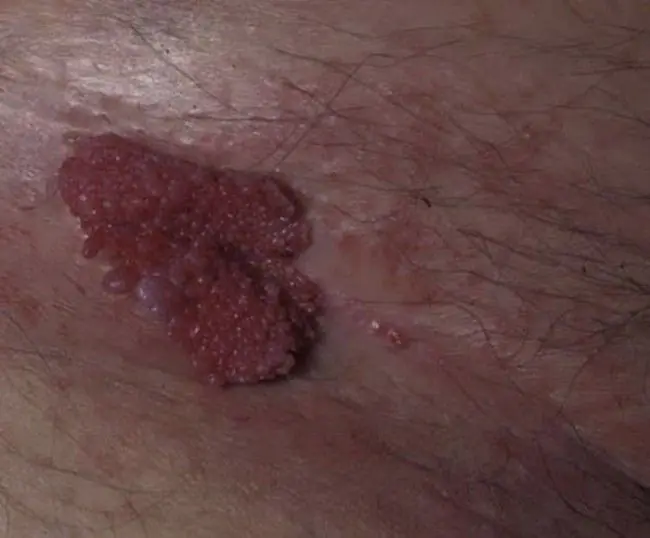
- Reasons for appearance
- Symptoms of genital papillomas
- Diagnostic methods
- What is the danger
- Treatment methods
- Medicines
- Removal of genital papillomas
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
Pointed papillomas are neoplasms that occur mainly on the human genitals. The disease is caused by papillomavirus of various types. The issue of diagnosis and treatment of HPV has recently been under the special control of doctors, since the virus is highly contagious and has a certain oncological potential.
Causes of genital papillomas
These neoplasms were known to the doctors of Ancient Greece. Hippocrates called them “genital warts.” Both warts and papillomas are caused by one virus - HPV. This is a pathogen that is transmitted exclusively from one person to another through sexual and household contact.
To date, over 100 strains of this virus are known. Each type of HPV can cause the growth of certain tumors. Strains 6, 8, 11, 16, 18 are responsible for the appearance of genital papillomas.
Diseases caused by HPV are considered one of the most common infectious diseases on the planet, as the pathogen is very contagious. According to various sources, about 80% of the world's population is infected with it.
Transmission of virus strains that cause genital papillomas in women and men occurs in more than 50% of cases during unprotected sexual intercourse. The most typical manifestation of such infection is the formation of neoplasms in the anogenital zone.
The virus is very small and is able to penetrate the mucous membrane through microcracks, small abrasions and cuts. However, the entry of HPV into the blood does not always mean that a person will develop papillomatosis. Only 60-65% of infected people show signs of the disease 3-4 months after contact with an infected partner.
For a long time, an infected person can remain just a carrier of the virus and transmit it to others. Activation of the pathogen that causes genital papillomas occurs under certain circumstances:
- Decreased immune defense - general and local;
- The presence of other infectious diseases, especially sexually transmitted diseases;
- Frequent stress, nervous strain, overwork;
- Inflammatory processes in the genitals and urethra;
- Frequent change of sexual partners;
- Fluctuations in hormonal levels.
Read also how the human papillomavirus is transmitted.
Symptoms of genital papillomas
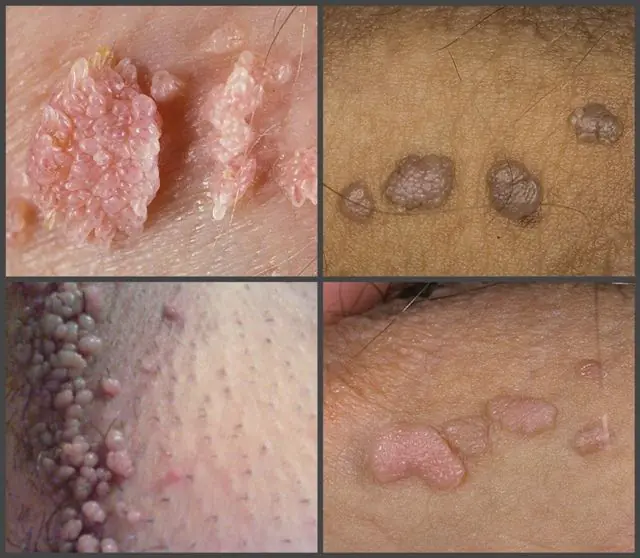
In the photo there are pointed papillomas
In the case of genital papillomas in men and women, the incubation period ranges from 3 to 24 weeks. Representatives of both sexes are equally susceptible to this disease. New growths most often appear between the ages of 22 and 30 years.
As a rule, genital papillomas affect the genitals and perianal area. If a person’s immunity is quite low, for example, with HIV, then growths can also form on the face, eyelids, and ears.
In men, these tumors appear on the penis, urethra, scrotum, and anal area.
Pointed papillomas in women can affect both the external genitalia (labia, vulva), anal area, and the cervical canal, cervix, and vagina. In 20% of cases of detection of these tumors on the external genitalia, growths are also found in the cervical canal.
Many people are interested in what genital papillomas look like. Elements of growths are smooth or pointed papules. They usually do not differ in color from healthy mucosa. Most often they are grouped into “inflorescences” that resemble cauliflower. Their size rarely exceeds 1-1.5 cm.
In places where new papillomas appear and there are already formed ones, patients often feel itching, burning, and discomfort. Sometimes genital papillomas can bleed. This happens if they are in an area that is often injured, for example, in the anal folds or on the labia.Methods for diagnosing genital papillomas

When genital papillomas are localized on visible areas of the genital organs, diagnosis, as a rule, is not difficult for a specialist. However, even if this disease is suspected, differential diagnosis should be carried out with the following diseases: secondary syphilis, molluscum contagiosum, bowenoid papulosis, lichen planus, lichen planus, folliculitis, soft fibroma, pilar cyst.
In some cases, along with a visual inspection, a test with acetic acid (5%) is carried out. The solution is applied to the tumor for 5-10 minutes. After this, the genital papillomas become whitish.
If pathological formations are found on the internal genital organs of a woman, advanced diagnostics may be prescribed:
- Colposcopy. Examination of the cervix and cervical canal using a special microscope.
- Oncocytology. Biomaterial is taken from the cervical canal for cytological analysis.
- Histology. A biopsy is taken - a piece of pathologically altered tissue, which is examined in a clinical setting for the presence of malignant cells.
- PCR blood test. The blood is examined for the presence of pathogen DNA and its type is determined.
- Immunological blood tests. They help establish the concentration of the virus in the blood and the immune response to it, as well as the interferon status of the patient.
Both women and men are required to donate blood for a general analysis, and also undergo a series of tests for the most common sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV and syphilis.
- Read also, which doctor to contact for papillomas
What is the danger of genital papillomas?
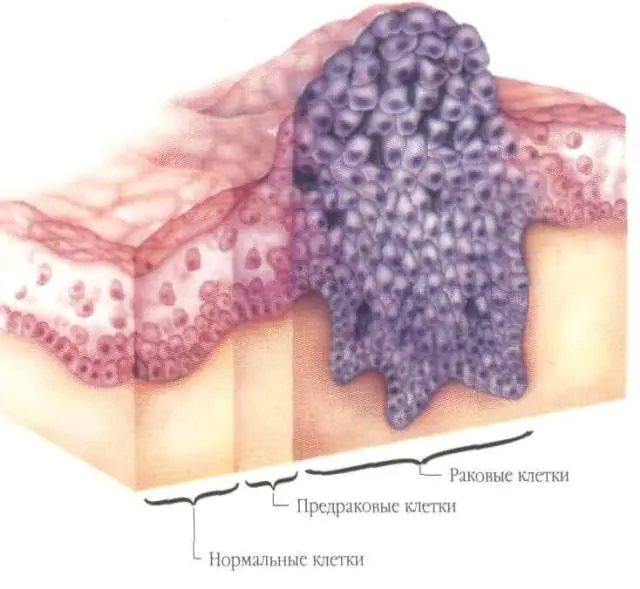
It should be remembered that genital papillomas or condylomas are not at all harmless rashes. They contain papillomavirus in high concentrations and cause active spread of the pathogen during various contacts with healthy people.
In addition, the accumulation of the virus in tissues can cause changes in the genome of epithelial cells and mucous tissue. This can lead to serious complications in the future. Thus, in men, genital papillomas can provoke penile cancer. They are also dangerous for women, as they cause cervical cancer. Almost every patient with a similar diagnosis was found to have HPV of oncogenic strains.
Long-term papillomatosis of the genital organs is considered in medicine to be a precancerous condition. In addition, papillomavirus causes cervical dysplasia and hyperplasia - pathological conditions of the epithelium. In some cases, HPV is transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth; the risk is especially high if a woman has genital papillomas on the genitals.
Large neoplasms or large accumulations of them can often become injured, bleed, and become inflamed. They also interfere with normal intimate life, represent a cosmetic defect and cause psychological discomfort during intimacy.
Elimination of genital papillomas is not a reason to talk about a complete cure. These neoplasms are prone to frequent relapses. The causative agent of the disease can remain in a passive state for a long time in the healthy-looking mucous membrane of the genital organs.- See also the differences between papilloma and condyloma
Treatment methods for genital papillomas
If suspicious growths are found on the genitals, a person should definitely consult a doctor. For women, this specialist is a gynecologist, for men - a venereologist. Only a doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe comprehensive treatment. Self-medication at home in such cases is unacceptable.
Treatment of genital papillomas with medications
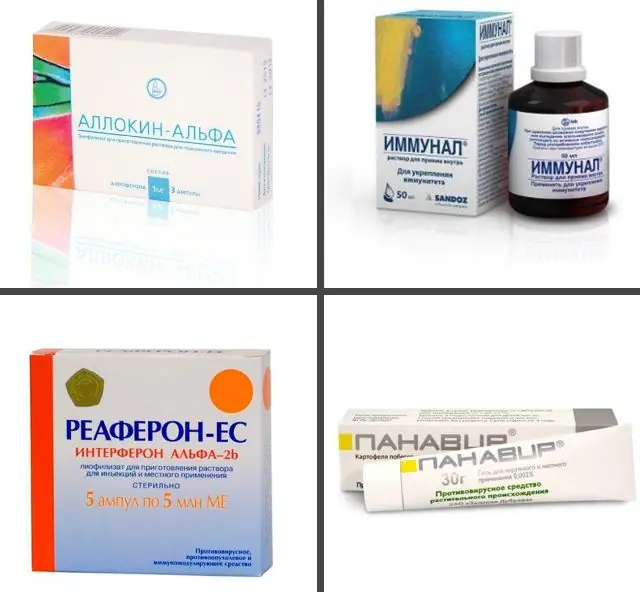
In the photo are drugs for genital papillomas
Medicines are prescribed by the doctor after studying the patient's test results. If the concentration of the virus in the blood is too high, you should take a course of antiviral drugs. If the patient suffers from reduced immunity, it is necessary to stimulate it and take a course of special immunomodulatory drugs.
If you ignore drug treatment, the problem will not be solved. Pointed papillomas will reappear, since their relapse depends on the activity of the pathogen in the blood and the body's defenses and its ability to suppress infection.
For the treatment of genital papillomas, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antiviral. They can take the form of tablets, solutions for injection, sprays, gels, suppositories, creams. They are prescribed depending on the location of the growths and the individual characteristics of the patient. Isoprinosine (from 650 rubles), Allokin-Alpha (from 3800 rubles), Panavir (from 150 rubles) and their analogues Vartotsid (from 1900 rubles), Epigen Intim (from 1000 rubles) are popular.
- Immunomodulators. They can also be prescribed in the form of suppositories, tablets, and powders for oral administration. To stimulate the immune system, Immunal (about 400 rubles), Reaferon (from 600 rubles) and their analogue Polyoxidonium (from 800 rubles) are used.
It should be remembered that it is impossible to completely get rid of genital warts and papillomas using only general medications. It is necessary to remove these tumors. This is the only way to eliminate them from the body. For this you can use local necrotizing agents, which cauterize the growth, and it falls off over time.
Such aggressive drugs include concentrated alkalis and acids. They provoke a chemical burn on the mucous membrane and skin. A small wound remains at the site of exposure, which heals over time. Treatment of genital papillomas should be carried out only on the recommendation of a doctor or under his supervision. Otherwise, you can cause deep tissue damage, which will lead to scar formation in the future.
The following cauterizing drugs are used in medicine: Superchistotel (from 20 rubles), Feresol (from 60 rubles), Kondilin (from 600 rubles) and their analogs Solkoderm (from 900 rubles) and Collomak (about 300 rubles).
The above drugs can only be used to treat genital papillomas on the external genitalia.Removal of genital papillomas
Most often, in order to completely get rid of a problem such as genital papillomas, one has to resort to instrumental treatment methods. These are the most modern and effective methods of therapy. Let's consider the most popular:
- Laser coagulation. This is a low-traumatic and virtually painless method of exposure. During the procedure, the laser beam evaporates the liquid from the papilloma cells. After drying, the growths fall off, and in their place a small wound remains, which soon disappears without a trace. The cost of removing genital papillomas with a laser is 700-2000 rubles in Russia and 270-650 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Electrocoagulation. A special electric knife is used to excise the growth. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, as it is quite painful. Not only a wound is formed on the mucous membrane, but also an electrical burn. The latter burns out pathological tissues of neoplasms. Sometimes scars may form after this surgery. The price of the procedure is 650-1200 rubles in Russia and 230-450 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Radio wave removal. It is usually performed using the Surgitron device. The impact is carried out by high frequency radio waves. The method is optimal for removing genital papillomas on the internal genital organs. There are practically no traces left after such a procedure. The cost of radio wave removal is 1700-2700 rubles in Russia and 450-1200 hryvnia in Ukraine.
- Removal with a surgical scalpel. This method, although considered outdated, is used in cases with particularly large papillomas on the mucosa. The operation is performed under anesthesia, the injury site is stitched with threads. Small scars may remain. The price of the procedure is 550-800 rubles in Russia and 170-300 hryvnia in Ukraine.
Another popular way to remove papillomas is cauterization with liquid nitrogen - practically not used in the case of growths on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. It is difficult to control the depth of penetration of liquid nitrogen into tissues, and therefore it can easily damage the delicate and thin mucous membrane.
Folk remedies against genital papillomas

Traditional medicine recipes should be used with great caution to treat genital papillomas. There is a risk of causing great harm to the body and genitals. Regarding all self-medication methods, you should consult your doctor.
At home, you can try to treat genital papillomas in the following ways:
- Lubricating growths with iodine solution. When the tumor is regularly lubricated with iodine, it dries out and disappears over time. However, this method can only be effective with small growths. In addition, be careful not to burn healthy mucous membranes with the aggressive alcohol iodine solution.
- Treatment with fresh celandine juice. This technique can also bring results if a small formation is being treated. It should be lubricated several times a day until completely eliminated.
- Garlic compresses. This remedy has antiviral effectiveness, and therefore can have a detrimental effect on the papilloma virus, which is found in high concentrations in genital papilloma. Apply a paste of crushed plant lobes at night for several days.
Taking decoctions and infusions to strengthen the immune system provides a good therapeutic effect. They provide real assistance to the body in the fight against the virus. The following plants enhance the protective functions: echinacea, coltsfoot, rose hips, raspberry and black currant leaves, eucalyptus, chamomile.
- Read also about the beneficial properties of propolis in removing papillomas
Prevention of genital papillomas
It is currently impossible to completely recover from papillomavirus. Therefore, the best way to combat it is prevention. It is simple and boils down to the following recommendations:
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene, regularly wash your genitals and monitor the integrity of the mucous membranes.
- Do not touch your genitals with dirty hands.
- Use barrier contraception when having sex with new partners.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle that helps maintain the body's protective functions at the proper level.
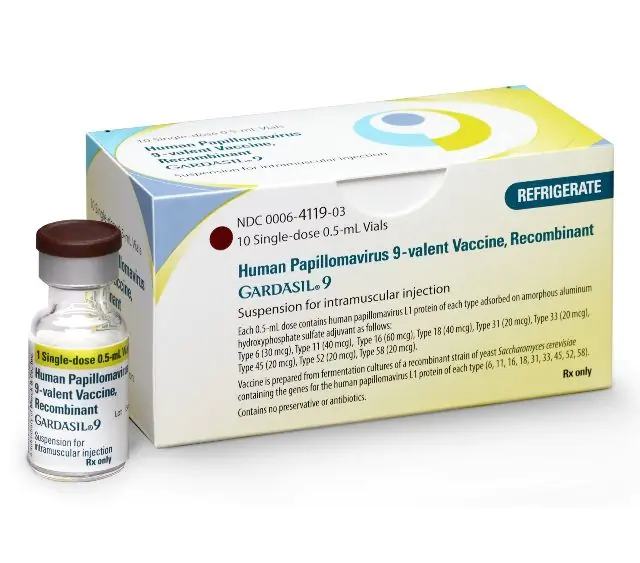
- Vaccinate children before sexual activity against the most oncogenic strains of HPV.
There are currently two main vaccines available against dangerous types of human papillomavirus - Gardasil and Cervarix. They should be vaccinated in childhood or adolescence.
- Read also about measures to prevent warts in adults
How to treat genital papillomas - watch the video:
Photos of genital papillomas can be found on the Internet. Most people are disgusted by their appearance. However, this is not a reason to hide the illness, but an urgent need to visit a doctor’s office to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe the correct course of treatment. It is possible to completely remove tumors and make the virus inactive. This will enable the patient to live a full life and not remember about HPV.
- Related article: How warts are transmitted from person to person



