
- Visitor question
- Answer from a dermatologist
Visitor question
Hello! It started around the age of 14, now I’m almost 18. The skin around the joints has increased and become denser, and there are reddish spots on it that are flaking. Thank you. Gender: male.
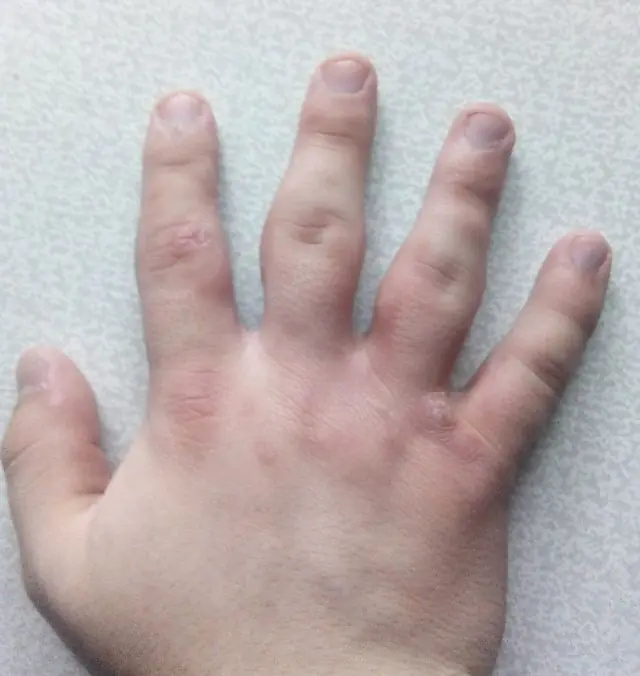
Photo of swelling and hardening of the skin around the joints from a visitor
Answer from a dermatologist
Hello! The symptoms you describe may indicate several diseases. Unfortunately, based on the available description, it is quite difficult to accurately diagnose without additional diagnostic procedures. It would also be useful to clarify additional symptoms, for example, the presence of low-grade fever, pain, the degree of joint stiffness, the presence of itching, etc.
The picture is very similar to rheumatoid arthritis. At the initial stage of the disease, damage to the cartilage in the small joints of the hands occurs in the form of erosion, and inflammation of the synovial membrane begins. Because of this, swelling appears, which can be mistaken for thickening of the skin around the inflamed joints. The inflammatory process also stimulates an increase in local and general temperature, and redness of the skin appears. The disease can impair blood circulation, causing the skin to lack nutrients and become noticeably flaky. The disease can develop at different ages, and the intensity of its progression varies, but in the overwhelming majority it leads to loss of ability to work and disability, so it is better not to delay a visit to a rheumatologist in order to try to keep the disease at its current stage and avoid significant deformation of the joints. It will be necessary to donate blood and take an x-ray.

It is also worth paying attention to the possibility of developing gout. This disease is associated with excessive deposition of uric acid salts in joints and soft tissues. For diagnosis, a blood test and x-ray are performed. The treatment is carried out by a rheumatologist.
Calcification can also cause rounded lesions to form near the joints. This disease is characterized by improper calcium metabolism in the body and insufficient magnesium. A blood test and monitoring of the thyroid gland are required. The danger of the disease is that pockets of calcium deposits can be in other parts of the body and over time disrupt the functioning of organs and systems, which can be quite difficult to notice in the early stages. You can contact an endocrinologist.
- Related article: What tests need to be taken for papillomas



