevus is often recorded. It appears under the influence of hormonal changes in old age. Soft reddish/pinkish moles are large in size and can be localized throughout the body. They rarely transform into malignant ones and are easily removed. They cannot “fall away” on their own.
| Fibroepithelial nevus |
Symptoms
The main distinguishing features of nevi are their appearance: shape, color, size. Some have hair follicles, roughness, warts and other “accompanying” elements. Others are distinguished by their smoothness, localization, and invisibility. Only a specialist is able to distinguish formations, give their descriptions, assign them to certain groups and identify the danger using diagnostic measures.
Diagnostics
The study of moles is an important point in diagnosis, with the goal of identifying the danger of transformation of benign nevus cells into malignant ones.
Diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
- Visual, anamnesis collection. By asking questions to the patient, the doctor finds out:
- period of nevus formation, whether it is congenital or acquired;
- whether changes in the appearance of the formation are noted;
- reasons for the changes that occurred (burns, injuries, etc.);
- whether there was an attempt to remove the mole, and in what way.
Important to remember! A timely visit to a dermatologist (at the first signs of transformation of a mole) for diagnosis can save a person’s life, preventing the formation of a malignant tumor.
A biopsy is not performed for diagnostic purposes!
Treatment of nevi
The treatment of pigmented formations is carried out by a dermatologist-oncologist. The therapeutic approach is carried out in a clinical setting using surgical intervention.
| Excision and laser therapy of nevus on the face |
First of all, we take into account moles that are subject to regular injury or risk of injury and are located:
- under the hair;
- in women on the back, in the area of the bra clasp;
- in men on the neck, face, chin (dangerous when shaving);
- in the groin area, skin folds;
- “on a leg” (they can tear or come off completely).
To remove nevi, use the following methods:
- Resection. The nevus (usually large in size) is excised along with three centimeters of the surrounding skin using a scalpel under local anesthesia. The disadvantage of this type is the presence of a scar after surgery and pain. The removed lesion undergoes histological examination.
- Cryodestruction. This is a procedure for freezing a nevus using liquid nitrogen. This method can also eliminate small formations. The advantages of cryodestruction are the absence of scars and the need for additional pain relief.
- Electrocoagulation. The nevus is cauterized using an electric current. Children undergo the procedure under general anesthesia, adults - under local anesthesia. Suitable for removing small and medium-sized moles.
- Laser therapy. Used to remove moles on the face and neck. Possessing high precision, the laser does not leave scars on the skin. The main point of this procedure is the depth of penetration of the laser beam under the skin to completely destroy the nevus cells.
| Laser mole removal |
Postoperative complications
Removing birthmarks does not always go smoothly; sometimes complications arise, including:
- development of the inflammatory process in cases of improper wound care in the postoperative period;
- malignancy (the process of formation of cancer cells) in the place where the nevus was not completely removed;
- cosmetic defect - the presence of a scar.
It is important to know! The method of surgical intervention is determined by the doctor, taking as a basis the characteristics of the nevus and the functionality of the medical institution. The patient can express his wishes, but his opinion is not decisive.
Prevention of melanoma
To prevent the development of melanoma, a malignant tumor, exposure to pathological factors should be excluded. Melanoma is dangerous because it can metastasize to the brain, liver, and other organs. Death from skin cancer occurs in 50% of cases.
Of course, complete prevention of transformation into melanoma is impossible, but some recommendations, carefully followed, reduce the risk of benign cells degenerating into cancerous ones.
Tips concern:
- reducing the time spent under the sun's rays, especially during periods of sun exposure
special activity (from 12 noon to 17 pm);
- avoiding ultraviolet radiation that affects nevi;
- careful handling of moles so as not to injure them;
- timely contact a dermatologist-oncologist at the first signs of changes in moles regarding their shape, size, color.
Cosmetics designed to reduce the impact of ultraviolet radiation on the skin are not able to protect nevi from harmful effects.
Nevi (moles) are found on the body of almost every person and in most cases are not dangerous. What is a birthmark and is it dangerous? Only some types of this formation are dangerous because they can become malignant, i.e. transformation into melanoma. Therefore, it is important to monitor every mole on your body.
What are nevi and what do they look like?
Many people do not know about the nature of moles and, due to the fact that these formations do not bother them throughout their lives, they do not even remember their existence. What is a nevus from a medical point of view? This is an accumulation of pigment cells on the surface or layer of the skin, which can be congenital or acquired. Congenital spots can be of different sizes - from 0.5 to 10 cm in diameter. The location on the body and the size of these formations are initially embedded in human DNA and are already present in a newborn, but are not visible until a certain age.
Causes of nevi
Acquired nevus - what is it and what causes moles? Pigment cells located between the epidermis and dermis can accumulate for the following reasons:
- ultraviolet radiation – provokes excessive production of melanin by skin cells;
- hormonal changes – due to hormonal changes in the body, new moles may appear and old moles may disappear;
- different types of radiation, injuries can cause migration of pigmented cells;
- heredity - the amount, type, location of congenital pigmentation is determined genetically.
Types of moles
Pigment formations can be classified according to their origin, size, color and location on the skin. Congenital birthmarks come in different shapes, colors, and some can reach 10 cm in diameter. Depending on the location on the body, they may have hair on the surface (Becker's spot). By their nature, there are the following types of nevi:
- vascular - arise due to atypical growth of capillaries (hemangioma, anemic);
- pigmented - due to an excess of melanin in the skin.
Pigmented nevi have a number of varieties:
- by location - borderline (on the palms, feet, genitals), nevus of Ota (pigmentation on the face);
- by color, nature of distribution - blue (cyan), brown, violet and pink spots, Setton's nevus or halonevus (spot surrounded by white non-pigmented skin), linear (several nodules in a chain);
- in shape - flat and convex, papillomatous, warty, fibroepithelial, verrucous;
- by the nature of the forming cells - melanoform, melanocytic, sebaceous glands;
- by location in the layers of the skin - dermal, intradermal, intradermal, dysplastic, superficial.
Congenital nevus
Birthmark (ICD name - congenital non-tumor) or congenital nevus - what is it? In the photo on the Internet you can see congenital skin formations of enormous size, which can be located on any part of the body and have different colors. Congenital pigmentation of a certain area is genetically determined with which a person is born. More often it does not pose a threat, but many factors, external and internal, can provoke the growth and transformation of cells that can form melanoma - the most dangerous type of human malignant tumor.
Acquired moles
Melanoform nevi, which consist of cells with melanin, are most often congenital, but can also appear during life. Acquired moles are often melanocytic - with different types of cells, incl. and pigmented. During life, under the influence of many environmental factors, a person can develop a formation of any nature. Such acquired skin tumors must be monitored to avoid the risk of their malignancy (transformation into a malignant formation).
What is a histological examination of a mole?
Histology of nevus - what is it? This is an examination of a mole to determine the risk of melanoma arising from it. Any birthmark carries a potential threat; under the influence of various factors it can develop into a malignant formation - melanoma. This type of cancer is considered the most dangerous due to the lack of response from the body. Melanoma can develop on any part of the skin, on the mucous membrane and even on the retina of the eye. Therefore, it is important to have your moles checked at least once a year by a dermatologist.
Melanocytic nevus
Due to the appearance of neoplasms, they are divided into melanocytic and melanoform. Melanocytic spots can form from three types of cells. Thus, melanocytic neoplasms, often benign, are:
- epidermal;
- dermal (intradermal);
- mixed origin.
Epidermal moles are dark in color, often flat and small in size. Sometimes they have hair. If epidermal spots protrude above the surface of the skin and become papillomatous, this may indicate a risk of developing melanoma from them, so it is important to carry out histology on time. Melanoform spots are formed from cells with melanin, so they are brown in color, are congenital, harmless, and can appear in a child during adolescence.
What are nevi on the skin that are not melanoma dangerous?
The concept of a melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-non-hazardous mole implies that there is a risk of melanoma forming from it. Only a doctor can tell exactly which mole is dangerous after a histological examination. However, there are medical statistics that show that some types of spots have a pronounced risk of forming melanoma and these include nevi: pigmented borderline, giant congenital, blue, nevus of Ota, Spitz, Dubreuil. Descriptions and photos of dangerous spots are easy to find on the Internet, but only a doctor can tell about the danger of a particular formation.
Diagnosis of nevi
The type and danger of spots on the skin are determined by the following methods:
- fluorescence microscopy - a special device, a dermatoscope, illuminates the skin to identify the cells that make up the mole, at what depth they are located and how they are formed;
- computer diagnostics – multiple magnification of a pigmented spot, measuring it and identifying its structure;
- histology – laboratory determination of tumor markers.
Treatment of moles
If pigmented areas of the skin do not bother you throughout your life and look normal, then most likely they do not pose any danger, but this does not mean that you can not monitor their condition. Timely diagnosis of changes will help to treat or remove the pigmented area in time to avoid its malignancy. How to treat moles that have caused suspicion? Today, surgical methods are used to remove suspicious formations on the skin.
Surgical removal of nevus
If the danger of a pigmented spot is identified, the doctor makes a decision regarding its removal. There are several surgical methods that are used depending on the type, location and nature of the tumor:
- resection – removal of the nevus surgically (excision) with a scalpel. Disadvantages – pain, scars remain;
- targeted irradiation of pigmentation with low doses of radiation;
- electrocoagulation – a bloodless method of removal with sealing of vessels;
- laser removal is quick, bloodless and painless, leaving no scars;
- cryotherapy – cauterization with dry ice or liquid nitrogen (not suitable for treating intradermal spots).
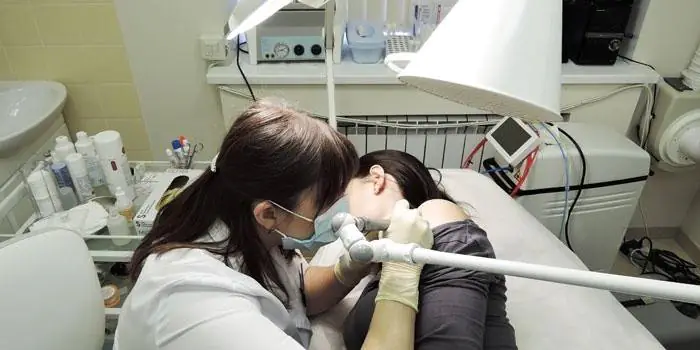
Treatment of nevi with folk remedies
Many people, having noticed new spots on their body, immediately begin to look for information from photos on the Internet, and then ways to treat them. There are many recipes for traditional treatment of moles on the Internet, but how effective are they? Among the existing recipes are the following:
- Treatment with vinegar. In folk recipes it is advised to apply directly to the affected skin. Such treatment can be dangerous due to burns.
- Mixtures based on lemon juice. Lemon is known for its ability to whiten the skin, so using such recipes can only change the color of the skin, and not cure it. Lemon juice helps fight seasonal pigmentation on the face and neck.
- Chalk mixtures that lighten the skin.
- Lapis pencil. This remedy has been mistakenly attributed to methods of combating moles, but it is effective only against warts.
Based on these recipes, we can conclude that it is simply dangerous to take on the treatment of skin pigmentation of any kind on your own. Intradermal, papillomatous and other neoplasms can only be diagnosed and treated by a doctor. A dermatologist or oncologist will be able to identify the nature of the formation on the skin, the degree of its danger and methods of treatment. Do not self-medicate so as not to injure your health and avoid the consequences of dangerous methods.



