A mole is a pathological neoplasm on the skin that is benign in nature.
They differ in size, shape and color.
The danger of moles is that exposure to irritating factors can lead to their transformation into a malignant tumor.
At what age do these neoplasms appear, are they dangerous, what should you do with moles? These questions should be addressed.
When does a child get moles?
Some babies develop moles in the womb. Over time, their number on the body gradually increases. The safest moles are brownish pigmented spots that cannot be felt to the touch. Even if these spots are scattered throughout the body, you should not worry. But the presence of moles that have begun to rapidly change shape and size requires contacting a dermatologist. Such neoplasms may be pathological in nature.
If we talk about the age at which moles begin to appear on the body, the exact timing has not been established. Approximate periods of activation of age spots are:
- age from 6 months to 2 years. During this period, the first moles began to appear in babies.
- 5-6 years. A second wave of neoplasms is observed.
- Adolescence. During puberty, children's hormonal levels change, which causes the appearance of new age spots.
Causes of birthmarks in children
The appearance of moles can occur for a variety of reasons. Why they occur depends on many factors, namely:
- genetic predisposition. This is especially true for birthmarks that appear at the DNA level. They may appear in a child in the same place as in his relatives.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. Exposure to ultraviolet rays promotes the production of melanin. This is the substance that is the basis of all moles. Excess melanin in the body, especially in the warm season, leads to the appearance of a large number of moles. Excessive amounts of them lead to a serious disease – melanoma.
- Trauma to spots. Any mechanical impact on a mole can lead to its enlargement and the appearance of new pigment spots of a pathological nature.
- Hormonal changes in the body. One of the hormones is responsible for the release of melanin into the body. Therefore, very often during puberty there is an increased appearance of moles throughout the body.
Types of neoplasms, mechanism of occurrence and care
The mechanism of the appearance of a neoplasm directly depends on its type. There are these types of moles:
- Small spots of red color. They are most often observed in newborns. The location of such spots is usually the forehead, the back of the head, and the bridge of the nose. They appear as a result of intrauterine friction against the mother's bones. Typically, such spots gradually disappear during the first year of the baby's life.
- Flat moles of burgundy color. They are areas with dilated blood vessels. The location of such moles is the face or head. They continue to grow over time and may gradually become pathological. Therefore, such tumors require removal. They don't go away on their own.
- Flat brown spots. Their color can vary in shades of brown. When palpating, no pathological compactions are felt. In some cases, they gradually disappear, but they can remain for life. They do not pose a danger and therefore do not require removal.
- Strawberry hemangioma. It is a convex neoplasm of a bright red or burgundy hue. When palpated, the neoplasm is soft. Most often, this is a congenital pathology or occurs in the first weeks of a baby’s life. Most often, experts do not recommend getting rid of such moles, despite the discomfort from an aesthetic point of view. Since any impact on strawberry hemangioma can lead to dangerous consequences.
- Cavernous hemangioma. These are neoplasms on the skin, which are large elements of blood vessels with unclear boundaries. These birthmarks should not be treated. Because by puberty they disappear on their own.
In order to avoid complications, special care for moles is needed. It provides for compliance with the following rules:
- Birthmarks should not be covered with adhesive tape;
- avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- After swimming in ponds, the child’s skin must be wiped dry; moisture can cause burns on age spots;
- If a child’s mole is injured, a sterile bandage should be applied to it, and then immediately consult a doctor.
Damaged birthmarks should never be treated with antiseptic agents. This can significantly worsen the condition. Simply rinse the affected area.
Removal of a mole in children should occur exclusively in a hospital setting. This should not be done at home. There are several methods for removing spots on the skin, namely:
- laser exposure,
- electrocoagulation,
- removal with liquid nitrogen.
Watch a video on this topic:
After performing these procedures, you must strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations. for faster wound healing.

Moles in newborns.
Many people are sure that moles are spots on our body that we were born with. However, is this really true? In fact, quite a few children are born with moles on their body. Moles got their name for a different reason. First of all, moles, or nevi, are transmitted genetically through parents. Hence the name “moles”. Popular moles that a child had at birth are called birthmarks. Such spots actually appear with the birth of a child and grow with the growth of the newborn.
The question of when moles appear in newborns may sound incorrect. The fact is that birthmarks on the body of a newborn can be noticeable, or they can be barely visible. At first they appear as a bright spot that is difficult to see with the naked eye. Over time, the spot becomes darker, and you realize that your child has a “birthmark”, a sign of “breed”. By the way, many parents are proud of their birthmarks, which are passed on from generation to generation, so the appearance of a pedigree birthmark on a child is eagerly awaited.
Many people are interested in the question of why moles appear in children.
- Genetics. First of all, it’s all about a genetic predisposition to this, for example, dad or more likely mom has the same mole in the same place or nearby. There's nothing you can do about it. But it happens that children develop moles that do not decorate them in any way, but they should not be removed while the child is very small, because The nevus may appear again and you will have to have surgery again.
- Hormones. This is also a common cause of moles in children, but it is extremely rare that it occurs in infancy.
- UV rays. Newborns do not sunbathe or go to the beach with their parents, so this option is also excluded.
In addition, you can independently understand in advance with a high probability of coincidence that the child will have a birthmark at birth. The fact is that most often the following are born with nevi:
- Light-skinned children
- Girls (about 4-5 times more often than boys),
- Premature babies.
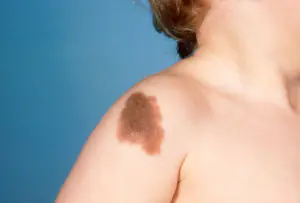
Moles in children.
Most often, the first nevi appear in childhood. But when children have moles, only parents know who remember every centimeter of the child’s body. It is impossible to say specifically that moles in children appear strictly at 3 years or at 5 years - everything is individual and depends on several factors:
- Child maturation
- Staying in the sun
- Genetics.
A genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out, so if the parents’ first moles appeared late, then the child will probably not get moles early, and if the parents have a lot of moles, then the baby will have a lot of moles.
Attention! To protect your child from the appearance of new moles, try to protect him from sun exposure, especially from sunburn. In summer, the baby should wear clothing (not warm) that covers exposed skin, such as a Panama hat. Always apply sunscreen to your child's skin before leaving the house, and at the beach, make sure he plays in the shade, such as under a beach umbrella.
So at what age do moles appear? According to statistics, the first moles appear in children at the age of 1-2 years. By this age, children are taken with them to the dacha or to the beach for a couple of hours, but this is already enough for the mole to appear. Daily walks along the street and park are enough, because... ultraviolet rays cause the appearance of new nevi.
If you are concerned that your child is developing moles, contact your pediatrician or immediately see a dermatologist who will examine the child and the growths and can tell you whether there is a danger from moles on the body. However, malignant moles in a child are extremely rare, but still watch how the mole develops and grows, how it manifests itself and how the child reacts to it.
Such different “children’s” moles...
It is rare to see the moles that we are used to seeing in children. But still, congenital birthmarks are those that appeared immediately after birth or appeared in the first 2-3 months of the baby’s life.
Moles can be:
- Vascular,
- Not vascular or ordinary.
Moles that consist of many blood vessels are called vascular. The color of these moles varies from pink to bright red. Vascular nevi can be either flat or convex. These moles are benign, but they are removed not because of the fear of melanoma, but because of their appearance.
Non-vascular moles have a smooth surface, appear in the first years of a child's life and can range in color from light brown to black. Such moles can be either flat or convex; hair growing from the mole is often considered a good sign. You should worry about moles on your palms or soles, because... Such nevi are extremely easy to damage.
Separately, it is worth highlighting vascular moles in a child. Pay attention to whether there are pinkish-red or bluish spots on the child’s body with a slight swelling in diameter? If there is, you should consult a doctor. Vascular nevi are:
- Hemangiomas,
- Stork bites or salmon-colored birthmarks,
- Port wine stain or flaming nevus.
Hemangioma may not be visible immediately, because... for the first time it appears only 2-3 weeks or even 6-12 months after the birth of the baby. It appears anywhere and can grow quickly, although after 1-1.5 years it usually turns pale and flesh-colored. In most children, hemangioma goes away by the age of 10.
“Stork bite” is most common and appears on the back of the head, bridge of the nose and eyelids in the form of a large pink spot or a cluster of small spots.
Flaming nevus is most often flat and red, appears on the face or scalp and grows as the baby ages and grows. Over time, the “wine stain” does not disappear, it cannot be removed, and it is pointless, but you can undergo treatment with the help of:
- Infrared radiation;
- Laser therapy.
If the stain cannot be cured, try either removing it if it is bothering you or hiding it with cosmetics. But trying to hide a birthmark under tanned skin is useless, because... the nevus will only darken (it will become darker than tanned skin). It is better, on the contrary, to hide birthmarks from the sun, use sunscreen and hide the spots with decorative cosmetics.

Why do moles appear?
If small moles appear on the body in large clusters, this is sometimes frightening, but, as a rule, parents, because... Children rarely pay attention to the fact that a new point has appeared on the body. But for what reasons do moles appear on a child’s body, what is the reason for this and how to prevent it?
Be aware that moles often appear among sun lovers and tanning beds. This also applies to children. Often young mothers take their children to the beach with them and teach them to sunbathe “correctly.” However, few people know that the sun's ultraviolet rays (this includes solariums) not only irradiate human skin, but also affect the appearance of new moles. To prevent them from occurring, you need to choose a sunscreen with a high level of protection and apply it to your child’s skin every time before going outside, especially before going to the beach. Spend as little time in the sun as possible, wear a hat and try to stay in the shade.
Moles also appear during hormonal imbalances in the body, i.e. not only with the surge of hormones, but also with their decline. Hence the consequence is that moles appear in children - during adolescence, in women - during pregnancy, and even under severe stress and diseases that affect the hormonal background.
Moles (or nevi, in scientific terms) are an absolutely normal phenomenon. By themselves, they are completely harmless and do not cause any harm to health, but there are those that begin to grow unevenly or change color. Such neoplasms require increased attention and can cause the development of a malignant tumor if they are not removed in time. The prognosis is positive: in 95% of cases, patients recover. But if you don’t pay attention to the changed mole and waste time, there will be only a 20% chance.
As for children, they also have moles, but there are very few cases of dangerous degeneration of a nevus into an unfavorable form in young patients in medical practice. Moles, as a rule, do not appear from birth, although there are exceptions (in such cases they speak of birthmarks, not moles). So when do moles appear in children? Can neoplasms be dangerous? Why do moles appear in a child? Let's look at these questions in more detail below.

Moles in newborns
Very few children are born with moles on their body, and if such spots are observed, they are rather called birthmarks. Birthmarks, by the way, “grow” with the child; this is normal and should not cause concern.
Moles got their name not from the time they appeared on the human body (immediately after birth), but rather for another reason: because nevi are transmitted genetically, i.e. if the parents’ body is covered with such spots, then the grown-up child will most likely will face the same thing.
At what age do moles appear? On the body of a newborn, nevi can be barely noticeable and very light, indistinguishable, so that parents will notice them only when the child grows up. The predisposition to the appearance of nevi, as already mentioned, is transmitted genetically, that is, even before birth, a certain number of such marks are “laid” on the body.

If we talk about newborns, then most often premature and fair-skinned children are born with moles (birthmarks). Girls are born with brown spots approximately four to five times more often than boys.
From six months to two years
When do moles appear in children? Many parents begin to notice new growths on the skin of their babies from six months to two years. But here, of course, everything is individual and depends on many factors (genetics, exposure to the sun and the pace of development of the child - this will be discussed in more detail later), and not just on age.
From the age of six months, they usually begin to slowly take the child with them to the dacha, the beach or a picnic, and go on longer walks. Even a couple of hours of exposure to sunlight is enough for a mole to appear that was not visible before. As a rule, daily walks are enough, since the appearance of tumors is caused by ultraviolet rays.
If you are alarmed by the fact that your child has moles on his body or if you think there are too many “spots”, contact your local pediatrician or immediately see a dermatologist. The specialist will examine the child and tell you whether there is a danger. You should also contact a dermatologist if you notice two or three large moles (more than 5 mm in diameter). It is worth mentioning here that nevi that degenerate into malignant formations are extremely rare in children.
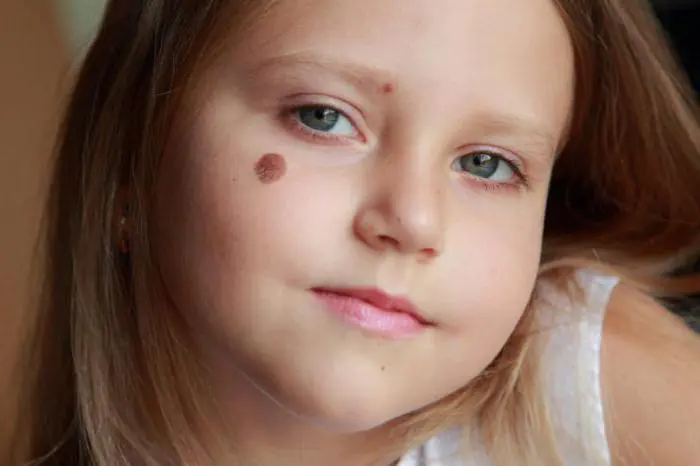
From five to seven years old
What time do children get moles? The next wave of active appearance of neoplasms is observed at five to six years. This is a period of rapid growth of a little man, when all organs and systems are actively improving, and the adaptive properties of the body are significantly improving. In just one year, a child can gain height and weight as rapidly as babies in their first year of life. Pediatricians even call the age of five to seven years the period of “first physical traction.” So it is not surprising if a child has a lot of moles at the age of five to seven.
During adolescence
When do moles appear in children? In adolescence, hormones interfere with the formation of nevi, which, as a rule, sharply increases the number of moles. It is generally accepted that during puberty (that is, at about twelve to fifteen years old) and before twenty-five, 80% of moles appear that will accompany a person throughout his life.
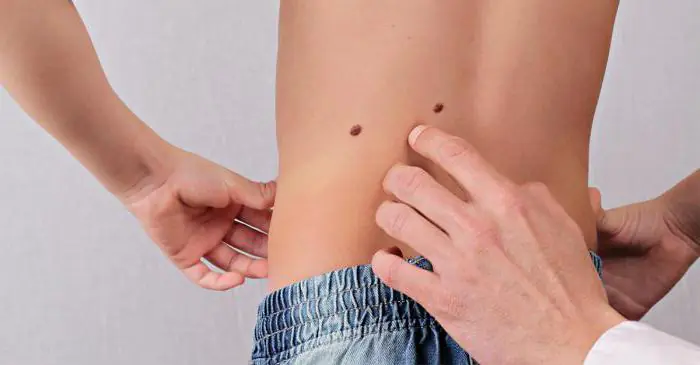
Causes of moles
The number of neoplasms and the age at which they appear directly depends on several factors. At the moment, doctors identify three main reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. A child inherits a tendency towards neoplasms from his parents; in addition, if a mother or father develops moles only in adulthood, then most likely the child will also encounter nevi only as an adult.
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays. Parents who are worried that their child is developing moles on his face or body should be wary of this reason. Prolonged exposure to the sun significantly increases the risk of dangerous degeneration of birthmarks, so for walks you need to choose the right places (shaded), do not forget about products with an SPF factor and a hat.
- Hormonal changes. Moles appear in large numbers during adolescence, when hormonal levels change. The number of nevi may increase during pregnancy, menopause, illness or prolonged stress.
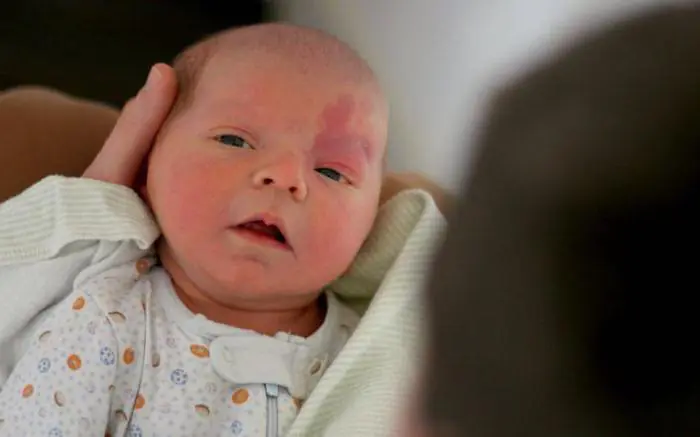

Vascular moles in a child
Vascular moles are made up of a large number of small blood vessels. They are usually red in color and can range from light pink to deep, bright red. Such neoplasms can be either flat or convex. If a child has a red mole, it won’t hurt to go to the doctor, but, as a rule, these are benign neoplasms that pose absolutely no health hazard. The dermatologist may recommend removing the nevus due to its unsightly appearance, which may subsequently cause embarrassment or discomfort in the child, especially if the red mole is located on the face or in a visible place.
Common nevi
Regular (non-vascular) moles have a smooth surface and range in color from light brown to black. Such nevi can be either convex or flat. As a rule, hairs growing from a mole are a good sign. You should only worry if the tumors are located in the palms or soles, or in the folds of the skin, as they are easy to damage.
Hemangiomas
Hemangioma is a type of vascular nevus. When do moles appear in children? Such neoplasms are difficult to detect on the body of a newborn; as a rule, they appear several weeks or months after birth. Moles are located in different areas and can grow quickly, but most disappear by the age of ten. It won’t hurt to consult a dermatologist or pediatrician, but parents shouldn’t immediately think about removing such a tumor.
"Wine Stains"
A flaming nevus, or port-wine stain, is a flat, red growth that appears on the face or scalp. As the child grows, the “spot” increases in size. Such neoplasms, fortunately, are amenable to physiotherapeutic treatment using laser therapy or infrared radiation, but removing them using radical methods, as doctors say, is not always desirable. However, a mole can disappear on its own as the child grows and develops.
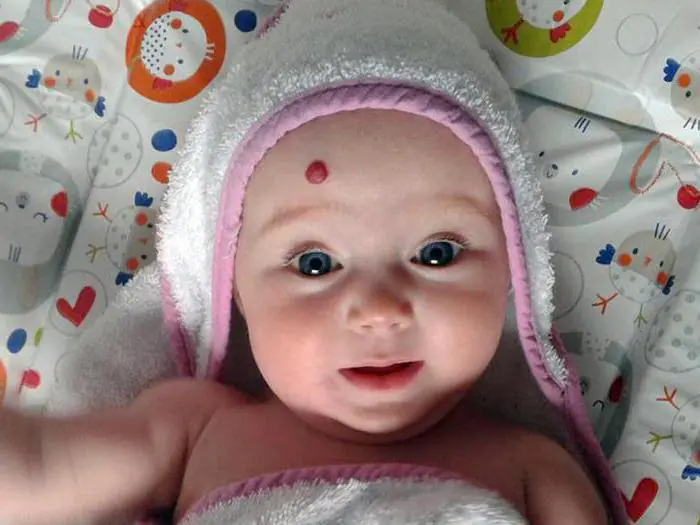

"Stork Bites"
Salmon-colored birthmarks that are localized in the occipital region, on the bridge of the nose or eyelids are called “stork bites” or “angel kisses.” Outwardly, such moles look like a pink spot or a cluster of many small spots.
Medicine explains the appearance of such moles much more prosaically. The thing is that the baby in the uterus is under pressure from the muscular wall and bones of the mother’s pelvis. In places where the pressure is too strong, insufficient blood supply to the tissues or “focal ischemia” occurs.
At what age do children get moles? They've been like this since birth. Over time, the “stork bites” fade, but become brighter when the child is under great stress or anxiety. They usually disappear completely by the age of five, but in rare cases they persist for life.
These nevi do not have any negative consequences for the child’s health; the only problem is a cosmetic defect, and only if the “bite” is too bright. “Stork bites” do not require special treatment; as a rule, they fade as the child grows older and finally disappear after a few years.
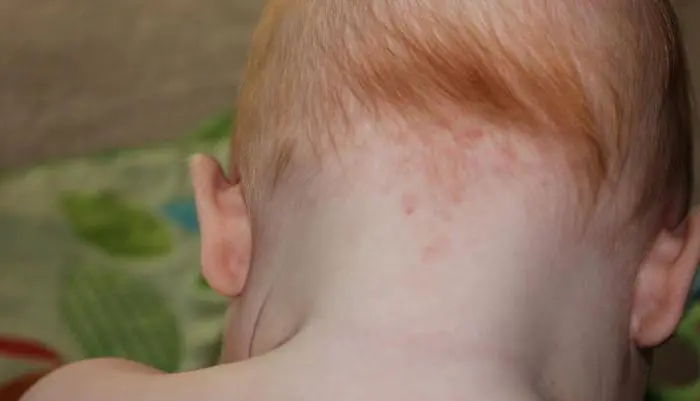
Monitoring moles
Moles need to be monitored so as not to miss the moment of their possible degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. Do not cover nevi with adhesive tape, expose them to prolonged exposure to sunlight, or allow injury. If a mole changes color, grows in size, or changes in any other way (this is more common in adolescence or adulthood than in childhood), you should see a dermatologist. The doctor will examine the disturbing growth and tell you whether you need to worry about this wire. The specialist will also suggest (if necessary) a suitable method for removing the nevus.



