The unnatural skin color is a sacred gray-blue pigmentation. This anomaly is inherent in newborn children of the Mongoloid race. A child is born with a congenital pigmented nevus, which disappears in the early years of life. As such, no treatment is required for this phenomenon. However, you must consult a specialist to confirm the diagnosis.
What is a Mongolian spot
The anomaly got its name based on the fact that more than 90% of children of the Mongoloid race are born with this defect. According to studies, Asian peoples are more susceptible to the anomaly. However, there are cases when such a spot was observed in 1% of Europeans. Another deviation occurs in the Negroid race. The Mongolian spot is a pathology predominantly found in Asia.
Statistics show: every 200th representative of the Asian people has a special gene that belongs to their common ancestor who lived in the 10th century. Scientists call imperfection differently: Genghis Khan's stain. According to research, more than 16 million people of the Mongoloid race are descendants of the Great Warrior. People interpret the meaning of a defect as a sign from above. Due to its localization on the skin near the sacrum and coccyx, experts call the formation “sacral spot.”
The anomaly appears as an area or areas on the skin whose color resembles a bruise (hematoma). The skin in the pathogenic zone can be bluish, black, green, blue. Mongolian spots in newborns are a type of congenital nevus associated with melanin (skin pigment) in the connective layer of the skin. Localization is always the same. This is the sacrum, hips, and rarely the back.
Causes
There are two interconnected layers in the human skin. The deep one is called the dermis, and the superficial one is called the epidermis. It is known that skin pigmentation occurs from the presence of pigment cells – melanocytes – in the epidermis. These cells secrete the pigment responsible for skin color. However, the color of the skin is determined only by the functionality of these cells, and not by their number.
In representatives of European nations, melanin is formed due to the influence of ultraviolet rays. People of other races always produce pigment. Skin tone is predetermined. During embryonic formation in the embryo, melanocytes migrate into the epidermis from the ectoderm. Doctors believe that the anomaly is formed due to the incompleteness of this process of migration of melanocytes, which remain in the dermis. The pigment they absorb probably leads to the appearance of the defect. The exact causes of the Mongolian spot are unknown.
Manifestation of the Mongolian spot
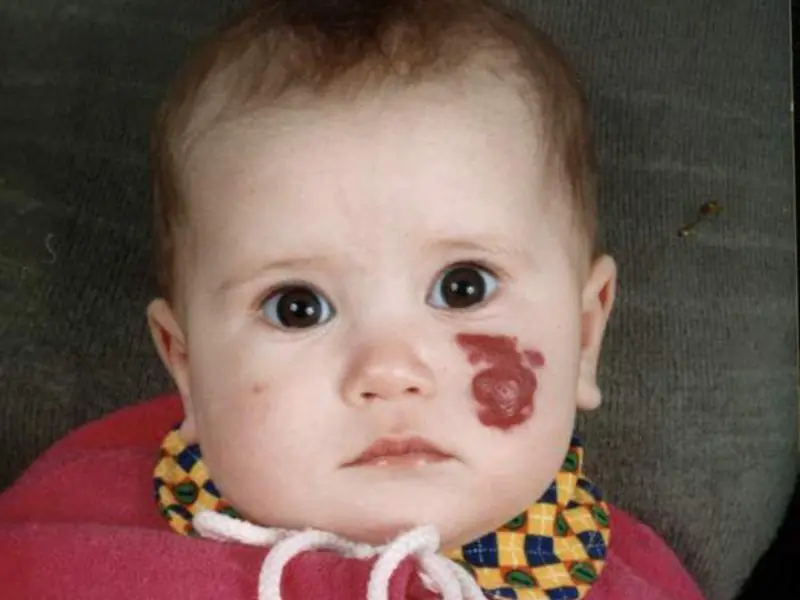
Pigmentation appears in the first days and disappears on its own. Often the spot remains for up to 5 years or does not go away at all. Does not cause discomfort to adults. A blue spot is a congenital imperfection. The shade of the pathology can be gray-blue or even bluish. The clinical manifestation of the Mongolian spot is oval, rounded in shape. Each case is individual. The size of the speck is variable, as is the shape. This false bruise can cover the body in patches (buttocks, buttocks, lower back or legs). In dermatology they know: an anomaly does not develop into cancer (oncology).

Diagnostics
A newborn with unnatural pigments on the skin should be seen by a dermatologist. The doctor is obliged to make a differential diagnosis of the defect. With the help of such a dermatological examination, a specialist will distinguish pathology from dangerous diseases and get rid of assumptions about a possible tumor. Differentiation of changes from other nevi consists of:
Diagnosis of the Mongolian spot is mandatory! A doctor must definitely confirm the suspected diagnosis, because the spot can be melanoma-dangerous and become a problem and even a threat to the baby’s health. Then the child is registered with an oncologist and a dermatologist. To be sure of the proposed diagnosis, a doctor (both a pediatrician and a dermatologist) may suggest a histological examination and siascopy.

Forecast
Dermatologists do not consider this deviation a disease. This change in skin color does not require prevention or treatment. When determining a diagnosis, a specialist will not prescribe therapy, because the formation will disappear on its own over time. The prognosis for Mongolian spot is favorable. The aberration never regenerates once it has completely disappeared. A child with such an abnormality develops normally.
Found an error in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we will fix everything!
The Mongolian spot is a congenital pathology. It occurs infrequently and causes moral discomfort to a person. Is such education dangerous, how to get rid of it?
Concept
The Mongolian spot is an area on the skin with a distinctive color. The color of this area can vary from light gray to dark, almost black.
In most cases, it is noted on the buttock, sacrum, back of the legs, and in some cases it may appear on the back.
The spot got its name due to the fact that it appears in children of the Mongoloid type in 90% of cases. The Mongolian mark is often found among the Chinese, Vietnamese, Koreans, Japanese, and blacks.
Another version is that every two hundred Asians have the Genghis Khan gene. About sixteen million people are his descendants, so many children of these peoples are diagnosed with a similar spot.
In a Caucasian newborn, the spot is diagnosed in very rare cases.
Often a nevus located on the coccyx is called a sacral spot; great importance is attached to such a mark. The pathology is an area of the skin of an unnatural color, reminiscent of a bruise. It can be detected already in the first days after birth. Mongolian nevus does not cause trouble or discomfort to the child. In the first months it has an intense color, becoming paler over time. Disappears in most cases in the first or second year of life. Occasionally, marks remain on an adult; they are almost invisible.
The size and shape of the spot varies. Sometimes the mole reaches ten centimeters in diameter.
A nevus can “migrate”—move from one place to another, but this phenomenon rarely happens.
Refers to melanoma-mono-dangerous nevi; degeneration into a malignant form has never been recorded.
Causes and symptoms of the Mongolian spot
Why does a Mongolian spot form in humans? The pathology is congenital and is diagnosed in a person in the first days of life. What reasons influence the development of such spots on the skin?
A nevus develops in the womb. Every person's skin consists of two layers, superficial and internal. In the epidermis (first layer), the synthesis of melanocyte cells responsible for pigmentation occurs.
During the development of the baby in the womb, cells migrate from the deeper layer - the dermis - to the surface. Sometimes the process is not completed on time, melanocytes remain in the dermis.
The pigment produced gives the skin certain shades. This is the main theory of the appearance of Mongolian pezhins. The exact reasons have not been established. What symptoms are characteristic of such a spot?
Signs:
- The first and main feature is the appearance immediately after birth.
- Sizes vary and can cover large areas of skin.
- Pezhina has a uniform color over the entire surface, from gray to black.
- The shape is irregular, sometimes round or oval.
- Located on the buttocks, sacrum, legs, back.
- Mongolian birthmarks are mostly isolated. Rarely – multiple.
Treatment of the disease in newborns and children
After the examination and confirmation of the diagnosis of “Mongolian formation”, treatment is not prescribed. A spot of this type does not cause discomfort to the patient, does not degenerate, and therefore does not require removal or therapy. In most cases, the pathology goes away on its own.
The prognosis is favorable due to the fact that the phenomenon is not a disease.
In newborns
Parents, having discovered a blue spot on their newborn’s bottom, are often frightened and do not know what to do. You should contact your pediatrician. He will conduct the necessary tests for the presence of melanoma cells and make an accurate diagnosis.
The Mongolian pezhina does not cause discomfort to the baby. In the first days it is quite bright, gradually begins to brighten. In most cases, it becomes smaller or disappears completely by two years. Parents need to monitor the condition of the spot and note its changes.
A Mongolian nevus on a child’s bottom is often called Genghis Khan’s spot. Representatives of many nations are sure that this sign means great luck and happiness for the newborn. There is no need to worry about the presence of a Mongolian mole on your baby’s bottom; it will disappear over time.
Treatment in children
In an older child, the Mongolian spot is slightly expressed. By the age of ten, almost all children get rid of this pigmentation. It practically never happens to teenagers. In rare cases, it can be diagnosed in adults.
Diagnostics and prevention
Mongolian formation on the skin requires careful diagnosis. A dermatologist examines the baby at birth. If there has been no examination, then it is necessary to visit a specialist in the first days.
Some congenital moles have a tendency to degenerate into malignant formations.
Dangerous:
- Pigmented nevi (hair nevi),
- Nevus Ota,
- Moles are blue.
To exclude the presence of melanoma-dangerous moles, various examinations are carried out.
Examinations:
- Dermatoscopy. The spot is examined using a special device that magnifies the nevus several times. The method allows you to study the structure of education.
- Siacopy. The method involves research using spectrophotometric scanning of pigmented areas.
- Biopsy. Histological examination of pieces of the formation. Helps determine the possible presence of dendritic cells with melanin present (present in pathology).
A complete examination allows you to make the correct diagnosis. If there are formations that can degenerate into malignant ones, the necessary treatment is prescribed.
There is no prevention of Mongolian pezhin, it is impossible to influence its formation. If detected, you should contact a specialist in time and monitor changes in the mark.
The Mongolian spot is a congenital pigment formation on the skin. It does not cause much trouble, does not require treatment, and disappears on its own with age. A newborn child should be shown to a doctor in time to rule out melanoma-dangerous formations.
Child at 8 months nevus - video
Scientists have not yet determined how a birthmark appears in a newborn baby. But they know that such formations are not dangerous for the baby and in rare cases require correction. There are different types of nevi. Some disappear on their own, while others need to be constantly monitored. If the mark becomes inflamed or changes, doctors recommend starting treatment as early as possible.
Causes of birthmarks in a newborn
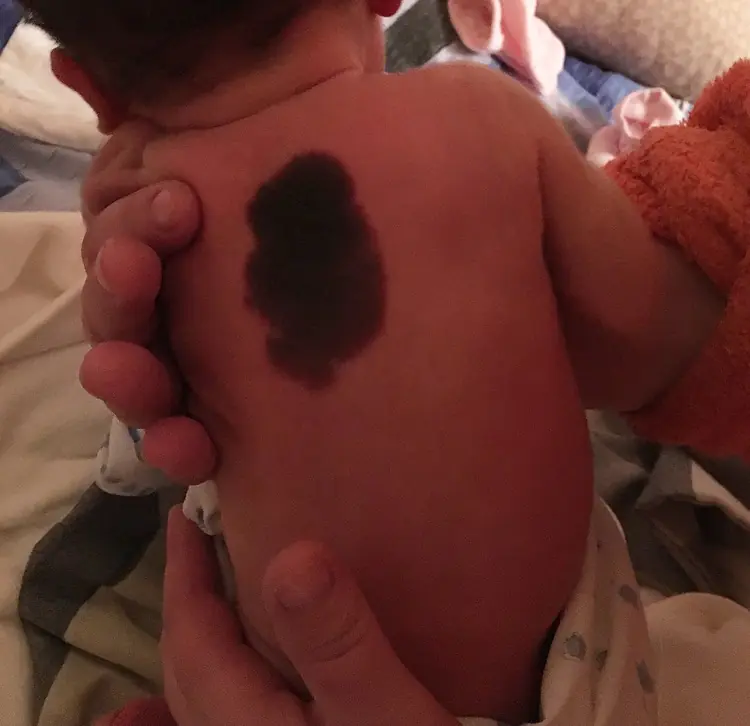
The process of formation of nevi has not yet been fully studied. But scientists were able to determine the range of pathological conditions that provoke the formation of a skin defect. These include:
- Heredity.
- Hormonal surges.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Poisoning by poisons or radiation exposure.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Phototype of the baby's skin (in a child with light skin, marks are formed more often than in infants with dark skin).
- Gender (female babies have moles on their bodies more often than male babies).
- Fetal maturity (children born prematurely are more likely to be born with visible birthmarks).
Types of nevi
The name implies the fact of the transfer of marks by inheritance (by family). Often the same defects are detected in children and their parents. Many babies are born with clear skin. But this does not mean that there is nothing on the covers. It happens that the spots are weakly colored, and at first it is difficult to see them without examining the integument with a magnifying glass.
Distinct birthmarks from birth are detected in only one baby out of a hundred. For the rest, invisible marks darken over time and become visible by the age of five.
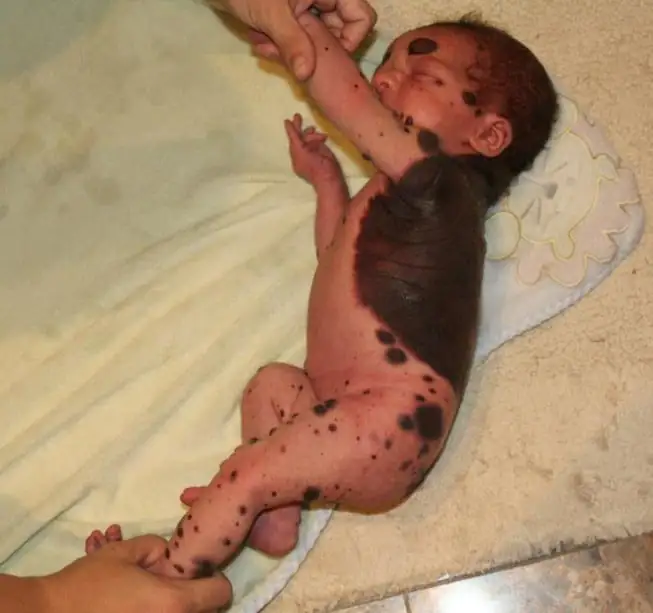
In infants, birthmarks of two types can form on the body:
- pigmented moles of brown or blue-black color;
- red spots (angiomas, hemangiomas) of pink, purple-violet, red color.
The color of the marks is determined by the cells involved in the formation of their structure. If the mark is formed from actively dividing melanocytes, the color of the nevi will be brown or black. And the formation of a formation structure from vascular cells gives the mole a red color.
Birthmarks, the structure of which contains pigment cells
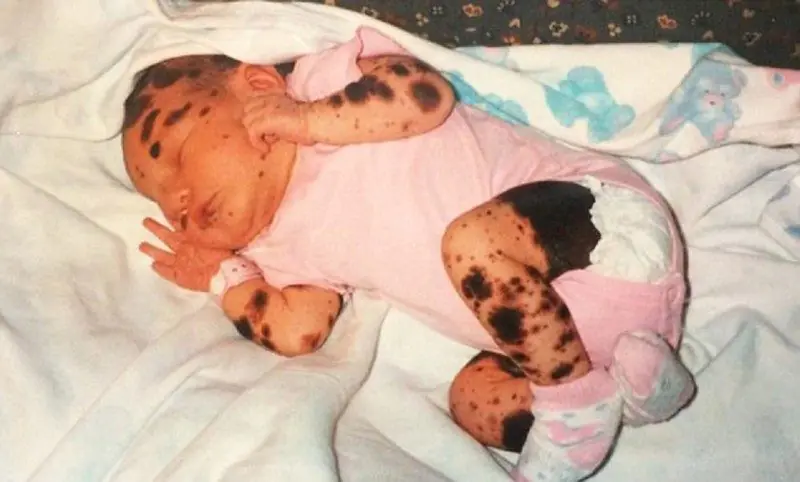
There are several types of pigmented formations, which are most often detected in infants. The reasons for the formation of such birthmarks are a high concentration of melanin in a small area of skin.
| Type name | Description |
| Mongolian spot | Appears on the body of infants with Mongoloid genes from birth on the lower back, in the sacrum area. Outwardly it looks like a bruise and disappears completely on its own by the age of five. The health and development of the child is not threatened |
| Dysplastic nevi | These markings are similar to irregularly shaped marks. They have different color intensities and vary in size. There are cases when dysplastic formations are formed from individual point-type elements |
| Moles | They resemble small spots of different colors and sizes and appear on any part of the body |
| Congenital nevus formed from pigment cells | Large markings. Each baby has a different shape of this spot; the color can be light, coffee or blue-black. Hair grows on the surface. This is the main diagnostic sign |
If there are several nevi on the child’s body at once, parents should observe them, control their size and color. If the shape changes, a sharp increase in the size of the formation, or asymmetry appears, you must immediately seek medical help.
You need to start sounding the alarm if the birthmark begins to change color and the skin next to it becomes swollen, red, begins to hurt or itch.
Vascular birthmarks
Hemangiomas appear on the baby’s body from birth; they are clearly visible already in the first weeks of life. The reason for their appearance is the active division of vascular cells, the interweaving of pathologically altered small capillaries. Such formations are constantly growing. By the age of one year, their growth stops, then regression begins: the mark decreases in size and by the age of five it completely disappears on its own without any drug treatment.
Scientists cannot understand why this happens. There is an assumption that the spot affects the vessels that nourish the skin and subcutaneous tissue. This happens due to a violation of the properties of collagen fibers, which are responsible for the strength of the walls of hollow tubes, and a disruption in the process of cell division that makes up the tissue. Most often, hemangiomas appear in children with low birth weight.
Such spots form under the skin or rise above its surface. They have an unpleasant appearance, so many parents insist on their removal. Pediatricians warn that they do not pose any danger and disappear on their own over time, so there is no need to fear for the health of the children.
Types of hemangioma
There are several types of hemangioma:
| Name | Peculiarities |
| Stork trail | A spot of intense pink color forms on the top of the head, on the back of the head, transitioning to the forehead and bridge of the nose. Its surface may consist of a scattering of small elements |
| Kiss of an angel | The entire surface of the face is covered by one pink-yellow spot. When the baby begins to cry, the intensity of the color intensifies |
| Nevus flamingo | Appears on the head, face, has a bright color, its intensity intensifies over time |
| Strawberry stain | The body of the formation rises above the surface of the skin and is shaped like strawberries. In the first months of life, it actively grows and develops; after the age of three, regression begins. By the time of the first hormonal changes (puberty) it completely disappears. Some children have a scar in its place |
| Cavernous hemangiomas | They can be located on any part of the body; such formations do not have clear boundaries, constantly grow, and quickly increase in size. Their structure consists of several seals located close to each other. If you place one palm on the hemangioma and the other on an area of clean skin, the temperature difference will become noticeable. Where the vascular formation is located, it will be several degrees higher |
| Spider nevus | The shape of the mark is similar to a star, therefore it has the second name “star nevus”. Completely disappears to the surface of the skin by the time of puberty |
Parents of children whose bodies have vascular formations should closely monitor them and try to prevent injury to the surface of the hemangioma. If a red birthmark forms near natural openings (near the ear, eyes, nose) and by the age of two it does not show signs of regression, then it is necessary to seek medical help.
Sizes of nevi and control over them
To facilitate monitoring of birthmarks, a classification of the size of benign formations was created.
- Spots between 5 and 7 mm in diameter are considered small. They do not spoil the appearance and do not pose a threat to the child’s life, so there is no need to remove them.
- Moles measuring from 7 to 12 cm, growing on the back, lower extremities, and forehead, require close monitoring.
- Giant formations have a diameter of more than 14 cm.
Experts recommend that parents take transparent paper in their hands, apply it to the birthmark, outline the contours of the formation, cut it out with scissors and save it. Such a template can then be periodically applied to the nevus and its new dimensions can be compared with the previous ones. It is useful to take photographs of birthmarks once a month and save them. This will also help track the dynamics of mark formation.
When is it necessary to remove birthmarks?
Radical treatment is used in extremely rare cases, when signs of a pathological change in the birthmark are detected. The following signs indicate its development:
- The surface and shape of the formation change (the birthmark becomes convex, rough folds form).
- The surrounding skin swells and turns red.
- The color becomes lighter or darker.
- The edges become uneven and take on a paneled shape.
The presence of just one sign may indicate the beginning of the transformation of a nevus into a malignant tumor. Therefore, it is important to immediately seek help from a pediatric oncologist when manifestations are detected.
Attention! Skin cancer is an aggressive disease that can metastasize quickly and extensively. Late stages are difficult to treat, but therapy undertaken in the early stages will help save the child’s life.
Methods for removing birthmarks in newborns
Those birthmarks that are localized in places of constant irritation (on the neck, scalp, inside natural folds) are subject to removal.
Indications for surgical removal:
- rapid growth of the birthmark;
- the appearance of small bleeding cracks on the surface of the mark;
- statement;
- pain when touching the mark.
To excise the spot, laser therapy, cryodestruction and the use of medications for external use (for older children) can be used.
The choice of remedy depends on various factors: the types of formations, the age of the baby, and the results of a diagnostic study are taken into account. In the absence of suspicion of the presence of malignancy processes, preference is given to laser treatment.
But if there are symptoms of malignancy, the birthmark is removed using the traditional surgical method. Only excision of the tumor with a scalpel will completely remove the formation and obtain biological material suitable for histology.
Prevention of complications
To prevent complications, parents should protect their child’s skin defect from exposure to active sun, injury, and overheating. You should not try to treat yourself with folk remedies, cauterize or lubricate the stain with the juices of medicinal plants. Many of them contain an aggressive formula that can damage the integrity of the formation and provoke its inflammation. It is important to regularly conduct diagnostic examination of the structure of the birthmark. For these purposes, you need to consult a dermatologist.
Birthmarks appear on any part of the body. But many children live with huge nevi on the forehead, lower face, body and limbs without complications. You don't always need to remove them. Any operation or treatment is an additional burden that not every child can easily bear.



