It's rare to see a person without small dark marks on their body. Is it worth paying attention to these points? Only a doctor will distinguish between dangerous and normal moles - malignant melanoma or harmless nevus - and give recommendations on what to do with them. Is it worth worrying about the appearance of new formations, when immediate contact with specialists is required, what are the signs of cancer development - the answers to these questions remain to be found out. No one is immune from disaster, and early diagnosis will protect you from severe consequences.
What is a mole
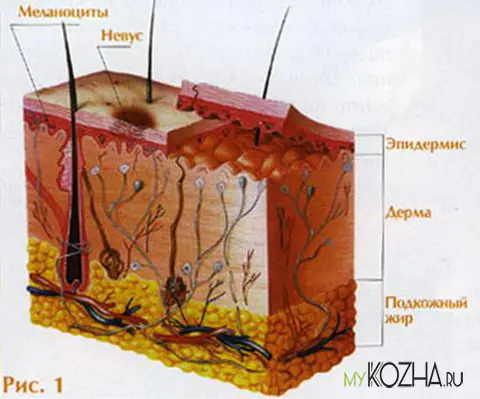
The first tiny spots may appear in children in infancy. A mole is a small formation on the skin - a nevus - that is considered benign and harmless. The basis for their appearance is melanocyte cells that accumulate the natural pigment melanin. Depending on its quantity, a difference in color is observed. Available colors:
The shape of the tumors depends on the location and concentration of melanin. They may have a stalk or be located under the skin, be flat and convex. The most common type is round, but there are exceptions. The development of neoplasms is provoked by ultraviolet radiation - natural from the sun, in a solarium. Hereditary factors cannot be excluded. A common cause of growth is hormonal imbalance, characteristic of periods:
- puberty;
- pregnancy;
- menopause.
What types of moles are there?
One person may discover very different tumors. Types of moles are classified according to several criteria. This helps in correct diagnosis in case of changes. They differ in:
- origin– congenital, newly acquired;
- structure– pigment, vascular;
- place of education – in depth, on the surface, in the boundary layer;
- raised above the skin – flat – even, protruding as a hemisphere, pedunculated, larger birthmarks;
- potential threats – dangerous, degenerating into melanoma, non-dangerous.
Safe moles
Those who have dark spots on their skin should be wary of their changes. In time, detected signs of degeneration into melanoma contribute to the timely removal of the formation and preservation of health. Safe moles are different:
- the presence of a stalk – it cannot be formed by malignant cells that grow randomly;
- long-term condition without changes.
Spots that appear soon after birth are not considered dangerous. It is important that they are small in size. Good – non-dangerous – signs of neoplasms include:
- flesh tone;
- unchanged pattern of the skin of the nevus and adjacent tissues;
- soft consistency;
- hair on the surface of the neoplasm - growing from the skin, indicates the absence of pathologies;
- diameter no more than 5 mm;
- symmetry;
- nevus in the form of a spot.
Which moles are dangerous?
Why do people with nevi on their bodies need to monitor their changes? There is always a threat of degeneration of non-dangerous tumors into a cancerous tumor. What moles are dangerous to health? Key signs you need to know:
- change in shades towards the dark side, the appearance of multi-color;
- rapid increase in size - exceeds two millimeters per year;
- occurrence of cracks;
- the formation of asymmetry due to uneven growth;
- lack of elasticity;
- the appearance of itching, burning;
- presence of discomfort.
The appearance of dangerous moles requires an immediate visit to a specialist to clarify the nature of the changes and the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Pathological transformations provoke:
- injury to the nevus due to negligence;
- self-removal;
- abuse of exposure to the sun, use of a solarium;
- location of the formation in places of frequent contact with clothing - on the neck, head, genitals, legs;
- placement in the hair, on the face, palms - where there is a high probability of injury;
- previously removed melanoma.
Why are moles dangerous?
Not a single person is protected from the sudden proliferation of cells of a harmless mole. Melanoma is an extremely serious disease. Changes not detected at the initial stage can result in death. The provoking factor is unsuccessful independent removal of tumors. Moles are dangerous because of their ability to:
- transform into an atypical – precancerous form;
- grow to large sizes;
- turn into cancerous;
- with minor external changes, metastases actively spread throughout the body through the circulatory and lymphatic channels.
How quickly does melanoma develop from a mole?
The transformation of a nevus into a cancerous formation can occur in different ways. The process depends on the stage of the disease and the type of tumor. Instant metastases are dangerous. Begins:
- growth of cancer (oncological) cells in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- their entry into the blood and lymph;
- penetration into the lungs, liver, kidneys;
- growth in these organs;
- complete damage to the body;
- death.
The growth phases of pigment cells are observed, along which melanoma develops from a mole. There are varieties:
- horizontal– damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs, lasting up to 10 years, but metastases do not appear;
- vertical– accompanied by the spread of cancer cells throughout the organs, can last two years, has an unfavorable prognosis;
- nodal – especially dangerous – characterized by deep spread within two months.
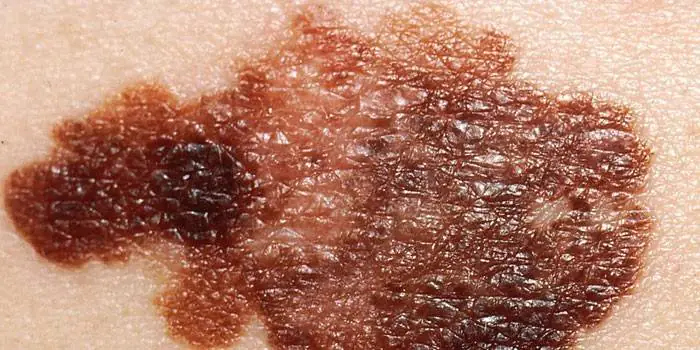
The first signs of melanoma
The patient can be assisted only when suspicious changes begin to be identified. The diagnosis, research, and referral for surgical treatment save a person’s life. The first signs of melanoma:
- increase in the height of the tumor;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of discharge;
- redness;
- burning, itching;
- swelling of tissues;
- softening of the nevus;
- the appearance of a crust;
- thickening;
- hair loss;
- expansion of pigmentation around the lesion.
With the further development of dangerous melanoma, the following are observed:
- significant change in size;
- the appearance of pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- surface ulceration;
- formation of new foci;
- bleeding from places of pigmentation;
- liquid separation;
- skin thickening;
- the appearance of an earthy tint;
- signs of metastases are chronic cough, weight loss, cramps, headaches.
How to distinguish a mole from melanoma
To recognize which moles are dangerous and which are not dangerous, you need to know what they look like. A person with nevi, in order to eliminate terrible consequences, must constantly monitor the appearance of new formations and changes that occur. You can distinguish a mole from melanoma by its signs. Non-dangerous neoplasm:
- symmetrical;
- with smooth edges;
- uniform in color;
- with dimensions not exceeding 6 millimeters.
Features of dangerous melanoma that require seeking help from dermatologists:
- growth in a short time;
- pronounced asymmetry of shape;
- heterogeneity in color - the presence of inclusions of several shades;
- lack of clear boundaries - the contour line is blurred, jagged, and looks like a coastline on a geographical map;
- increased diameter over six millimeters;
- variability of any parameters - color, size, shape.
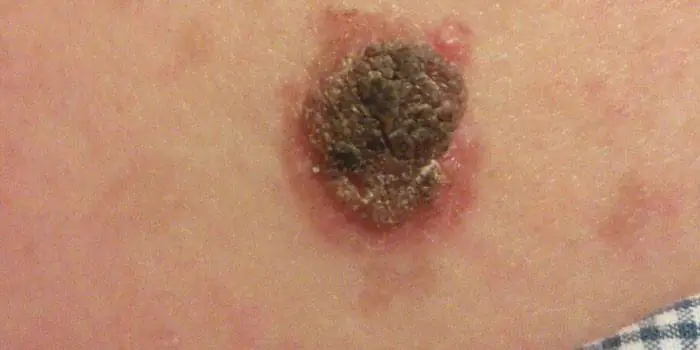
What dangerous moles look like
What do nevi that are subject to pathological changes look like? Only a doctor can correctly distinguish between non-dangerous tumors. Dangerous formations look like this:
- blue– compactions under the skin with clear boundaries, with dimensions no more than 10 mm;
- nodal– round, flat in shape, color – brown, black;
- cutaneous– often pale, convex;
- halo nevus – pigment surrounded by a light or white rim;
- spitz- looks like a dome-shaped tumor of pink shades, with the possible presence of a hole through which blood and liquid leak;
- connecting- connect individual entities into a whole.
Mole with jagged edges
One of the signs of a non-hazardous formation turning into a dangerous one is a change in contours. It often has blurred edges and scalloped borders. There are non-dangerous types of nevi - dysplastic. Only a specialist can make a correct diagnosis. A mole with uneven edges can be dangerous if there are additional signs of melanoma:
- accelerated changes in size;
- the presence of clearly defined asymmetry;
- the appearance of highly indented boundaries.
Rough mole
Such a neoplasm is harmless if its diameter is no more than 5 mm and remains constant in size. Often its appearance signals a lack of vitamins and nutritional disorders. Doctors advise coming for a consultation if it is discovered that:
- the smooth nevus turned into a rough one;
- bothered by burning, itching, tingling;
- irregularities and compactions appeared in the middle;
- areas with different shades formed;
- diameter has increased significantly.
A dangerous rough mole requires immediate examination if:
- the appearance of bleeding;
- development of the inflammatory process;
- rapid change in size;
- formation of asymmetry;
- formation of purulent discharge;
- the occurrence of painful sensations when touched;
- the emergence of an irregular shape, blurred boundaries, along the edges of the neoplasm.
Large moles
Large formations on the skin are pigment spots. When they remain unchanged and do not cause inconvenience, this is a harmless phenomenon. It is important to constantly monitor their appearance, color, and size. To eliminate worries, you need to consult a dermatologist. During the visit, the specialist will conduct a diagnosis and give a forecast of the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm. Large moles become dangerous if they:
- injured;
- thickened;
- started to itch;
- were unsuccessfully removed independently;
- changed in size, shape;
- are bleeding.
What moles can be removed
Often nevi cause trouble for women when they are in a visible place - the face, neck. Even if they do not bother you, using removal will be the right decision - the appearance will improve significantly. After the procedure, the doctor must send the tissue for histological analysis to decide whether the mole is malignant or not. If the neoplasm is not dangerous, does not bother you, and does not change in size, surgery is not required. What moles cannot be removed? Experts believe:
- there are no contraindications;
- It is important to choose the right excision technique.
You should be careful about skin growths; it is unacceptable to remove them yourself. Only the doctor will determine whether a nevus is dangerous or not and decide what to do with it. You can delete it if:
- injured from clothing - on the neck, in the groin area, under the armpits;
- cause pain when touched;
- are located under the hair on the head and can be damaged when combing or cutting;
- change color, shape, outline;
- significantly increase in size;
- characterized by the presence of burning, itching;
- accompanied by inflammation and bleeding.
A mole (nevus) is a benign neoplasm on the skin, which is caused by an accumulation of pigment cells - melanocytes. When there is an excess of melanin, the substance that gives color to the skin, dark growths form. When the production of this substance decreases, a person may develop a white birthmark.
There are several classifications of birthmarks on the body:
- Depending on the depth at which they formed, they are divided into epidermal, intradermal and borderline;
- Based on their appearance, they are divided into melanocytic (flat), noncellular (convex) and organoid (warty);
- Also, moles vary in size and are conventionally divided into small, medium, large and giant;
- By color they can be divided into red (vascular), dark (pigmented, non-vascular) and white.
Places of formation of moles
Neoplasms can be congenital - appear immediately at birth, or acquired - appear throughout life. Most of them are formed during pregnancy, puberty, and also during menopause in women, since the formation of melanin is influenced by melanotropic hormone, the production of which increases with hormonal changes in the body.
Nevi can appear anywhere on the skin, including mucous membranes. Depending on the depth of the skin layer on which they formed, they are divided into the following types:
- Epidermal - formed on the top layer of skin;
- Intradermal - formed in the dermis (deeper layer of skin);
- Borderline - formed at the border of the epidermis and dermis.
Appearance of moles
Moles differ from each other not only in the place of formation, but also in appearance:
- Flat (melanocytic) nevi are the most common and safest type. Usually these are small, smooth, oval-shaped spots.
- Noncellular (convex) dark-colored neoplasms rise above the skin and have a flat or rough surface on which hairs can grow;
- Organoid (warty) nevi are black, brown or blue in color, which in appearance resemble warts - they protrude above the skin and are pedunculated. This species requires special attention, as it is more susceptible to injury than others.
Mole size
Nevi vary in size:
- Those that have a diameter of up to 1.5 cm are classified as small neoplasms;
- Moles with a diameter of up to 10 cm are considered medium;
- Large moles have a diameter of over 10 cm;
- Giant moles are very large. They can cover most of the chest, face, lower legs - that is, affect the entire anatomical region.
Giant nevi are the most dangerous - the risk of transforming into a malignant tumor reaches 50%, so such moles require mandatory consultation with a doctor.
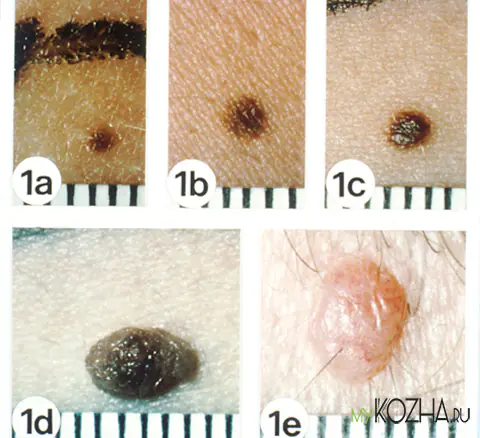
Red (vascular) nevi
Red moles occur due to disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels - capillaries, arteries, veins and lymphatic vessels. Depending on which vessel malfunctioned, the neoplasms can be of different sizes and colors (pink, red and blue-red):
- If the neoplasm appears from capillary vessels, then it is flat and rises slightly above the skin;
- If the red neoplasm occurs due to a malfunction of the arteries and veins, which are located deeper in the dermis, then it rises in the form of a tubercle above the skin.
The most common types of vascular neoplasms are:
- Hemangioma;
- Vascular malformation (port stains and stork bites).
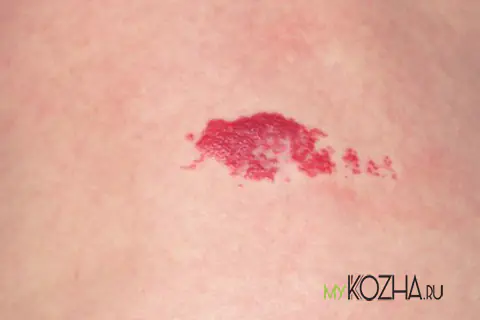
Hemangioma
You can often find another name for hemangioma - strawberry birthmarks. They appear in the first 2–4 weeks of a child’s life. First, light plaques or small red swellings form on the skin. Gradually, the edges of the hemangioma acquire clear outlines and turn red.
Typically, strawberry moles disappear on their own by the age of 7. The process of reverse development of hemangioma begins from the center: the color becomes more saturated cherry-red, over time the surface gradually turns pale, becomes less elastic - the hemangioma disappears.
Vascular malformation
These are congenital red moles that appear during the first weeks of a child's life. Vascular malformation causes malfunction of blood vessels, which manifests itself on the skin in the form of red growths:
- Port wine stains are usually located on the face, arms and torso. At first they are pink in color, over time they darken and become a rich red or bright crimson color. If the child is nervous, crying or has a fever, the color becomes brighter and more intense. Port wine stains do not disappear with age, they only change their color and texture. In adults they are purple and the surface is more lumpy.
- A stork bite is another common type of vascular harmless neoplasm on the skin of a newborn in the neck, forehead, back of the head and temples. Their formation is associated with fetal hypoxia, which leads to compression of blood vessels. These moles are red or orange-pink in color. As a rule, they are irregular in shape with unclear boundary outlines. Their sizes are also different: most often they are small specks, like a fingerprint. Such vascular neoplasms disappear without treatment in the first year of a child’s life.
Pigmented nonvascular moles
Almost every person has dark pigment changes on the skin. Unlike vascular neoplasms, which appear from abnormal malfunctions of blood vessels, this type of birthmark occurs from excess production of melanin, the coloring pigment. The color of such spots ranges from gray to brown. They can also have different surfaces (rough and smooth) and hairs. Common safe types are:
- Lentigo;
- Mongolian spots;
- Coffee stains.
Lentigo (flat moles)
This is the most common type of pigmented neoplasm that can be found on the body of every person. Lentigo is a spot with an equal color range, ranging from light brown to brown. It appears due to increased production of melanin. The color becomes more intense when exposed to ultraviolet light.
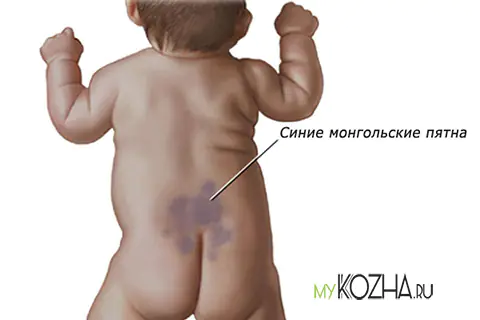
Mongolian spots
Such neoplasms are round pigment spots of a bluish tint, which are most often located in the lumbar and sacral zone. They disappear without treatment before adolescence.
Coffee stains
These are small flat spots the color of coffee with milk. The presence of 1–2 café-au-lait-colored neoplasms is not considered pathological. If there are 3 or more spots, additional diagnostics are required, as they may be a symptom of neurobromatosis, a disease in which a tumor is formed from nerve cells.
Melanoma-dangerous moles
Some pigmented neoplasms can develop into malignant melanoma, so sometimes they are classified into a separate group - melanoma-dangerous. The most common types of melanoma-dangerous moles:
- Blue nevus;
- Dysplastic nevus;
- Nevus Ota;
- Papillomatous birthmark;
- Pigmented borderline neoplasm;
- Giant pigmented mole.
Blue nevus
Pigmented nevi of a blue or dark blue hue. Their diameter is up to 2 cm. They are often shaped like a hemisphere and have a smooth surface. Localized on the buttocks, face and limbs.

Mole Ota
A large pigmented neoplasm on the face that is blue-gray or dark brown in color. It doesn't go away on its own. Requires treatment.
Dysplastic nevus
Pigmented neoplasms of various shapes with a diameter of more than 1 cm. A distinctive feature is blurred outlines and reddish tints. Localized on the buttocks and chest. Passed on by inheritance.
Papilomatous nevus
A convex pigmented mole with irregular outlines and an uneven surface. Color ranges from flesh to dark brown. Most often localized on the head, the surface may be riddled with hairs.
Pigmented borderline neoplasm
The nodule is black or dark brown with a dry and smooth surface. Diameter - up to 10 mm. Pigmented border nevi are most often localized on the genitals, in the areas of the palms and soles, as well as on the nail beds.
Giant pigmented mole
The giant nevus has a warty, loose, heterogeneous surface from gray to black. There is dynamics in development - the nevus is growing every year.
White moles
Unlike pigmented neoplasms, which appear when there is an excess of melanin, a white birthmark is formed when the production of cells that produce melanin decreases. White moles can be of different sizes and have different surfaces (smooth or rough). Often, light-colored neoplasms are symptoms of serious diseases, but sometimes they can only be an individual feature of a person’s skin and are not dangerous to health. Therefore, white moles must be observed by doctors.
As you can see, there are different types of birthmarks. They have one thing in common - they require careful treatment and control to prevent their transformation into melanoma (cancer) - a malignant neoplasm on the skin.
A common phenomenon for most people, which many do not notice or do not attach due importance to, is moles. But due to the connection of most of these types of birthmarks to oncology, they deserve close attention. Moles on the body can have different types, sizes, surface texture, color and shape.
Moles, acquired and congenital
All moles that appear on the body can be divided into congenital and acquired. The first, in turn, can be classified by size:
- Small ones reach a size of one and a half centimeters in diameter.
- Average moles can reach ten centimeters.
- Large spots exceed ten centimeters in diameter.
- Giant birthmarks are localized over the entire anatomical region, that is, they cover the entire face or chest.
Small moles, which very rarely can develop into cancer, are considered harmless. The most dangerous are considered to be giant moles, which develop into cancer in half of the cases. Owners of such neoplasms should visit a dermatologist regularly for consultation. Many experts insist on removing particularly large birthmarks in order to avoid unwanted consequences.
Due to individual characteristics of a person at the genetic level, acquired moles may appear. Most often, they form in early childhood during the period of intense pigment spots appearing on the surface of the skin. Dividing moles by location, they can be classified into the following types:
- Epidermal birthmarks characterize the accumulation of melanocytes in the upper layers of the skin.
- Intradermal moles are accumulations of melanocytes in the deep layers of the skin.
- Clusters of melanocytes at the border of the dermis and epidermis are borderline moles.
Many doctors insist on removing almost all types of acquired birthmarks.
Moles - types of moles on the body with photos
In my own way location and form moles can be of the following types:
Hemangiomas are vascular formations. The vessel from which they are formed determines their main color: red, pink or with a hint of blue. They reach different sizes and may have uneven edges. They, in turn, can take the form of capillary moles, which are flat in structure and located on the surface of the skin, or cavernous, located in the thickness of the skin, lumpy and nodular.- Non-vascular moles, similar to pigmentation of the skin, can also rise above the skin in the form of warts. According to their characteristics, these can be multiple or single elements with a keratinized surface of different shapes and colors from gray to brown. In some cases, they can be covered with hair and reach a black tint in color.
- It can be a light or dark formation in the upper layers of the epidermis from melancites and have the familiar name of a mole or a flat birthmark, which is familiar to many. Over time, their number and size do not change.
- Pigment spots of a brown or brown hue, which increase in intensity in old age or adolescence, are called lentigo. They can develop into a so-called disease, lentiginosis.
- In the deep layers of the epidermis, convex spots can form, which are bumpy or smooth formations with a diameter not exceeding ten millimeters and in most cases having a hair in the center of the growth. The color scheme can vary from black to yellow. Locations in intimate areas, on the palms or soles of the feet.
- A mole that looks like a smooth hemisphere with a diameter of up to two millimeters or a small dense growth with an elevation above the surface of the skin is called a blue nevus or blue mole. It can be located on the face, buttocks or limbs and range in color from light blue to dark blue.
- The congenital formation is a giant pigmented nevus, which is represented by colors of gray, black or brown. This pigmented spot has its own peculiarity: it increases in size along with the growth of the human body.
- Formations of moles with different shapes and sizes exceeding one centimeter are called dysplastic nevus. They are birthmarks with blurry outlines that have genetic inheritance.
Description of melanoma-dangerous moles on the body
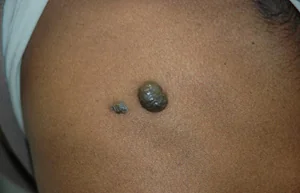
Blue nevus, localized on the buttocks, limbs or face. Represents dense nodule, without hair, does not exceed five millimeters in diameter. The color can vary from light blue to dark blue.
Nevus of Ota is a large dark brown pigmented spot on the face and is a type of blue nevus. The location can be any part of the face, which creates the effect of dirty skin.
A borderline pigmented nevus is a nodule with a flat, dry and smooth surface, not exceeding ten millimeters in diameter. The color ranges from dark brown to black with localization in the intimate area, nail beds, palms or soles of the feet.
Giant pigmented nevus resembles a wart with a cracked, bumpy surface and has a gray to black color. This species is capable of increasing along with the growth of the human body.
Dubreuil melanosis is a single pigmented spot of pre-melanoma skin lesion with slow growth. From a light brown color, the spot acquires a dark brown tint as it grows, even black. It is localized in open areas of the skin, but is most often located on the face in patches with a diameter of up to thirty millimeters.
Melanomic types of moles
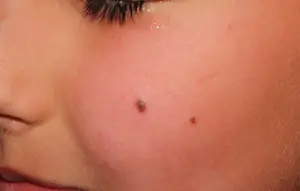
Nevus of Setton is a red or brown nodule reaching a size of five millimeters in diameter. It rises slightly above the surface of the skin. A round or oval nodule, usually surrounded by a white ring of depigmented skin. Such a nodule is capable of spontaneous disappearance and is located mainly on the arms and torso.
Nevus fibroepithelial It is a slowly growing formation with a soft elastic surface and a spherical shape. The dimensions do not exceed a diameter of ten millimeters. May contain vellus or bristly hair and have a natural color. The color scheme can also have a bluish, pinkish or dark brown tint. It can be located singly or in dozens throughout the body or on the face. It differs from the borderline pigmented nevus in that it has a less saturated color, regular outline and the presence of hair.
An intradermal pigmented nevus is a simple brown birthmark that can be located in any part of the body.
Mongolian spot located in the lumbosacral area. A mole is a round, irregularly shaped spot of blue or brown color. Appears in children from birth and goes away on its own by adolescence.
A papillomatous nevus is a formation with irregular outlines and an uneven surface. The color is usually natural or dark brown with dimensions up to several centimeters. Typically, a mole is riddled with hairs and is most often localized on the scalp.
Nevus verrucous is a type of papillomatous nevus. The difference is the greater pigmentation and roughness of the surface, often cut by deep cracks.
Differences between good types of moles and bad ones
Many owners of such formations on the skin are concerned with the question of how to distinguish a benign mole from a malignant one. This is quite simple to do; you just need to carefully examine the mole. Can be considered non-hazardous clearly defined birthmarks small size. They have a uniform structure and do not protrude much above the skin. The color range varies from light yellow to black. But if in doubt, it is better to undergo an examination by a dermatologist using special studies.
Bad birthmarks include the appearance of intense pain of various types in their area. If within two months the mole has increased significantly or itching has appeared in its area, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. Additional concern should be caused by the appearance of additional crusts, bulges or ulcers on the surface.
Moles on the body and the reasons for their appearance
The appearance of these benign formations can be influenced by various factors that stimulate excessive division of skin cells in a limited area of the skin. Modern doctors the following factors are identified, as the main ones, when moles appear:
Ultraviolet radiation.- Hormonal imbalances and related diseases.
- Genetic changes in the body contribute to the hereditary transmission of birthmarks to children, identical to the birthmarks of the parents, appearing in certain places of the body.
- Various defects in skin development that lead to the appearance of congenital moles in children starting from the age of two months.
- The possibility of the appearance of moles with long-term use of drugs containing homones.
- Long-term and untreated viral and bacterial infections.
What moles should be removed and methods for their elimination
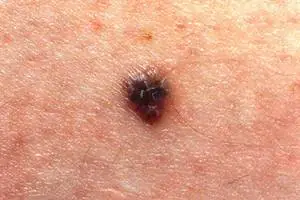
Only those birthmarks that are pose a potential threat for humans and can turn into cancer. Removing a mole cannot provoke the development of this dangerous disease. Surgeries to remove birthmarks are completely safe and can have side effects only in the event of an allergic reaction to certain medications.
Modern medicine welcomes several methods for getting rid of birthmarks:
- Surgical operations.
- Laser exposure.
- Removal using liquid nitrogen.
- Exposure to electric current.
- Removal by radio waves.
The method of treatment for removing a birthmark is selected at an appointment with a dermatologist strictly on an individual basis. Removal using laser or liquid nitrogen refers to more gentle methods of combating unwanted tumors. All manipulations are carried out without the appearance of blood and are as gentle as possible on the skin around the mole.



