You can get perfect skin without a single spot, perhaps, only through Photoshop. All kinds of birthmarks, freckles, uneven pigmentation, moles - all this forms a real living image of a person, and it would be ridiculous to consider them an unambiguous disadvantage. But sometimes they cause concern, especially if they have an unusual shape, color, start to grow, or are located in an inconvenient location. A mole can appear in the eye in the same way as on the cheek or stomach, and this is a legitimate concern. Is it safe enough and should we be concerned about the consequences?
Types and location of moles on the eye
In common parlance, a mole is called not only a nevus, but also a papilloma, although these are completely different things. They differ not only in appearance, but also in origin, although both are neoplasms. A dense and elastic speck of a dark color is most likely an ordinary nevus, but a papilloma has a loose structure and looks like a soft outgrowth of skin that has accidentally appeared.
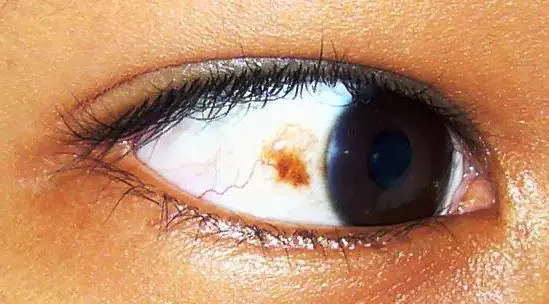
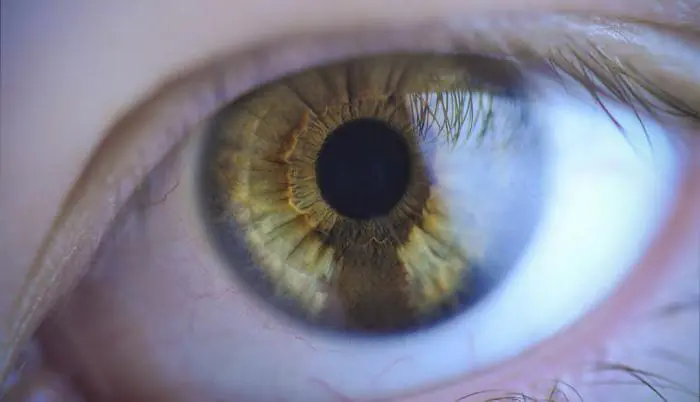
If there is a mole in the eye, then it is precisely a nevus, and they differ only in location. If a brown spot is visible on the iris or on the white of the eye, then this is most likely a conjunctival nevus. If the neoplasm is deep and cannot be detected with the naked eye, then it is a choroidal nevus - it is detected during an ophthalmological examination.
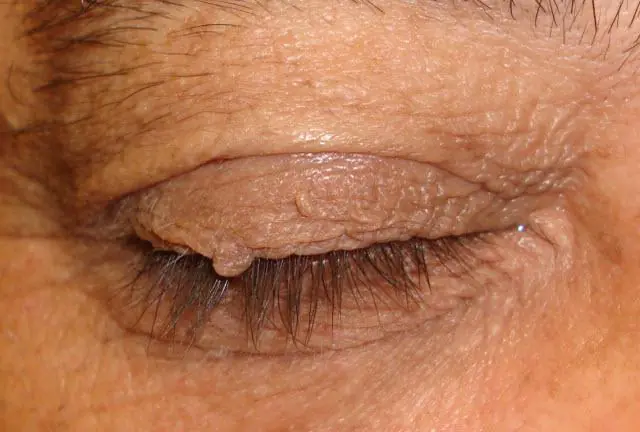
There may be nevi and papillomas on the eyelids; the latter often develop with age, hang down, interfere with vision, and, if the location is particularly unfortunate, can provoke constant lacrimation.
Conjunctival nevus
A mole in the eye can be located on the iris or on the white of the eye. A nevus on the iris looks like an area with a different color, it can even look original. Since the pupil, as a rule, is not blocked, this neoplasm does not interfere with vision.
Conjunctival nevus can be pinkish or with a red tint, any shade of brown, sometimes even gray or almost black. In the absence of melatonin, the nevus will be practically invisible and is detected only during a special examination or if it suddenly changes color due to changes in hormonal levels or other reasons.
Choroidal nevus
If a nevus appears in the depths, almost on the fundus or in the area of the so-called equator of the eye, then it can only be detected during examination. If a mole in the eye does not affect the quality of vision and does not suddenly begin to enlarge, then there is no need to worry.
Scientists have differing opinions about the rarity of choroidal nevus. This neoplasm is found in approximately 3% of cases, but some experts believe that almost 20% of people have a nevus in the eyeball, it’s just that the vast majority lack pigmentation and are harder to detect.
Mole on the upper eyelid
Depending on the type and location of the tumor on the upper eyelid, it can be a piquant feature of the image or an annoying cosmetic defect. A small nevus on the border of the eyelashes in women is successfully hidden by cosmetics, but a soft papilloma can actually significantly spoil the appearance and even interfere with vision.
To remove a mole on the eye, you need to contact a specialist and, depending on its type and location, choose a removal method. Despite the fact that the eyelids are generally a very delicate area that requires careful handling, this is a simple procedure that is performed under local anesthesia and does not require any complex actions. You can choose surgical removal, electrocoagulation, laser surgery.
Mole on the lower eyelid
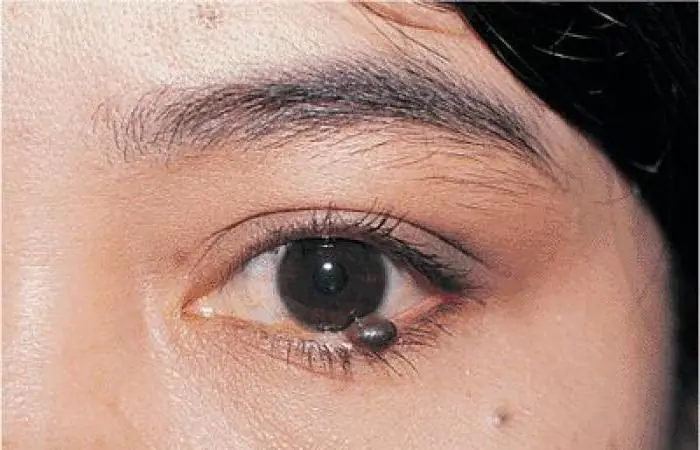
From a doctor's point of view, the location of the mole is not of any decisive importance. Perhaps, if the nevus is located near the tear ducts, this may cause some concern, and it is better to remove such a mole before it begins to change size under the influence of external reasons.
Other neoplasms, papillomas or condylomas, can cause discomfort and increase in size over time. Removal of a mole under the eye is carried out taking into account the least amount of tissue trauma. If a tumor biopsy is required, surgical excision of tissue is preferable. The removal methods are the same as for the upper eyelid, especially if, in addition to a cosmetic defect, the tumor interferes with blinking, pulls the eyelid, provokes increased lacrimation or, on the contrary, makes it difficult.
Hanging moles on the eye
The biggest concern is caused by hanging tumors, in most cases these are papillomas. Over time, they begin to grow, acquire dark pigmentation and become coarser. They are usually called “senile warts”, the medical name is age-related keratoma. They appear under the influence of the human papillomavirus and gradually progress.
Age-related keratomas can appear anywhere on the skin, and the eyelids are no exception. As the disease progresses, such a “hanging mole” can become keratinized, covered with scales, and significantly increase in size. After removal of a keratoma or papilloma, a study of the removed tissue and comprehensive treatment for the papilloma virus are required. In most cases, this is a benign form of the so-called precancer, which does not pose a danger to the body, but it is better to be safe.
The increase in age-related keratomas over time and the appearance of new ones is a completely normal process in the body infected with the human papillomavirus. There is no need to panic; at pre-retirement age, several tumors suddenly appeared, including on the eyelids or in close proximity to the eyes. Modern methods of cosmetic surgery make it possible to get rid of nevi, papillomas and age-related keratomas quickly and painlessly.
Degeneration of nevi
Wherever the mole is located, it must be observed, recording its dimensions. Choroidal nevus is observed once a year using special ophthalmological equipment, the size of the neoplasm is recorded, and if a change in the boundaries, shape and size is observed, removal is prescribed.
The degeneration of nevi into dangerous melanoma occurs much less frequently than is commonly feared. Of course, you should not expose yourself to additional risk - injuries and excessive sun exposure can spur processes that contribute to pathological changes in the tumor. However, in most cases, a nevus is a harmless and even cute feature, even if it is a mole in the eye. Photos of such nevi are often shown as an original version of heterochromia.
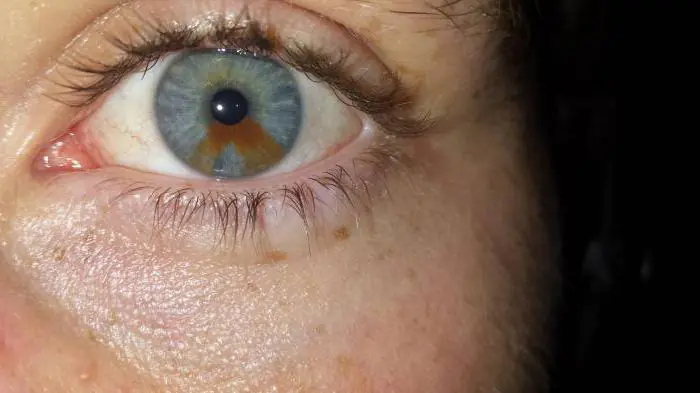
If a mole interferes
Practitioners often cite an inconvenient location as an indication for removal of a stable, non-enlarging mole. Nevi or papillomas can be located in potentially traumatic places, and if a mole constantly rubs against clothing or shoes, then it is better not to expose it to additional risk. In a situation where someone has a mole on their eye, removal becomes the preferred option.
Even if such a mole does not hang down and does not pull down the eyelid, it is still exposed to excessive sunlight. Nevi on the eyelids of women are constantly in contact with cosmetics, in addition, they are easily injured just by unsuccessfully rubbing the eye. If the nevus is located not on the eyelids, but directly in the eyeball, then the quality of vision is first taken into account. Ophthalmologists claim that deterioration in visual acuity due to nevus occurs much less frequently than for any other reasons.
Doctors warn!
Despite the ineradicable love for traditional medicine, doctors categorically insist on medical methods for removing any tumors. You cannot use bandaging with a “magic” thread while reading spells, especially if these are hanging moles under the eye or on the upper eyelid. Under no circumstances should you be fooled by the apparent simplicity and cheapness of strange methods such as burning moles with alcohol tinctures of various plants.
Firstly, the skin on the eyelids is very thin and can easily be damaged. Secondly, it is too easy to get the burning solution into the eye, the consequences of which can be extremely serious. Finally, do not forget that it is external negative influences that can force a harmless nevus to become a dangerous and active form of cancer.
If a suspicious spot appears on the iris or on the white of the eye, you must make an appointment with an ophthalmologist and clarify the diagnosis. If the tumor has reduced the quality of vision, a visit to the doctor becomes urgent. It is better to entrust moles on the eyelids to an experienced surgeon in a modern medical center, and soon you will not even think about the nevus or papilloma.
Most Caucasians have moles (nevi). Pigment spots form on the body, face and even the eyeball. Nevi differ in shape, color, size, and location. A mole in the eye occurs in people belonging to different age groups. Nevus tumor is found in adults, elderly patients, adolescents and young children. Eye moles are benign.
Causes
Moles in the eye are formed under the influence of melanocytes - cells containing pigment. Melanin, accumulating in tissues, gives them a certain color. The color of skin, hair, iris, and birthmarks depends on this substance.
The following factors lead to the formation of nevi in the eye:
Light-skinned people are at risk. Their epithelial tissues contain a small amount of melanin. The likelihood of mole formation decreases with a sufficient concentration of pigment in the skin cells.
Types of moles in the eye
There are 2 types of birthmarks in the eye:
- Vascular moles. Red nevus spots and hemangiomas appear when blood or lymphatic vessels are damaged.
- Non-vascular (pigmented) moles. Neoplasms develop from melanocytes. The spots are colored brown and black. There are no blood vessels passing through them.
Among pigmented nevi there are:
By nature, ocular nevi are:
- benign;
- malignant.
Based on location, there are 2 types of moles in the eye:
- Nevus of the conjunctiva. The spot forms on the mucous layer of the eyeball. Such moles are easy to notice. The unusual pigmentation on the protein itself catches the eye of people around it.
- Choroidal nevus. The doctor identifies the spots by examining the patient using specialized equipment. Moles appear in the deep layers of the eyeball.
The ICD 10 code for an ocular mole is assigned depending on the type of neoplasm: D31-36.
Conjunctival nevus
Vascular moles that appear on the conjunctiva cover the entire thickness of the mucous layer in the eye. New growths of pink and red shades are formed from capillaries.
Pigmented nevus of the conjunctiva occurs when there is an excessive concentration of melanin on the mucous membrane of the eye. The spots are colored brown and black.
Cyst-shaped nevi that appear on the conjunctiva are formed from lymphatic vessels. They are cystic formations, the internal cavity of which is filled with colorless exudate. The outgrowths from the inside look like a honeycomb.
In stationary conjunctival nevi, the shape and size are unchanged. They are benign and do not threaten health or life. Such growths are not treated or removed. The doctor simply observes the dynamics of the tumors. For preventive purposes, the doctor examines such patients once a year.
Progressive birthmarks constantly change:
- increase in size;
- transform, take on different shapes;
- compress the vessels.
If the need arises, the doctor insists on removing the transforming birthmark. The mole is removed using microsurgery methods or laser.
Treatment of progressive nevus is carried out in the following cases:
- if dystrophic changes appear in the retina or epithelial tissues with pigmentation;
- tissue detachment occurs.
Choroidal nevi
Birthmarks can form on the vascular membranes of the eyes. Such outgrowths are formed from vascular cells.
Birthmarks on the choroid appear during periods of hormonal changes. Outgrowths appear singly and do not form groups. Usually a mole forms in one eye. Bilateral lesions are quite rare.
Choroidal birthmarks, like iris nevi, are divided into stationary and progressive. Stationary growths are benign.
Progressive spots transform: they take on different shapes and grow. Large tumors limit vision, impair vision, and compress blood vessels. In this case, patients focus on the presence of a foreign body in the eye.
Locations
Birthmarks form in different areas of the eye:
- external and internal areas of the protein;
- tearful month;
- semilunar fold;
- iris or retina;
- limbo.
Location of conjunctival nevi
An ocular nevus forms on the inner and outer parts of the conjunctiva. Birthmarks are detected on the inner corner of the eye, the periphery of the cornea, the lacrimal month, and the semilunar fold. Sometimes neoplasms appear on the inside of the eyelid. Although moles are located near the pupil, they do not block the view or impair vision.
Localization of choroidal nevi
- on the back of the eyeball;
- on the fundus;
- at the ocular equator.
The spots are invisible to others; they are discovered by a doctor who performs diagnostics using specialized equipment. But an ophthalmologist is not always able to identify a nevus of the choroid of the eye. Diagnosis is difficult if the tumor lacks pigment.
Color and size
Eye birthmarks vary in size and color.
Conjunctival moles
The color of conjunctival nevi is influenced by the cells from which the tumor is formed. The color of the spots varies from pink to black. Some moles do not develop pigmentation. With a sharp hormonal surge, the color of the nevi changes. In some people, tumors become discolored as they age.
The shape of such pigment spots is flat, with clear outlines and a velvety surface. The size of the iris in diameter reaches 4 mm.
Choroidal moles
The outgrowths that arise on the choroid have a flat shape with pronounced outlines. They are clearly visible when examining the patient. The spots are painted in dark colors. If moles do not contain pigment, they cannot be seen. The size of the growths in diameter reaches 6 mm.
What is the danger
Eye moles do not manifest themselves for many years and do not cause a person any discomfort. However, when certain factors come together, they begin to undergo transformation. Progressive nevus is the most dangerous type of eye mole. Changing pigment spots cause:
- deterioration and loss of vision;
- degenerate into a cancerous tumor - melanoma.
After discovering a birthmark, you should regularly visit an ophthalmologist. This will prevent the development of melanoma. In case of negative dynamics, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen or decide to remove the nevus.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the following complications occur:
- a mole makes it difficult to see;
- the quality of vision decreases;
- a foreign body is felt in the eye;
- the size and color of the spot changes.
With timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. A nevus in the eye transforms into cancer in 1 patient out of 500. Close attention must be paid to the spots:
- the thickening of which has reached 2 mm;
- with subretinal exudate;
- with orange pigmentation;
- located on the posterior disc of the eyeball.
Removal
Before removing a nevus in the eye, the doctor determines the nature of the neoplasm. Interfering birthmarks can be removed in several ways. The ophthalmologist chooses the method of excision of a dangerous tumor. Patients are given:
- electroexcision followed by plastic surgery of affected tissues;
- microsurgical operation;
- laser excision.
With progressive choroidal nevus, the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account. Treatment tactics are influenced by:
- localization of the birthmark;
- tumor growth rate;
- age and condition of the patient;
- accompanying pathologies.
Progressive growths are removed using traditional microsurgery techniques or laser coagulation. Hard-to-reach moles are removed with laser. Removing problematic moles allows you to avoid the development of a cancerous tumor, the transformation of a nevus into melanoma.
In a child, a nevus is treated as a last resort when the eye mole grows rapidly.
Progressive medical technologies prevent the degeneration of eye nevi into cancerous tumors. Thanks to them, it is possible to preserve vision and health. The main thing is to seek medical help in a timely manner and undergo regular preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist.
The formation of moles on the eye is rare, but it is possible. They are formed due to accumulations of melanin and are created on any anatomical areas, including in the eye. The formation is of exactly the same nature as on the shoulder or arm. However, this area causes reasonable concern and concern, so it needs to be monitored and observed by a doctor.
Causes
A mole can appear in infants, adults and the elderly. In this case, the ocular nevus can be localized on the iris, on the white or on the cornea. In some cases, the mole is not visible and can only be detected using an ophthalmological microscope.
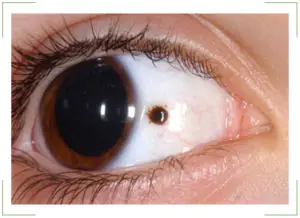
As a rule, a birthmark is visible from the side. It has a darker pigment composition. Therefore, the nevus is very noticeable in people with light eyes. To understand why it is dangerous, you need to understand the reasons for the formation:
Congenital feature
Then the pupil and white will have a nevus from the first days of the child’s life. In newborns, this spot is often small in size. But over time, the eye changes color and it grows. Moreover, its increase is very intense.
| Congenital nevus does not pose a threat to vision. It does not interfere with visual function and does not affect the functioning of capillaries. |
Acquired nevus
In this case, the mole appears throughout life. And this can happen at any moment. After all, the conjunctiva and the eye are exposed to different influences throughout life. Moreover, such effects can be directed not only directly to the conjunctival region. This is caused by severe stress, hormonal changes, pregnancy, and so on. In any of the above cases, there is a possibility of a birthmark appearing on the eye.
Types of moles in the eye
Typical nevus
Located on the iris of the eye. This area is also called the conjunctiva. Such moles are small spots with a diameter of several centimeters. As a rule, they have a clear shape and edges. The color of the nevus is often brown. 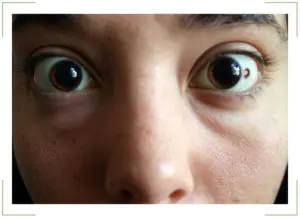
Atypical nevus
It may be colorless and located on the inner surface of the iris, where it is not visible. Accordingly, it is invisible from the outside. The initial nevus is also small in size. At the same time, they may not change during a person’s life. But when the mole enlarges, the subsequent stage is expressed by a more extensive nevus. It begins to take up a lot of space and switches to protein.
Conjunctival nevus
Covers the previous two types. Since this is the iris of the eye, the moles that are located on it are conjunctival nevi. This type of spots is further divided into cystic and vascular.
Thus, cyst-shaped ones do not have a pronounced color and are honeycomb-like formations. Meanwhile, capillary ones are created from small blood vessels. That's why they have a pale pink or red color.
Choroidal nevus
It is located inside the eye and is invisible to others. Actually, the choroid is a collection of vessels located on the inner surface of the eyeball. Therefore, a nevus can only be noticed during an examination. Such formations may have a constant shape and size, but there are times when they change.
Stationary and progressive nevus
| The appearance of a mole in the eye does not mean a risk of developing cancer. This sign can be completely safe. Moreover, the nevus does not affect visual acuity or eye function in any way. |
Nevus is not considered a disease. This is an education that every person has. It’s just that moles are usually located in other anatomical areas. For example, on the back, arms, and so on.
In this case, the nevus can grow over time. Such formations are called progressive. They change size and shape, gradually increasing. Often, growth occurs at a very rapid pace. So, in one year a mole doubles in size.
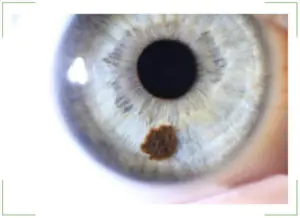
If any other spot begins to grow, this indicates a potential cancer threat. But this principle does not work regarding nevus in the eye. It is important to clarify the situation. An increase in the size of the spot does not mean that the mole is turning into a malignant formation. The risk of developing cancer remains throughout the entire period of existence of the nevus in the eye. Therefore, when a mole appears, it is necessary to consult a doctor, undergo an examination and monitor the dynamics of its condition.
What is the danger of pigmented nevi in the eye?
As stated above, education does not pose serious consequences for vision. They do not obstruct vision, do not narrow the field of vision, or impair its sharpness. At the same time, birthmarks do not cause any discomfort to a person.
The only threat is the likely development of the nevus into a malignant cancer. Therefore, many consider it necessary to treat and remove moles in the eye.
Symptoms of nevi
The main sign is that the stain is noticeable to others and to the person himself. The nevus can be located around the entire perimeter of the eye, this does not play any role.
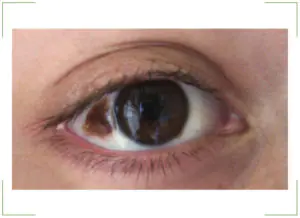
The only symptom of a birthmark is a change in corneal pigmentation or protein. The appearance of small spots and clusters in the form of bubbles indicates the initial stage of the nevus. If such formation causes concern, you should contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination. It is impossible to be sure in any other way what type of nevus it is.
Diagnosis of formations
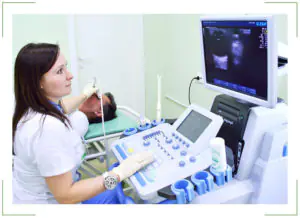
Detection of a birthmark is carried out using special equipment. After all, it is necessary not only to study the cornea or pupil. The doctor must look inside the eyeball, examine the fundus, and so on. Therefore, various techniques are used:
Ultrasound diagnostics
It is a well-known ultrasound examination. Only the patient's eye is the object. Using this technique, it is possible to identify accumulations of melanin in certain parts of the eye. This test is very accurate and provides a complete picture of what is happening inside the visual organs. There will be no hidden areas, which is very important for further treatment of nevus;
Angiography
This is a type of x-ray examination. It is necessary for studying and assessing the condition of blood vessels. As stated above, a nevus can form directly on a collection of blood vessels in the eye.
During the examination, it is recommended to use both methods. They complement each other perfectly and give an accurate picture of the development of the birthmark. A lot of information can be obtained by studying the nevus over several years.
Treatment methods
This phenomenon is not a disease. This is a condition of the eye in which there is an accumulation of pigmented formations. They form a nevus. It cannot be affected by medications or physiotherapeutic methods. The mole will not disappear from this.
Only birthmark removal is used. It can be removed using laser technologies, with local anesthesia, without placing the patient in a hospital.
| Such technology is safe and does not involve the risk of worsening the patient’s condition. |
Forecast
In the vast majority of cases, even if a mole grows, it remains safe and does not affect health. However, it can always be removed using a laser, thus eliminating the risks.
Can a nevus turn into cancer?
Theoretically, any mole can turn into cancer. And nevus is no exception. However, it is not a disease in itself. But in order to eliminate the risk, the formation should be removed.
Prevention of cancerous transformation of eye nevi
It is impossible to predict the growth of a nevus into a cancerous tumor. There is such a risk, although it is extremely insignificant. It is impossible to exclude such a case with the help of medicines, drops or traditional medicine potions. Therefore, the only option is to remove the nevus immediately after detection.



